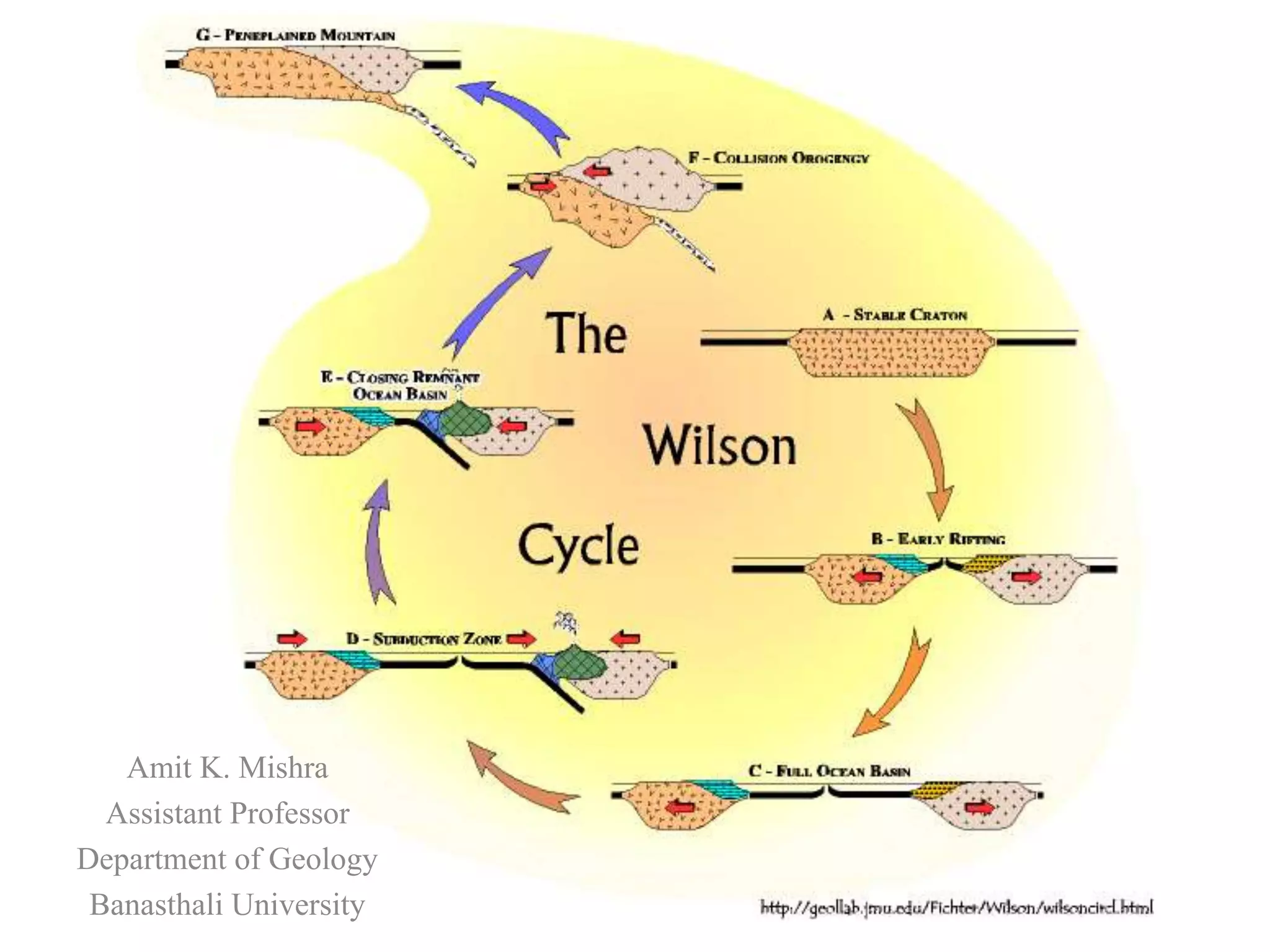
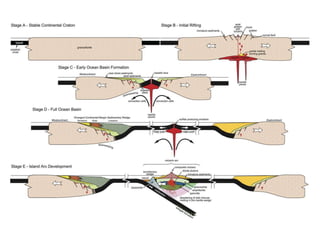
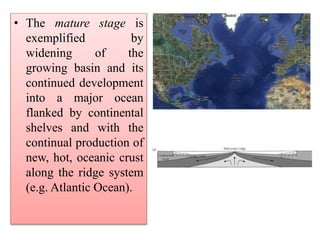
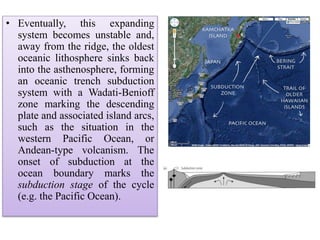
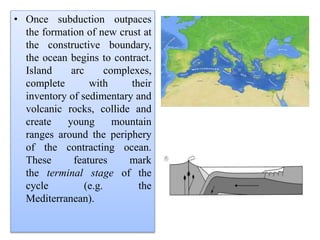
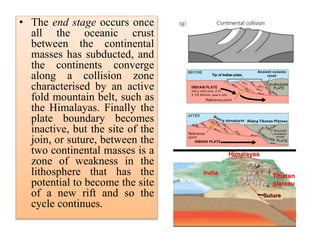
Amit K. Mishra discusses the Wilson Cycle, illustrating how plate tectonics affects geological structures over time through a series of stages from the embryonic formation of rift valleys to the eventual subduction of oceanic crust and the formation of mountain ranges. Key stages include the youthful formation of ocean basins, the maturation of oceans like the Atlantic, and the terminal phase marked by mountain-building during continental convergence. This cyclical process demonstrates the dynamic nature of Earth's geology, with ongoing potential for new rift formation.