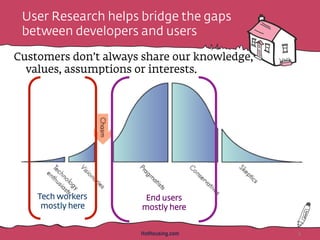
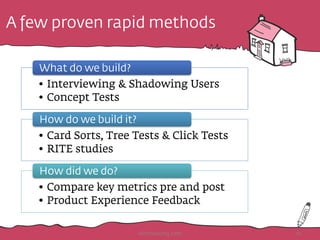
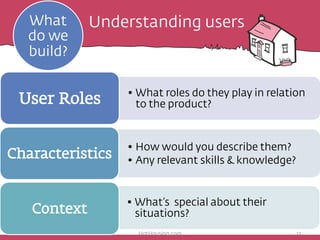
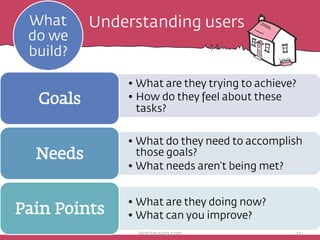
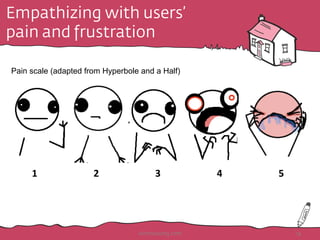
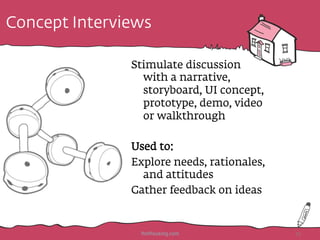
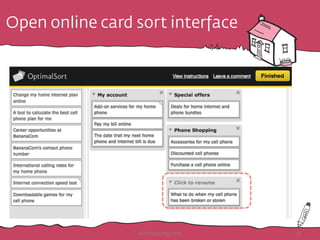
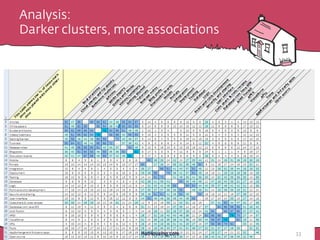
The document discusses the importance of rapid user research in bridging gaps between developers and users throughout the product lifecycle. It details various methods such as interviewing, shadowing, and concept tests, and emphasizes the need for executive buy-in, efficient data collection, and actionable insights. Additionally, it highlights techniques for evaluating user satisfaction and understanding user needs and behaviors to enhance product development.











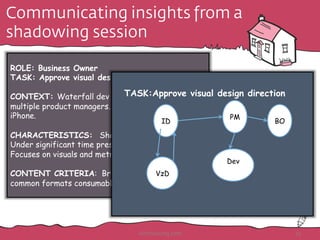
![Task Card: [task description]
Performed by Role: [role name]
Context of Use:
q Where and when is it performed?
q In what environment?
q What corporate culture?
q Where in development process?
q Direction of information flow?
q Device constraints/ media channels?
q Needs for
q Auditability
q Accuracy & Credibility
q Confidentiality
Task Characteristics:
q Frequency
q Regularity
q Continuity
q Intensity of use
q Timeframe to act
q Complexity
q Predictability
q Who controls the process?
q Legal/regulatory restrictions
q Operational/safety risks
q Other roles involved:
HotHousing.com 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rapidresearch-rosensteinagile2013-130816205421-phpapp01/85/Rapid-User-Research-a-talk-from-Agile-2013-by-Aviva-Rosenstein-20-320.jpg)









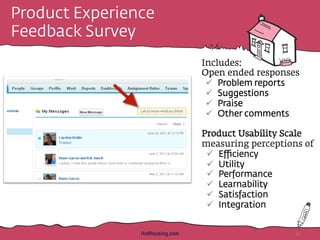
![Collect bugs first; then
group feedback by type
1.Have you experienced any problems or errors when using
[NAME OF FEATURE] in [PRODUCT NAME]?
(Yes/No-randomized)
2. Please describe any problems or errors you've noticed
while using [NAME OF FEATURE]
3. What, if anything, do you like most about [NAME OF
FEATURE]?
4. Do you have any ideas or suggestions for improving
[NAME OF FEATURE]?
5. If there is anything else you'd like us to know about the
[NAME OF FEATURE] in [PRODUCT NAME], tell us here.
HotHousing.com 44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rapidresearch-rosensteinagile2013-130816205421-phpapp01/85/Rapid-User-Research-a-talk-from-Agile-2013-by-Aviva-Rosenstein-44-320.jpg)
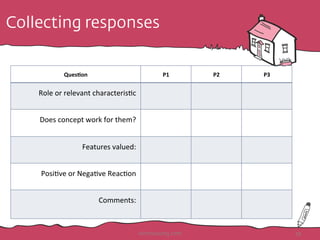
![Product Experience Ratings:
subjective experience metrics
6. Please rate how strongly you agree or disagree with
each of the following statements:
HotHousing.com 45
1) Strongly Disagree 2) Disagree 3) Neither agree nor disagree 4) Agree 5) Strongly Agree)
a. I
expect
to
use
[NAME
OF
FEATURE]
within
[PRODUCT
NAME]
frequently.
b. [PERFORMING
KEY
USER
STORY]
with
[NAME
OF
FEATURE]
is
easy
and
straighdorward.
c. I
am
sa<sfied
with
the
[NAME
OF
FEATURE]
in
[PRODUCT
NAME],
d. I
had
to
learn
a
lot
of
things
before
I
could
use
the
[NAME
OF
FEATURE]
effec<vely.
e. The
[NAME
OF
FEATURE]
works
seamlessly
with
the
rest
of
the
[PRODUCT
NAME]
applica<on.
f. When
I
use
the
[NAME
OF
FEATURE]
it
feels
quick
and
responsive.
Utility
Ease of Use
Satisfaction
Learnability
Integration
Performance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rapidresearch-rosensteinagile2013-130816205421-phpapp01/85/Rapid-User-Research-a-talk-from-Agile-2013-by-Aviva-Rosenstein-45-320.jpg)

