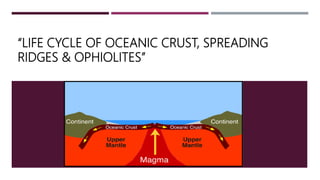
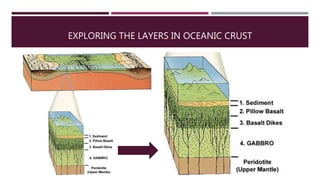
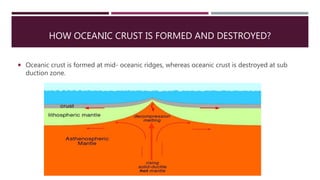
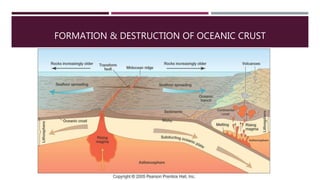
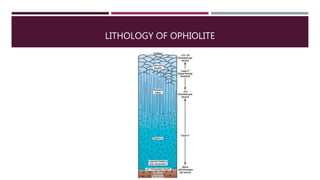
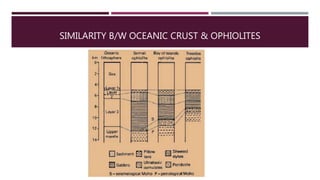
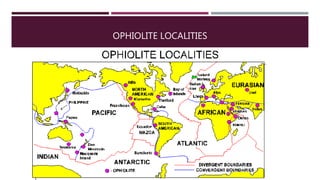
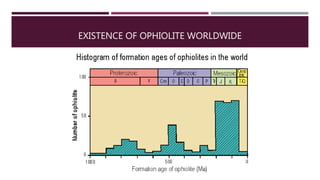
This document summarizes information about the life cycle of oceanic crust and spreading ridges. It discusses that oceanic crust is formed at mid-ocean ridges as molten rock from the mantle reaches the seafloor and solidifies. Oceanic crust is then destroyed as it is subducted at convergent plate boundaries. The document also provides information about ophiolites, which are sections of oceanic crust and upper mantle rock that have been uplifted and exposed on land.