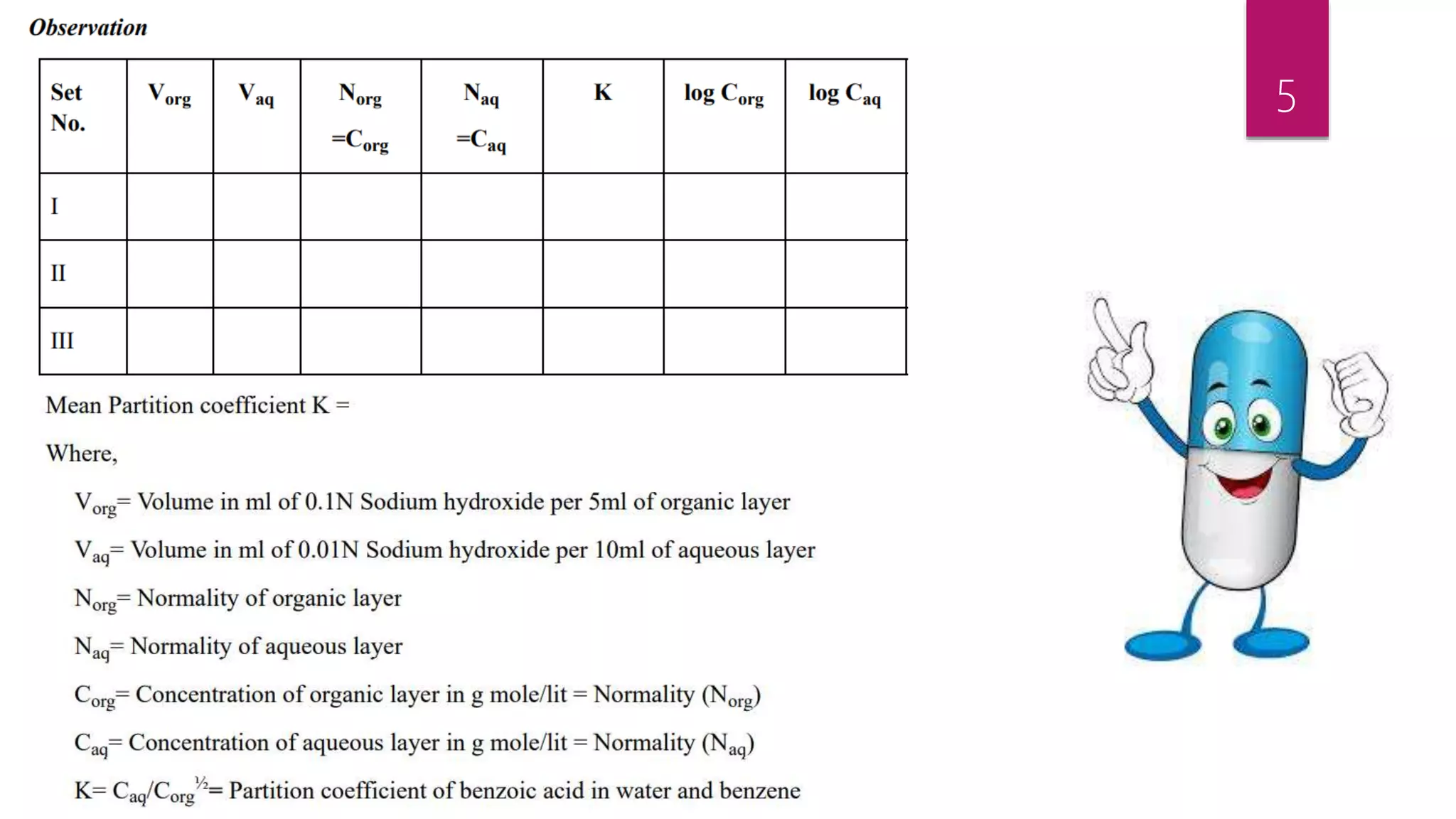
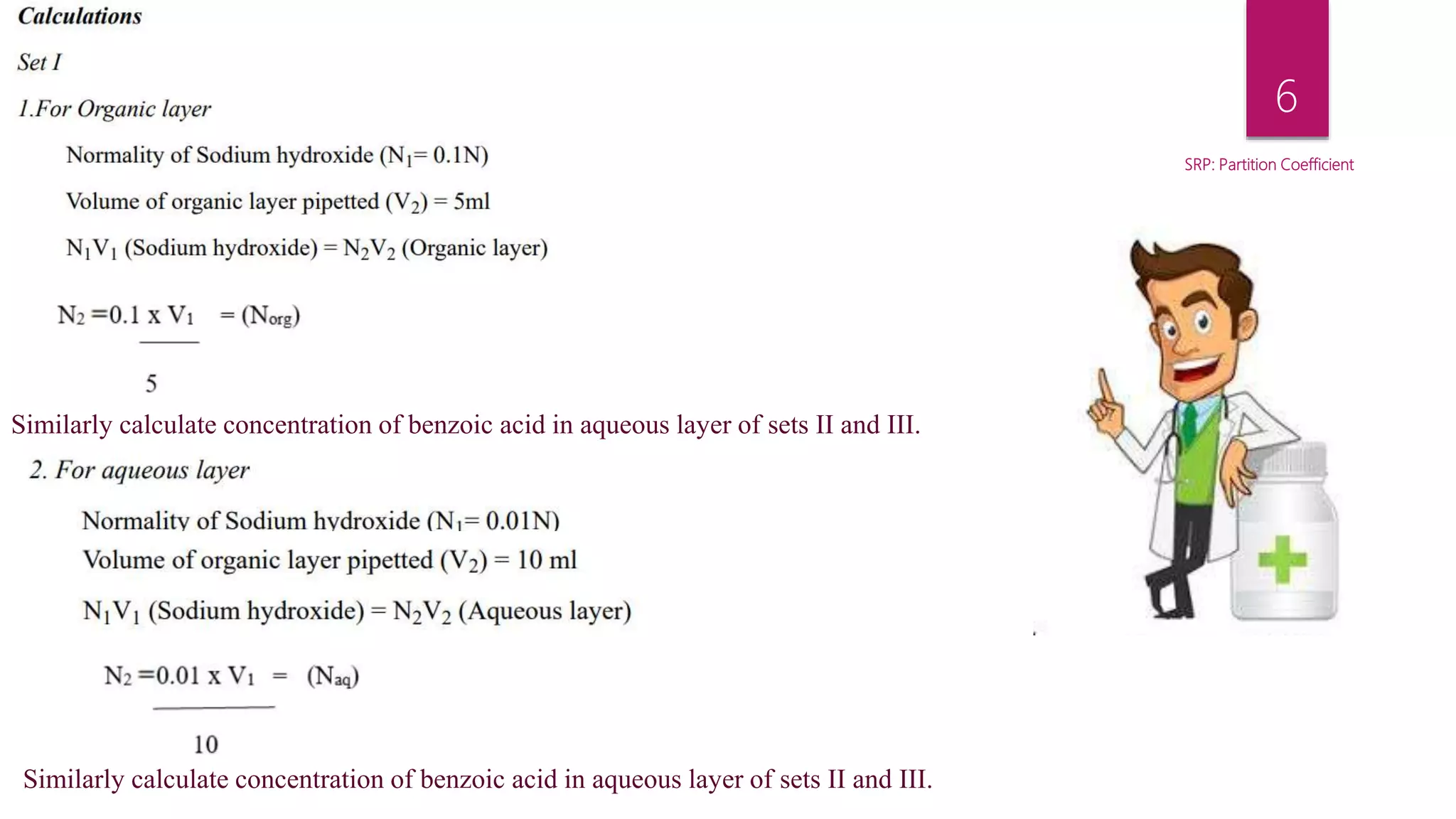
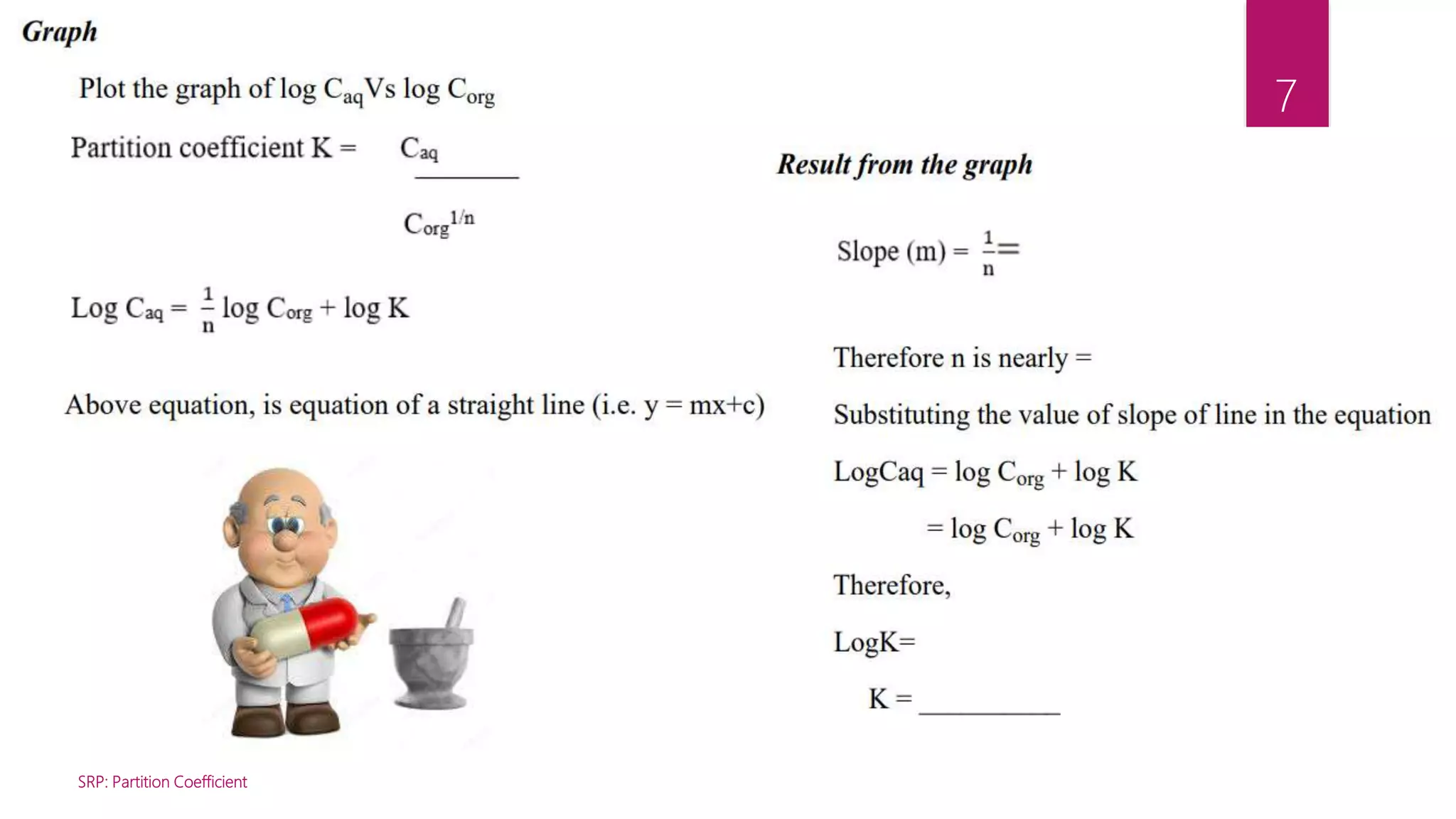
This document describes an experiment to determine the partition coefficient of benzoic acid between benzene and distilled water. The experiment involves preparing mixtures of benzoic acid saturated benzene solution and water in separating funnels, allowing the benzoic acid to distribute between the solvents, then measuring the concentrations in each solvent layer by titration. The partition coefficient is the ratio of concentrations of solute in the two solvents at equilibrium and this experiment aims to calculate it for benzoic acid between benzene and water.