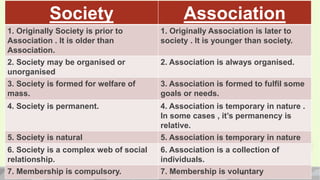
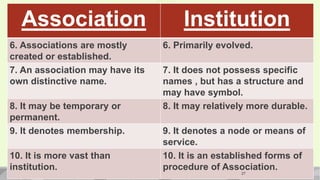
An association is a group of individuals organized to pursue common interests or goals through cooperation. The document defines associations and provides examples such as political parties, religious groups, student unions, and professional organizations. It describes the key characteristics of associations, including that they are formed by people, focus on common interests, require a cooperative spirit among members, and have some form of organization and rules to regulate member relations. Associations serve as means for members to achieve shared objectives and act as agents for transmitting ideas.