The document discusses configuring basic settings on a Cisco switch, including:
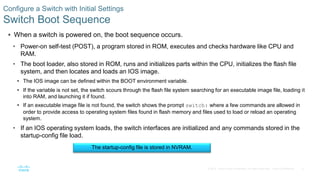
- Setting the boot system to define the IOS image loaded during startup.
- Configuring switch management access by assigning an IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway to the management VLAN.
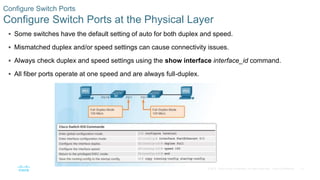
- Configuring physical switch ports by setting the duplex and speed settings to match connected devices and troubleshooting common layer 1 and 2 issues.
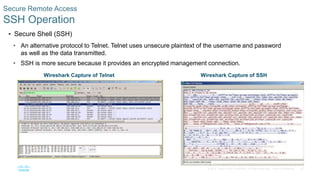
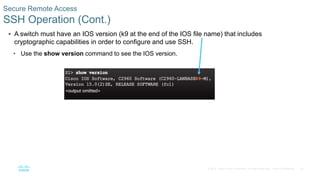
- Securing remote access using SSH instead of Telnet by generating RSA key pairs, configuring user authentication, and enabling SSH version 2.
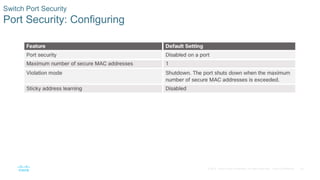
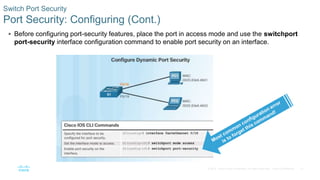
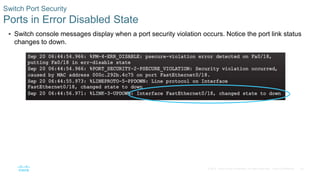
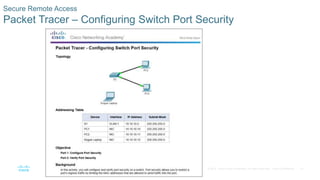
- Implementing port security to restrict which MAC addresses can transmit on switch ports and limit them to the configured number.