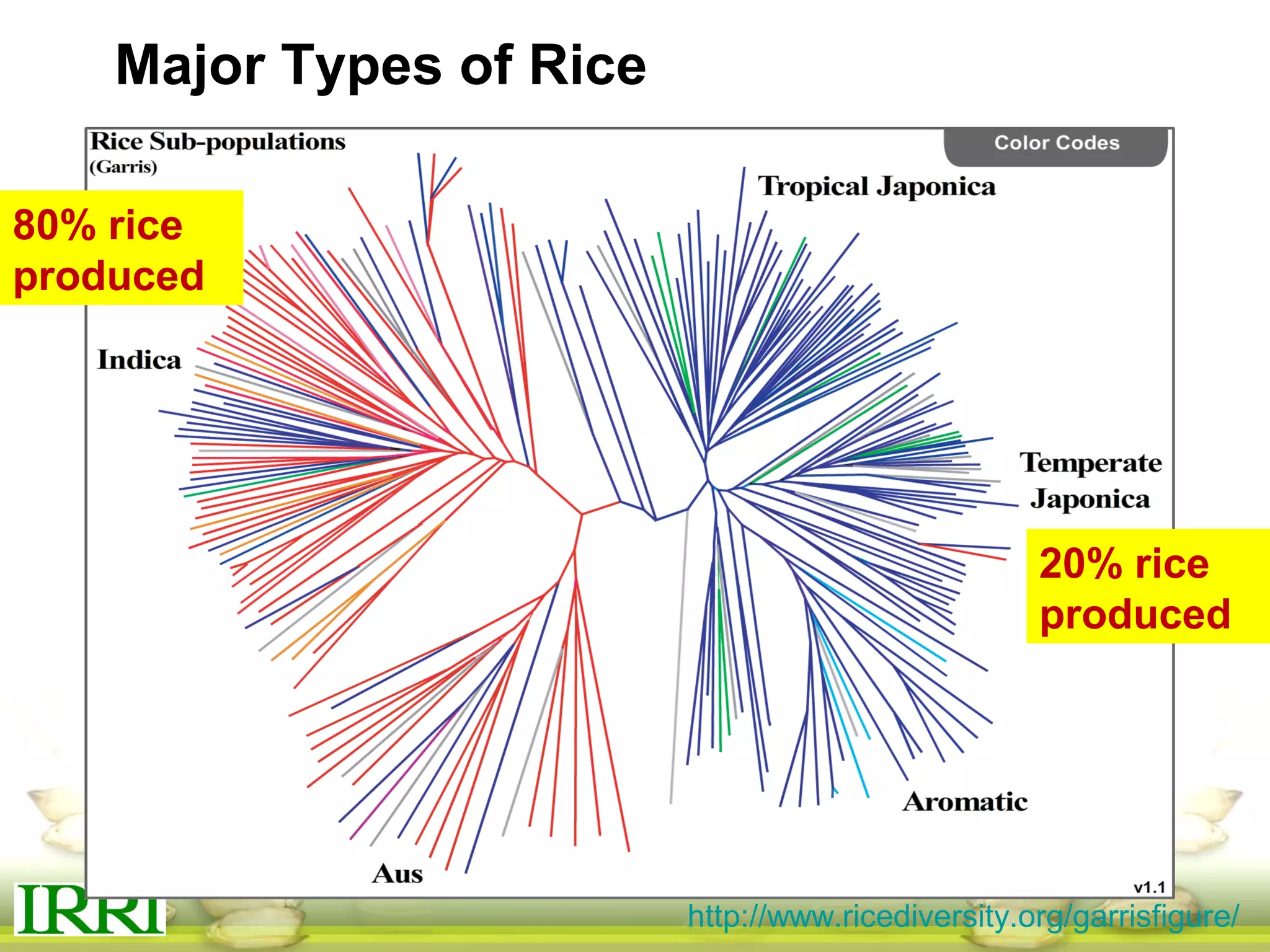
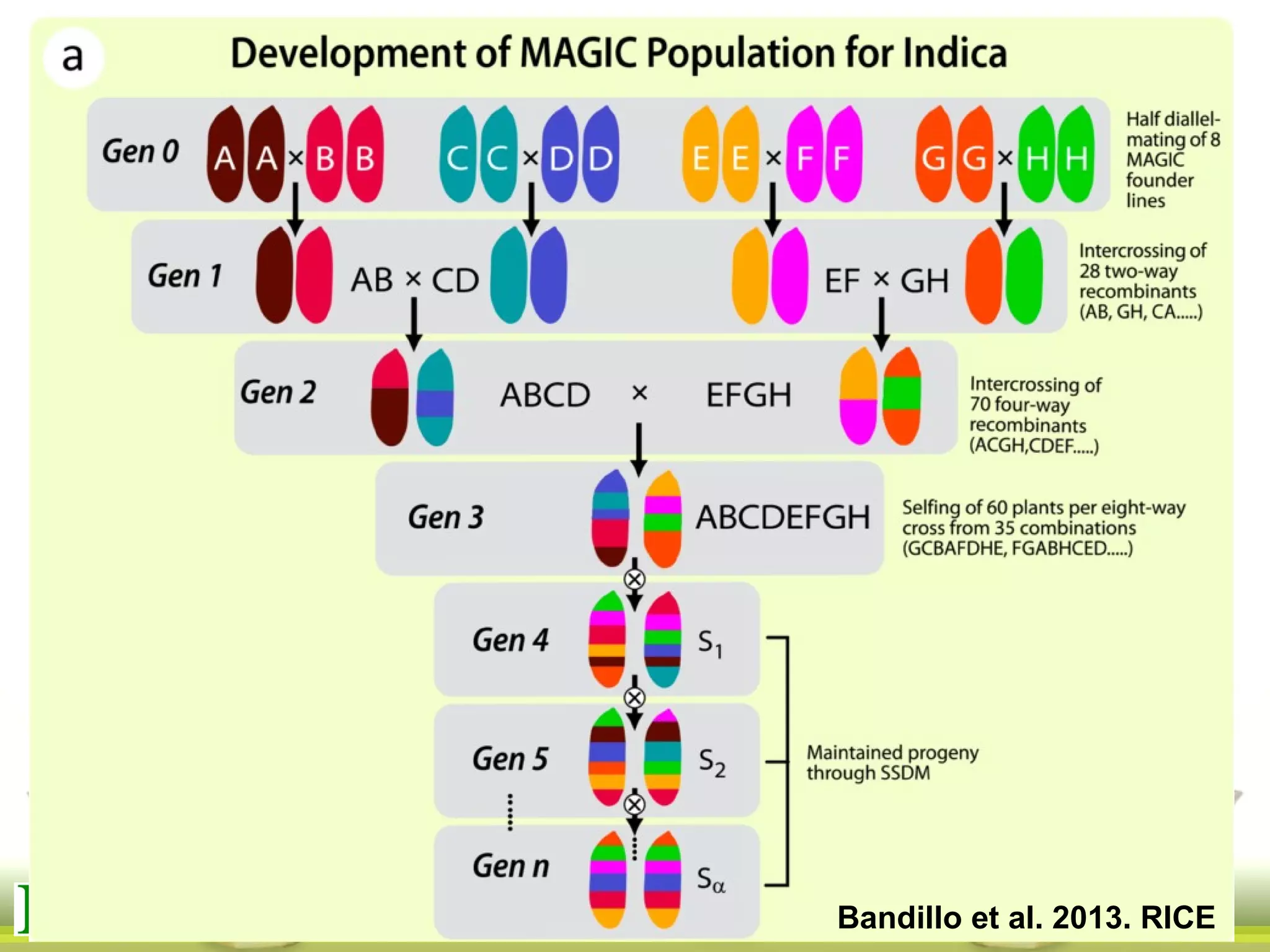
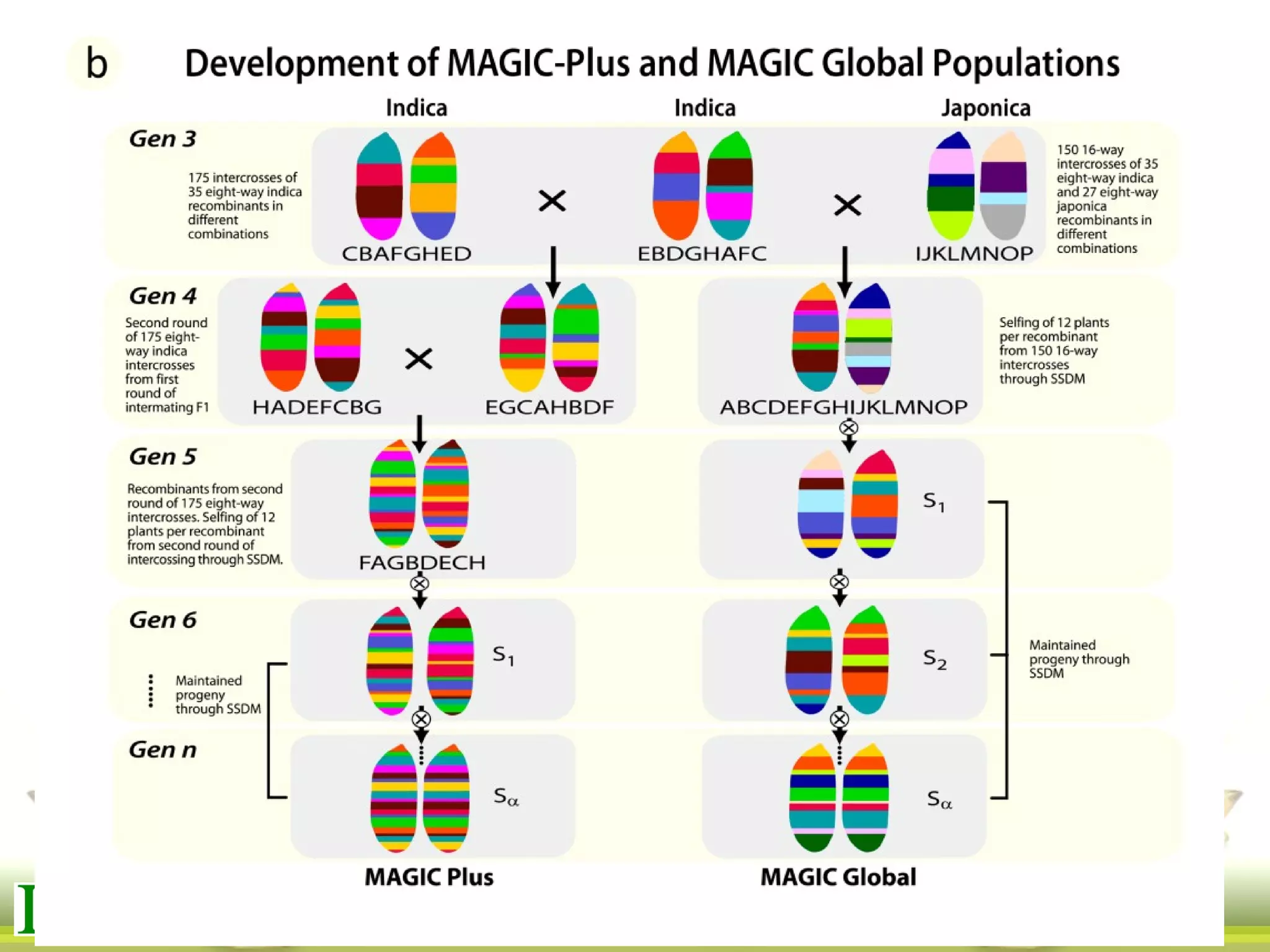
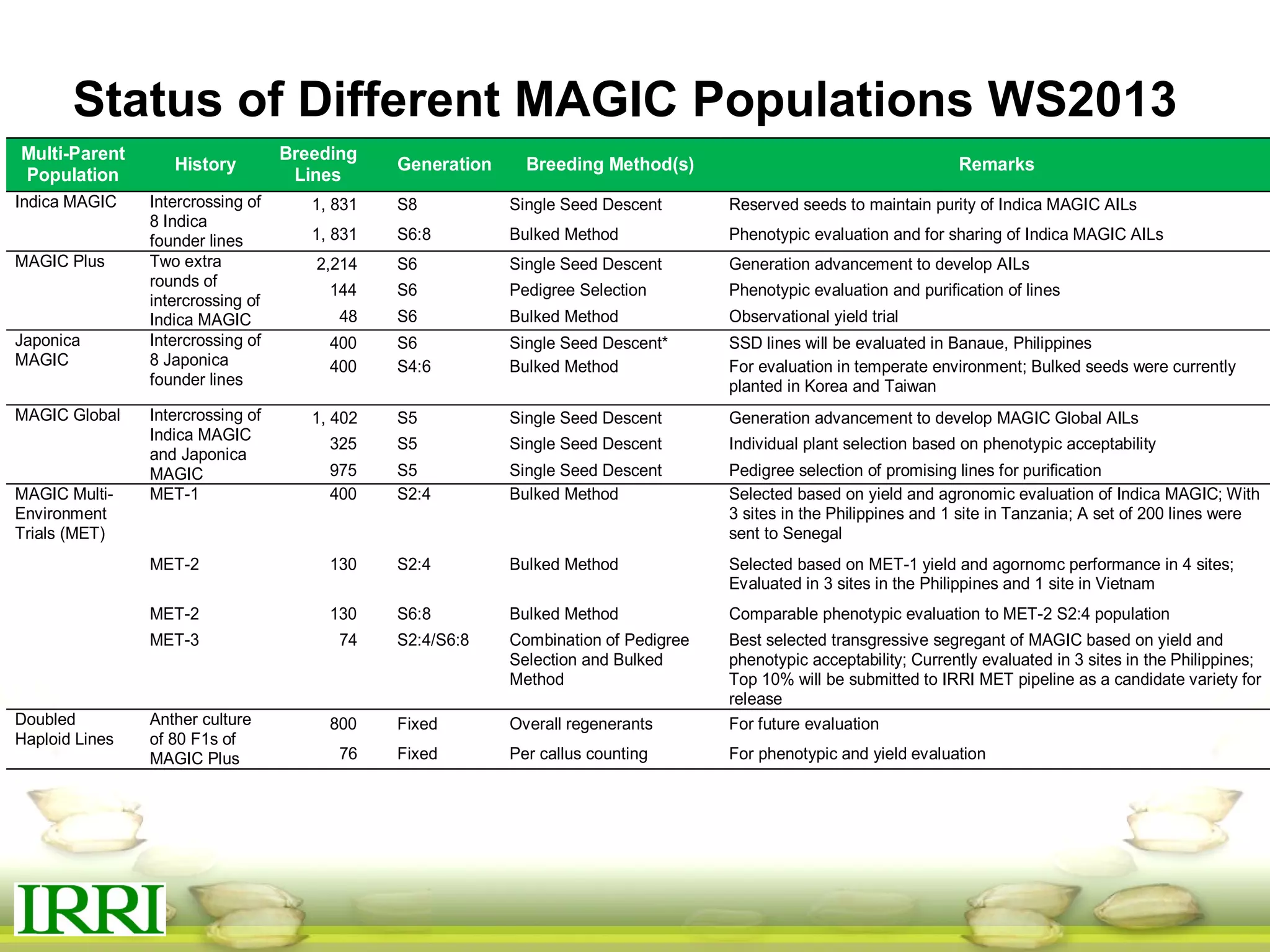
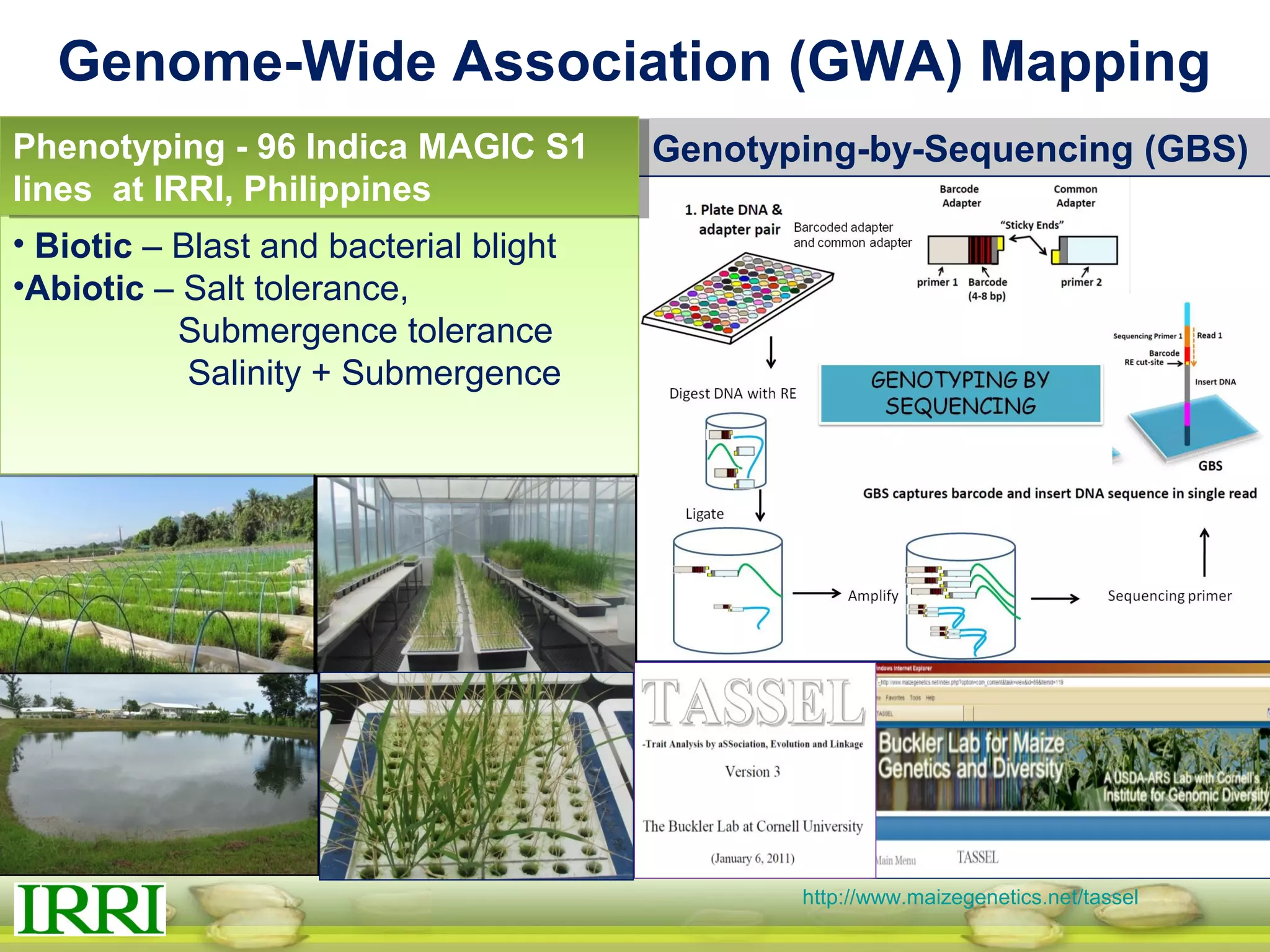
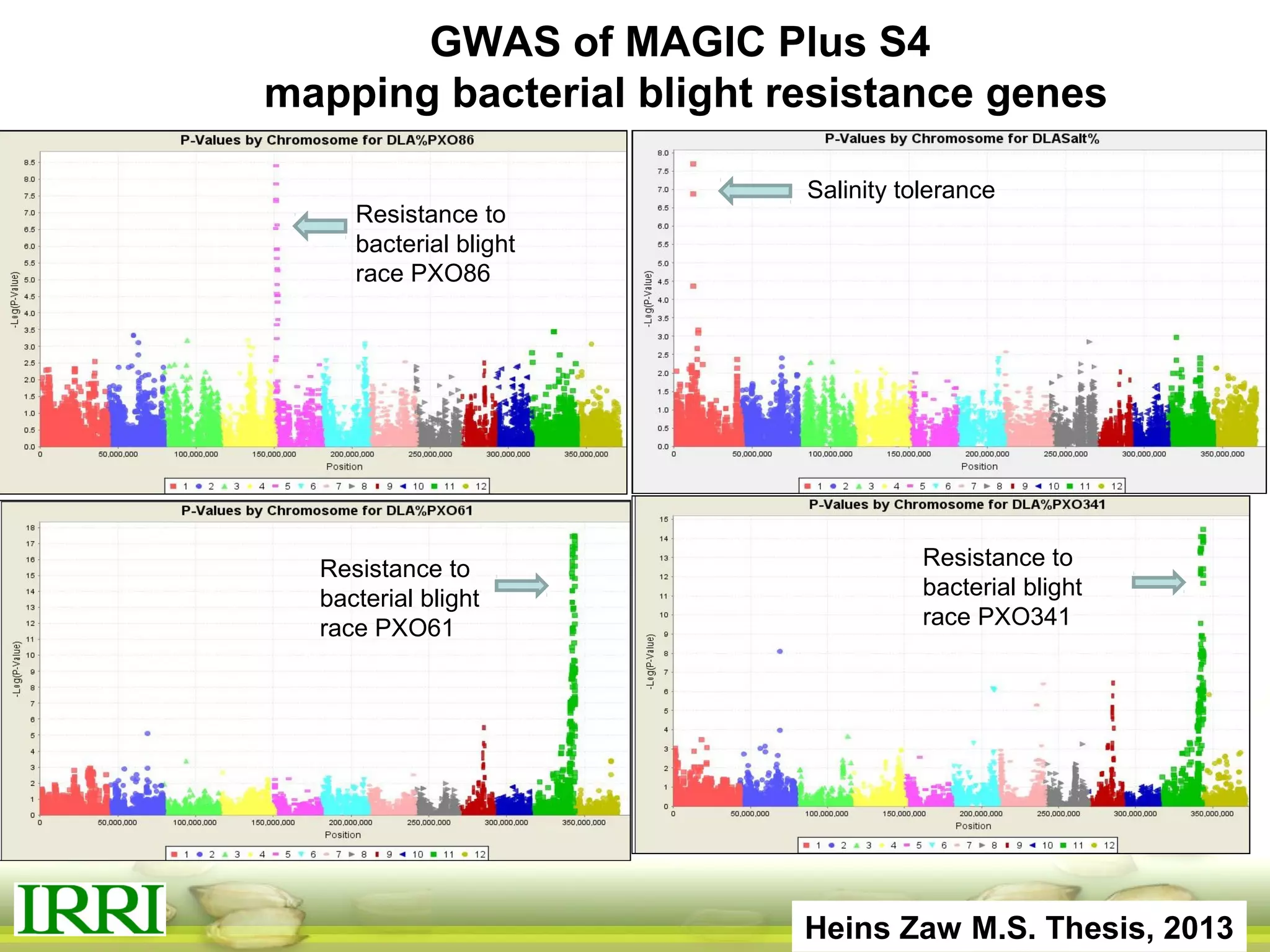
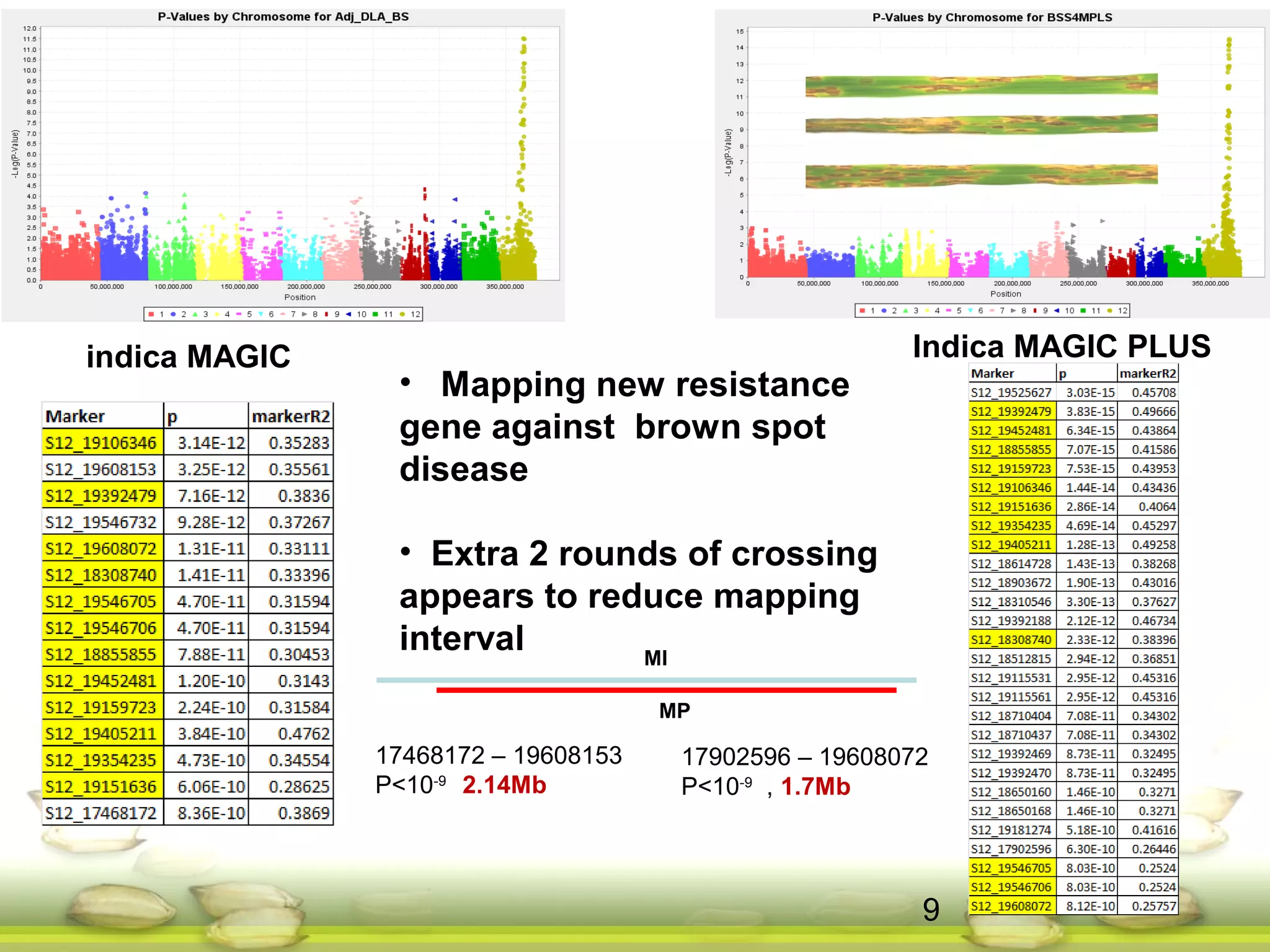
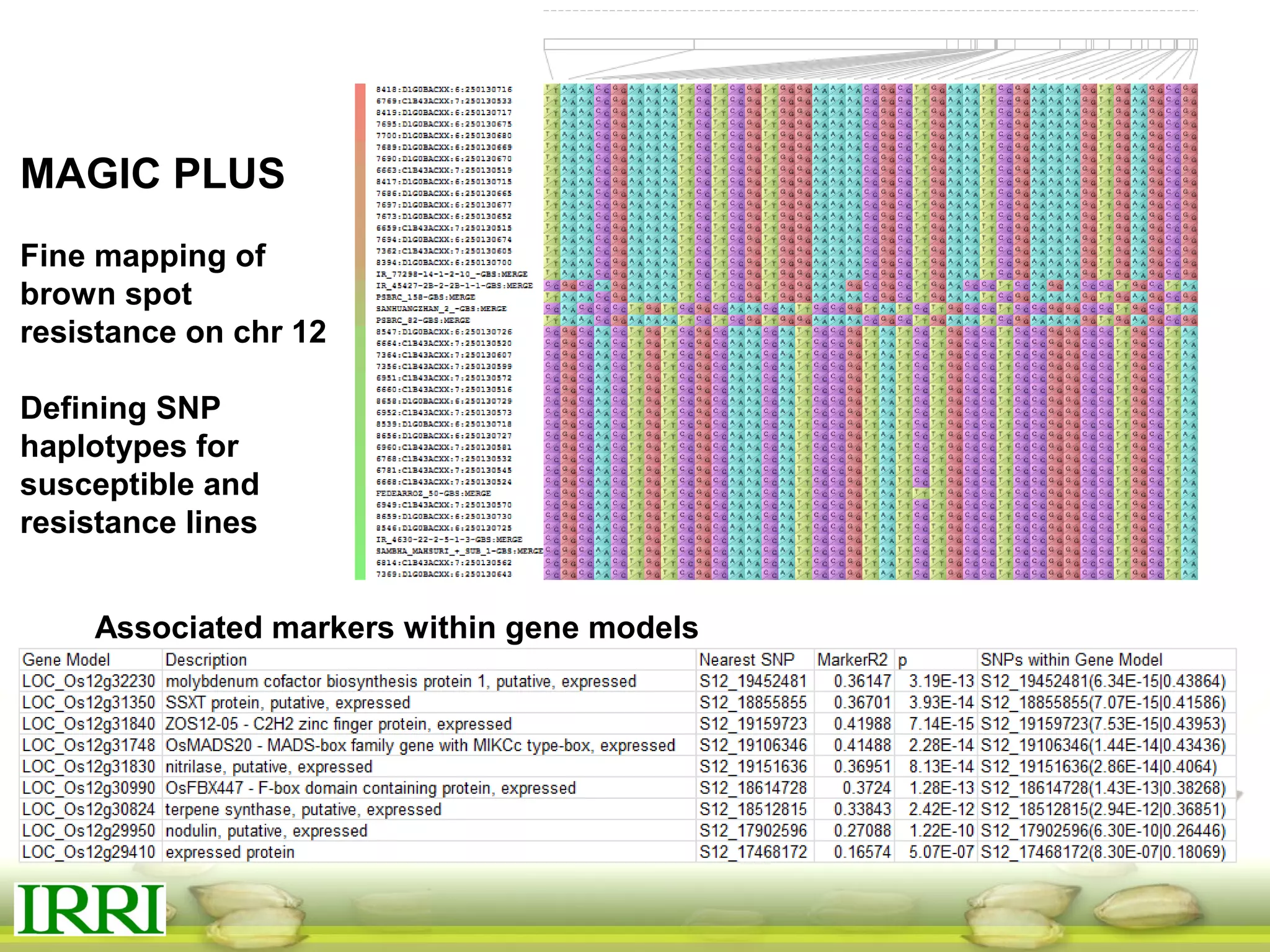
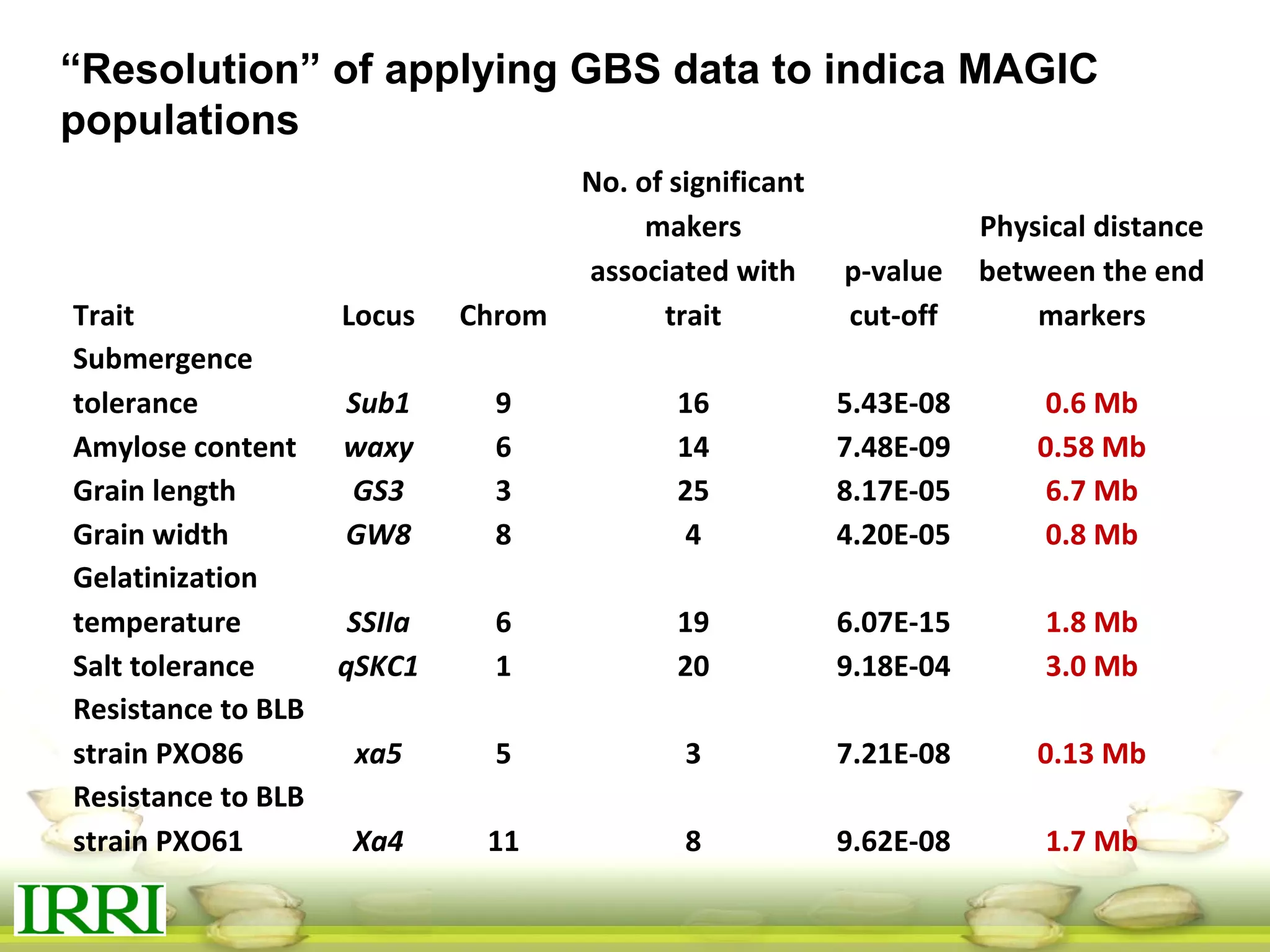
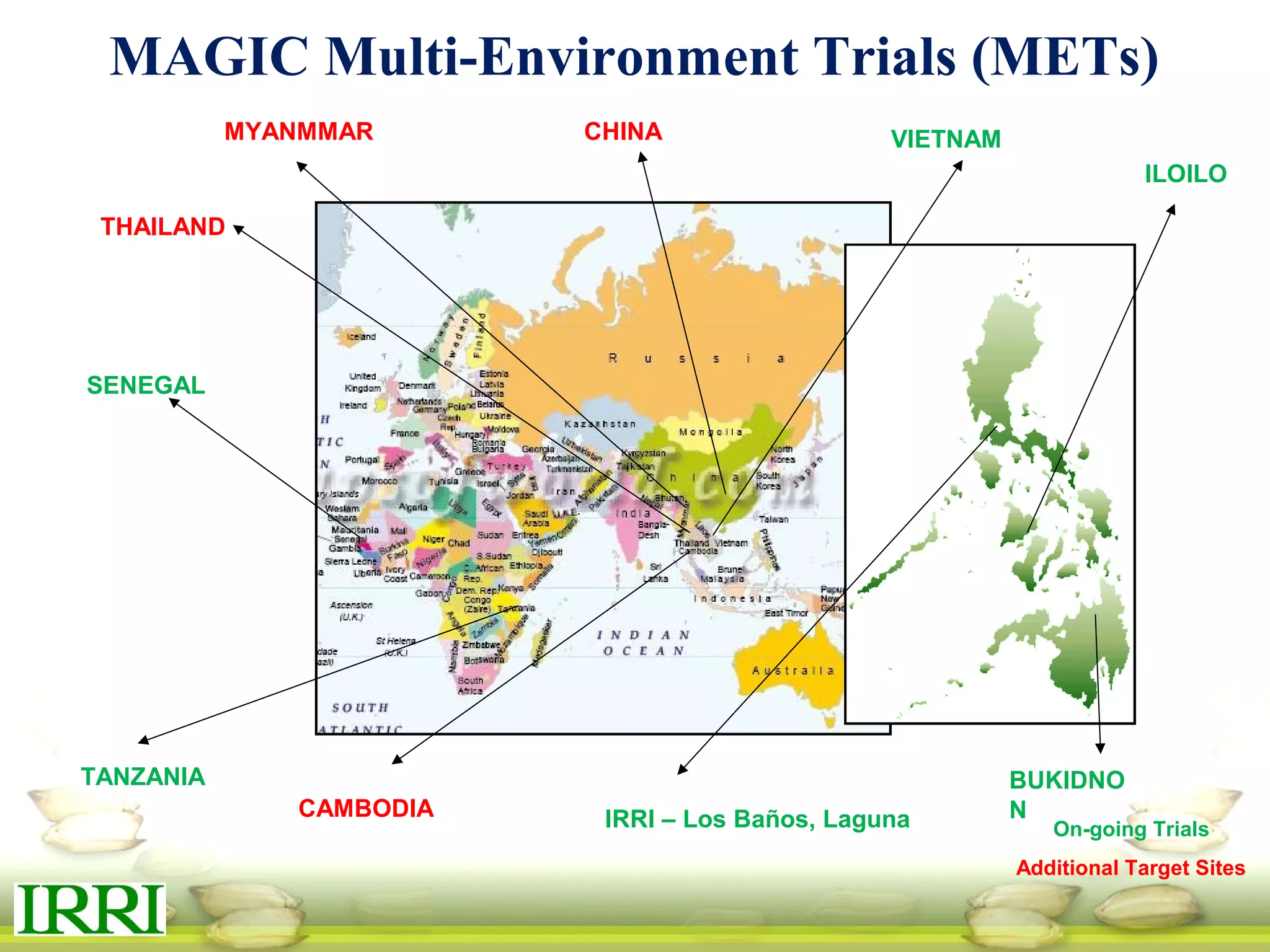
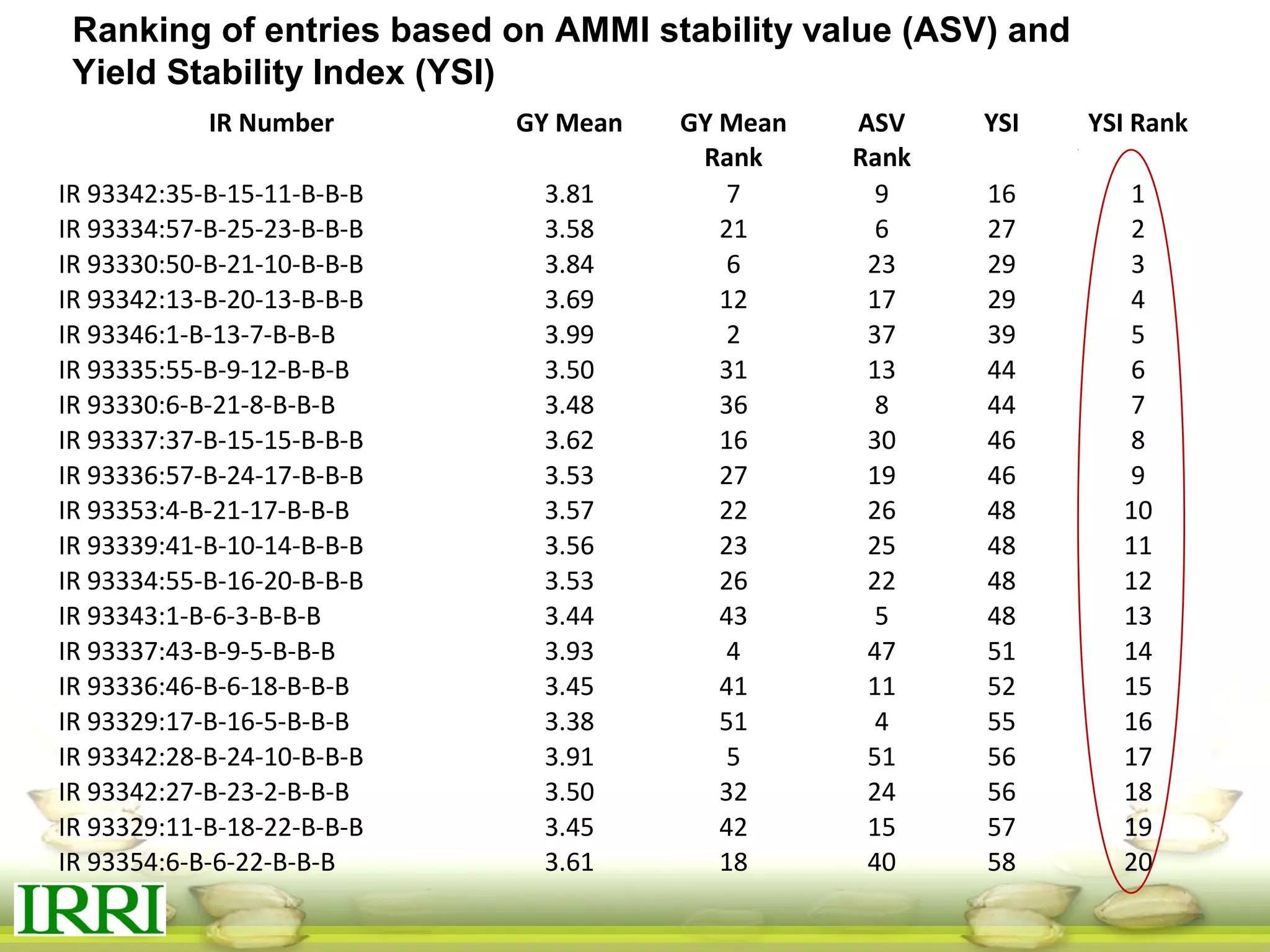
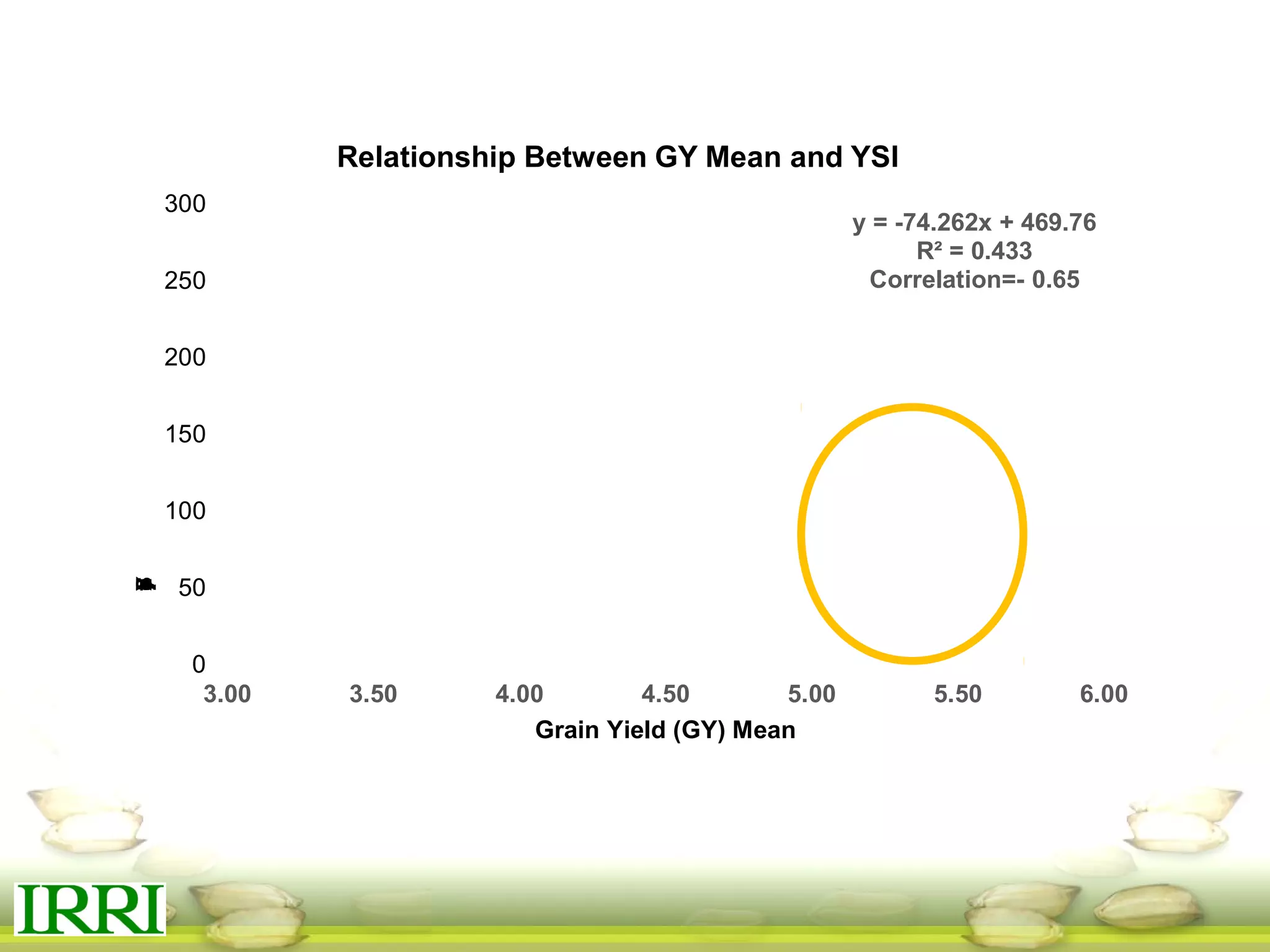
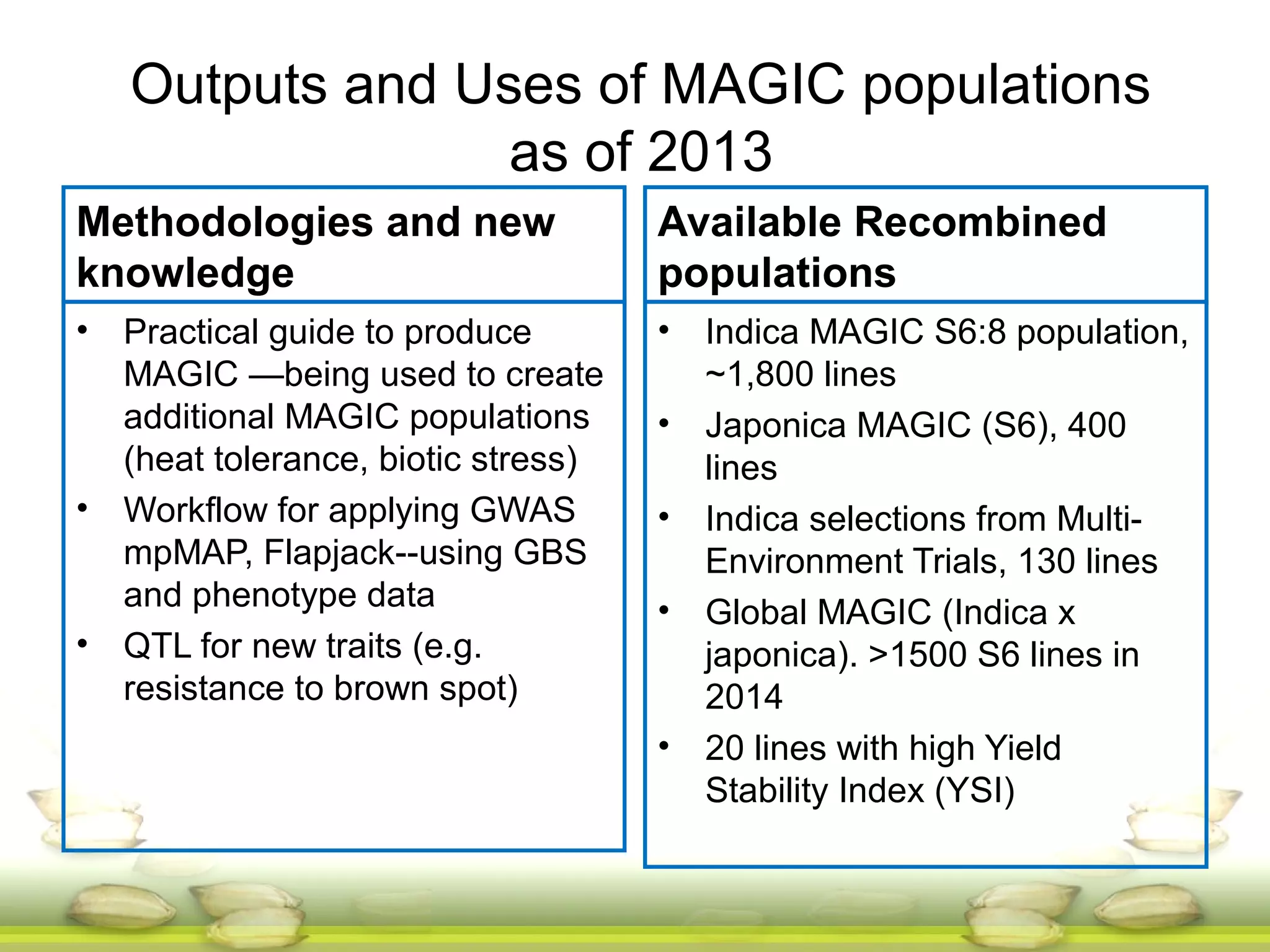
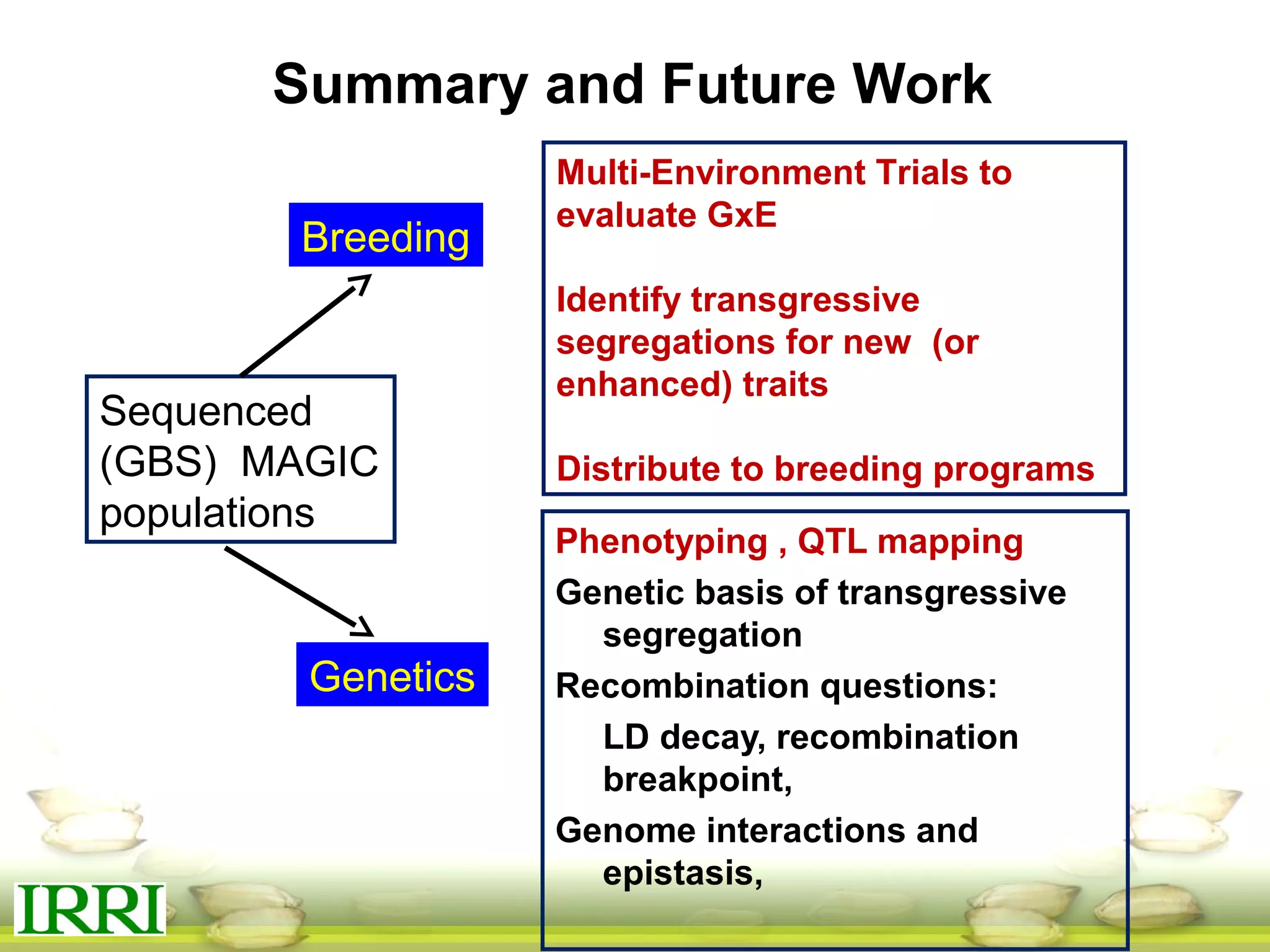
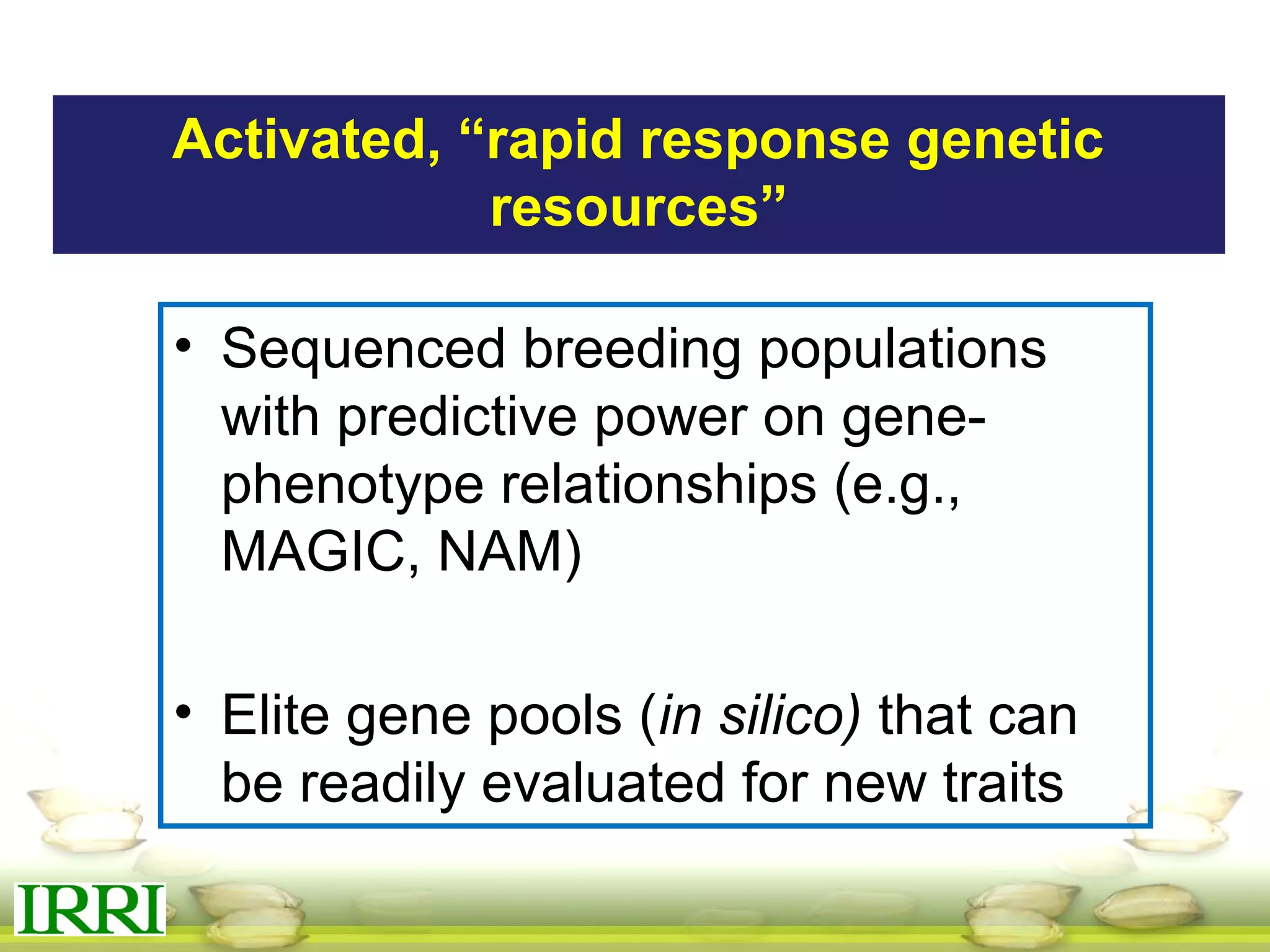
This document summarizes the status of different MAGIC (Multi-parent Advanced Generation Inter-Cross) rice populations including Indica MAGIC, Japonica MAGIC, MAGIC Global, and MAGIC Plus. It discusses genome-wide association studies conducted on these populations that have identified loci associated with traits like submergence tolerance, amylose content, and disease resistance. Multi-environment trials of different MAGIC populations are ongoing in several countries. The document outlines future work including continued phenotyping, quantitative trait loci mapping, and distribution of MAGIC lines to breeding programs.