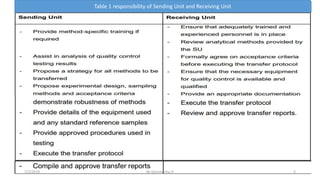
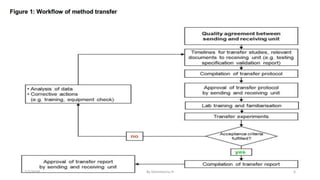
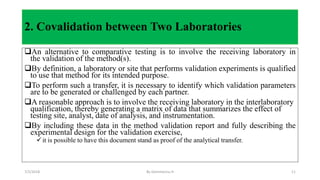
This document discusses analytical method transfer between laboratories. It defines analytical method transfer as qualifying a receiving laboratory to use a test procedure that originated in another laboratory. There are different types of method transfers, including comparative testing between laboratories, covalidation where both laboratories participate in validation, and complete or partial revalidation of methods in the receiving laboratory. Successful method transfers require several key elements, such as a pre-approved transfer plan, detailed description of test methods and procedures, description of test requirements, rationale for test parameters, acceptance criteria, and documentation of results. The goal is to verify that analytical methods produce equivalent results in different laboratories.


![Is the documented process that qualifies a laboratory (the receiving unit) to use an
analytical test procedure that originated in another laboratory (the transferring
unit),
o thus ensuring that the receiving unit has the procedural knowledge and ability to perform the
transferred analytical procedure as intended.
Is the verification that a method or test procedure works in an equivalent fashion
at two or more different sites or laboratories and meets all acceptance criteria.
In short, analytical method transfer qualifies a laboratory to use a test procedure.
The process is driven by compliance and can be governed by both a statistical and
practical treatment of the resulting data.
Introduction[1]
7/2/2018 By Gemmechu.H 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodtransfer-180702091134/85/Analytical-method-transfer-3-320.jpg)
![Introduction[2]
The importance of analytical transfer was underscored by the Analytical Research
and Development Steering Committee (ARDSC) of the Pharmaceutical Research
and Manufacturers of America (PhRMA) during its annual workshop held in
September 2000.
At this meeting, representatives from PhRMA member companies met with
facilitators to draft an acceptable analytical practice (AAP) that can function as
a suitable first step guidance document for conducting successful method transfer activities.
The focus of the AAP is
to provide such guidance and to clarify the essential elements that embody a complete and
compliant transfer.
7/2/2018 By Gemmechu.H 4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodtransfer-180702091134/85/Analytical-method-transfer-4-320.jpg)
![The drug development process[1]
Although there are a plethora of internal initiatives targeted at reducing the time
line of drug development and hence the overall time to market, the basic process
of drug development has remained unchanged.
Analytical method evaluation ring test (AMERT) by Crowther, this process allows
the quality unit to make comments and suggestions to their R&D colleagues
before the final validation of the method.
The knowledge base surrounding a compound increases steadily.
At the junction between R&D and operations, it is important to ensure not only
that the analytical methods are successfully used by the quality unit, but also that
the applicable knowledge and data are transferred or are readily accessible by the
receiving laboratory.
Although the quality unit might not require excessive detail regarding all
scientific research performed during the R&D period, some information transfer is
necessary.
7/2/2018 By Gemmechu.H 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodtransfer-180702091134/85/Analytical-method-transfer-7-320.jpg)
![The drug development process[2]
Figure 2 the phases of drug development from a clinical perspective.
7/2/2018 By Gemmechu.H 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodtransfer-180702091134/85/Analytical-method-transfer-8-320.jpg)



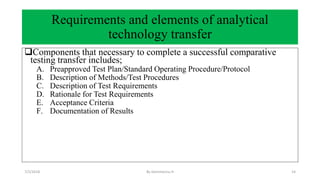
![A. Preapproved Test Plan/Standard Operating Procedure/Protocol[1]
Before the planning of any transfer, an approved document that describes both the
general transfer process as well as the specific acceptance criteria necessary for
the method(s) being transferred needs to be in place.
In many companies, it is common for both the R&D and quality units to have
general standard operating procedures (SOPs) that govern the transfer process.
These SOPs describe the details of a method transfer protocol that is specific to
the product and methods.
7/2/2018 By Gemmechu.H 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodtransfer-180702091134/85/Analytical-method-transfer-15-320.jpg)
![The contents of such a protocol were,
Clearly define responsibilities of both the transferring and receiving
laboratories
A list of all methods to be transferred via comparative testing.
Rationale for any methods not included, i.e., transfer waiver, must also be
provided.
The scope of the transfer should be provided with respect to what laboratories
and analysts are affected by the transfer.
In some cases, direct analyst-to-analyst transfer might be necessary due to
method complexity or the use of new or unfamiliar equipment.
The selection materials and samples to be used in the transfer should be
described in detail
A. Preapproved Test Plan/Standard Operating Procedure/Protocol[2]
7/2/2018 By Gemmechu.H 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodtransfer-180702091134/85/Analytical-method-transfer-16-320.jpg)







![Transfer of technical ownership[1]
At the heart of the technical transfer process is documentation.
The old adage “if it isn’t written, it isn’t done” certainly applies to analytical transfer.
The R&D component of the drug development process encompasses several years, during
which time the knowledge base surrounding a compound increases steadily.
At the junction between R&D and operations, it is important to ensure not only that the
analytical methods are successfully used by the quality unit, but also that the applicable
knowledge and data are transferred or are readily accessible by the receiving laboratory.
Although the quality unit might not require excessive detail regarding all scientific research
performed during the R&D period, some information transfer is necessary.
Rather than inundate the quality unit with a large number of lengthy reports, several concise
documents that meet the specific needs of an operations-based analytical unit are preferred.
In most companies, the most important reports are the method development/validation reports
and analytical development reports.
7/2/2018 By Gemmechu.H 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodtransfer-180702091134/85/Analytical-method-transfer-25-320.jpg)
![A. Method Development Report
This report should provide a concise summary of the development of the key
analytical methods used to assure the identity, quality, purity, potency, and
composition of the test article.
For HPLC methods, the rationale for the column and conditions chosen should be
documented.
For discriminating dissolution methods, the choice of media, type of apparatus,
and detection method should be given.
In all cases, a description or tabular list of unsuccessful approaches should be
included.
A good method development/validation report will include sample chromatograms
for approaches that have been tried.
Transfer of technical ownership[2]
7/2/2018 By Gemmechu.H 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodtransfer-180702091134/85/Analytical-method-transfer-26-320.jpg)
![B. Analytical Development Report
The analytical development report is a documented summary and logic flow of all
essential analytical information acquired during the R&D phase of the project.
It is a repository of all important analytical information pertaining to the project
and is
o therefore a source document for the quality unit, and
o it is also used in the preparation of the site inspection at the time of product approval.
All information contained in this report must be traceable to raw data and other
reports, if applicable.
The analytical development report is one of the most valuable documents written
by the R&D unit during the development process.
If properly composed and completed, it can serve as a powerful document for
many years after product approval.
Transfer of technical ownership[3]
7/2/2018 By Gemmechu.H 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodtransfer-180702091134/85/Analytical-method-transfer-27-320.jpg)

![C. Transfer File
Used as a means of ensuring that all key documents and relevant information are imparted to
operations or the receiving laboratory.
This file is merely a collection of important reports.
For analytical methods, such documents include the method development and validation
reports, impurity profiling report, stability reports and tables, and specification archive.
The power of such an approach is that it ensures that all information is conveyed
to the receiving laboratory.
This strategy is useful if operations will be relied on to continue the development process.
Examples include development for new formulation strengths for “brand support” or life
cycle management or the support of phase IV clinical trials.
Transfer of technical ownership[4]
7/2/2018 By Gemmechu.H 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticalmethodtransfer-180702091134/85/Analytical-method-transfer-29-320.jpg)

