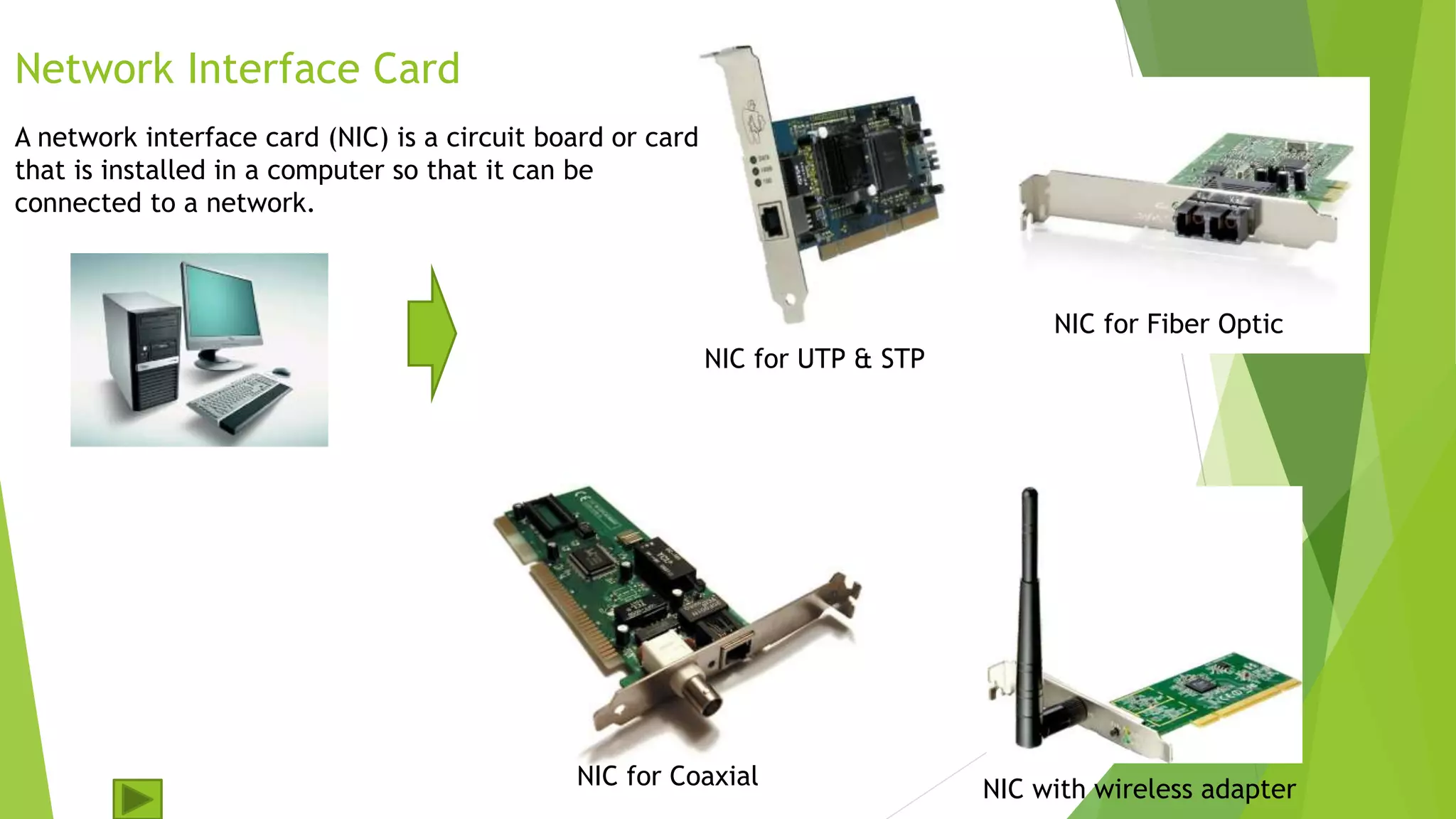
Network media refers to the communication channels used to connect nodes on a computer network. Common network media include copper cables like twisted pair and coaxial, optical fiber cables, and wireless transmission using radio waves. Key factors in choosing network media include the network topology, size, required transmission speed and distance, environment, and cost. A network interface card installed in each computer enables it to connect to the chosen network media type.