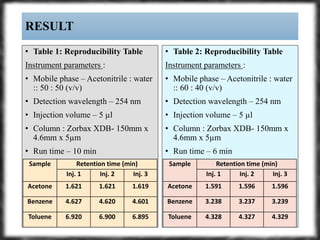
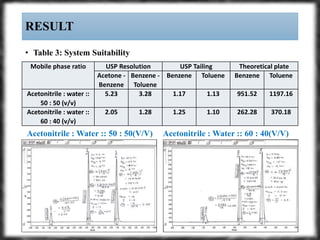
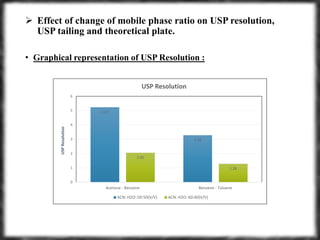
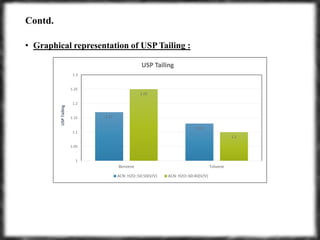
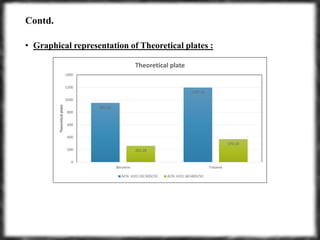
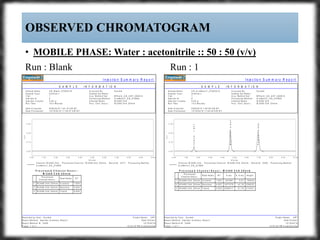
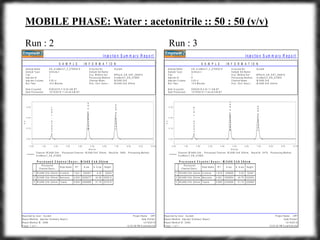
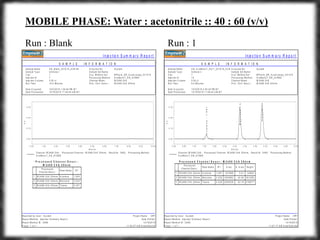
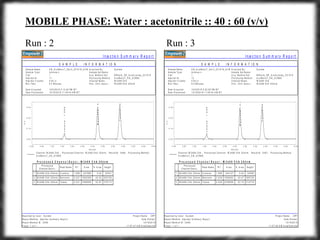
The document summarizes an experiment assessing system suitability parameters for an HPLC method using acetone, benzene, and toluene as analytes. The method evaluated resolution, tailing factor, and theoretical plates at different mobile phase compositions of water and acetonitrile. The results showed that resolution and theoretical plates decreased while tailing increased when the mobile phase composition was changed from 50:50 to 60:40 water:acetonitrile. Chromatograms are also presented to visualize the separation achieved with each mobile phase.