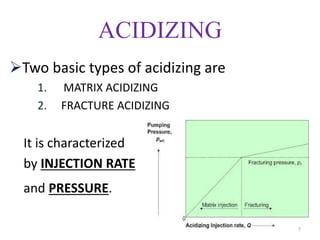
This document discusses well stimulation techniques used to increase oil and gas production. It describes two main types of well stimulation: acidizing and hydraulic fracturing. Acidizing involves injecting acid to dissolve rock and increase permeability. There are two types of acidizing - matrix acidizing below fracture pressure to remove damage, and fracture acidizing above pressure to create open channels. Hydraulic fracturing uses pressurized fluid to crack rock, with proppant like sand injected to hold the fractures open and increase conductivity. Both techniques aim to extend fractures and improve hydrocarbon flow into the wellbore.