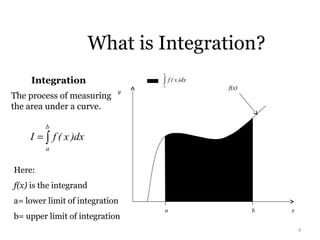
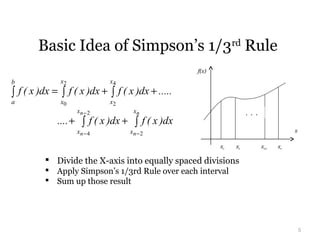
This document explains Simpson's 1/3rd rule for numerical integration. Simpson's 1/3rd rule approximates the integral of a function over an interval by breaking the interval into equal subintervals and approximating the function within each subinterval as a quadratic polynomial. The approximation takes the function values at the endpoints and midpoint of each subinterval. The approximations over all subintervals are then summed to give an approximation of the full integral. Important considerations for applying Simpson's 1/3rd rule include using an even number of equal subintervals and having a minimum of 3 points defined in each subinterval.




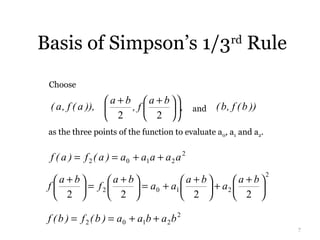
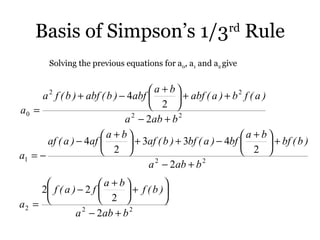
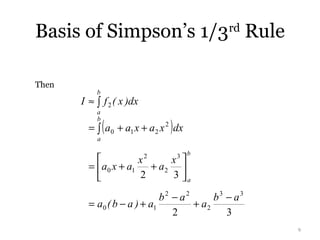
![Basis of Simpson’s 1/3rd
Rule
10
Substituting values of a0, a1, a2 give
+
+
+
−
=∫ )b(f
ba
f)a(f
ab
dx)x(f
b
a 2
4
6
2
Since for Simpson’s 1/3rd Rule, the interval [a, b] is broken
into 2 segments, the segment width
2
ab
h
−
=
it is called Simpson’s 1/3rd Rule.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simpsosonethirdrule-171204205226/85/Derivation-of-Simpson-s-1-3-rule-10-320.jpg)

