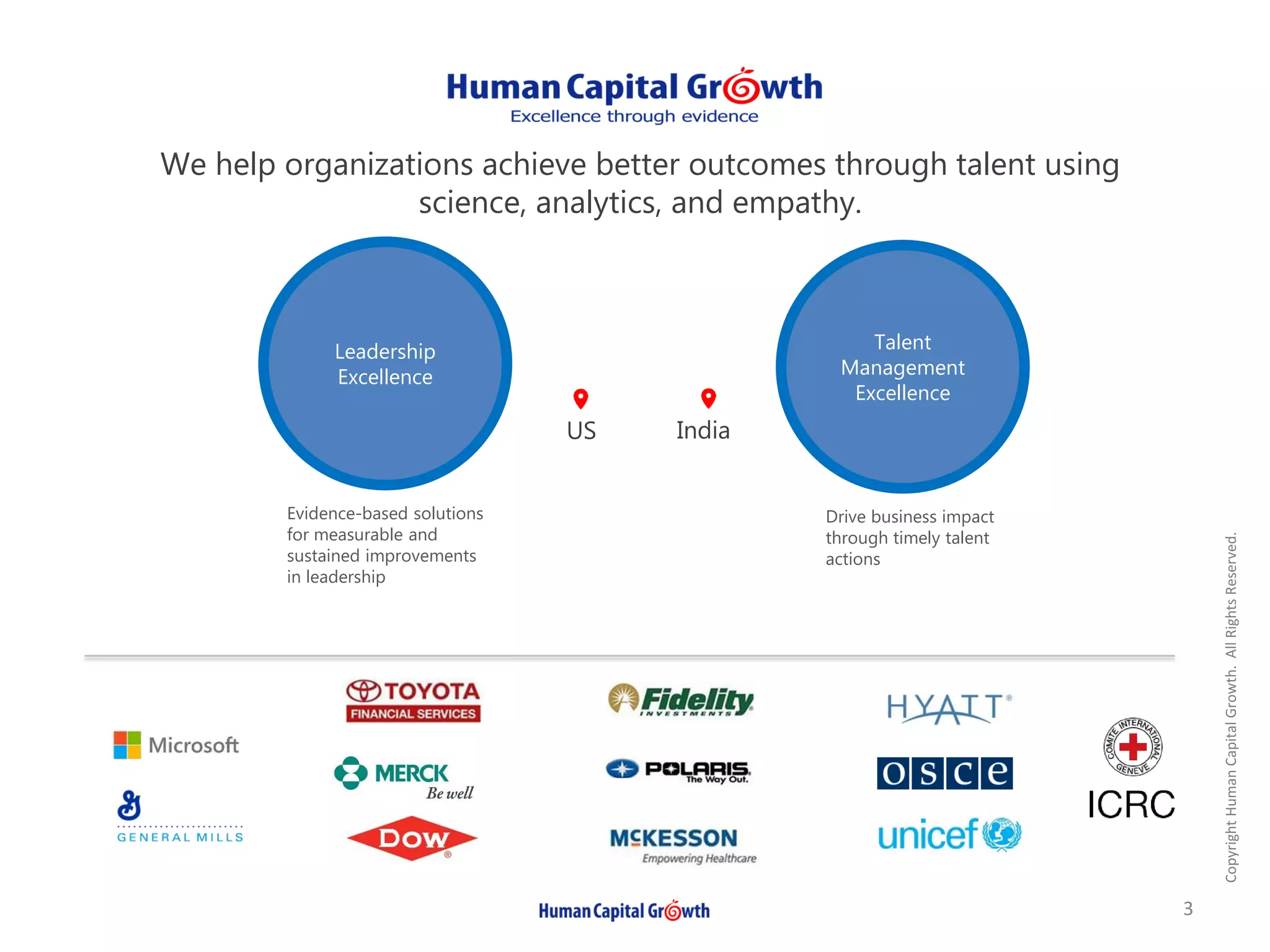
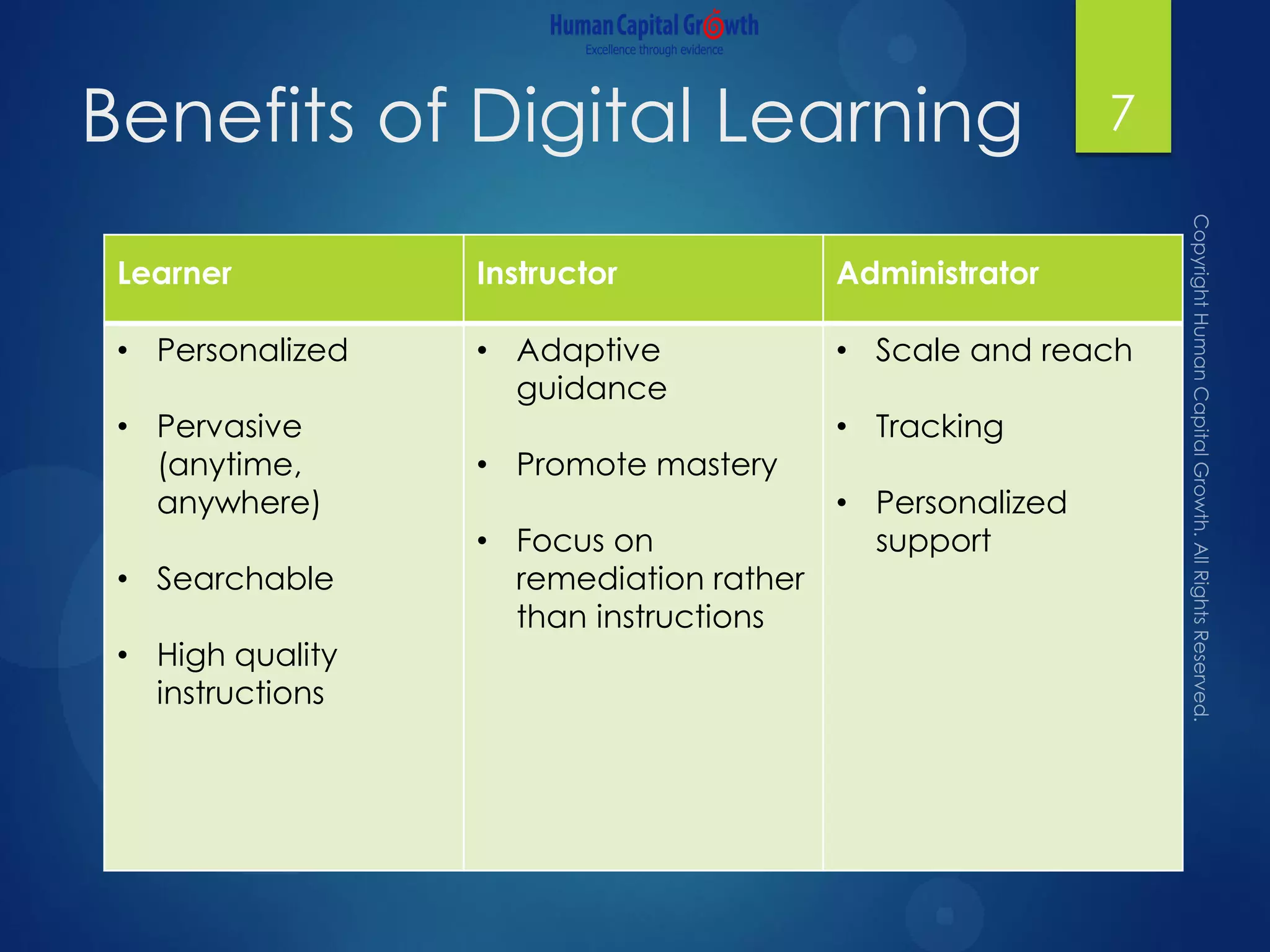
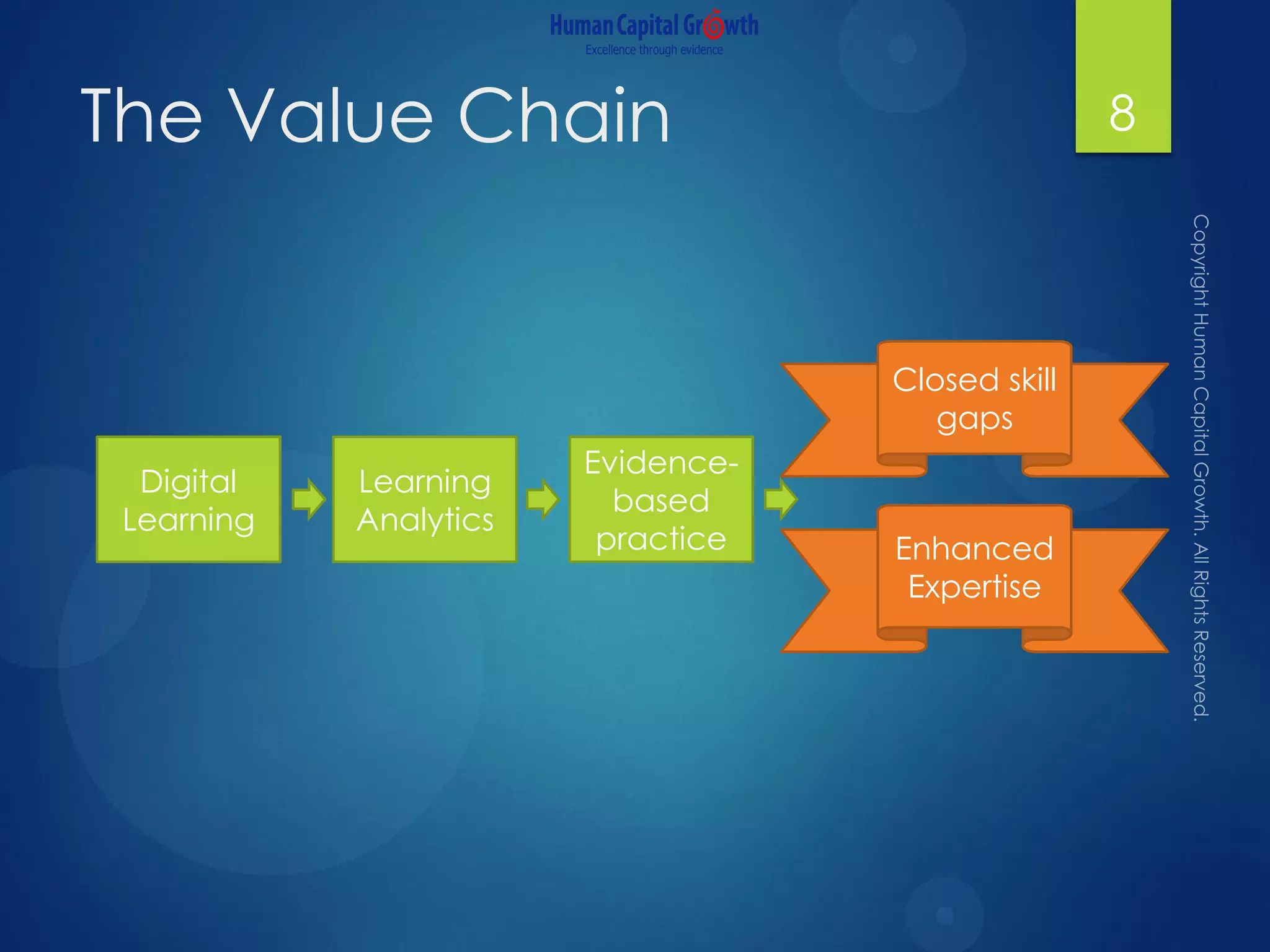
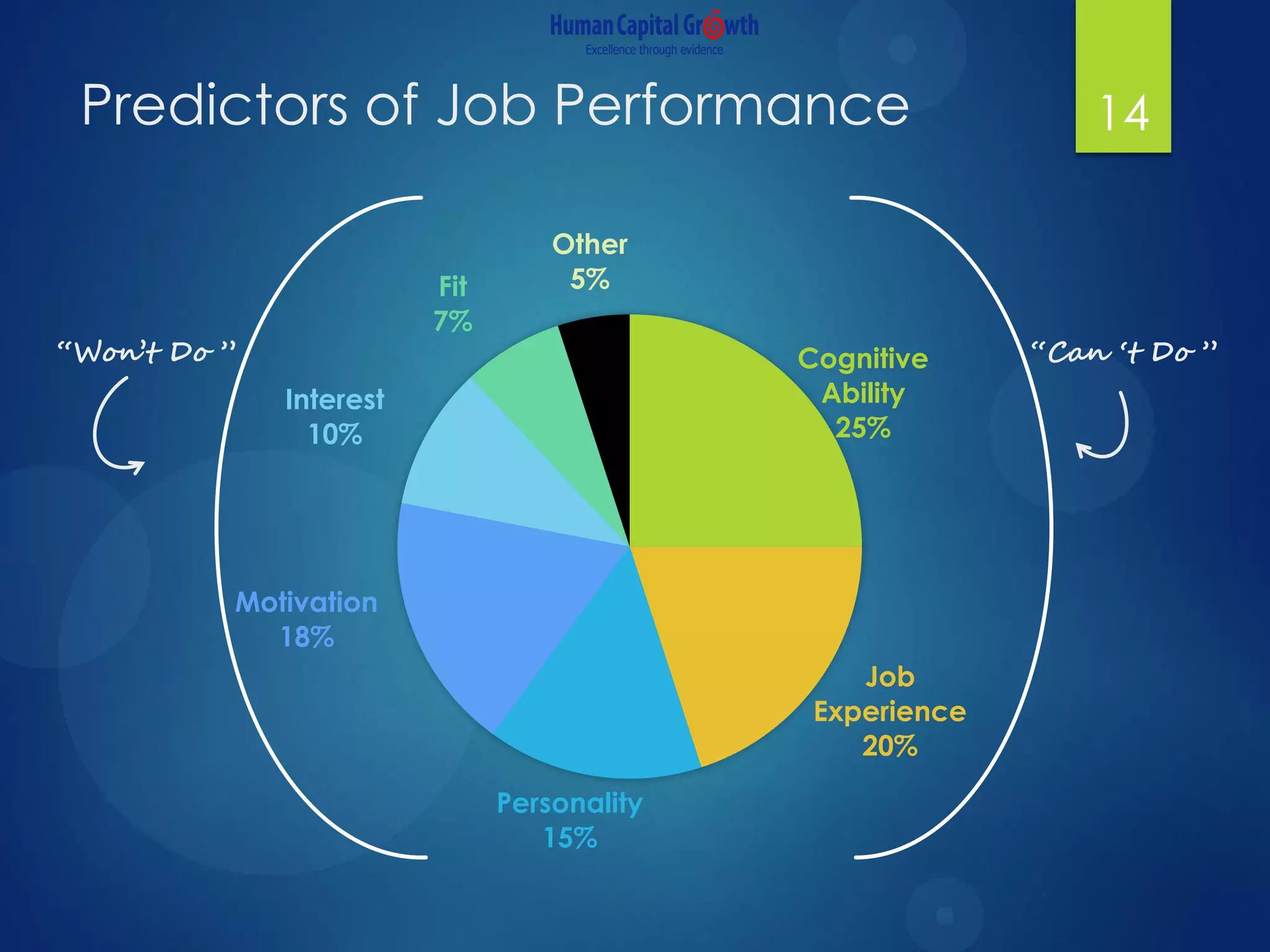
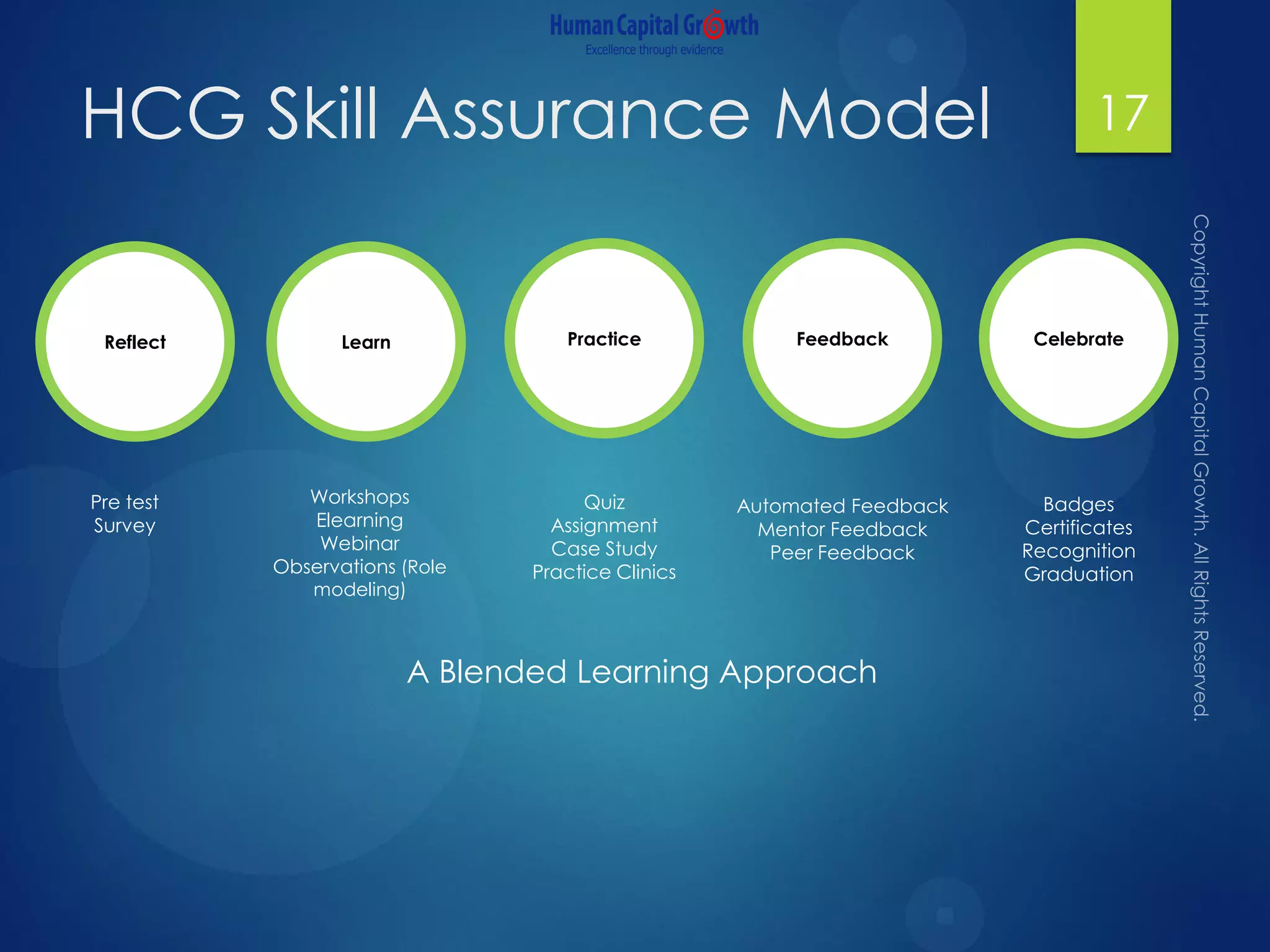
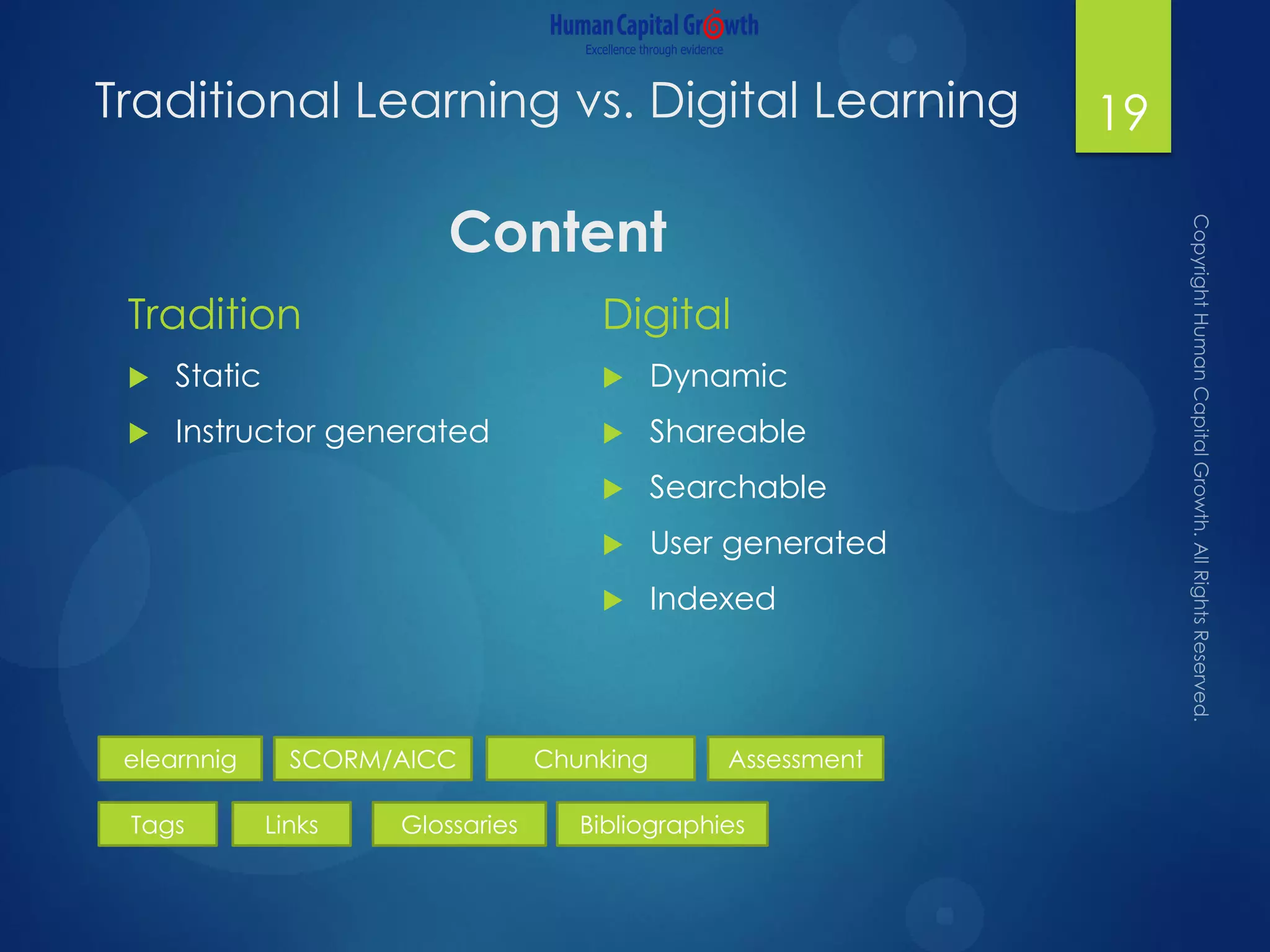
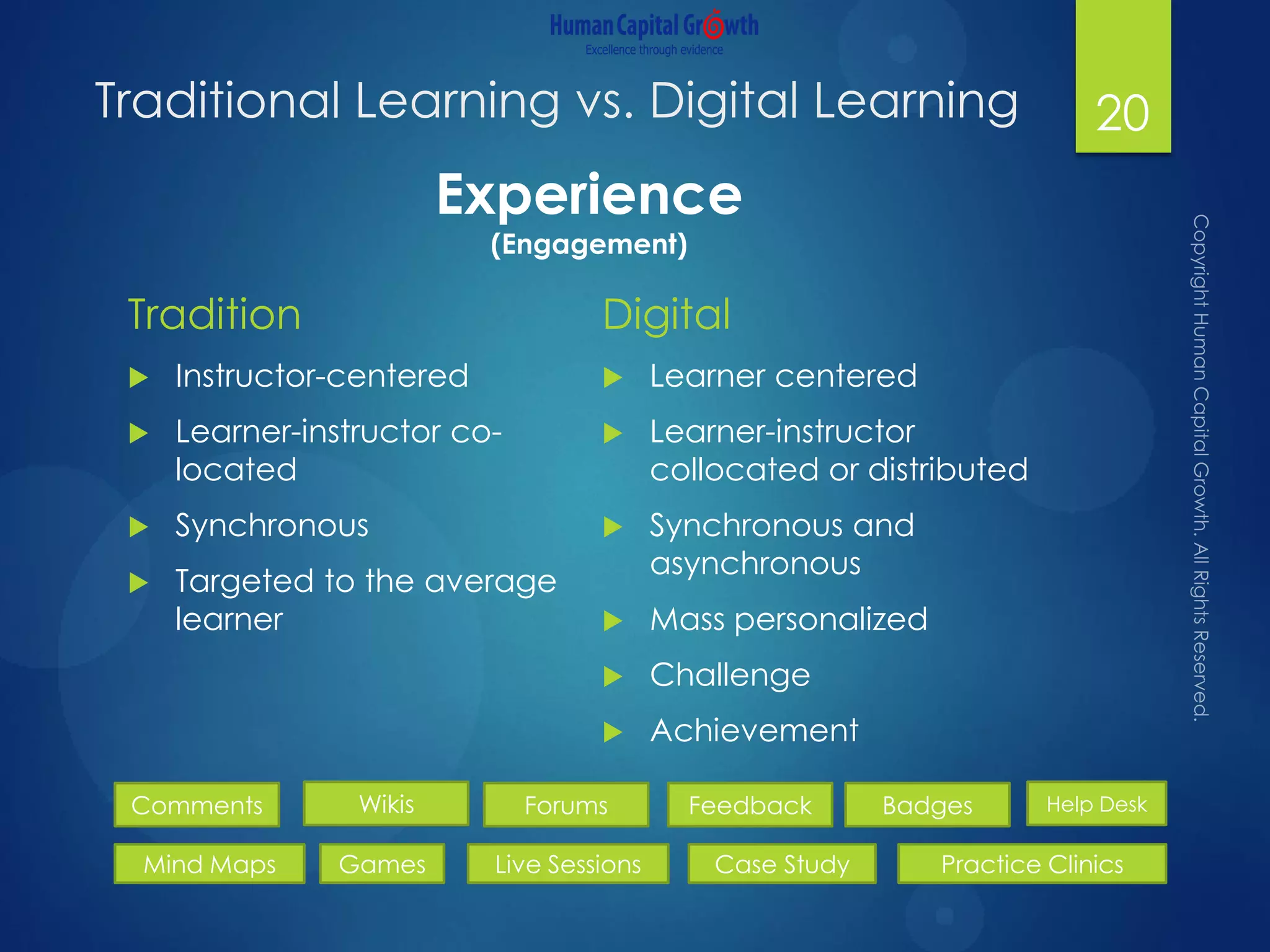
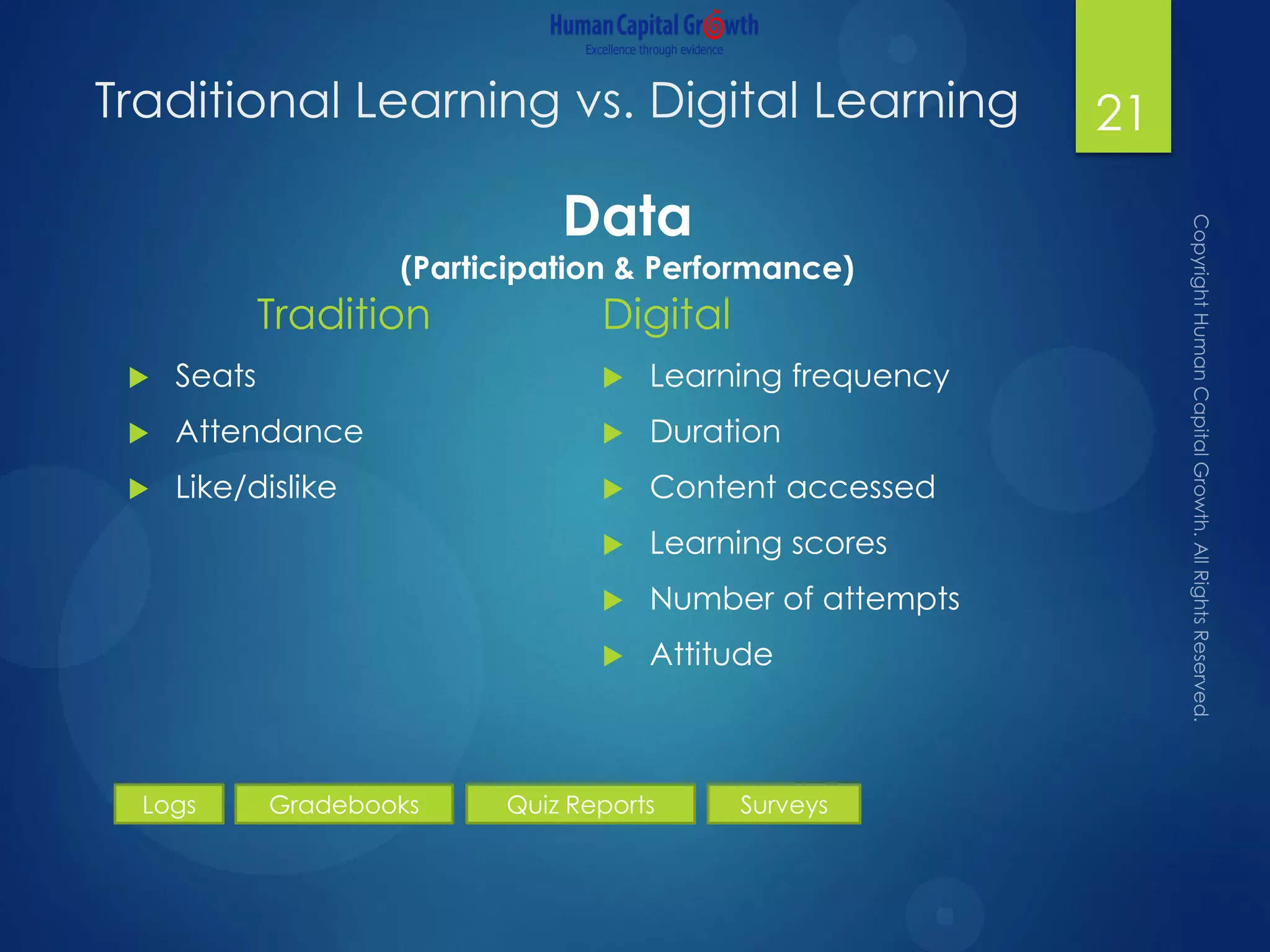
The document discusses the digitization of the learning and development function, presenting methods and benefits of digital learning such as personalized, accessible, and high-quality instruction. It highlights key considerations in talent and human capital development, questioning the needs and content suitable for digitization. It outlines various types of digital learning approaches and the skills required for effective implementation.