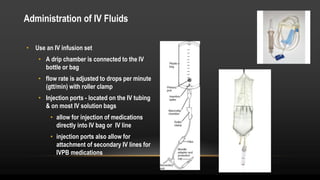
Intravenous (IV) therapy provides fluids, electrolytes, nutrients, and medications directly into the bloodstream. IV solutions consist of dextrose or electrolytes mixed with water. Several types of IV fluids exist including isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic solutions. Isotonic fluids maintain electrolyte balance while hypotonic fluids provide free water and hypertonic fluids pull fluid from tissues into the bloodstream. IV therapy requires selecting the appropriate solution and administration method based on the patient's needs. Complications can include phlebitis and infiltration which require discontinuing the IV and monitoring the site.