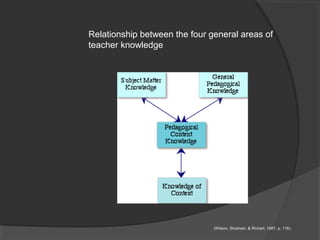
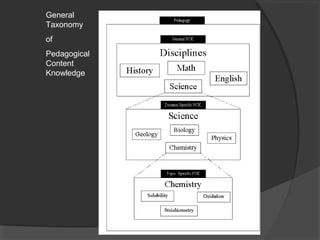
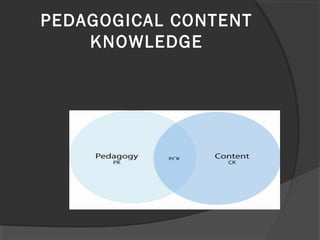
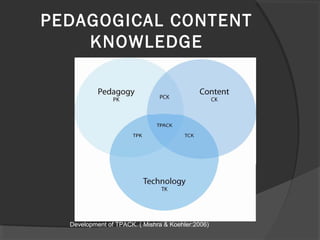
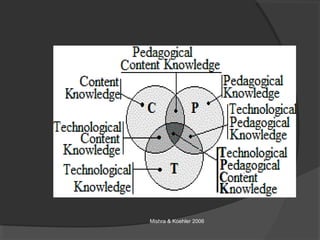
The document discusses pedagogical content knowledge (PCK). It begins by stating the learning outcomes, which are to explain teaching knowledge base, define pedagogy in relation to subject matter, and illustrate PCK. It then defines PCK as blending content and pedagogy to effectively organize and represent topics for diverse learners. PCK distinguishes the understanding of content specialists from pedagogues. Later sections discuss the elements of PCK and its importance for professional preparation of educators. Activities are included for participants to conceptualize their own subjects in terms of PCK.