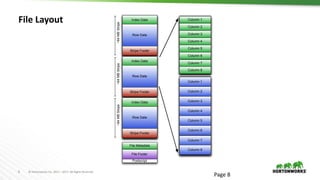
The document discusses ORC (Optimized Row Columnar) file format, highlighting its advantages over previous formats used in Hadoop applications, such as improved performance, self-describing structure, and support for schema evolution. It details the file and stripe structure, optimization techniques, and the integration of ORC with Hive and other tools. Additionally, it emphasizes current features like column encryption and the ability to handle ACID transactions for better data management.