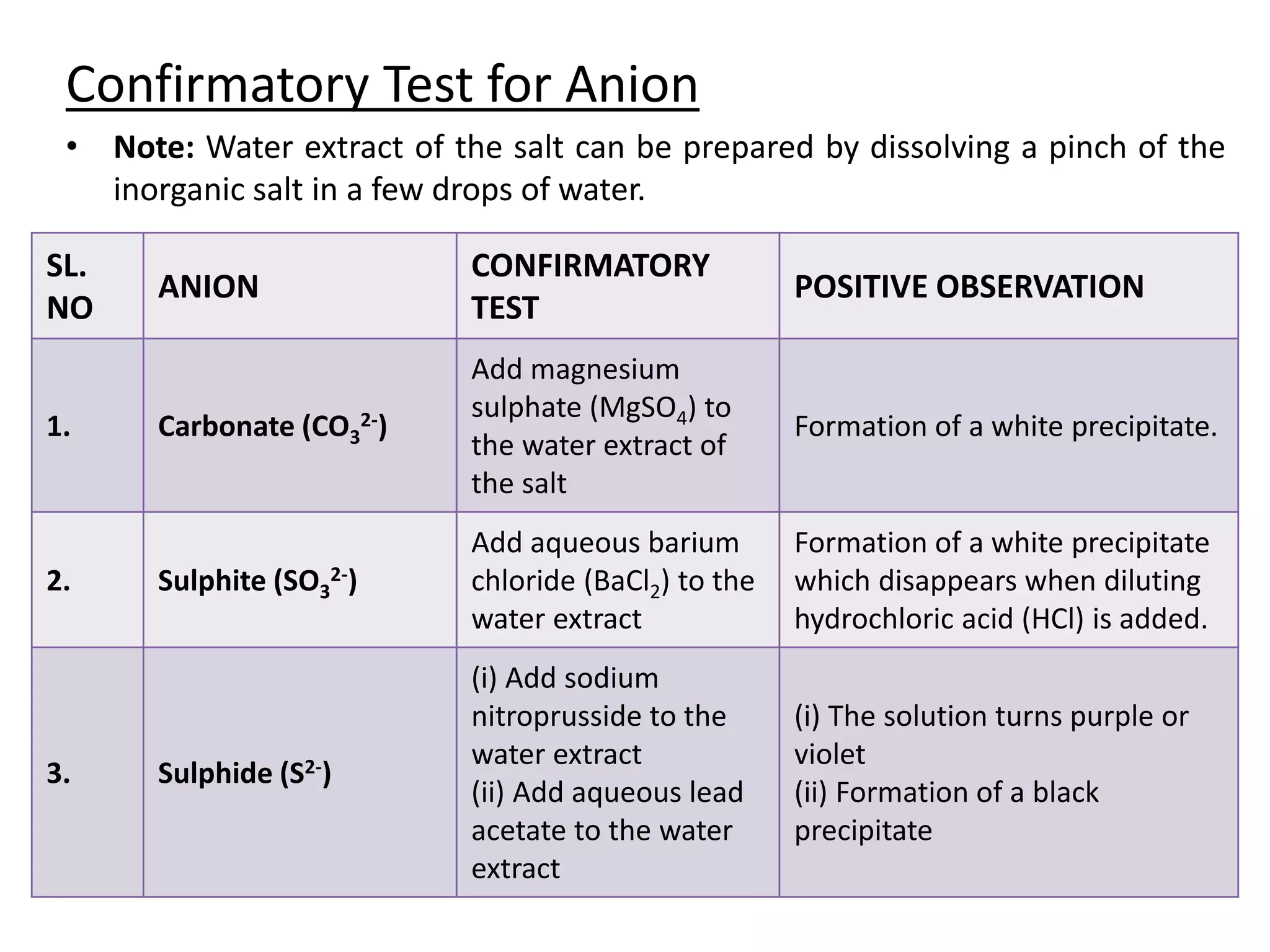
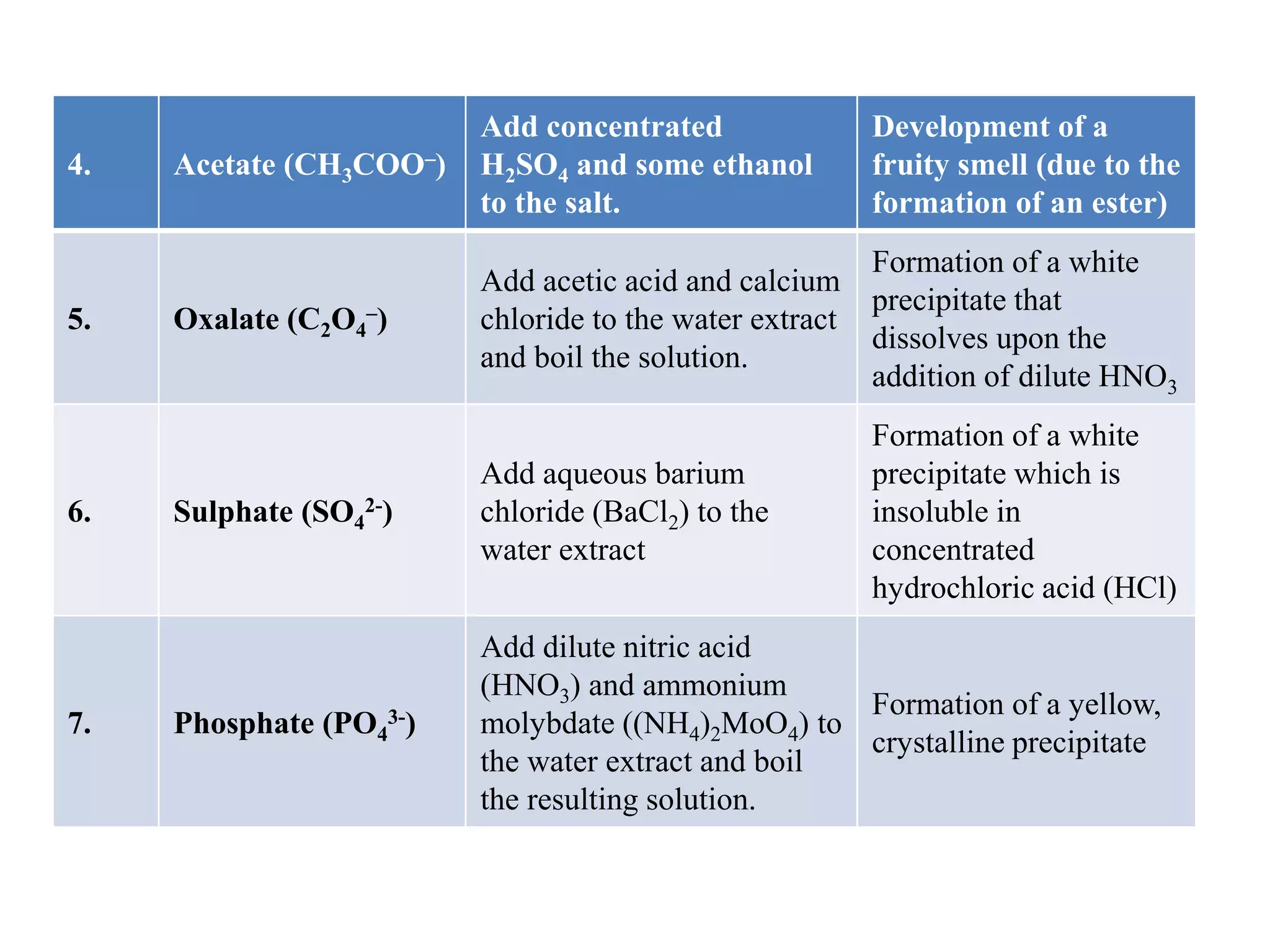
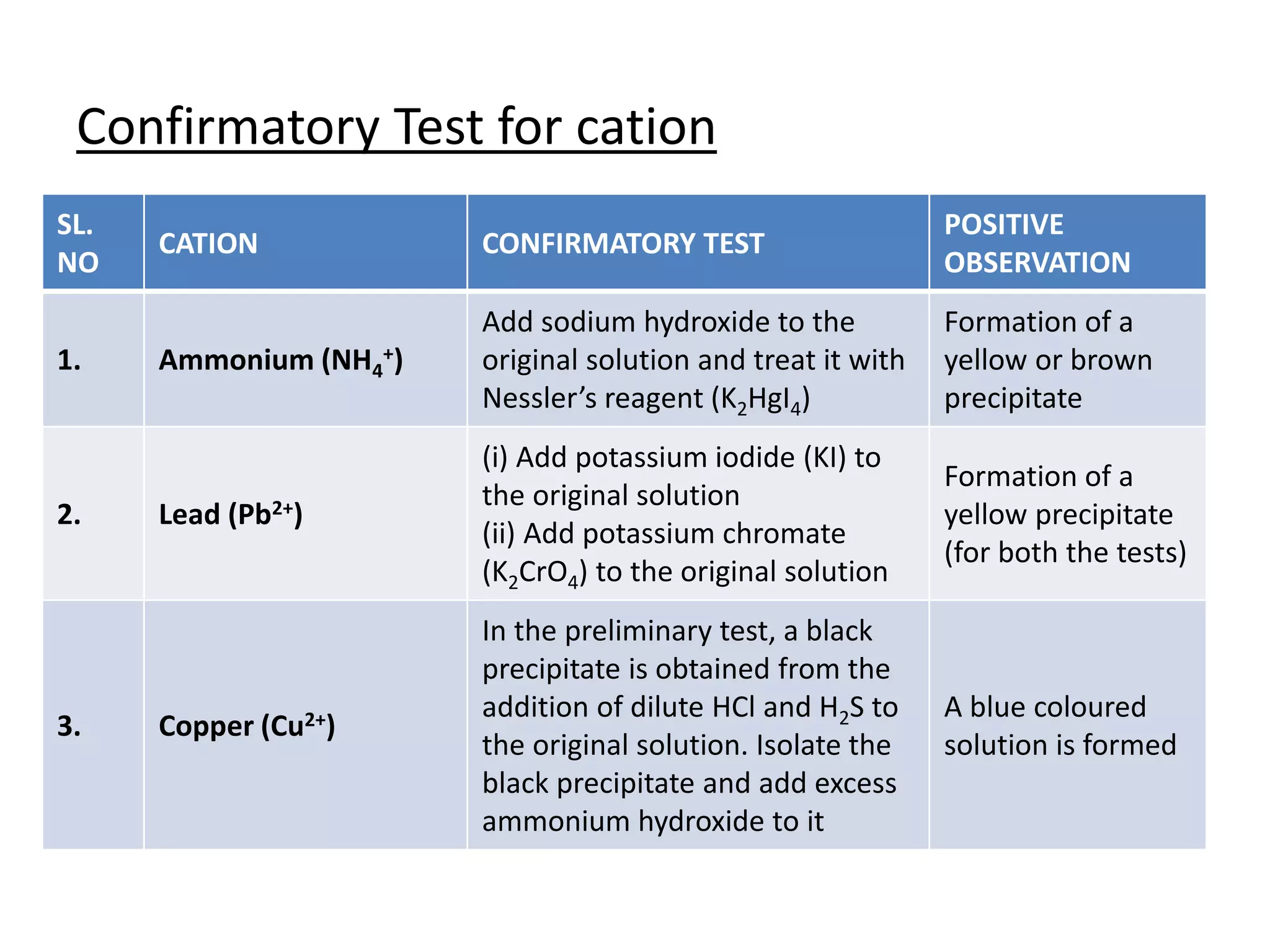
Salt analysis involves identifying the cation and anion in an inorganic salt through a series of confirmatory tests. Tests are done by dissolving the salt in water and adding other substances to look for precipitates or color changes. For example, adding barium chloride to the water extract will form a white precipitate confirming the presence of a sulfate anion. Similarly, adding sodium hydroxide and Nessler's reagent can confirm the presence of an ammonium cation through the formation of a yellow or brown precipitate. The document then outlines the specific confirmatory tests used to identify 11 common cations and 12 common anions through characteristic reactions.



![4. Iron (Fe3+)
Add concentrated nitric acid to the
original solution and heat it. A brown
precipitate will form. Add HCl and
potassium ferrocyanide (K4[Fe(CN)6]) to
it
A blue
precipitate is
formed
5.
Aluminium
(Al3+)
A gelatinous white precipitate is
obtained when NH4Cl and excess NH4OH
are added to the original solution.
Isolate the precipitate and dissolve it in
HCl. now add blue litmus and NH4OH to
it drop-by-drop
A floating, blue
layer is formed
on the surface
of the clear
solution
6. Cobalt (Co2+)
Add solid NH4Cl and excess NH4OH to
the original solution and pass H2S gas
through it. Dissolve the resulting blue
residue in water and add dilute
CH3COOH and KNO2 to it. Now warm the
mixture.
A yellow
precipitate is
obtained.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/identificationofcationsandanions-200425154256/75/Identification-of-cations-and-anions-7-2048.jpg)


