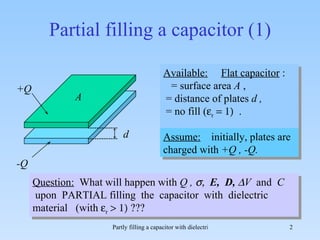
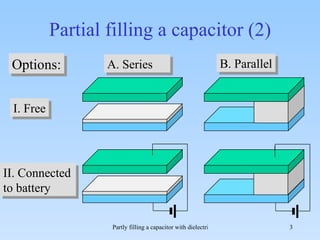
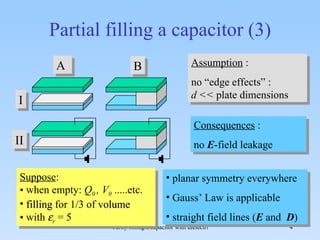
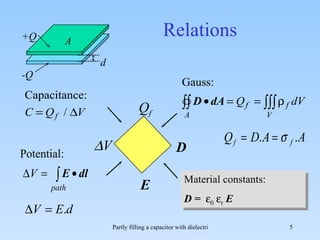
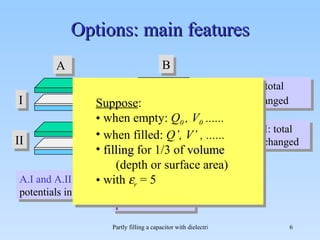
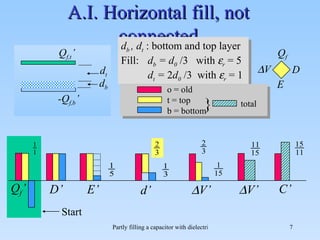
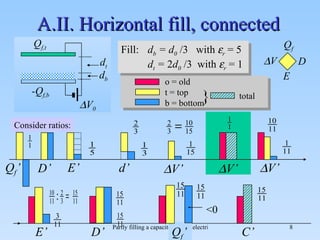
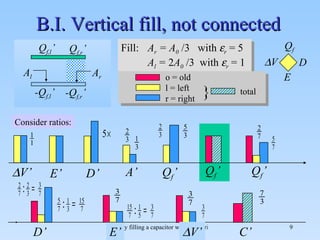
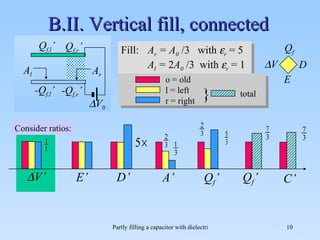
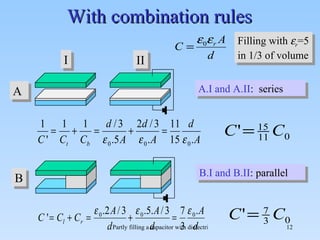
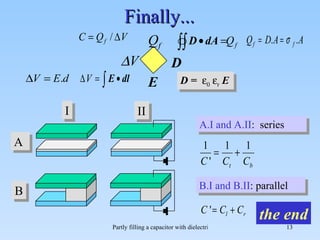
The document discusses the effects of partial filling a capacitor with dielectric material on various electrical parameters such as charge, potential difference, and capacitance. It presents different filling configurations (horizontal and vertical) and their implications on charge and potential when connected and disconnected from a battery. Key relationships and equations are provided for both series and parallel arrangements of capacitors during partial filling.