Embed presentation
Downloaded 17 times


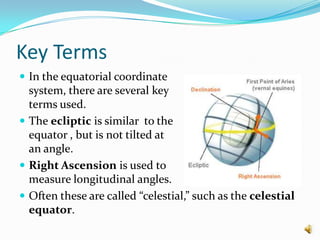



Measuring declination allows one to find the angle of celestial objects like the sun above or below the celestial equator. Declination is part of the equatorial coordinate system used to map objects' positions. Simple equations can be used to calculate an object's declination based on the day of the year, for example the sun's declination on October 30th is approximately -19.11 degrees. Declination is primarily used for celestial mapping but can also determine the angle of sunlight for a location on Earth.





