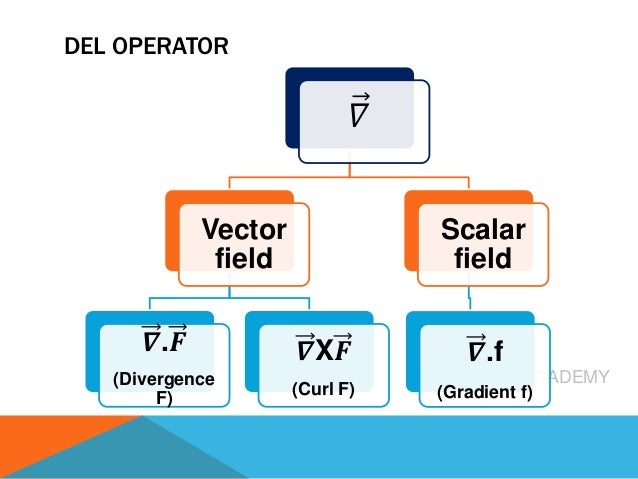
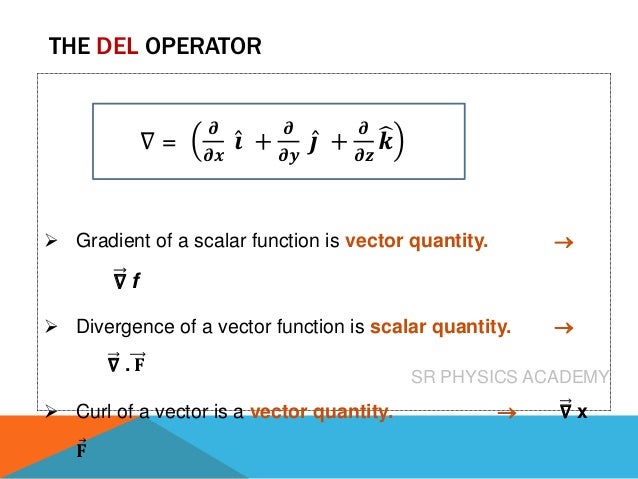
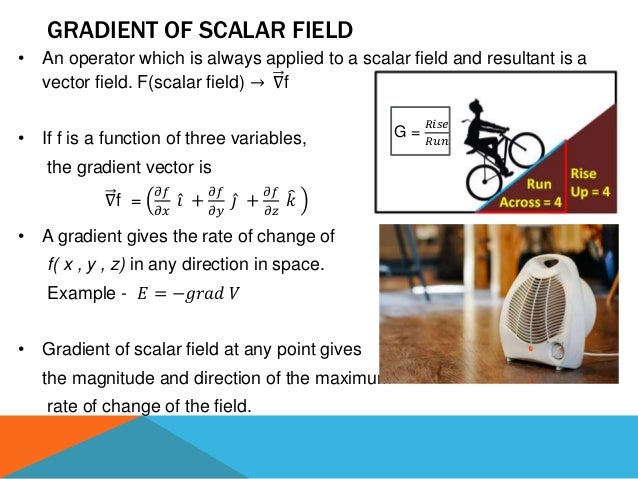
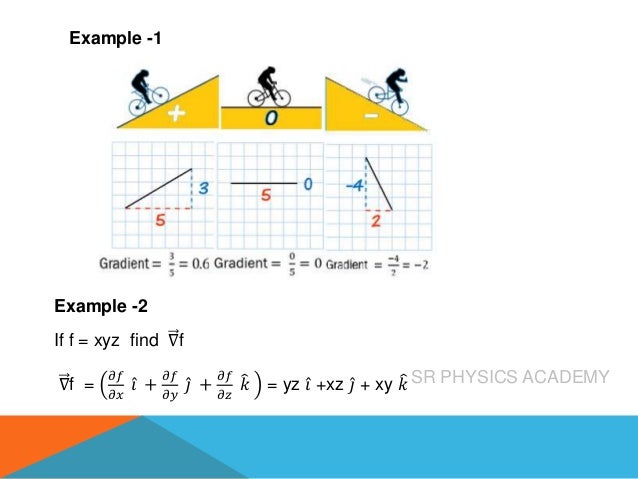
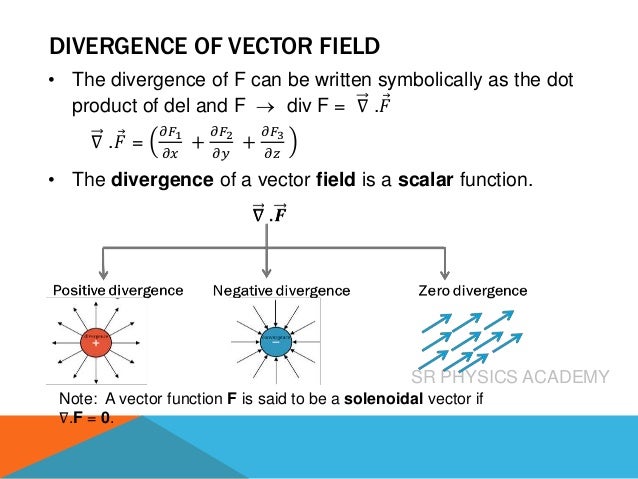
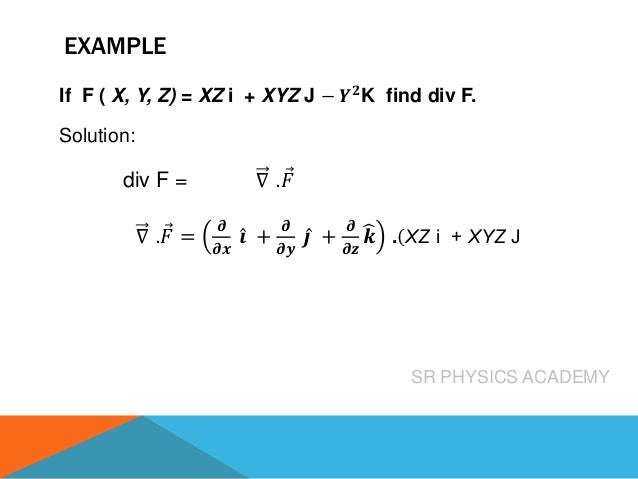
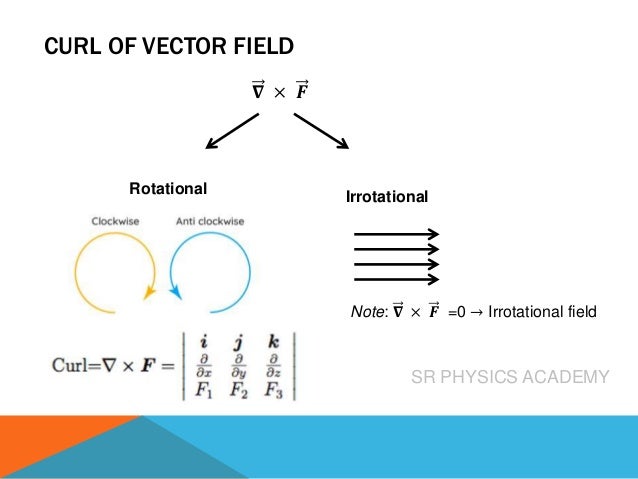
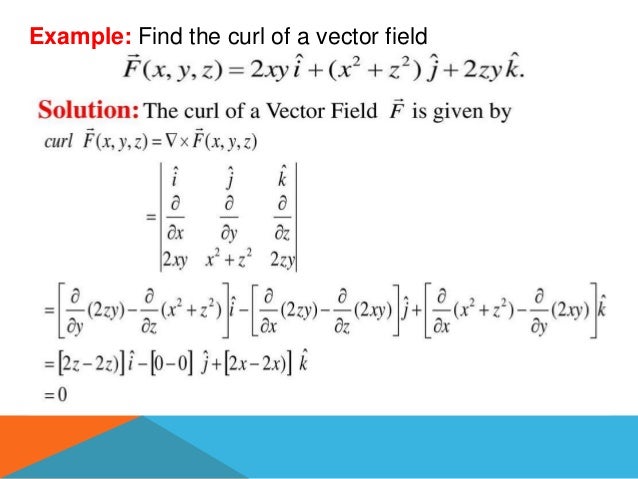
The del operator, also known as nabla (∇), is a collection of partial derivative operators used for scalar and vector fields in physics. It facilitates the computation of gradients, divergences, and curls, with specific outcomes for each; gradients yield vector quantities from scalars, divergences result in scalars from vectors, and curls produce vector quantities from vectors. The document includes examples and references a video for further learning about these concepts.