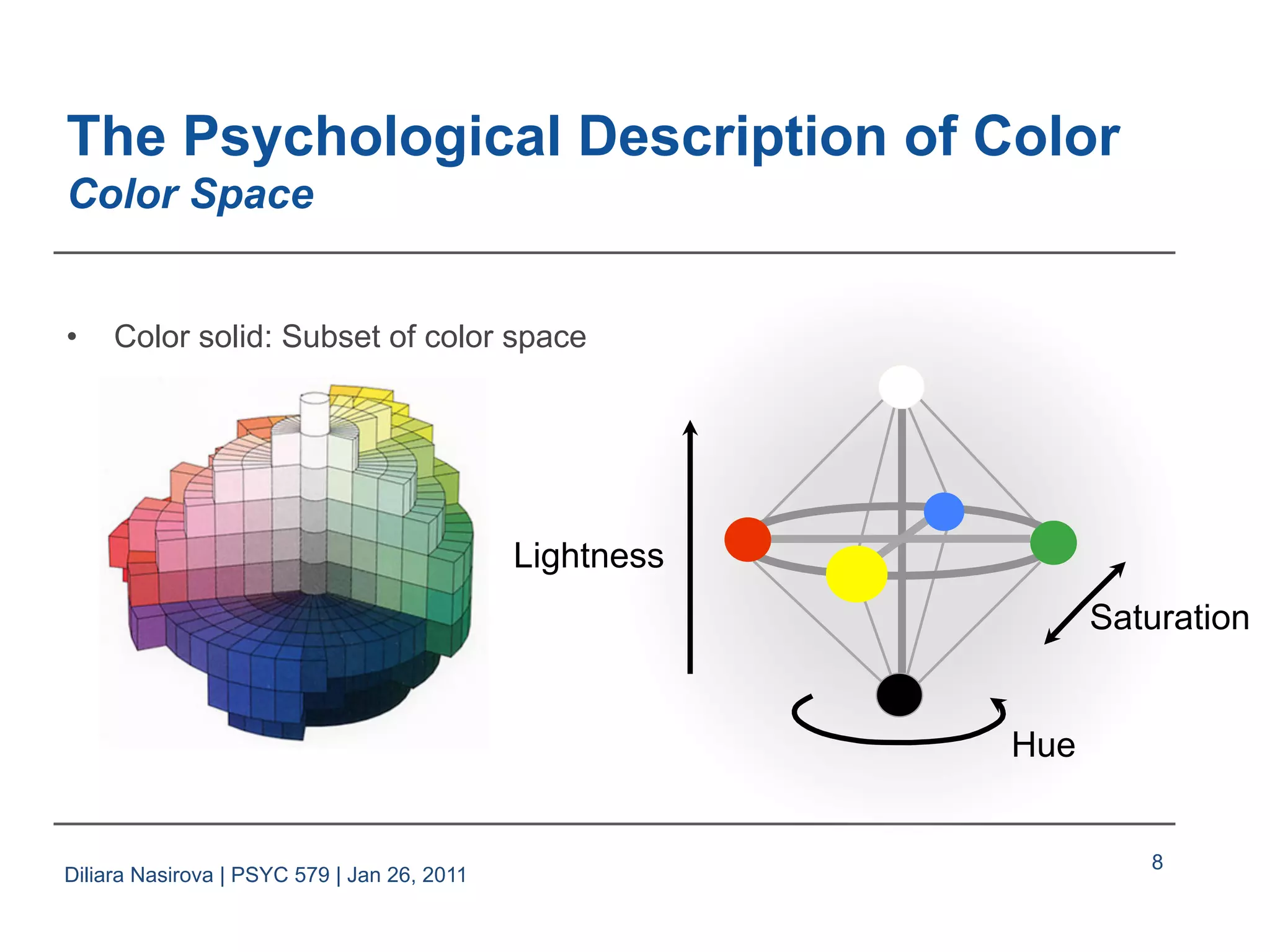
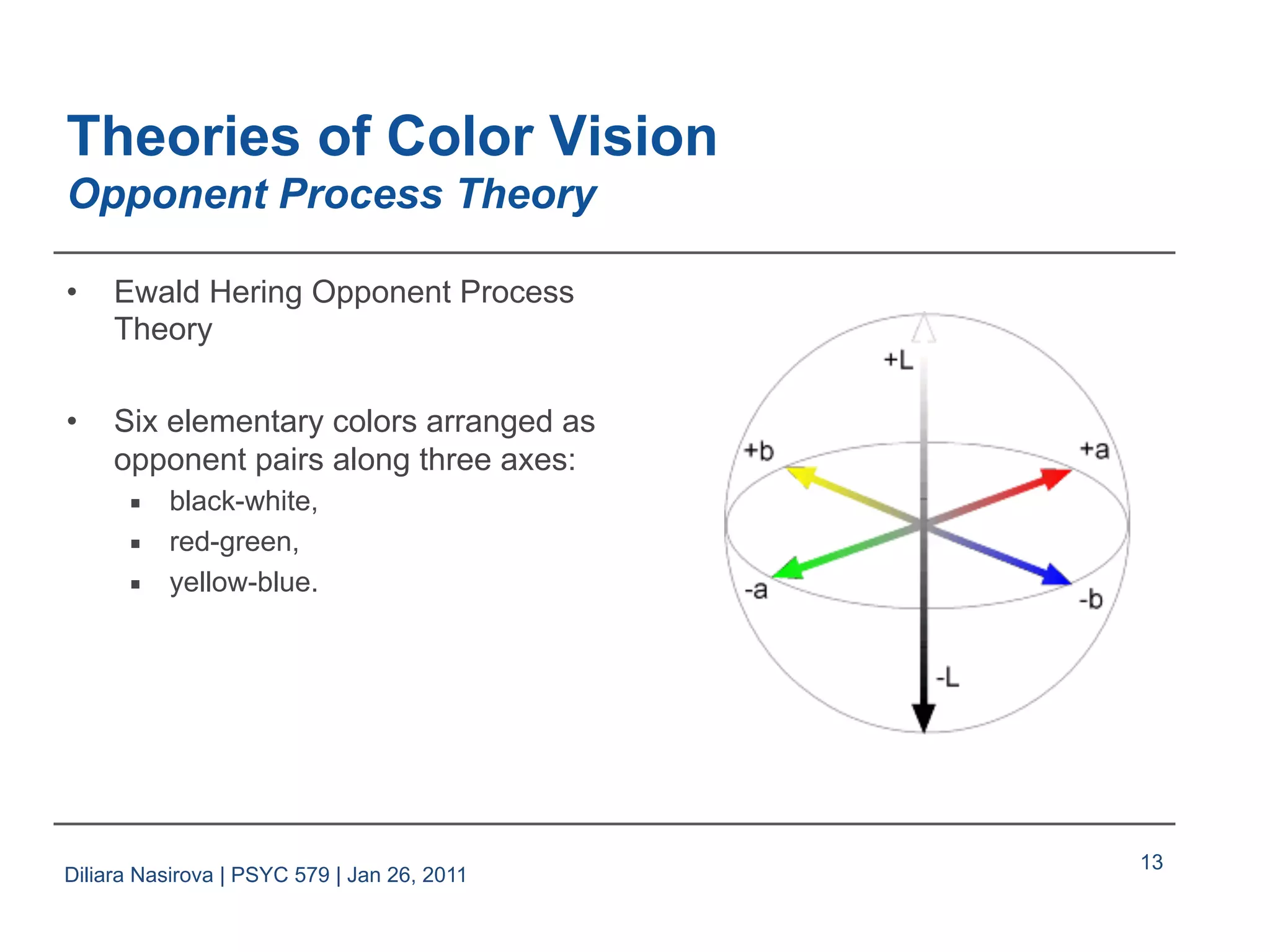
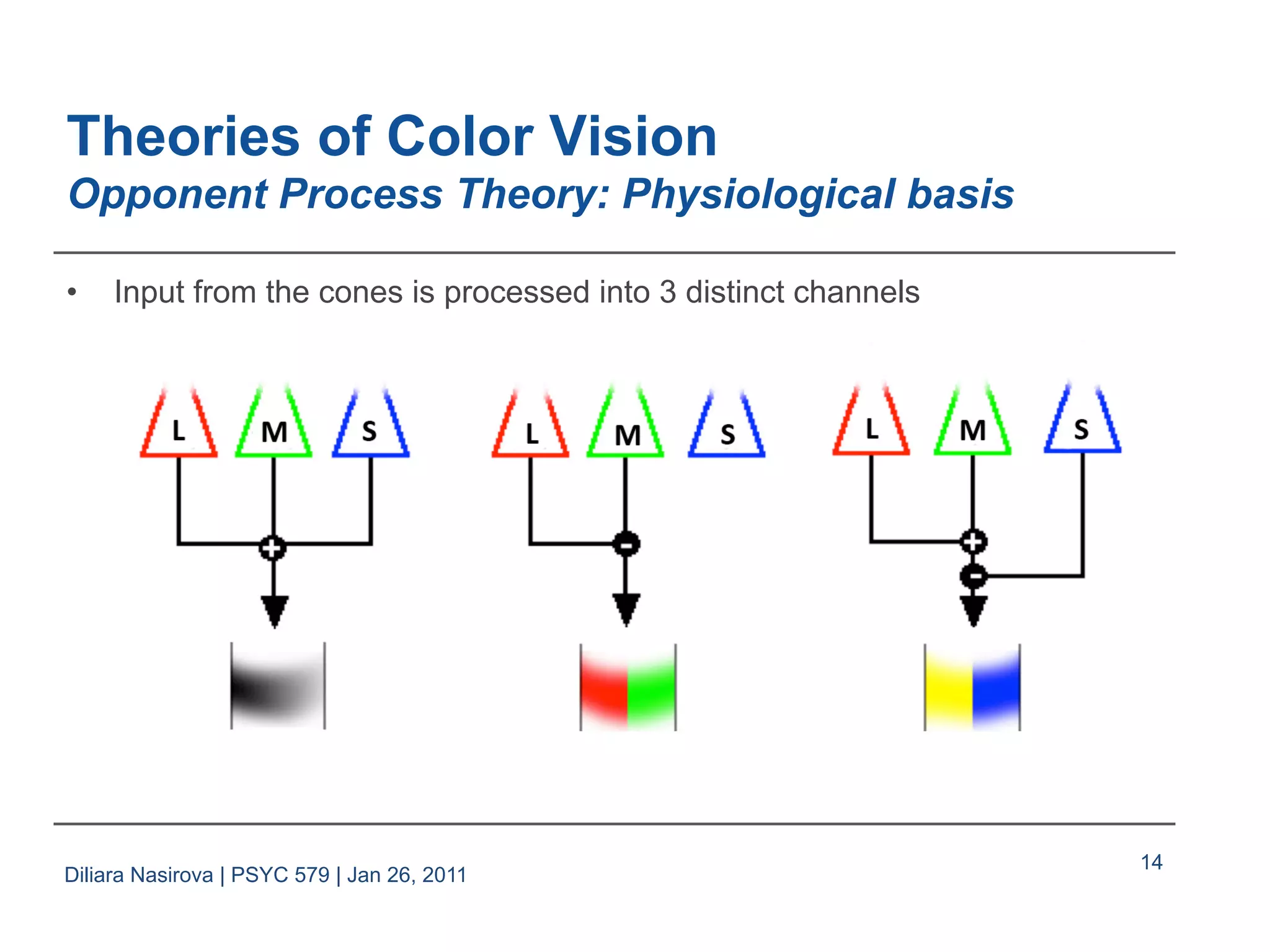
The document discusses color perception, covering the physical and psychological descriptions of light and color, theories of color vision including trichromatic and opponent process theories, and basic phenomena such as color blindness and afterimages. It also addresses the application of color in visual design, emphasizing the importance of color specification interfaces and factors to consider for effective labeling. References from various sources in visual perception and design are provided throughout the presentation.