Embed presentation
Download to read offline

![E -field of a thin disk Question : Calculate E -field in arbitrary points a both sides of the disk Available : A thin circular disk with radius R and charge density [C/m 2 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e-fielddisk-100804085228-phpapp02/85/E-field-disk-2-320.jpg)

![Analysis and Symmetry 1. Charge distribution: C/m 2 ] 3. Symmetry: cylinder 4. Cylinder coordinates: r, z 2. Coordinate axes: Z-axis = symm. axis, perpend. to disk Z X Y e r r e z z e ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e-fielddisk-100804085228-phpapp02/85/E-field-disk-4-320.jpg)
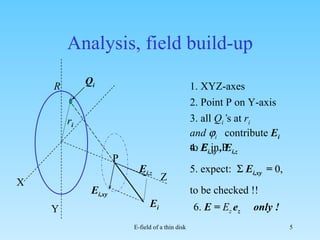

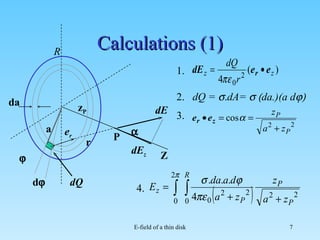

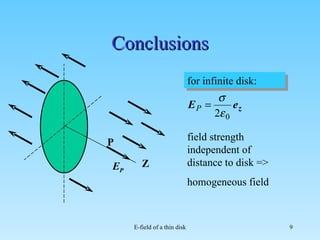


1. The document calculates the electric field (E-field) of a thin circular disk with a uniform charge density. 2. It sets up cylindrical coordinates and notes that due to the disk's symmetry, the only non-zero component of the E-field is Ez, along the z-axis perpendicular to the disk. 3. It describes calculating the E-field by integrating the contribution of elemental charge rings on the disk, showing that the E-field strength is independent of distance from the disk.

![E -field of a thin disk Question : Calculate E -field in arbitrary points a both sides of the disk Available : A thin circular disk with radius R and charge density [C/m 2 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e-fielddisk-100804085228-phpapp02/85/E-field-disk-2-320.jpg)

![Analysis and Symmetry 1. Charge distribution: C/m 2 ] 3. Symmetry: cylinder 4. Cylinder coordinates: r, z 2. Coordinate axes: Z-axis = symm. axis, perpend. to disk Z X Y e r r e z z e ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e-fielddisk-100804085228-phpapp02/85/E-field-disk-4-320.jpg)






