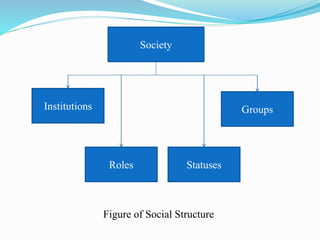
Social structure refers to the framework of social institutions, practices, and groups that organize a society. It establishes norms that govern behavior and the way people interact. Key components of social structure include institutions like education and religion, statuses like roles and positions in society, and social groups. Statuses can be ascribed, such as gender assigned at birth, or achieved through individual efforts. Roles define appropriate behaviors for a given status. Issues can arise when roles conflict or the demands of a role cause strain. Social institutions are purposive, structured groups that perform important social functions like socializing members of a society through families, education, government, and religion.