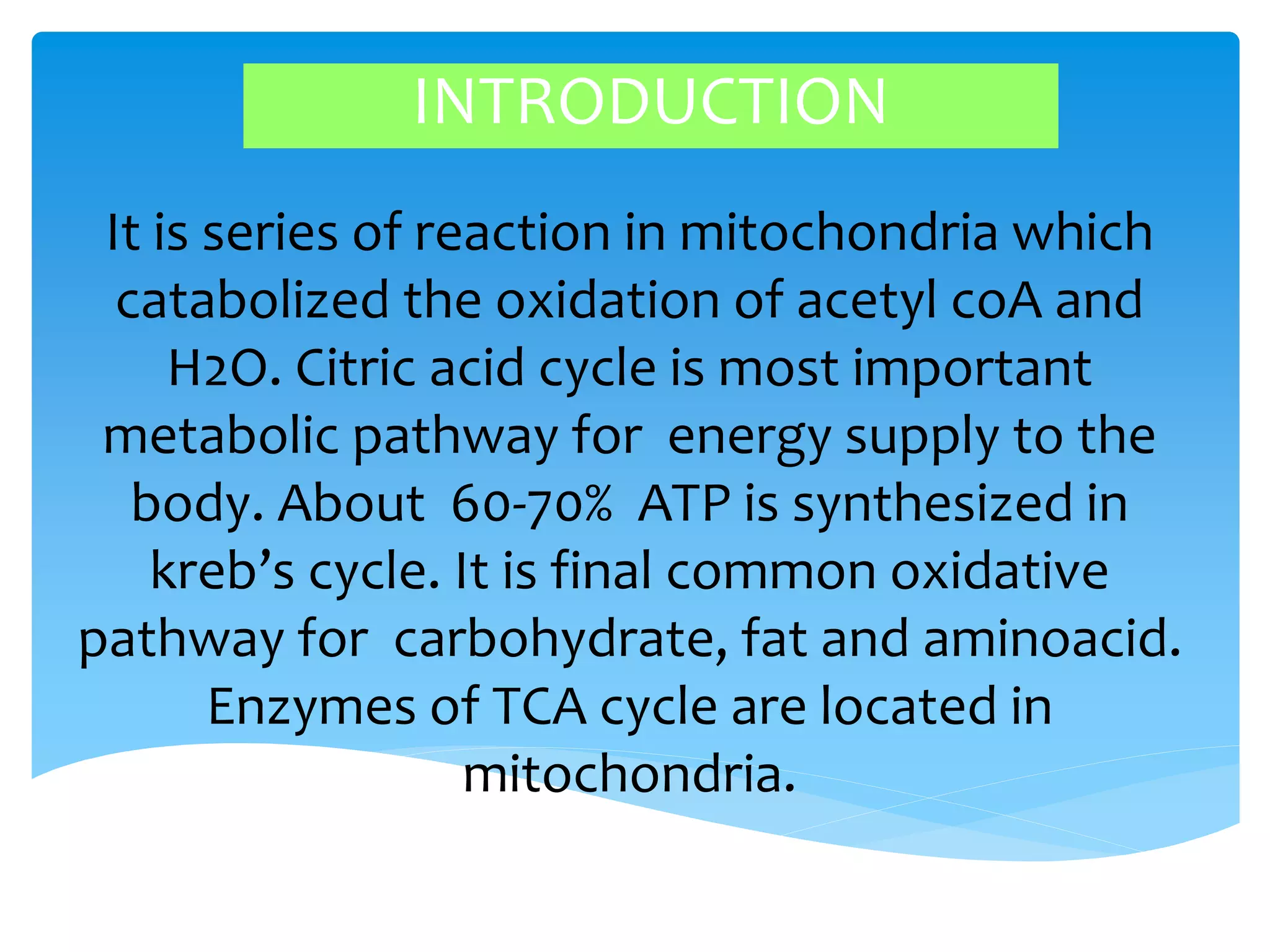
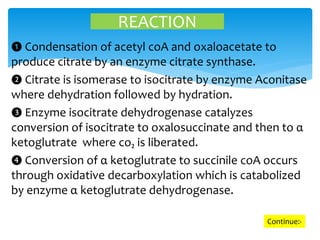
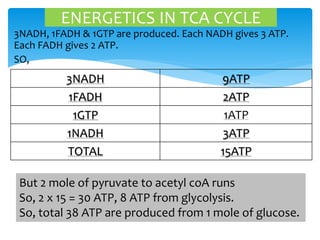
The citric acid cycle is a series of chemical reactions in mitochondria that breaks down acetyl-CoA molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins to generate energy in the form of ATP and NADH. About 60-70% of ATP is produced through the citric acid cycle. The cycle consists of eight steps where enzymes catalyze the oxidation of acetyl-CoA and the oxidation of hydrogen ions and carbon dioxide is released. For each turn of the cycle, three NADH, one FADH2, and one GTP molecule are produced, which generate approximately 15 ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. As two acetyl-CoA molecules are produced from each glucose, a total of 30 ATP are produced in one