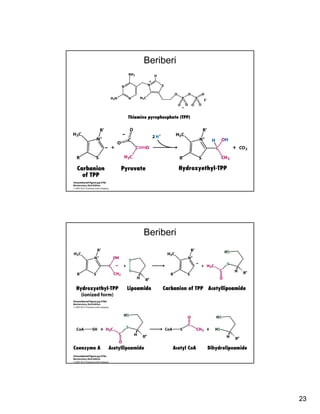
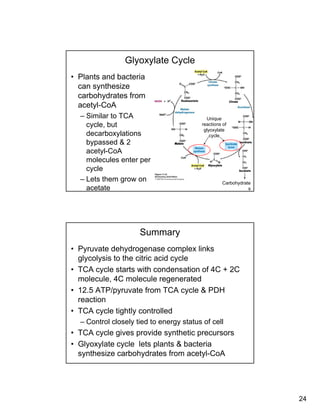
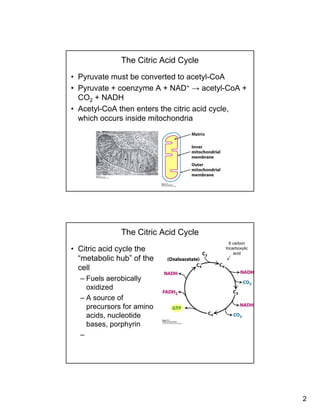
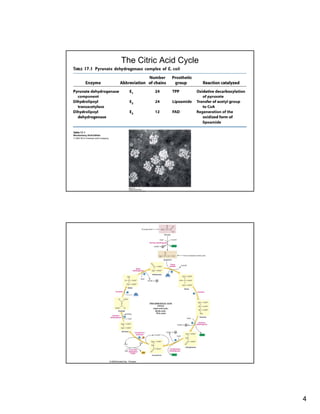
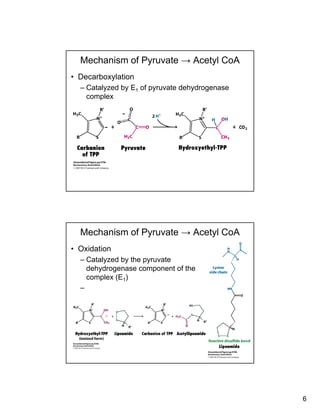
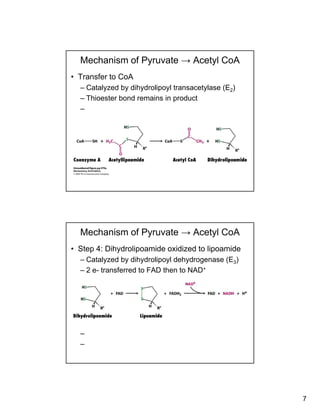
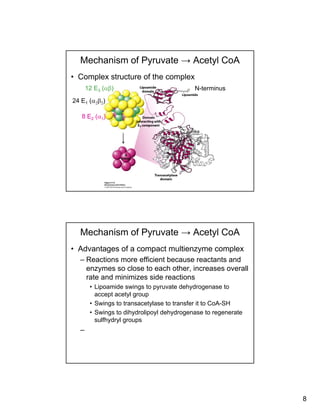
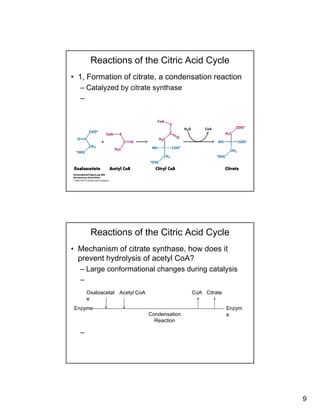
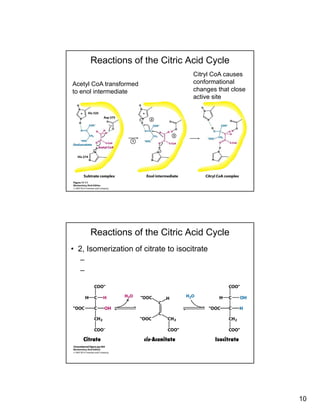
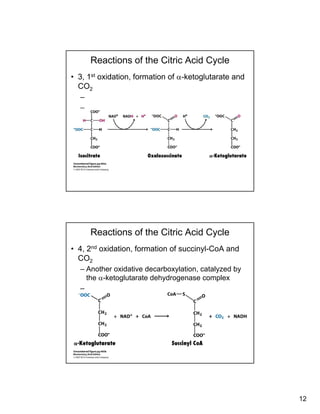
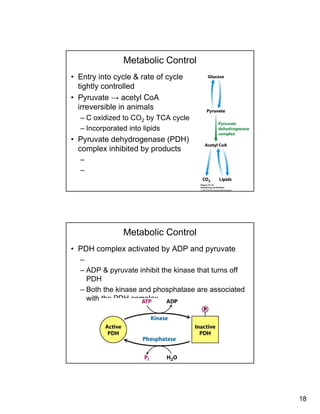
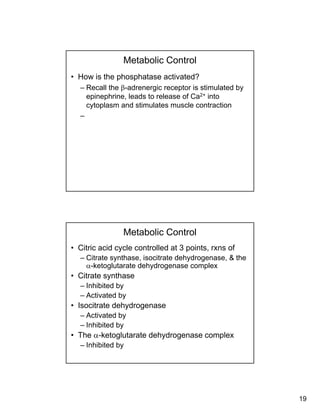
The citric acid cycle (TCA cycle) is a key metabolic pathway that occurs in the mitochondria. It involves 8 steps that fully oxidize acetyl-CoA derived from pyruvate to carbon dioxide, producing high-energy electron carriers NADH and FADH2 to fuel oxidative phosphorylation. The cycle is tightly regulated by product inhibition and feedback from cellular energy levels to balance energy production with biosynthetic needs.





![21
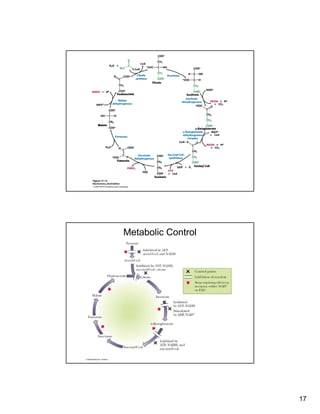
Metabolic Control
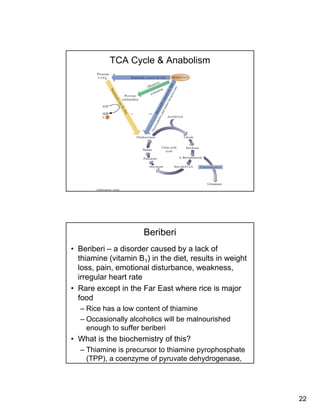
TCA Cycle & Anabolism
• Supply of cycle components need to be
replenished to keep cycle operating as they are
used for synthesisused for synthesis
– Anaplerotic reaction – reaction that replenishes a
citric acid cycle intermediate
– [Oxaloacetate] must allow acetyl-CoA to enter
cycle
In mammals Pyruvate + CO + ATP + H O →– In mammals, Pyruvate + CO2 + ATP + H2O →
oxaloacetate + ADP + Pi + 2 H+
–](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/17-tcacycle-151206095503-lva1-app6891/85/TCA-Cycle-21-320.jpg)