This document defines and compares key sociological concepts:
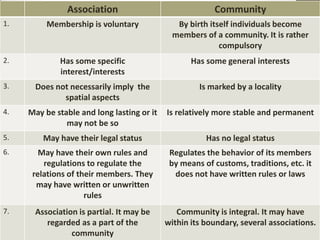
1) Society is a collection of individuals united through social relationships and interdependence, while community refers to a smaller group sharing a locality and sense of belonging.
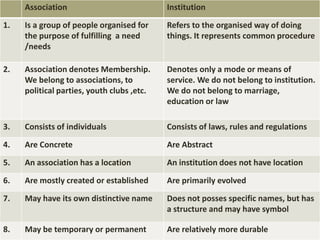
2) An association is a deliberately formed group pursuing shared interests through organization, whereas an institution represents established social norms and structures for meeting needs.
3) A social system consists of interacting individuals following cultural norms and common goals, distinguished from other systems by boundaries.