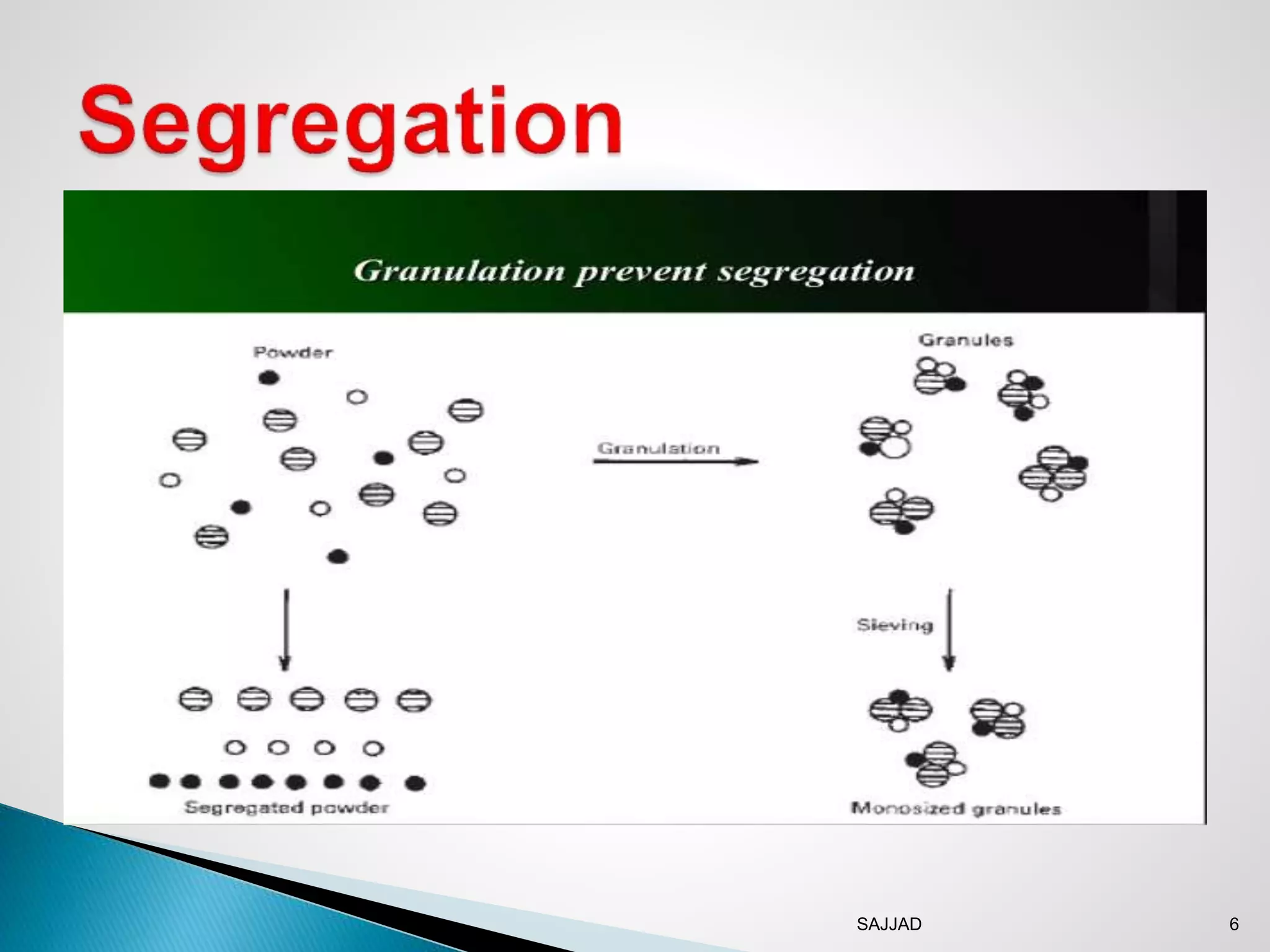
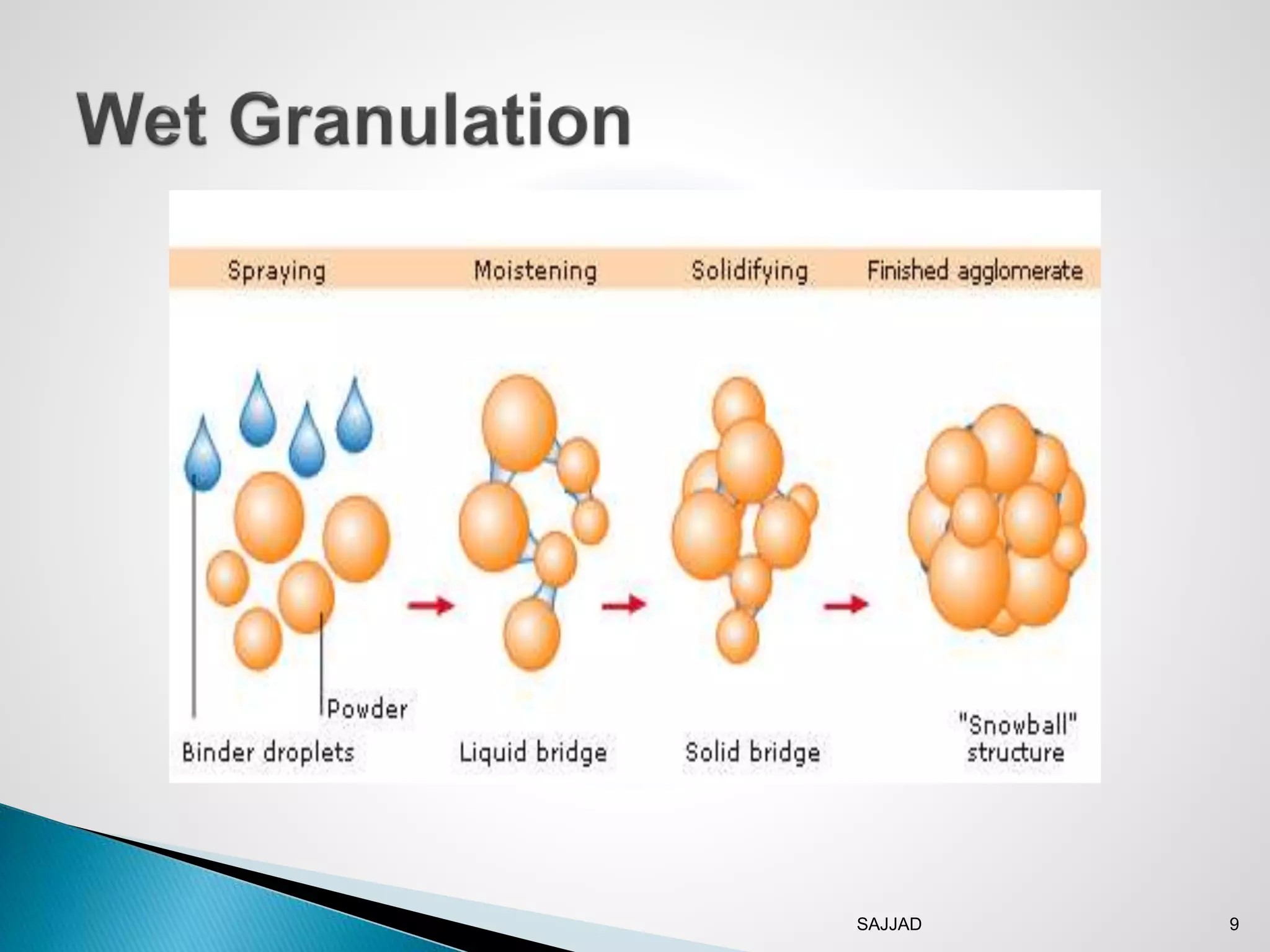
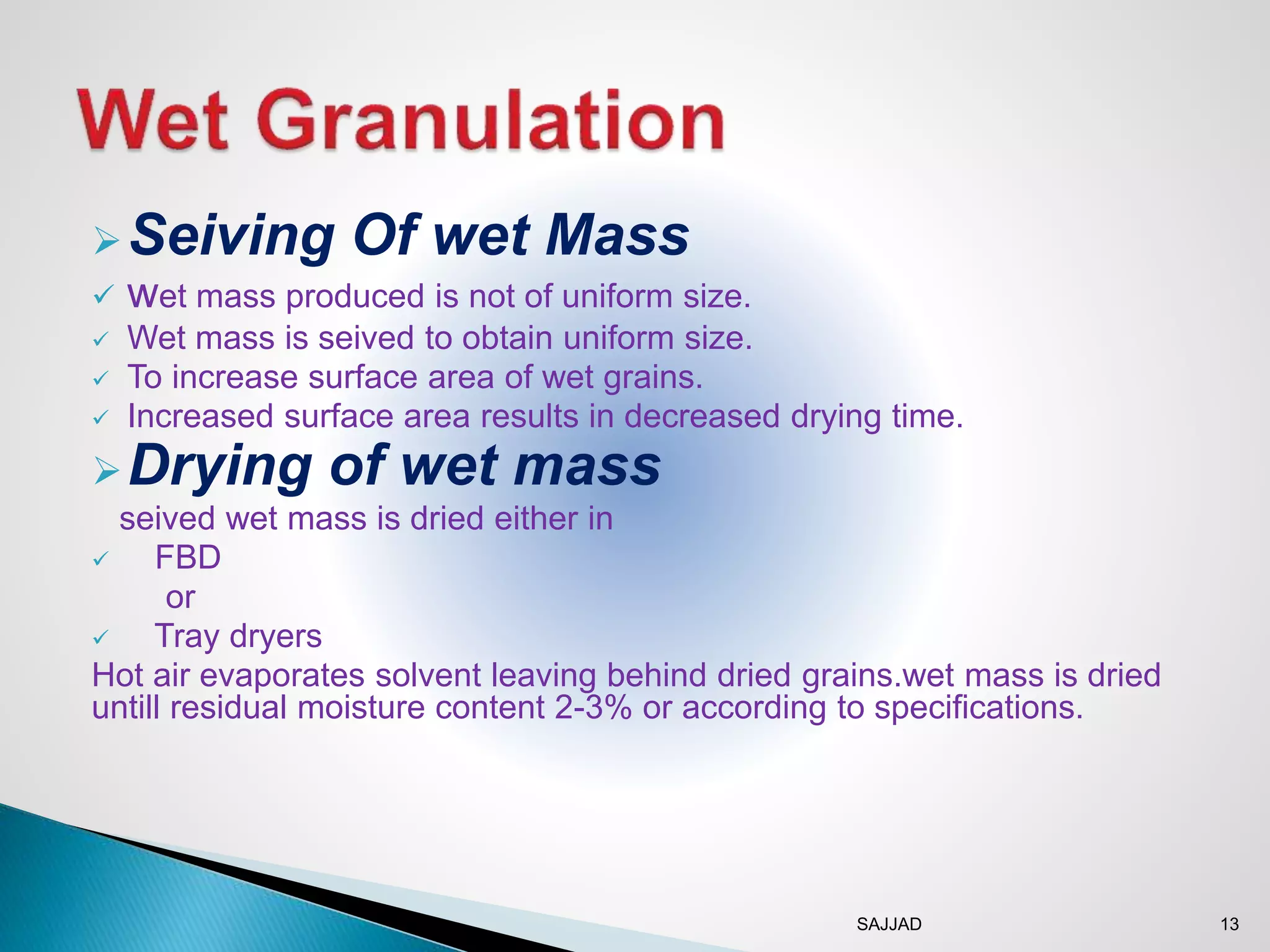
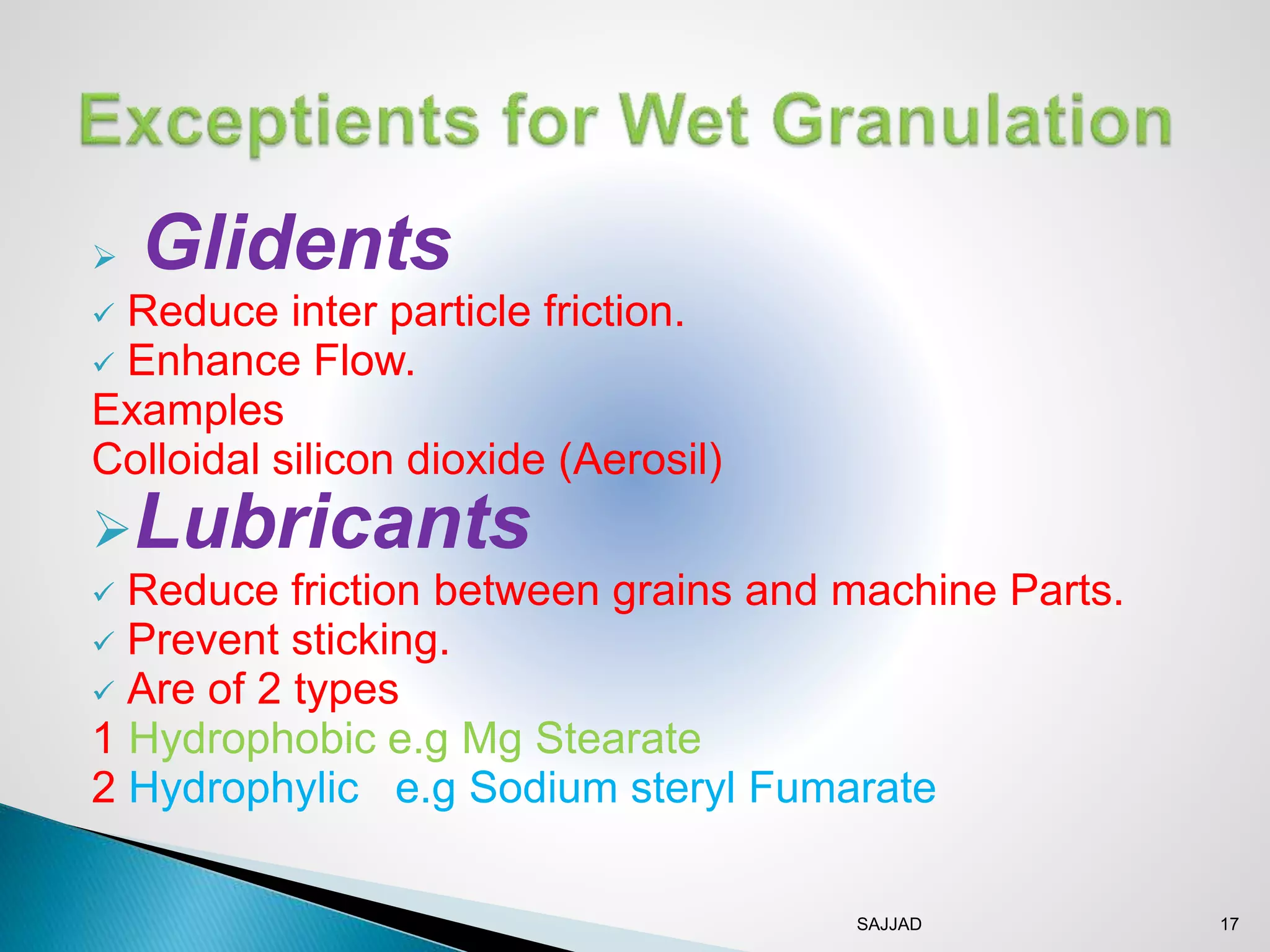
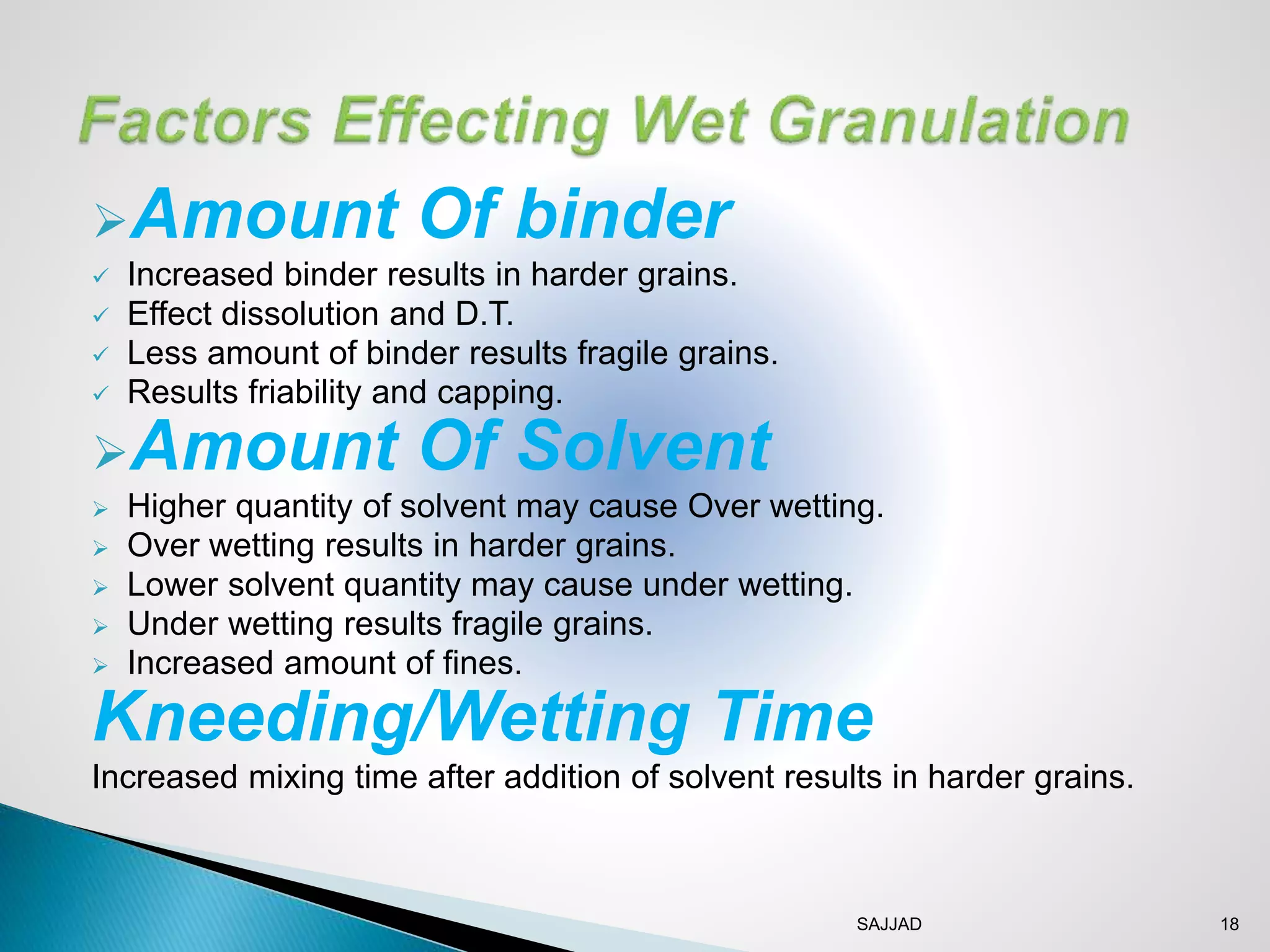
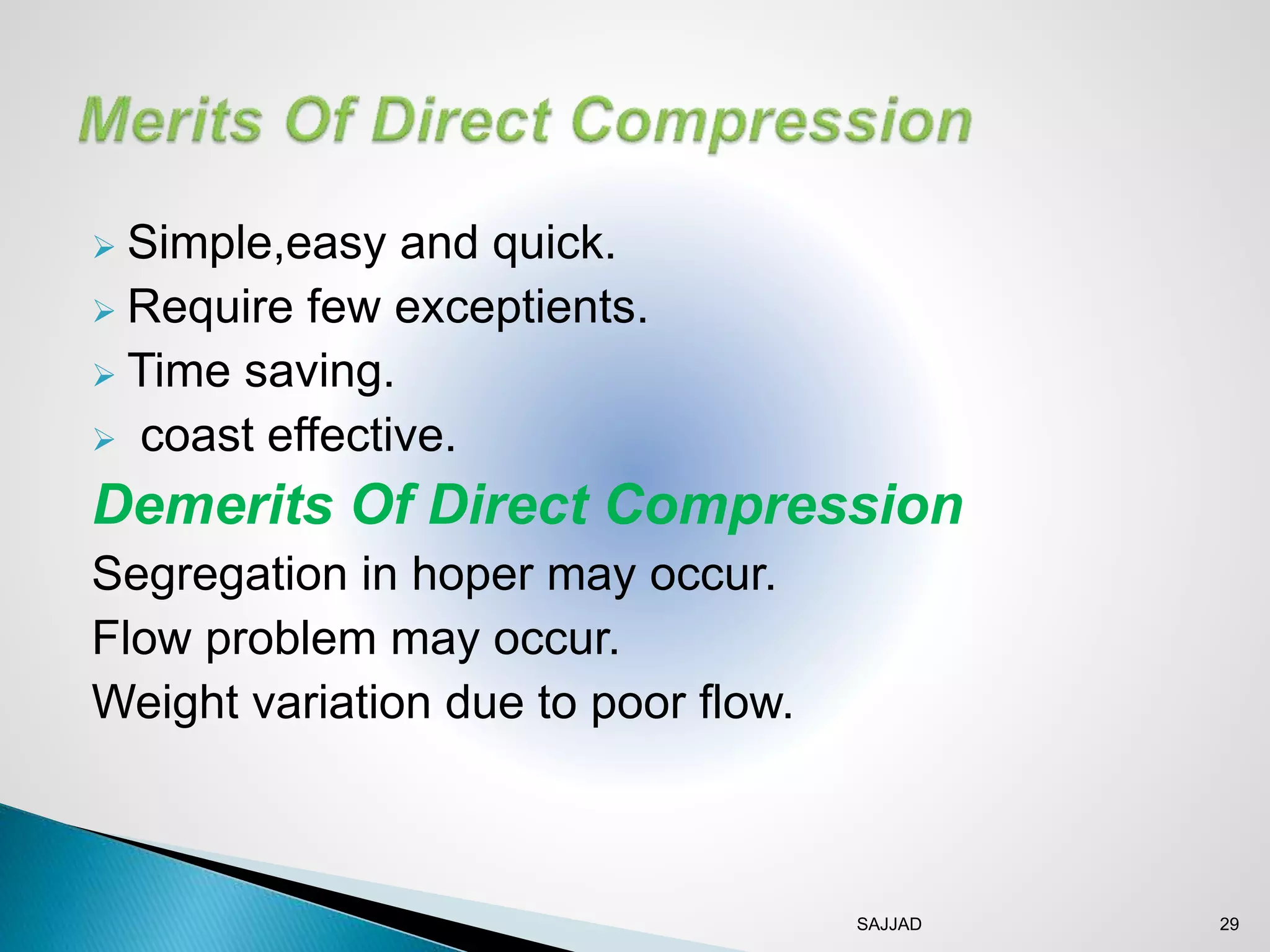
The document discusses different granulation techniques used in pharmaceutical manufacturing. It describes granulation as a size enlargement process used to improve properties like flowability and compressibility of powders for tablet making. The key granulation methods covered are wet granulation, dry granulation, and direct compression. Wet granulation involves using a liquid to form granules and allows for a wide range of excipients. Dry granulation uses pressure rather than liquid. Direct compression can be used for materials with good compression properties. Modern techniques like steam granulation are also briefly mentioned.