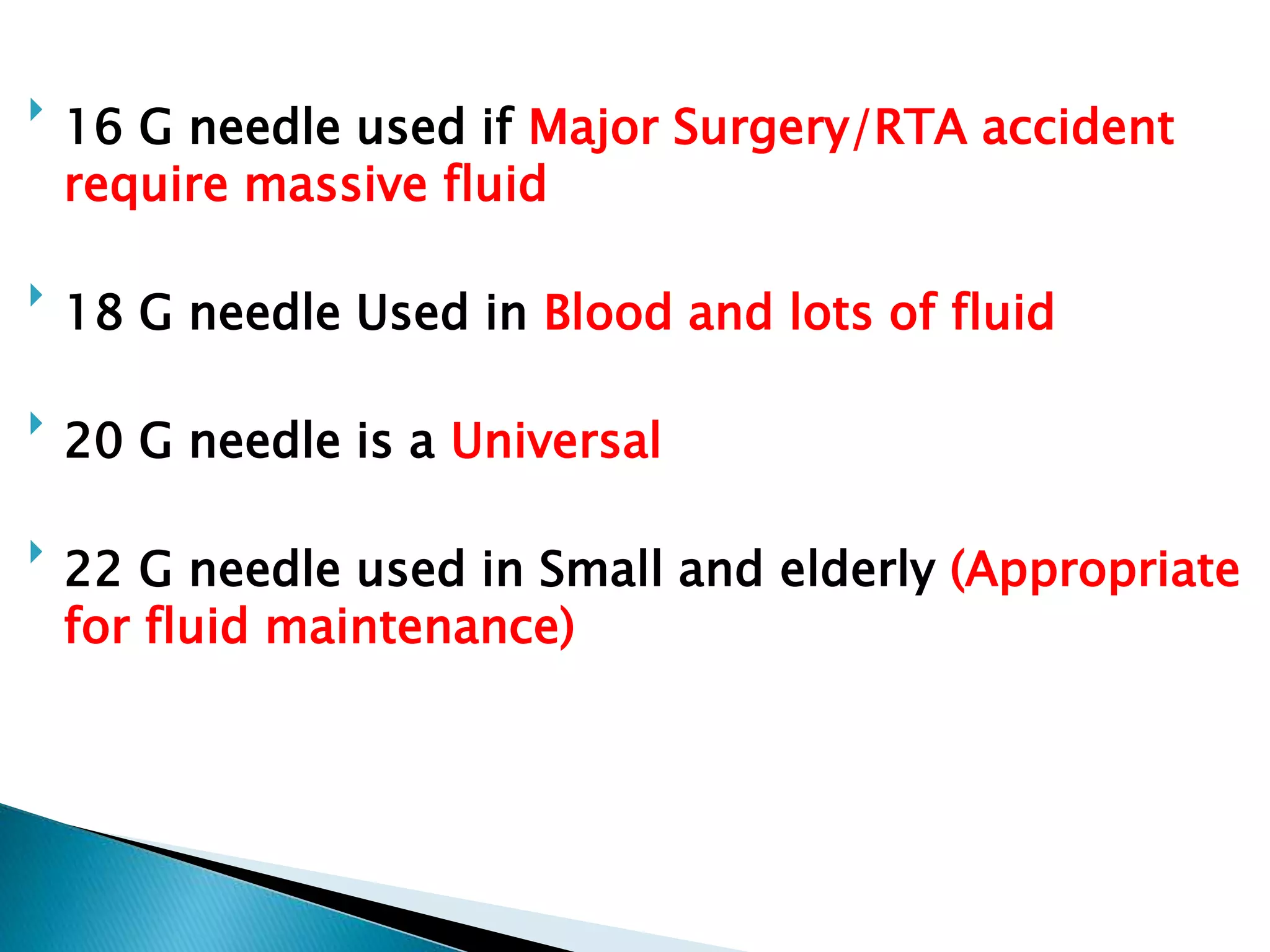
1. Intravenous therapy involves administering fluids directly into the bloodstream through a catheter or needle inserted into a peripheral vein to replace water, electrolytes, and nutrients.
2. IV therapy is used for patients unable to take oral intake, to rapidly replace fluids and nutrients, for unconscious patients, and during surgery or shock.
3. Solutions administered intravenously can be hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic depending on their electrolyte concentration relative to body fluids. The most commonly used solutions, like normal saline and lactated Ringer's, are isotonic.