Introduction to Plate tectonics and its consequences.pptx
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
0 likes•20 views
This slide introduces the basic concept of tectonic movement. It is mainly focused on, causes of plate movement, rate of movement, consequences of movement, and some natural phenomena related to tectonic movement.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to Introduction to Plate tectonics and its consequences.pptx
Similar to Introduction to Plate tectonics and its consequences.pptx (20)
The Creation of the Ocean FloorSCI209Running head .docx

The Creation of the Ocean FloorSCI209Running head .docx
Study of plate tectonics of the earth, or plate movement, 

Study of plate tectonics of the earth, or plate movement,
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY & SEAFLOOR SPREADING.pptx

CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY & SEAFLOOR SPREADING.pptx
WHAT IS A PLATE? MAJOR PLATES. Types of Earth’s Crust. Plate Boundary

WHAT IS A PLATE? MAJOR PLATES. Types of Earth’s Crust. Plate Boundary
Recently uploaded
https://app.box.com/s/7hlvjxjalkrik7fb082xx3jk7xd7liz3TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Recently uploaded (20)
21st_Century_Skills_Framework_Final_Presentation_2.pptx

21st_Century_Skills_Framework_Final_Presentation_2.pptx
On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows

On National Teacher Day, meet the 2024-25 Kenan Fellows
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx

HMCS Vancouver Pre-Deployment Brief - May 2024 (Web Version).pptx
Exploring_the_Narrative_Style_of_Amitav_Ghoshs_Gun_Island.pptx

Exploring_the_Narrative_Style_of_Amitav_Ghoshs_Gun_Island.pptx
Introduction to Plate tectonics and its consequences.pptx
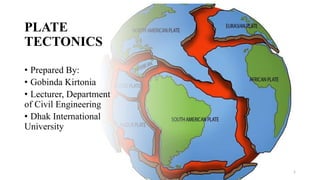
- 1. PLATE TECTONICS • Prepared By: • Gobinda Kirtonia • Lecturer, Department of Civil Engineering • Dhak International University 1
- 2. Introduction The surface of the Earth is split up into several large sections of rock called tectonic plates. A tectonic plate includes the Earth's crust and upper mantle. Earth has a rigid outer layer, known as the lithosphere, which is typically about 100 km (60 miles) thick and overlies a plastic (moldable, partially molten) layer called the asthenosphere. The lithosphere is broken up into seven very large continental- and ocean-sized plates, six or seven medium-sized regional plates, and several small ones. These plates move relative to each other, typically at rates of 5 to 10 cm (2 to 4 inches) per year, and interact along their boundaries, where they converge, diverge, or slip past one another. 2
- 3. Let’s enjoy a video. https://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=fzhPmemffII Gobinda Kirtonia, Lecturer, CE, DIU 3
- 4. The Tectonic Plates move relative to each other, typically at rates of 5 to 10 cm (2 to 4 inches) per year, and interact along their boundaries, where they converge, diverge, or slip past one another. Such interactions are thought to be responsible for most of Earth’s seismic and volcanic activity, although earthquakes and volcanoes can occur in plate interiors. Plate motions cause mountains to rise where plates push together, or converge, and continents to fracture and oceans to form where plates pull apart, or diverge. The continents are embedded in the plates and drift passively with them, which over millions of years results in significant changes in Earth’s geography. Gobinda Kirtonia, Lecturer, CE, DIU 4
- 5. Types of Plate Movements Divergent (Spreading):This is where two plates move away from each other. Molten rock from the mantle erupts along the opening, forming new crust. The earthquakes that occur along these zones, called spreading centers, are relatively small. The Great Rift Valley in Africa, the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden all formed as a result of divergent plate motion. Convergent (Colliding): This occurs when plates move towards each other and collide. When a continental plate meets an oceanic plate, the thinner, denser, and more flexible oceanic plate sinks beneath the thicker, more rigid continental plate. This is called subduction. Transform: When two tectonic plates slide past each other, the place where they meet is a transform or lateral fault. The San Andreas Fault is one of the best examples of lateral plate motion. Gobinda Kirtonia, Lecturer, CE, DIU 5
- 6. Continental drift The continental drift hypothesis was developed in the early part of the 20th century, mostly by Alfred Wegener. Wegener said that continents move around on Earth’s surface and that they were once joined together as a single supercontinent. Alfred Wegener proposed that the continents were once united into a single supercontinent named Pangaea, meaning all earth in ancient Greek. He suggested that Pangaea broke up long ago and that the continents then moved to their current positions. He called his hypothesis continental drift. If the current continents are placed together, they fit together like a puzzle, which is evident to validate Wegner’s Theory. Other evidences like rock of same type, fossils, same mountain formations are found at the edge of current continents. Gobinda Kirtonia, Lecturer, CE, DIU 6
- 7. Gobinda Kirtonia, Lecturer, CE, DIU 7
- 8. Sea-floor Spreading The seafloor spreading hypothesis was proposed by the American geophysicist Harry H. Hess in 1960. Hess postulated that molten material from Earth’s mantle continuously wells up along the crests of the mid-ocean ridges that wind for nearly 80,000 km (50,000 miles) through all the world’s oceans. As the magma cools, it is pushed away from the flanks of the ridges. This spreading creates a successively younger ocean floor, and the flow of material is thought to bring about the migration, or drifting apart, of the continents. The continents bordering the Atlantic Ocean, for example, are believed to be moving away from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge at a rate of 1–2 cm (0.4–0.8 inch) per year, thus increasing the breadth of the ocean basin by twice that amount. Gobinda Kirtonia, Lecturer, CE, DIU 8
- 9. Fig: Sea-Floor Spreading Gobinda Kirtonia, Lecturer, CE, DIU 9
- 10. Thank You 10 Gobinda Kirtonia, Lecturer, CE, DIU