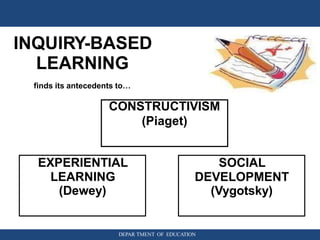
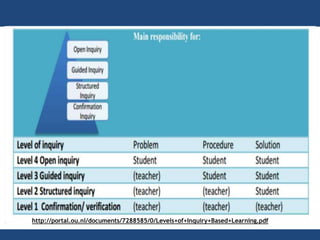
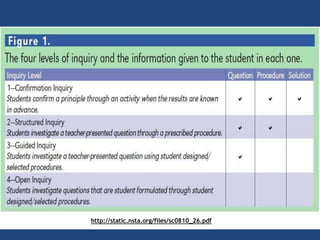
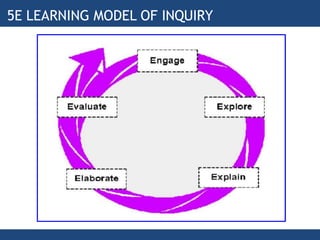
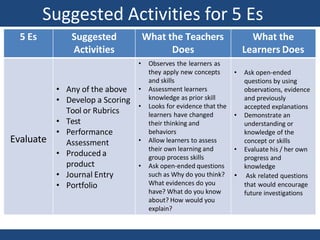
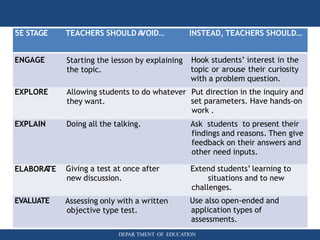
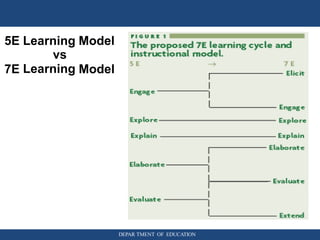
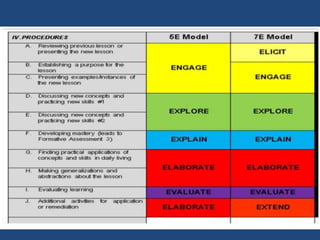
The document discusses inquiry-based learning (IBL), which places students' questions and ideas at the center of the learning experience. IBL involves open-ended, hands-on activities that stimulate inquiry and self-directed learning. It is a student-centered approach that develops useful problem-solving skills and prepares students for a changing world. The document outlines different levels of IBL, from limited confirmation inquiries to open inquiries where students derive their own questions. It also discusses the 5E learning model - engage, explore, explain, elaborate, evaluate - and provides examples of teacher and student roles in each stage. The 5E model is compared to the updated 7E model, which maintains the model's value with new knowledge.