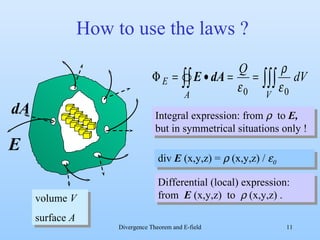
1) Gauss's law relates the electric flux through a closed surface to the enclosed electric charge. It can be used to calculate the electric field from a charge distribution if symmetry is present.
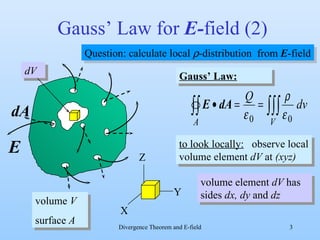
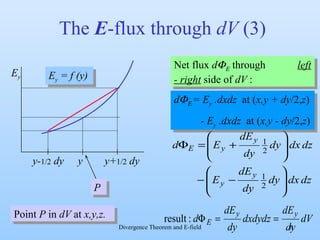
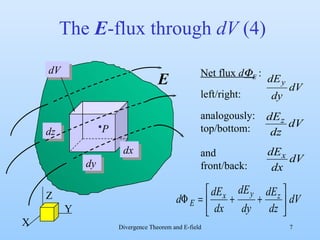
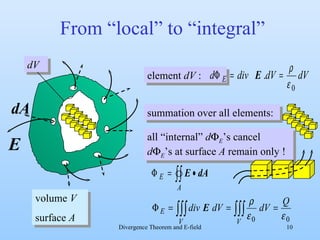
2) The document explores if there is an inverse expression that can locally calculate the charge density from the electric field. It examines calculating the electric flux through an infinitesimally small volume element.
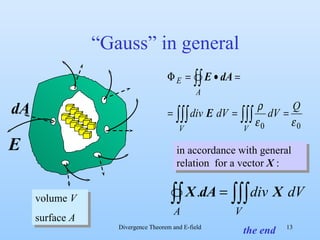
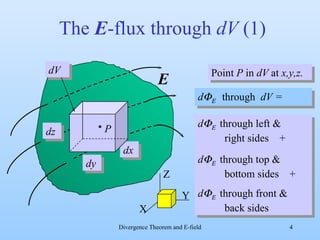
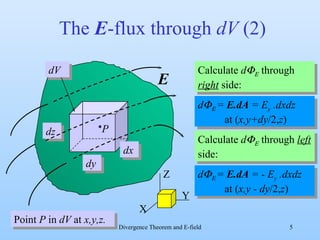
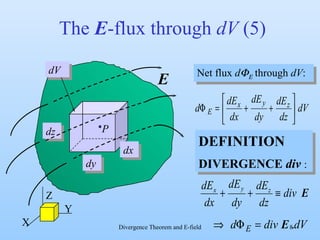
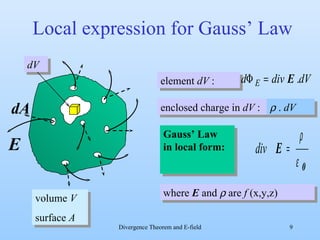
3) By taking the sum of the fluxes through all sides of the small volume element and equating it to the enclosed charge, it derives that the divergence of the electric field equals the charge density divided by the permittivity of free space. This allows locally calculating the charge density from the electric field.


![Physical meaning of div Divergence = local “micro”-flux per unit of volume [m 3 ] volume V surface A E dA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/divergencetheorem-100804085201-phpapp01/85/Divergence-theorem-12-320.jpg)