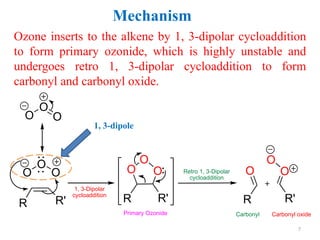
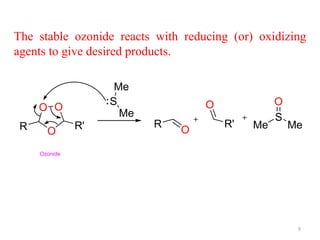
Ozonolysis is the oxidative cleavage of carbon-carbon double bonds using ozone. It involves a three step mechanism: 1) ozone inserts into the double bond to form an unstable primary ozonide, 2) the primary ozonide decomposes to a carbonyl and carbonyl oxide through retro cycloaddition, 3) the carbonyl oxide undergoes cycloaddition again with another carbonyl to form a stable ozonide. The ozonide intermediate can then be worked up using reducing or oxidizing agents to yield different products such as aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, or carboxylic acids.


![4
(1) Reductive work up using mild reducing agents such
as Me2S (or) PPh3 (or) Zn dust produces
aldehyde and ketone.
R1
R3
R2
H
R1
R3
R2
H
O O
O3
Mild Reductive
Work Up
R1
R3
R2
H
O
O O
Me2S/PPh3/
Zn dust
[Ozonide]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ozonolysis-191221173500/85/Ozonolysis-4-320.jpg)
![5
(2) Reductive work up using strong reducing agents
such as LiAlH4 (or) NaBH4 produces alcohols.
R1
R3
R2
H
R1
R3
R2
OH HO
O3
Strong Reductive
Work Up
R1
R3
R2
H
O
O O
LiAlH4/
NaBH4
[Ozonide]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ozonolysis-191221173500/85/Ozonolysis-5-320.jpg)
![6
(3) Oxidative work up using oxidizing agents such as
H2O2 (or) O2 provides carboxylic acids.
R1
R3
R2
H
R1
R3
R2
OH
O O
O3
Oxidative
Work Up
R1
R3
R2
H
O
O O
H2O2/
O2
[Ozonide]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ozonolysis-191221173500/85/Ozonolysis-6-320.jpg)