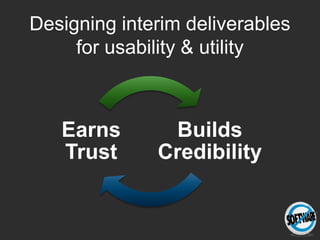
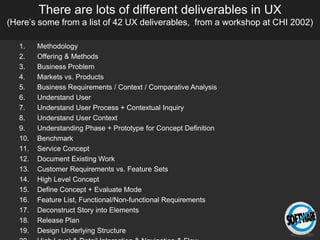
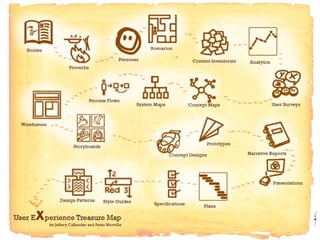
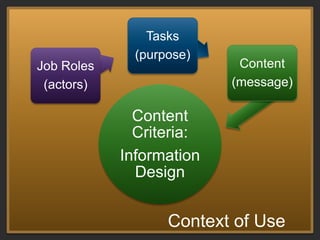
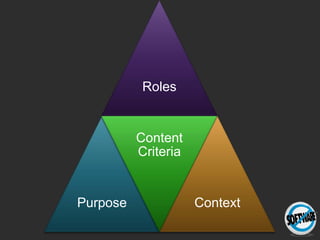
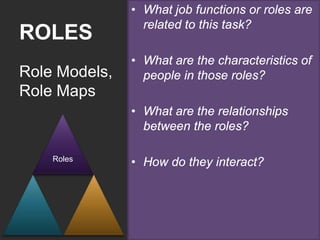
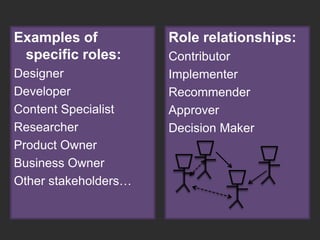
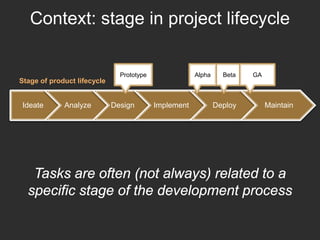
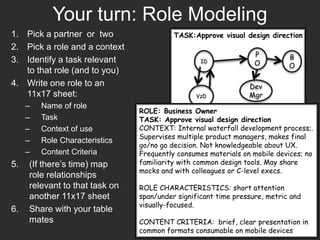
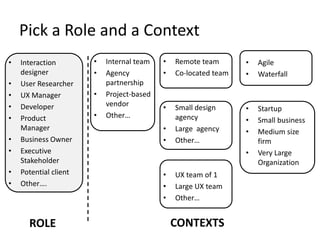
The document discusses the importance of usage-centered approaches in designing UX deliverables, emphasizing their role in facilitating effective communication among stakeholders during the design process. It outlines various types of UX deliverables and presents a framework for determining design criteria related to task, context, and roles of individuals involved. Practical examples and exercises are included to engage participants in applying these concepts to their specific contexts and goals.