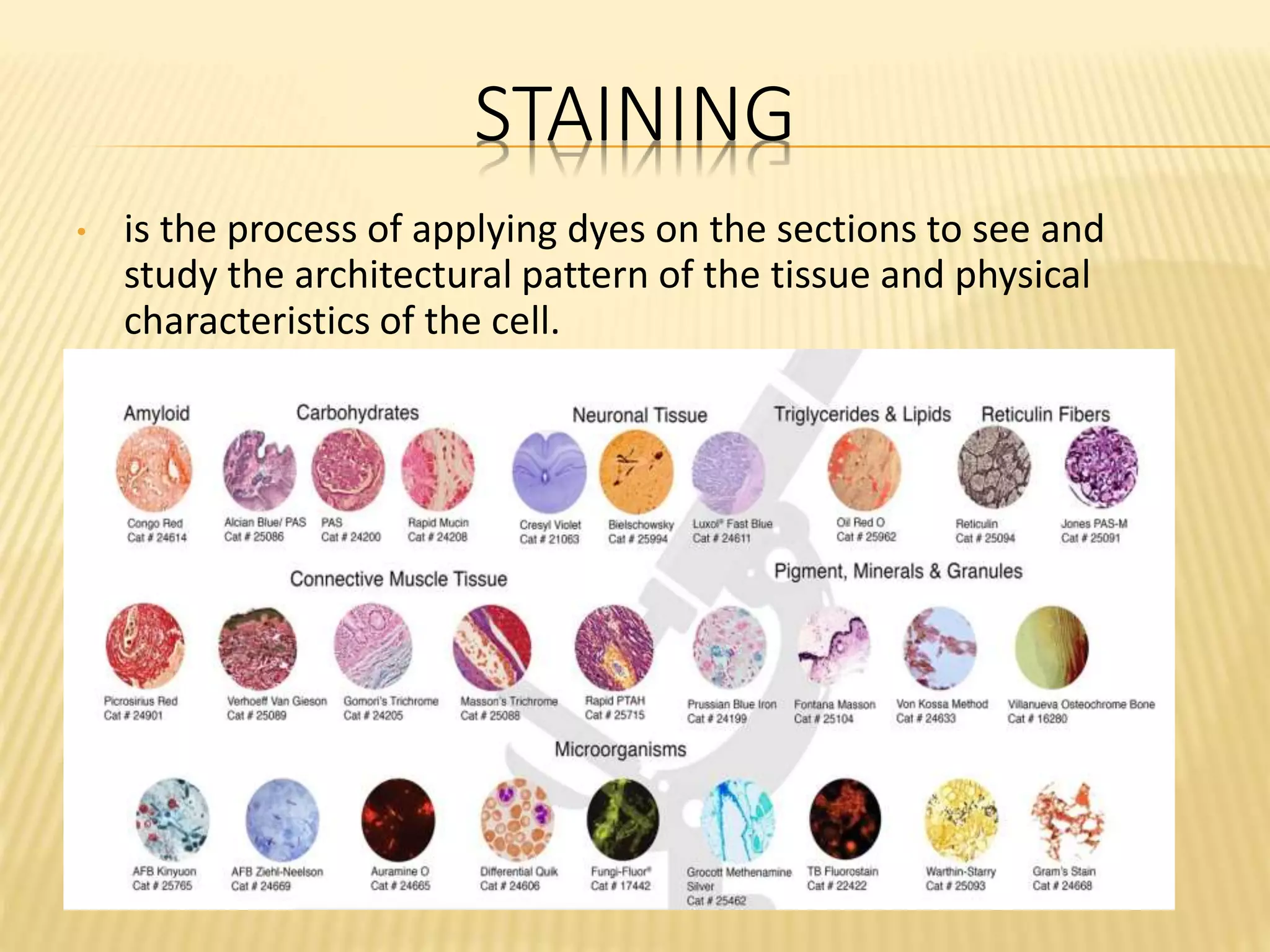
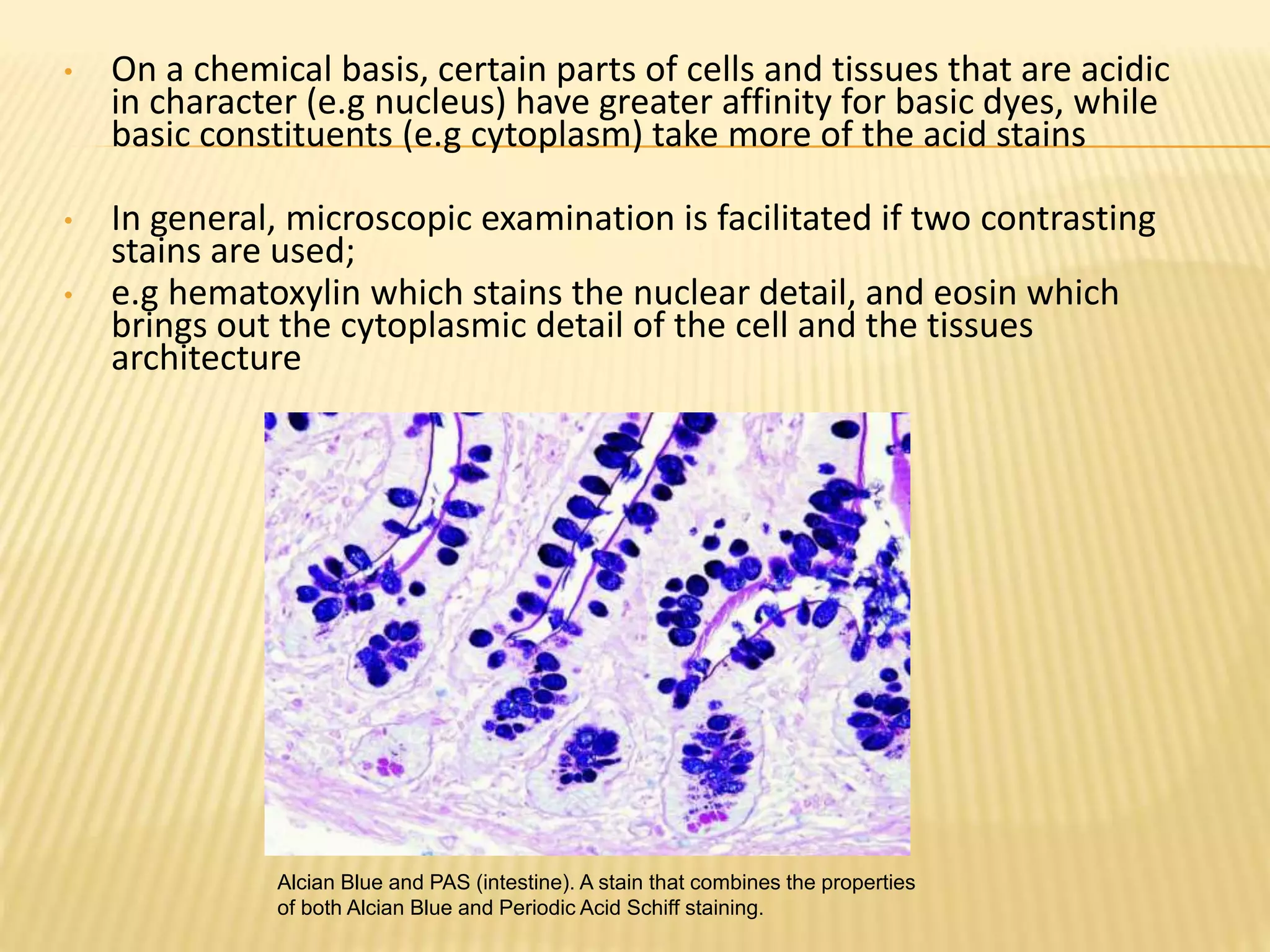
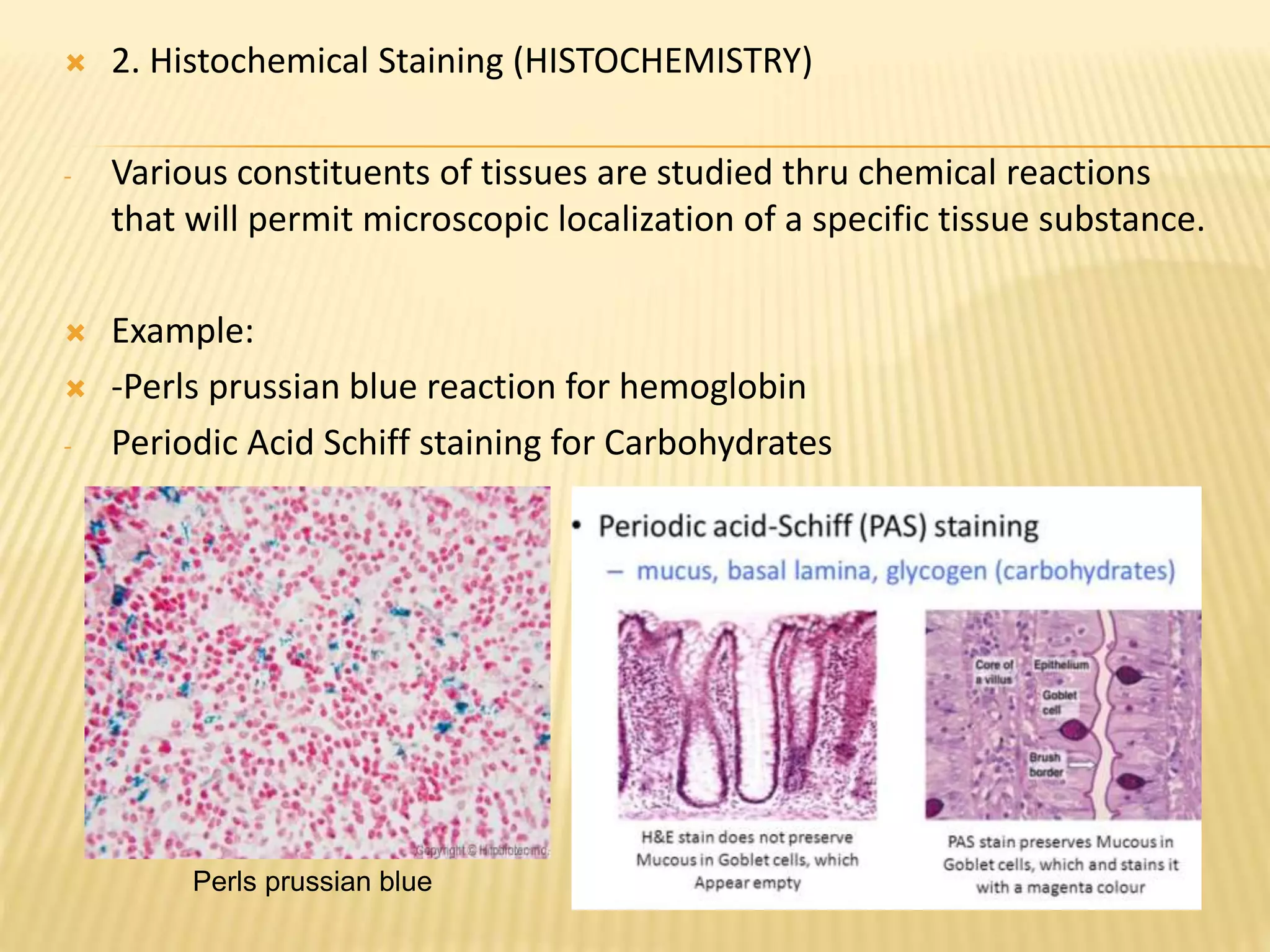
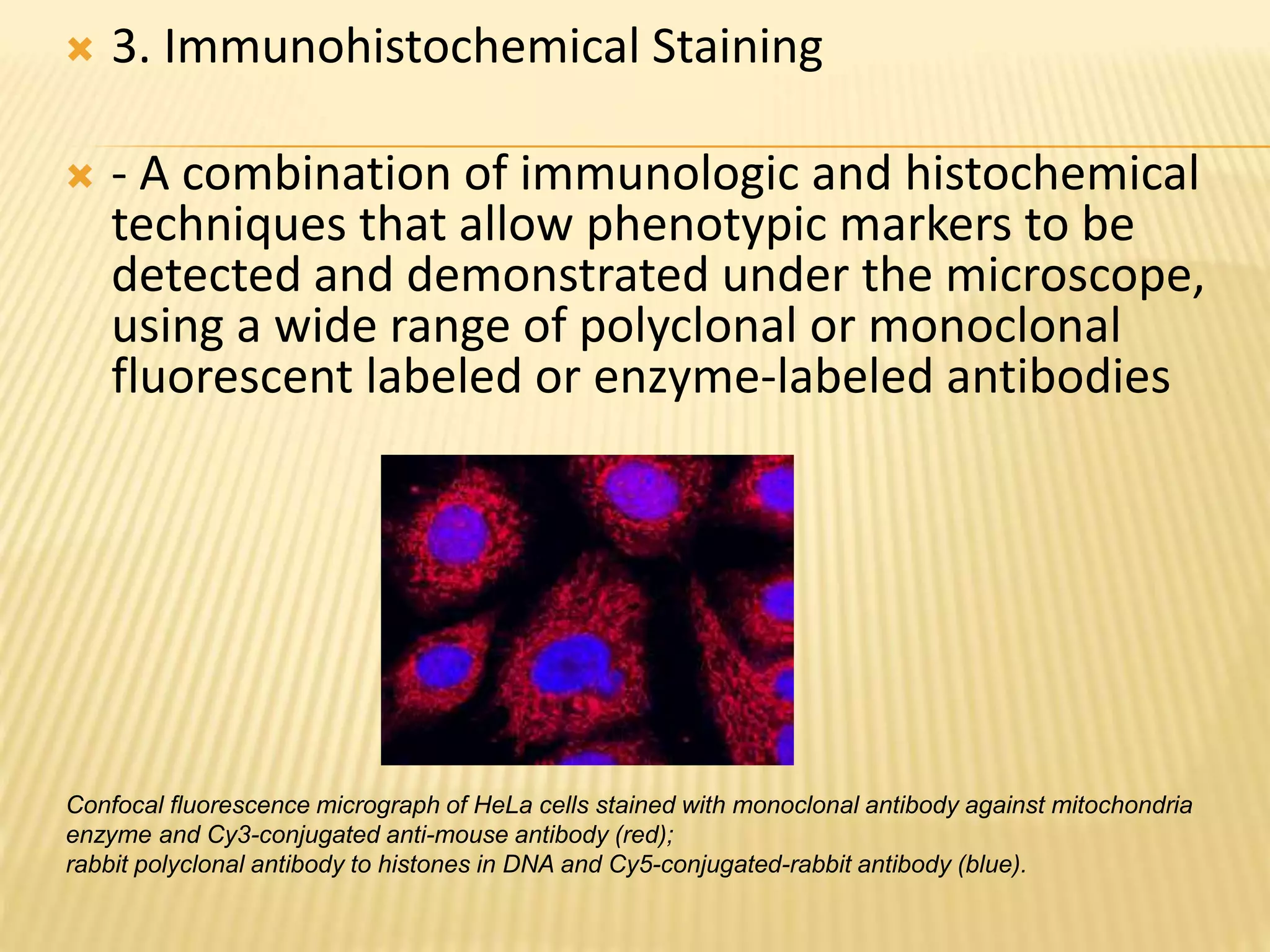
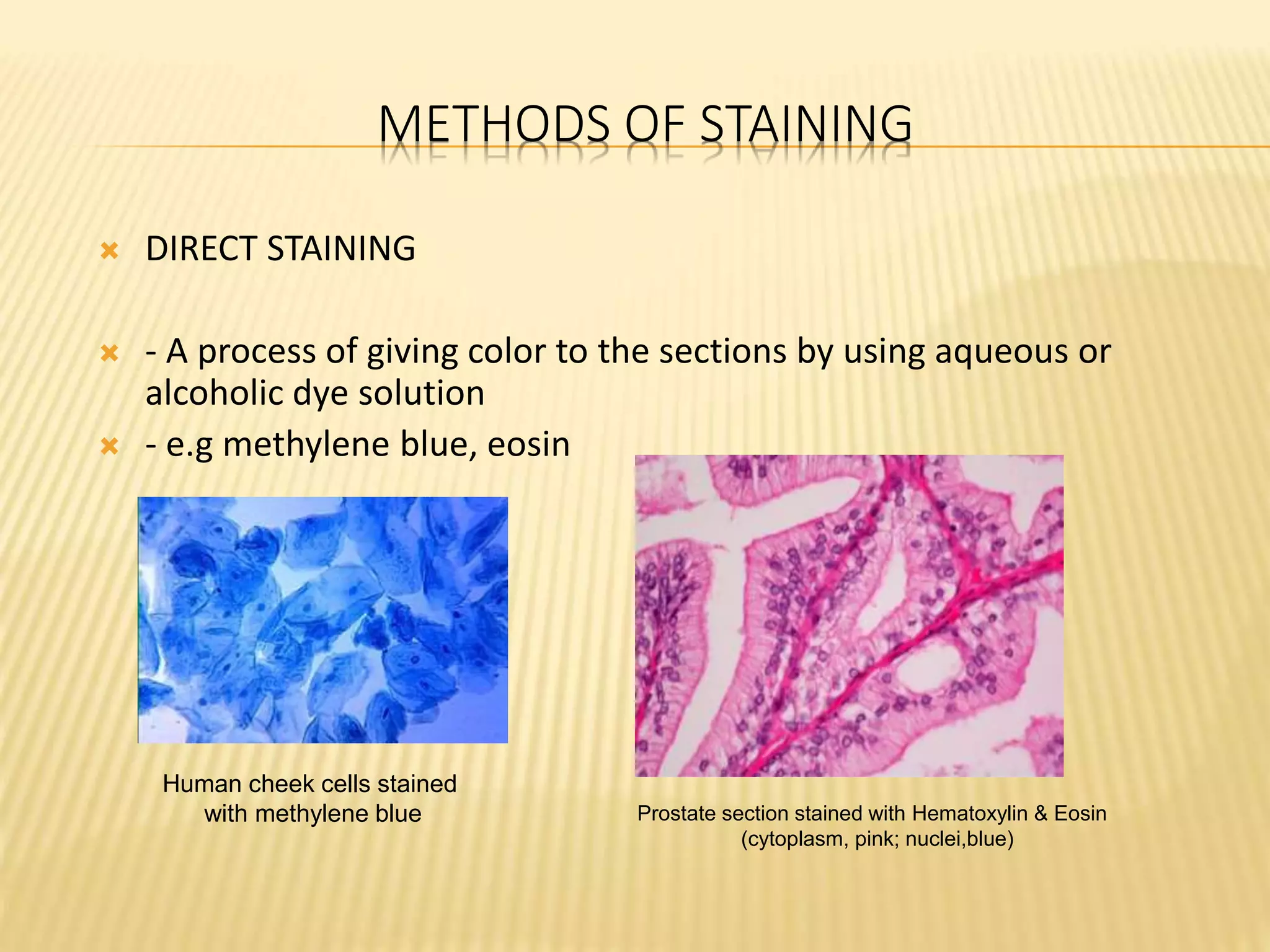
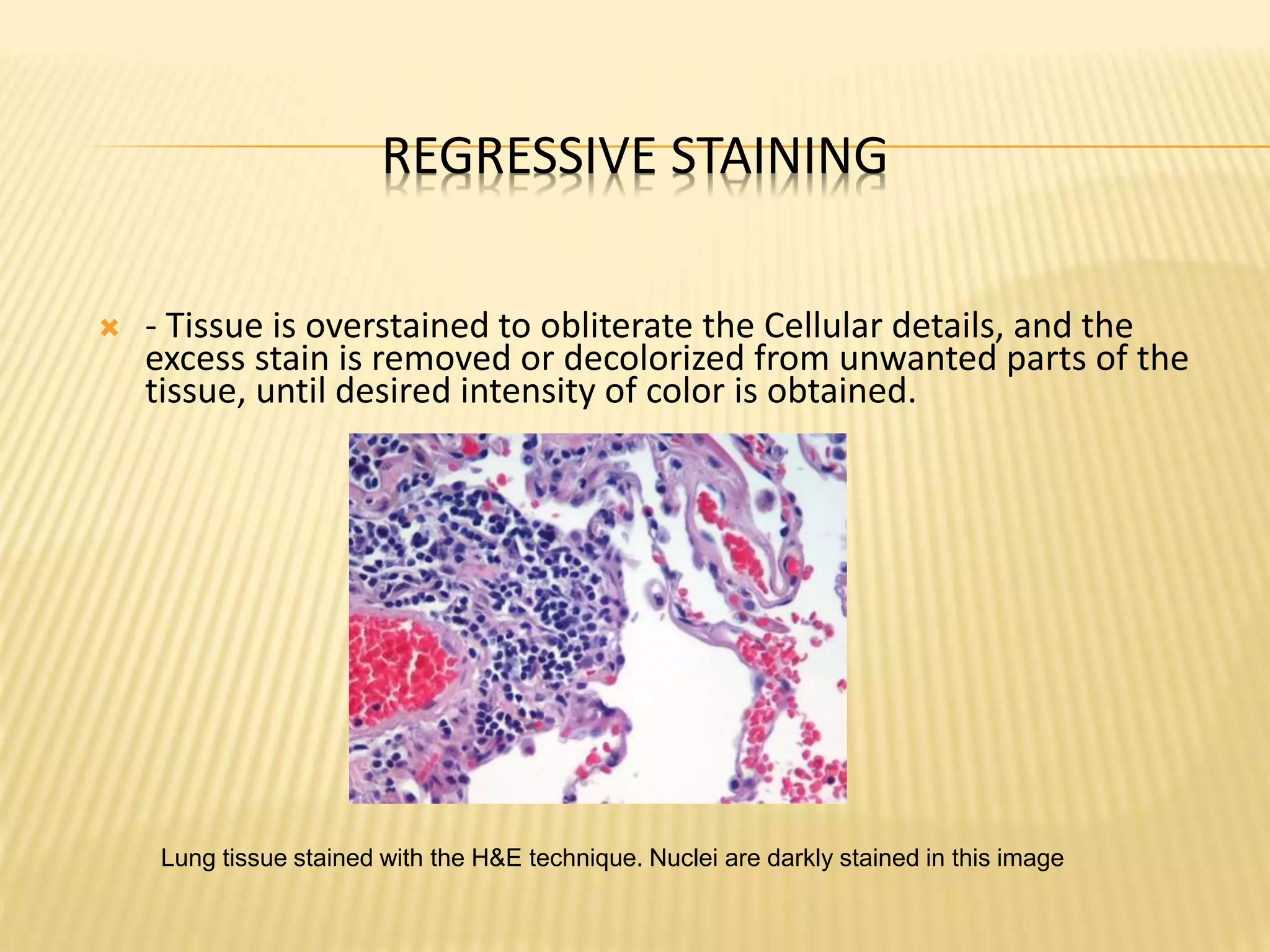
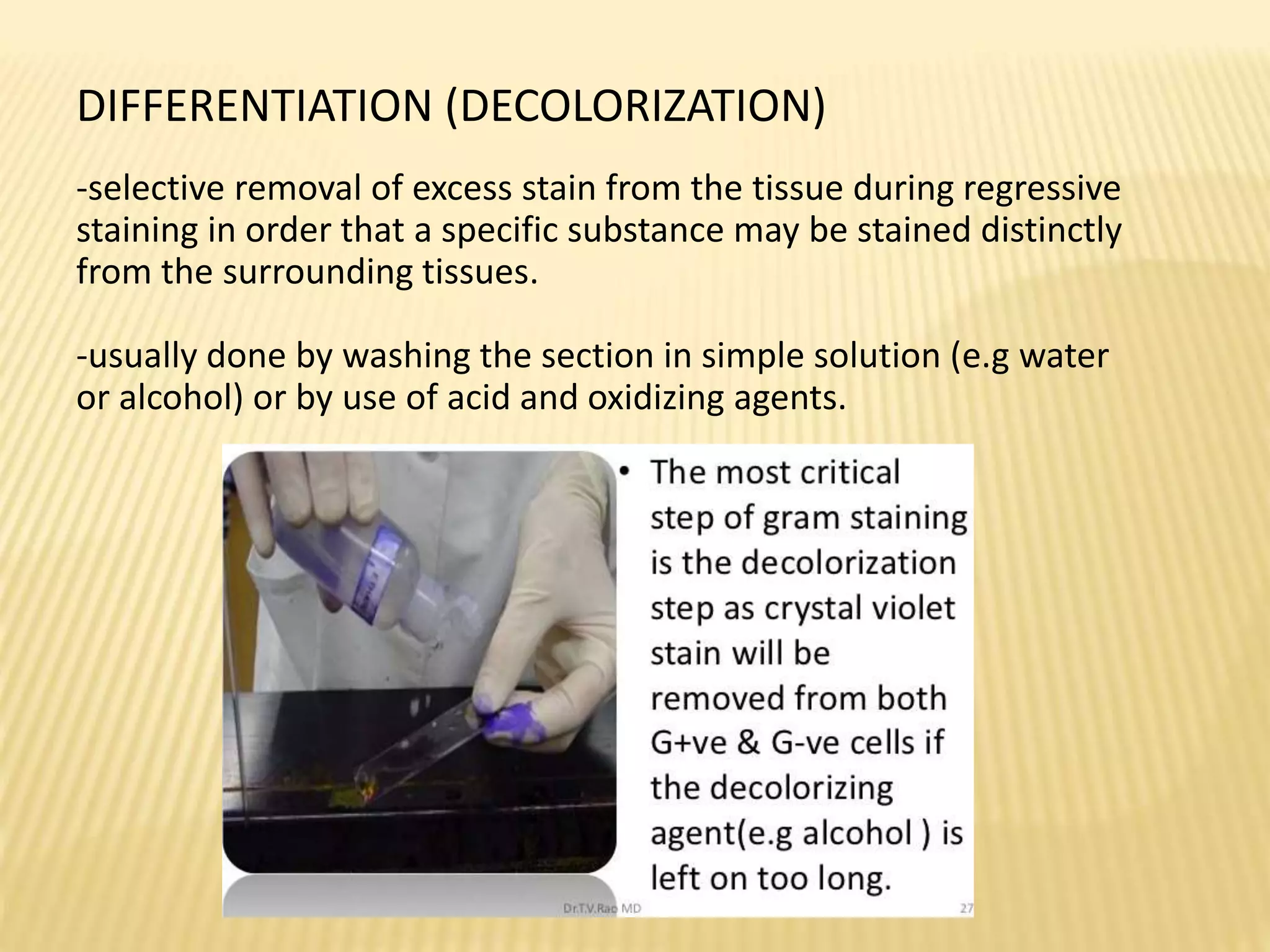
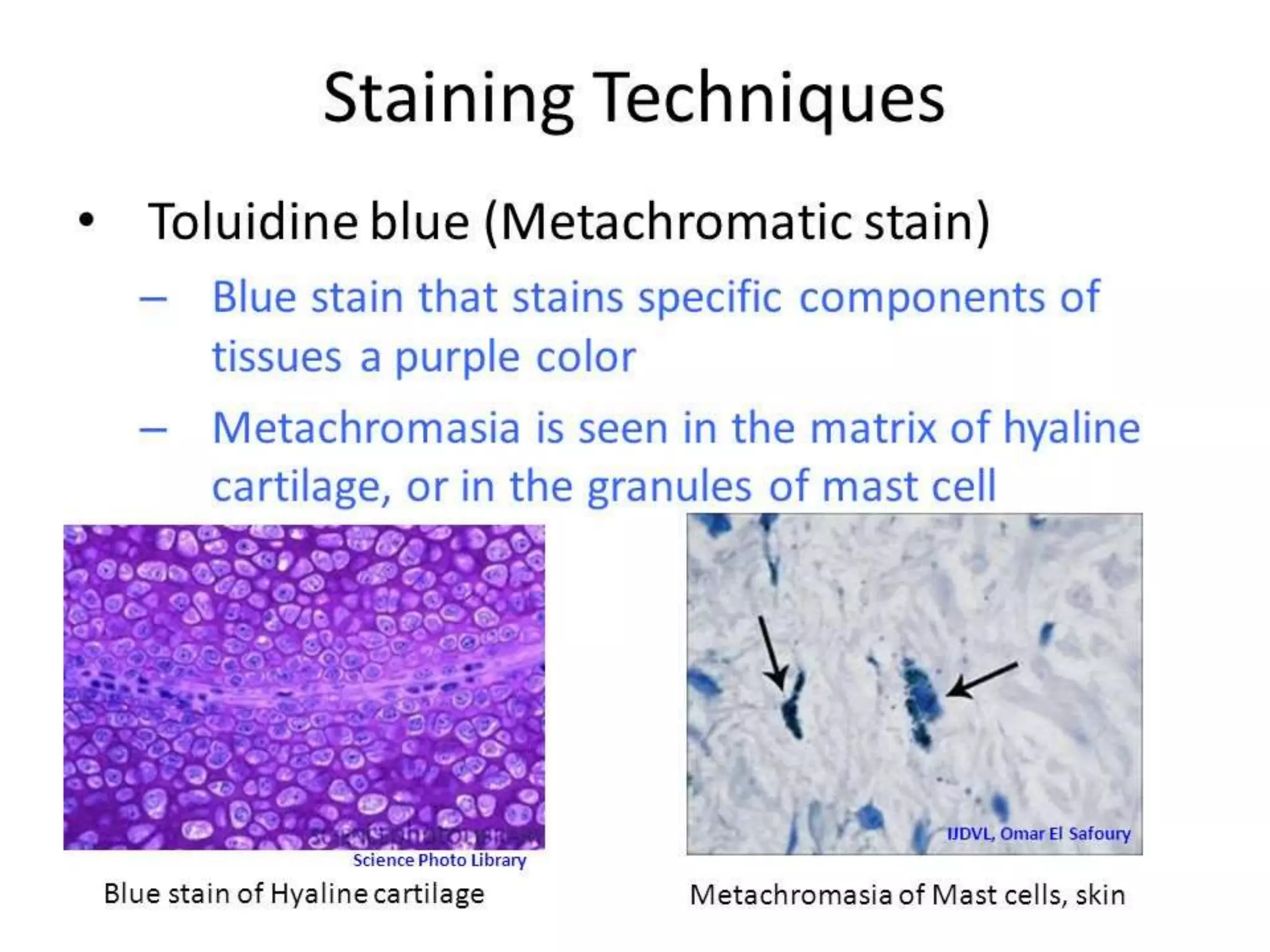
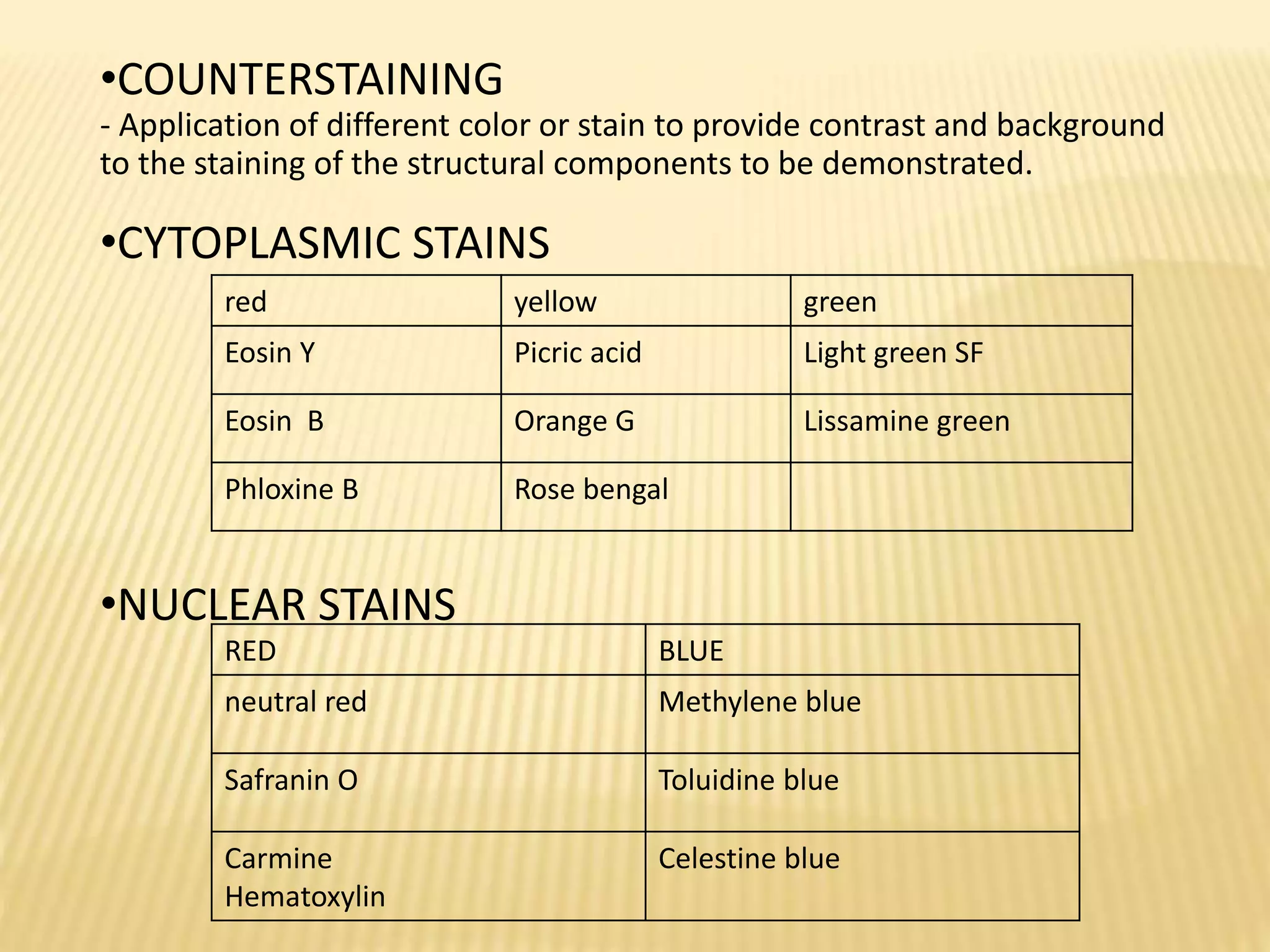
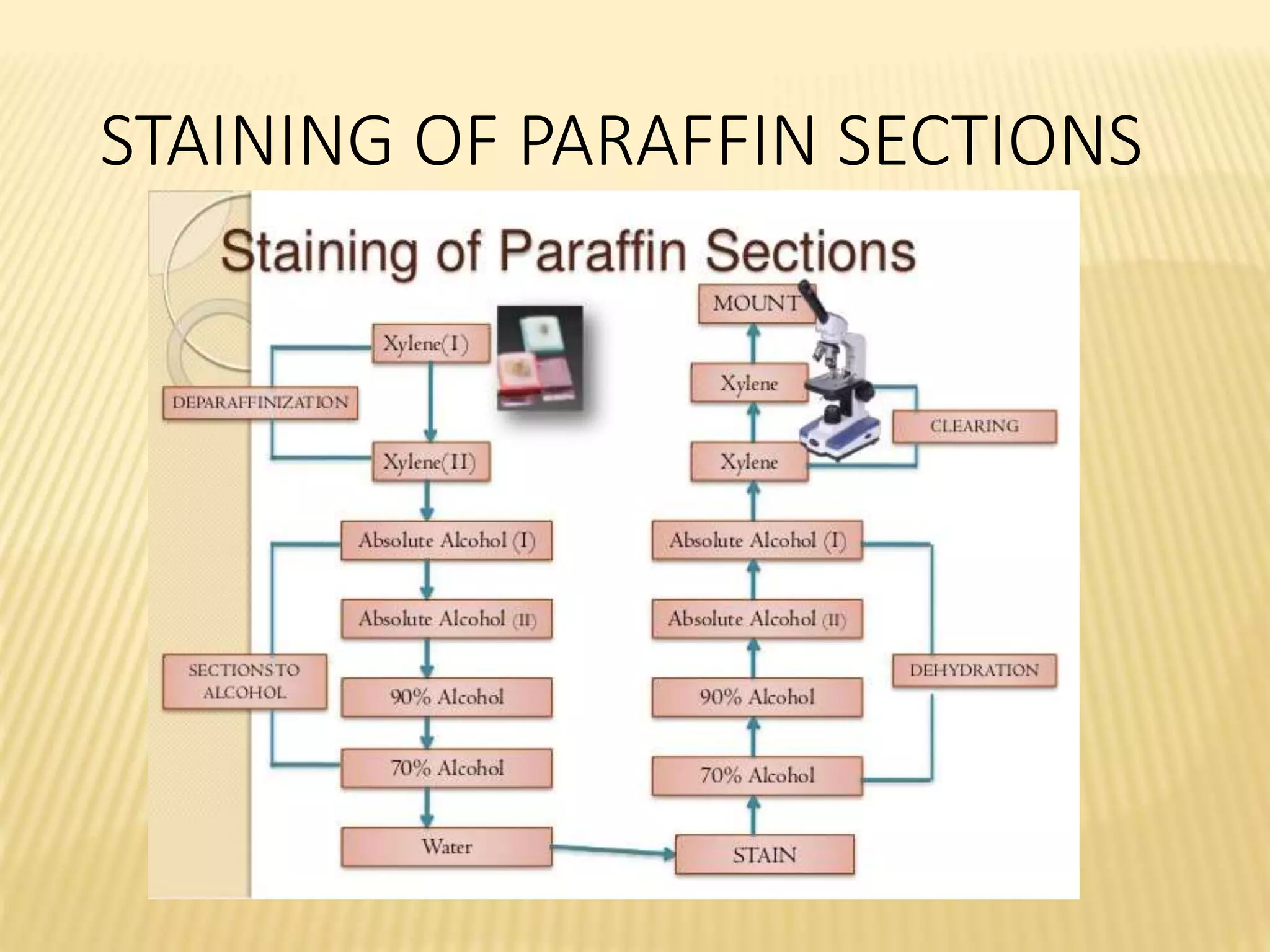
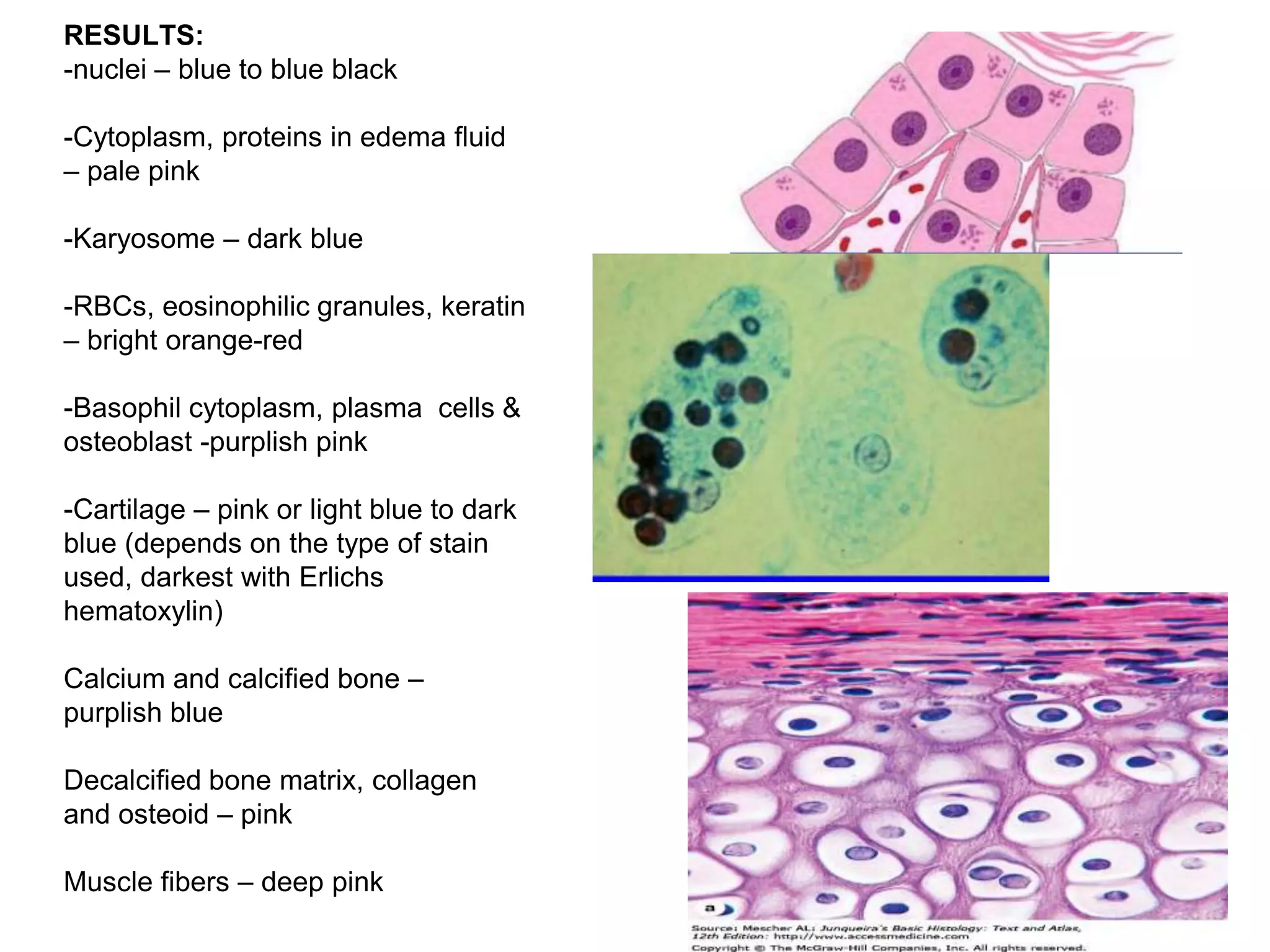
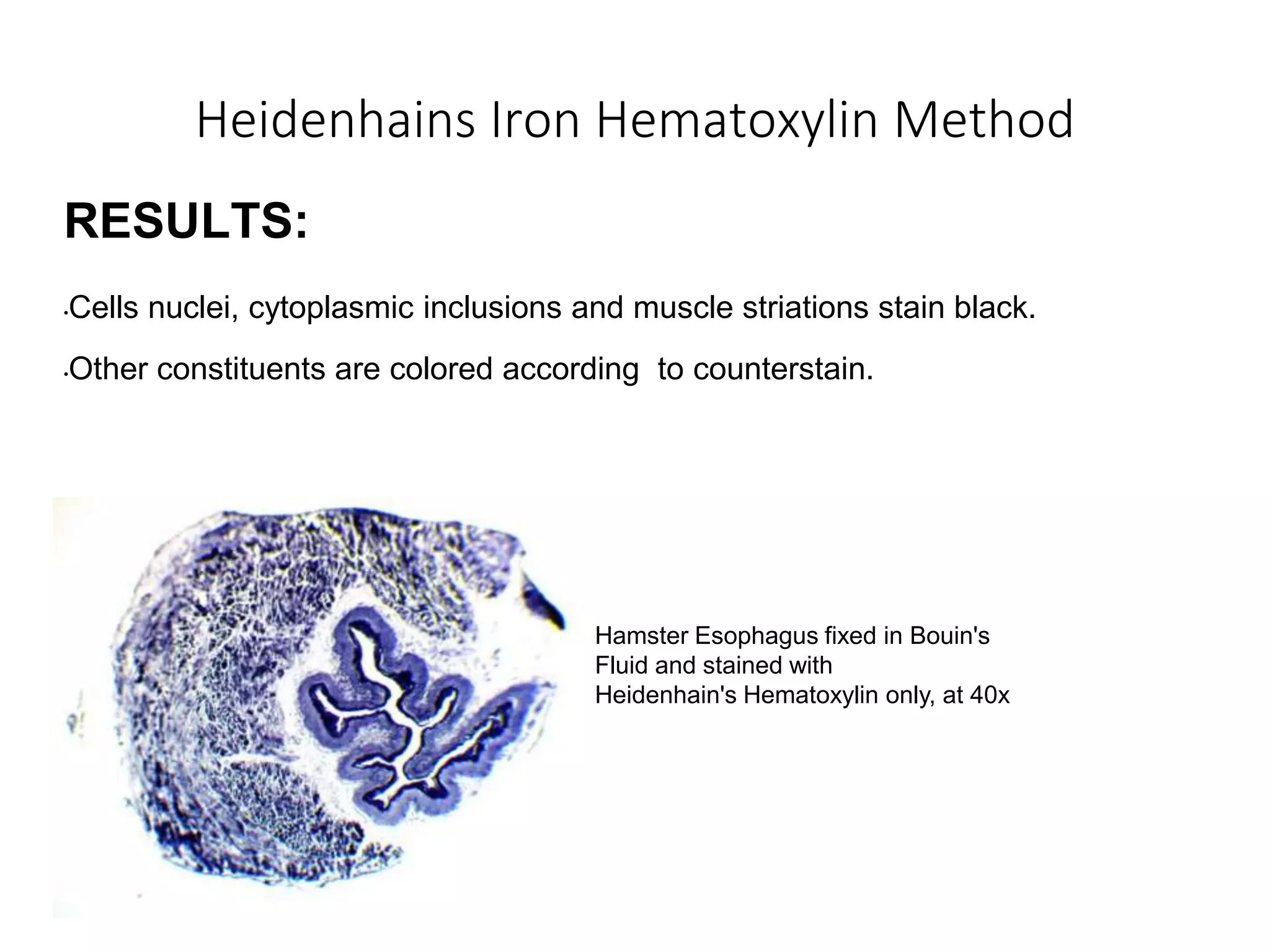
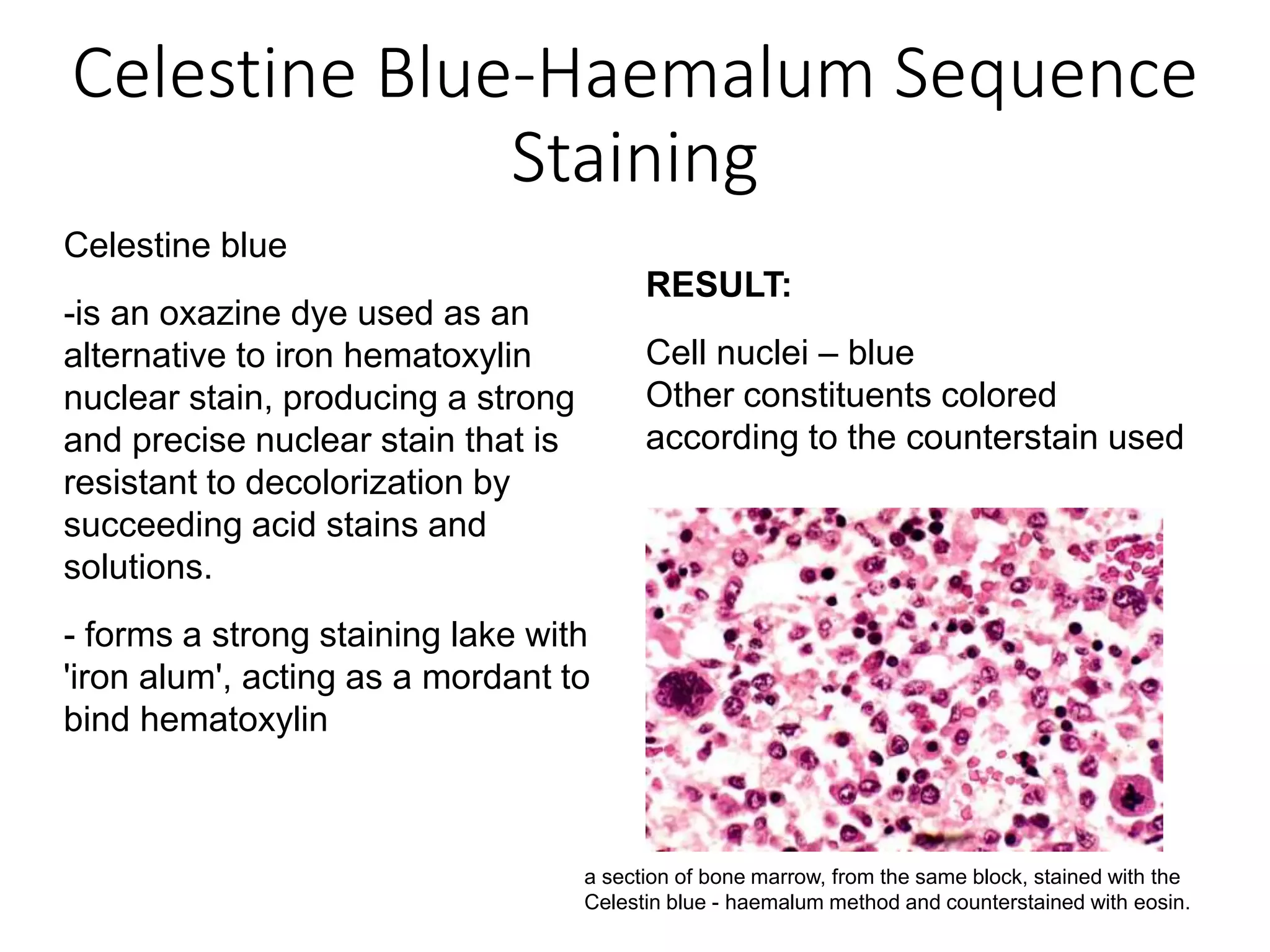
This document discusses various staining techniques used to differentiate tissues and cellular structures under a microscope. It describes the objectives of staining as revealing internal and external structures and producing specific chemical and physical reactions. The 3 major groups of staining are histological, histochemical, and immunohistochemical staining. Histological staining uses dyes to demonstrate tissue and cell relationships. Histochemical staining localizes specific tissue substances through chemical reactions. Immunohistochemical staining uses antibodies to detect phenotypic markers. The document outlines different types of stains, staining methods like direct, indirect and regressive staining, as well as procedures for staining frozen sections, paraffin sections, and broken slides.