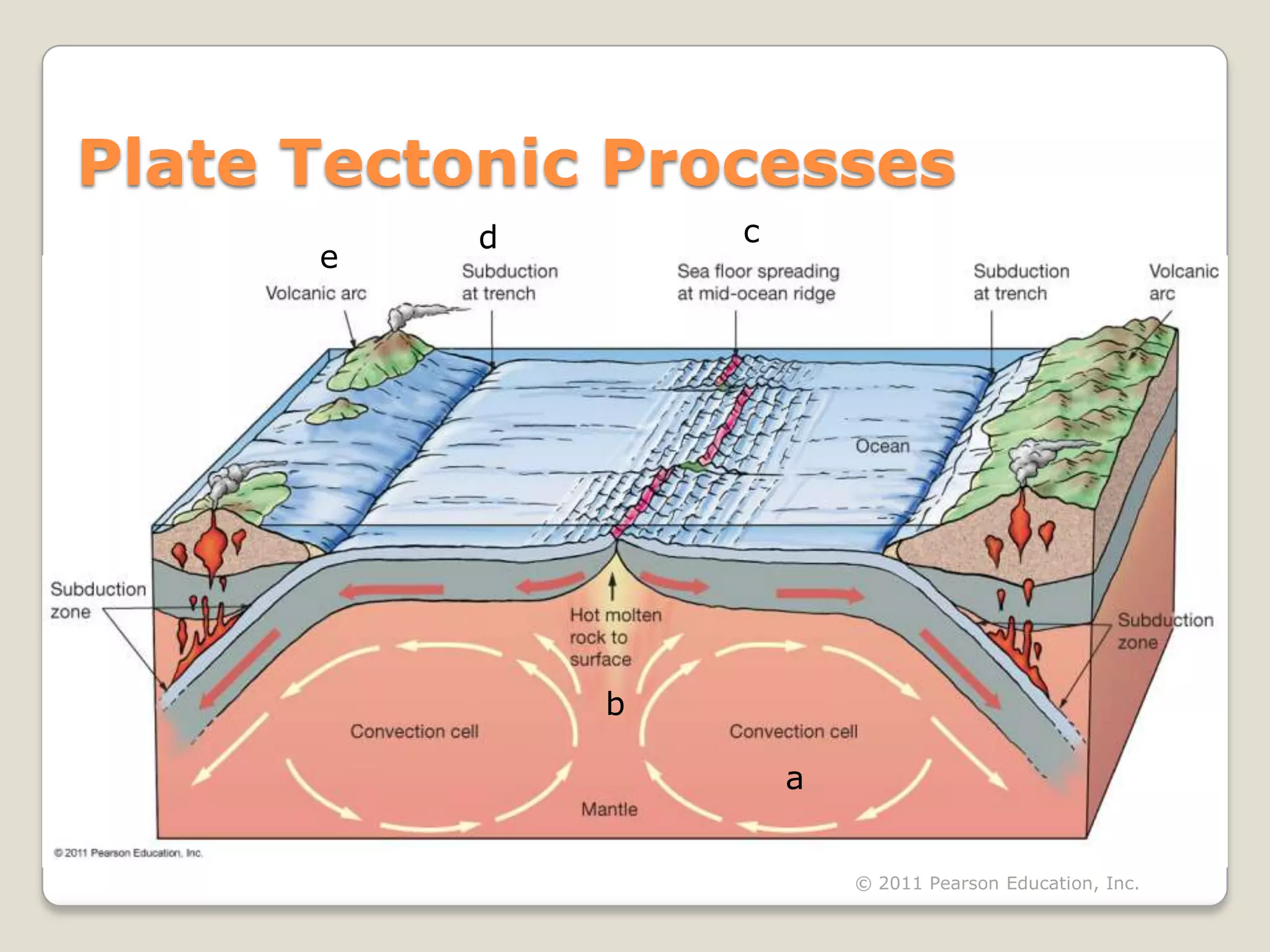
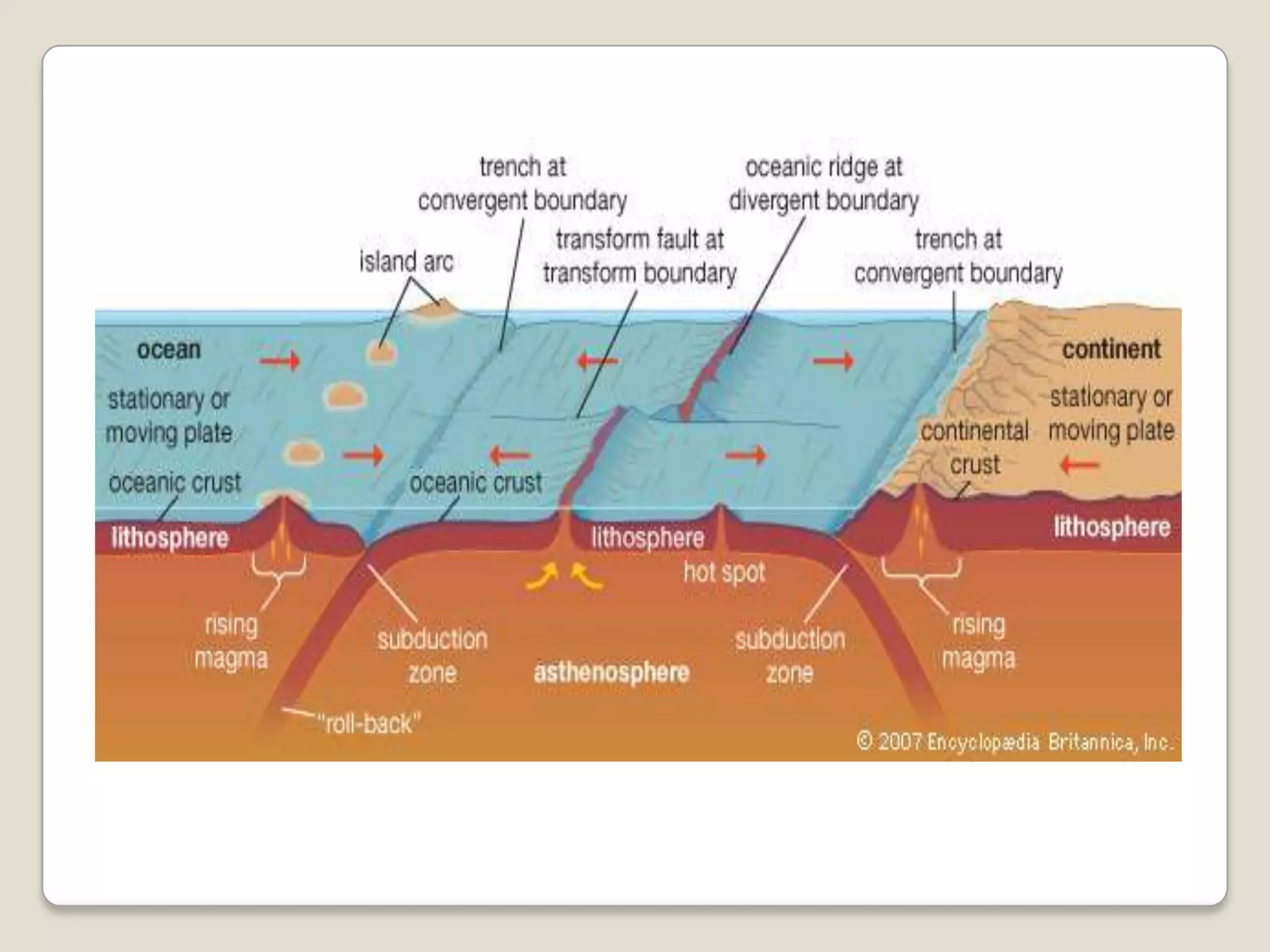
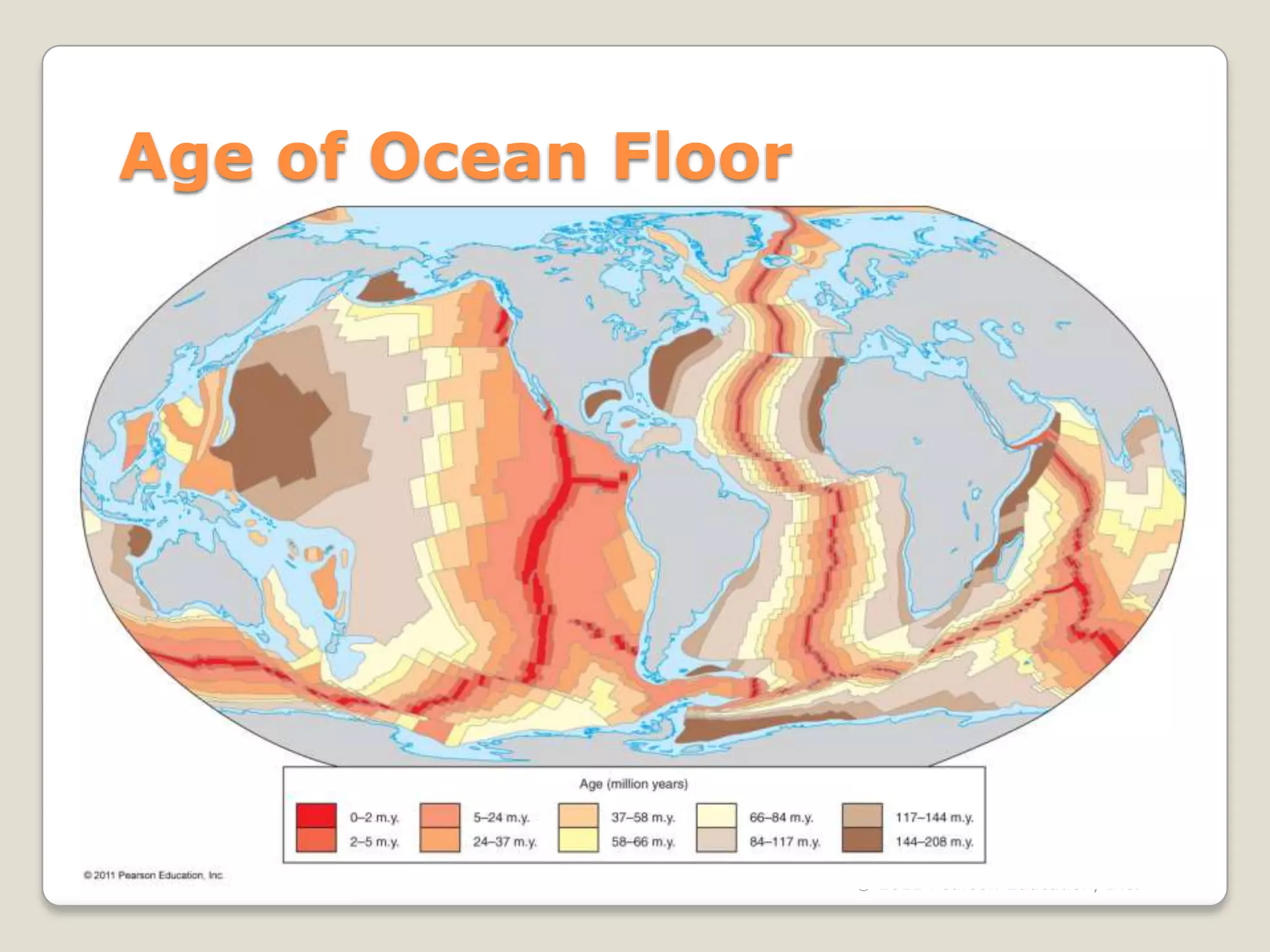
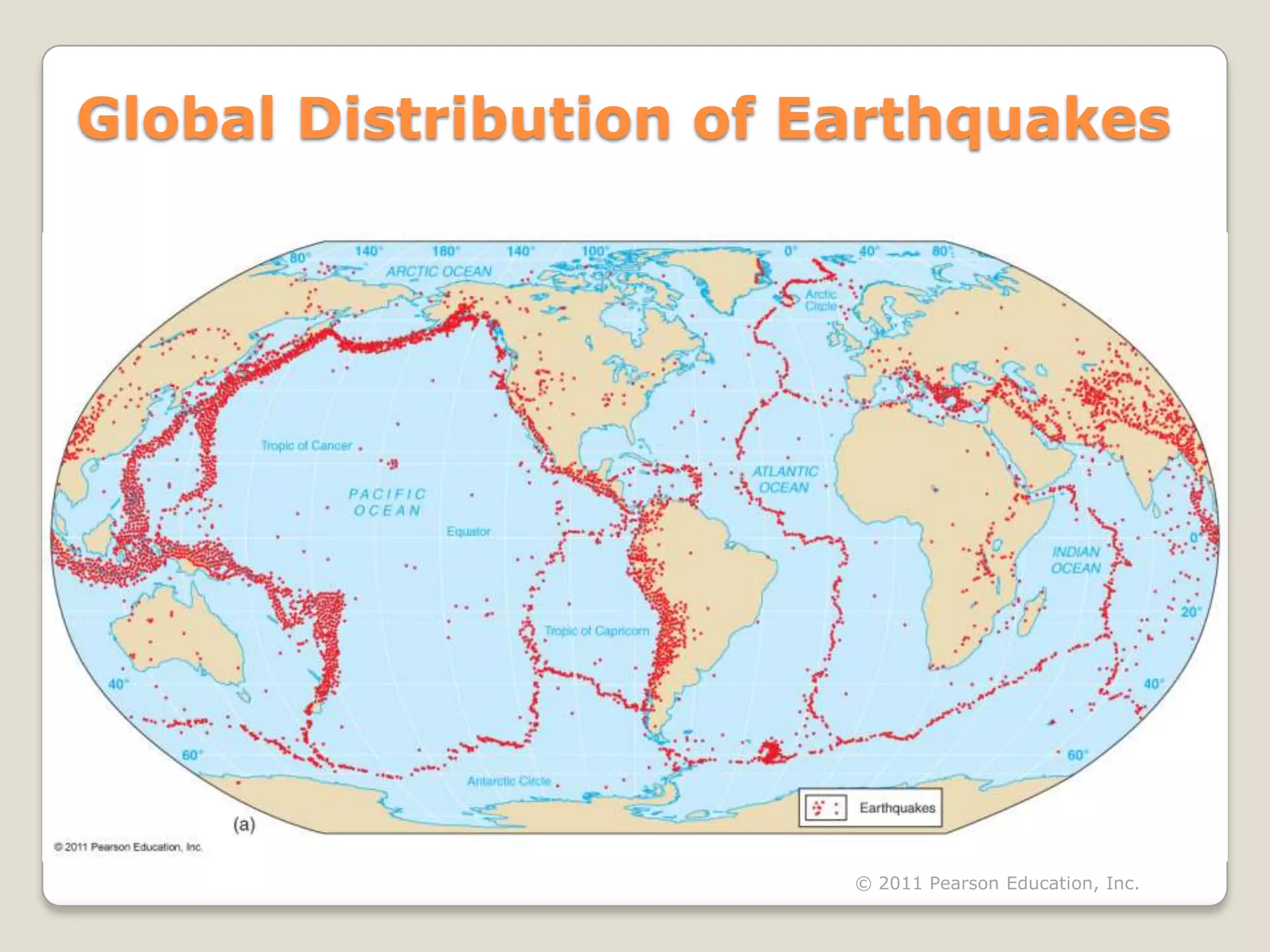
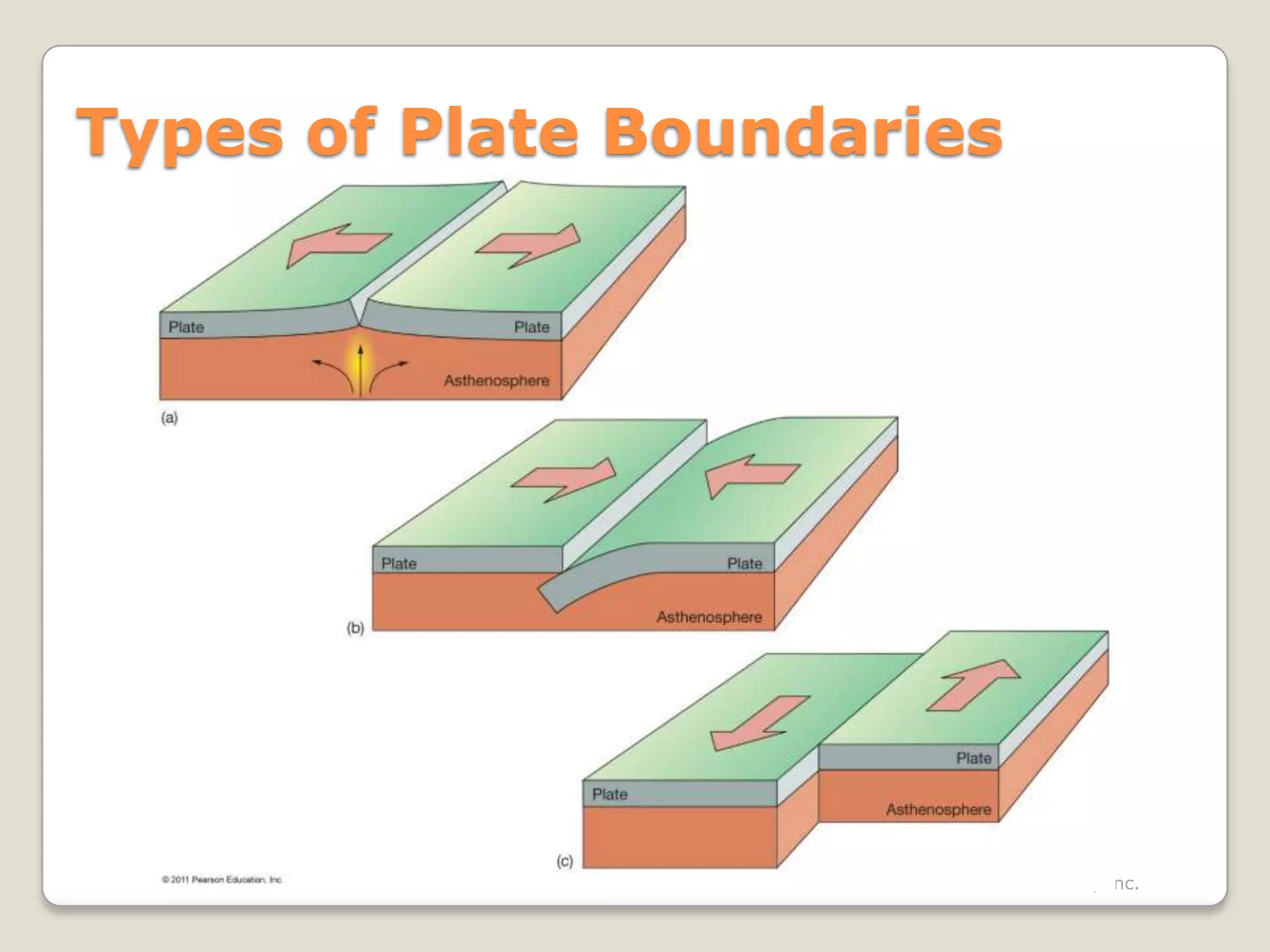
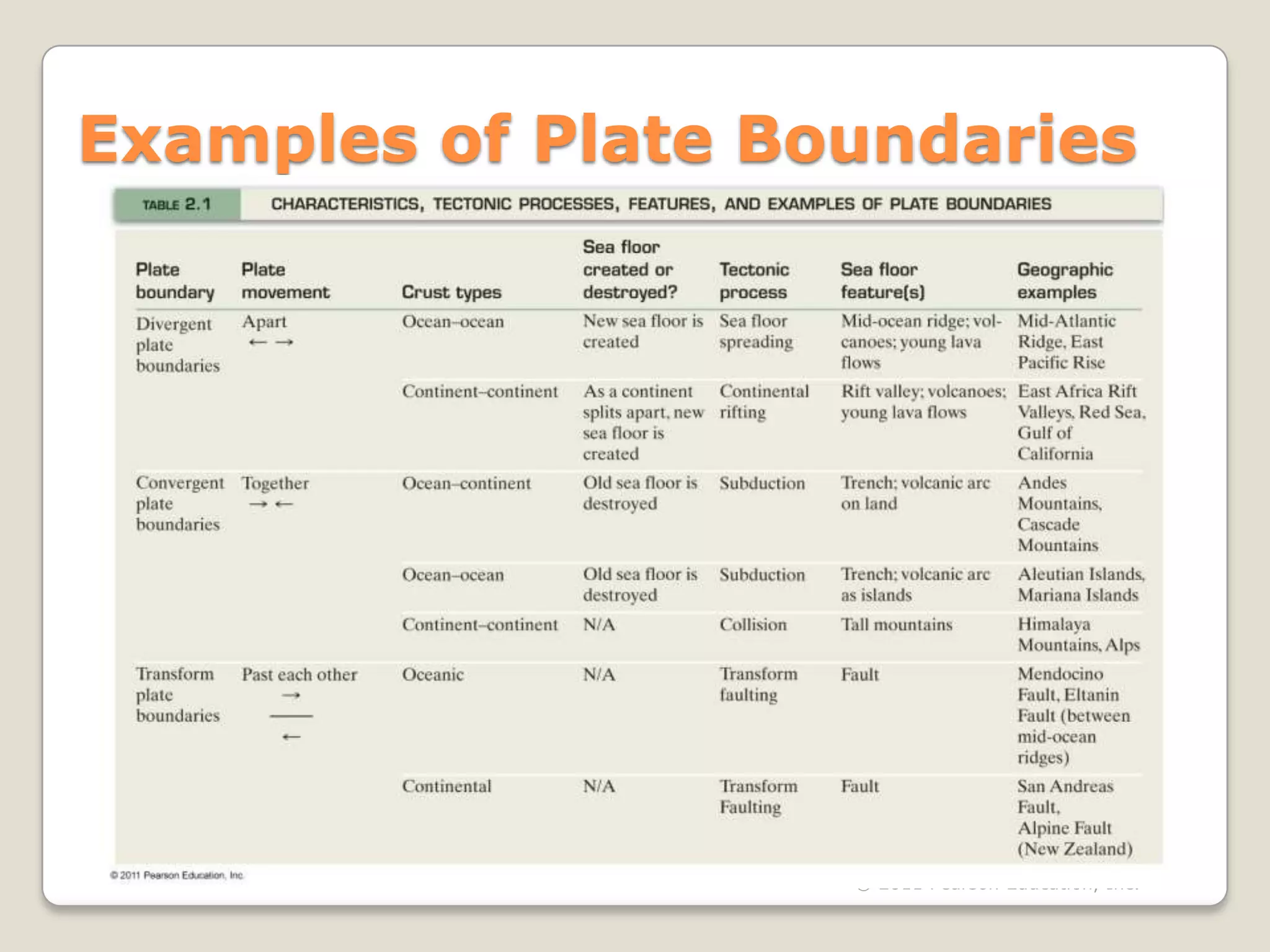
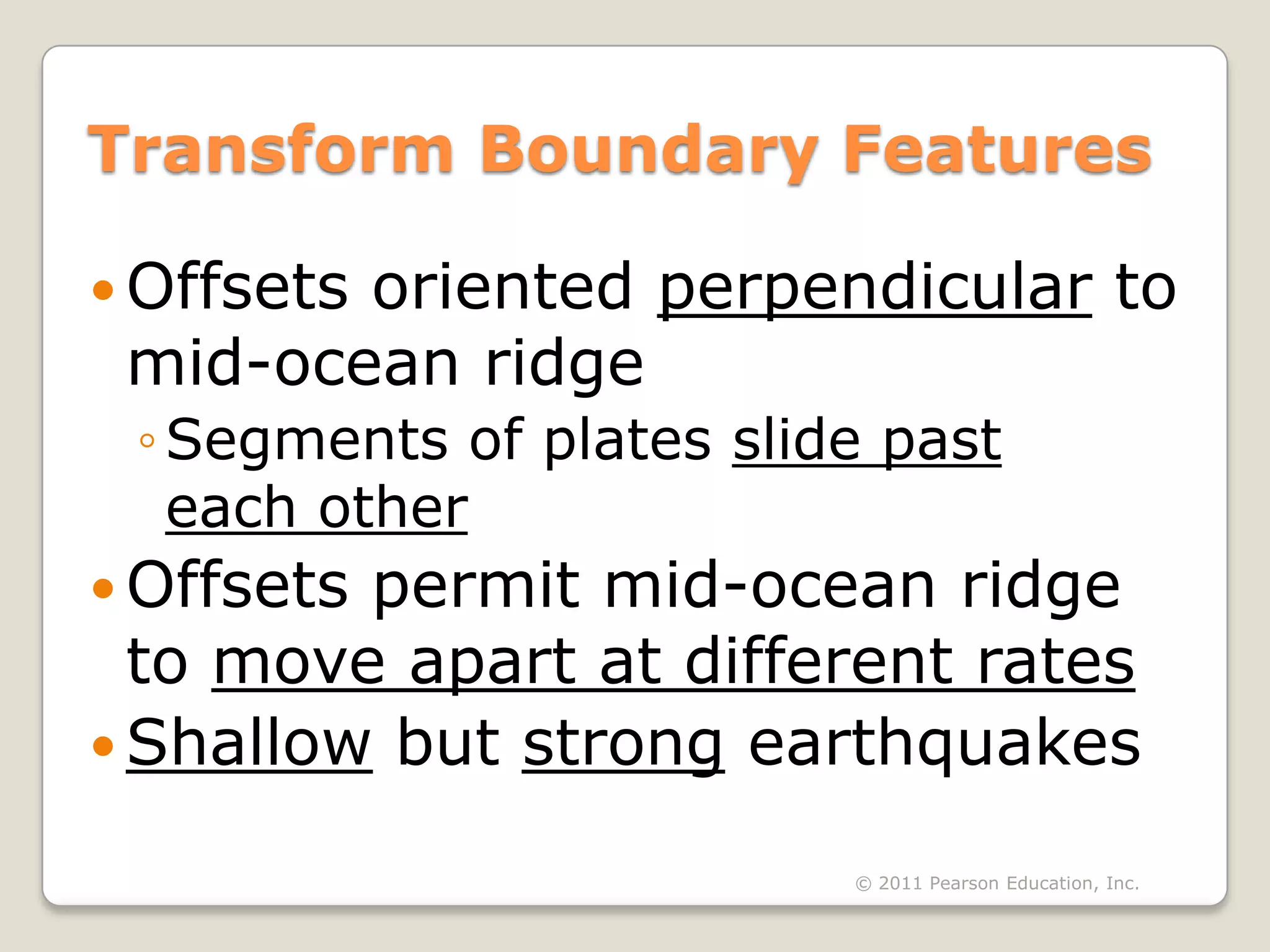
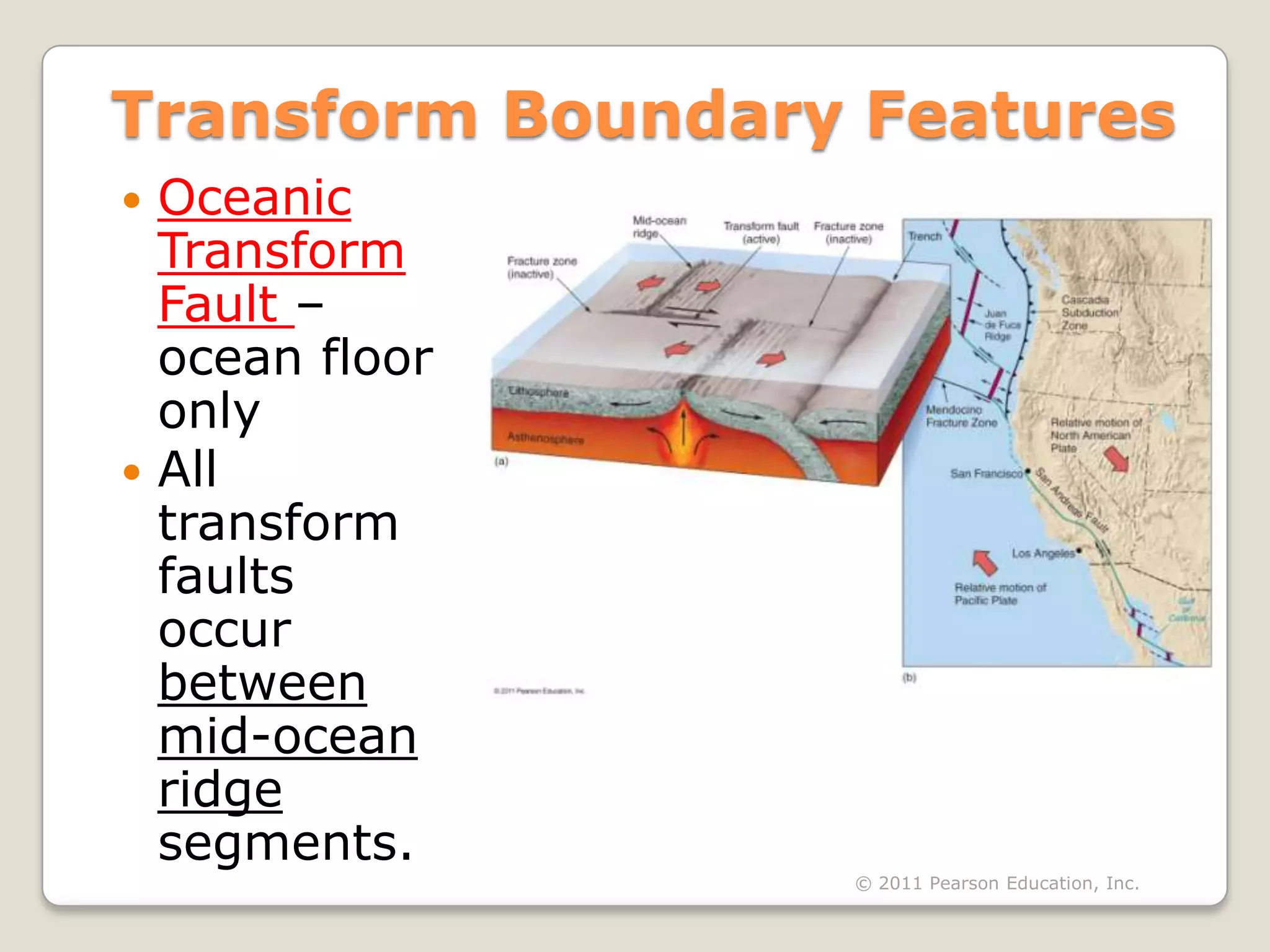
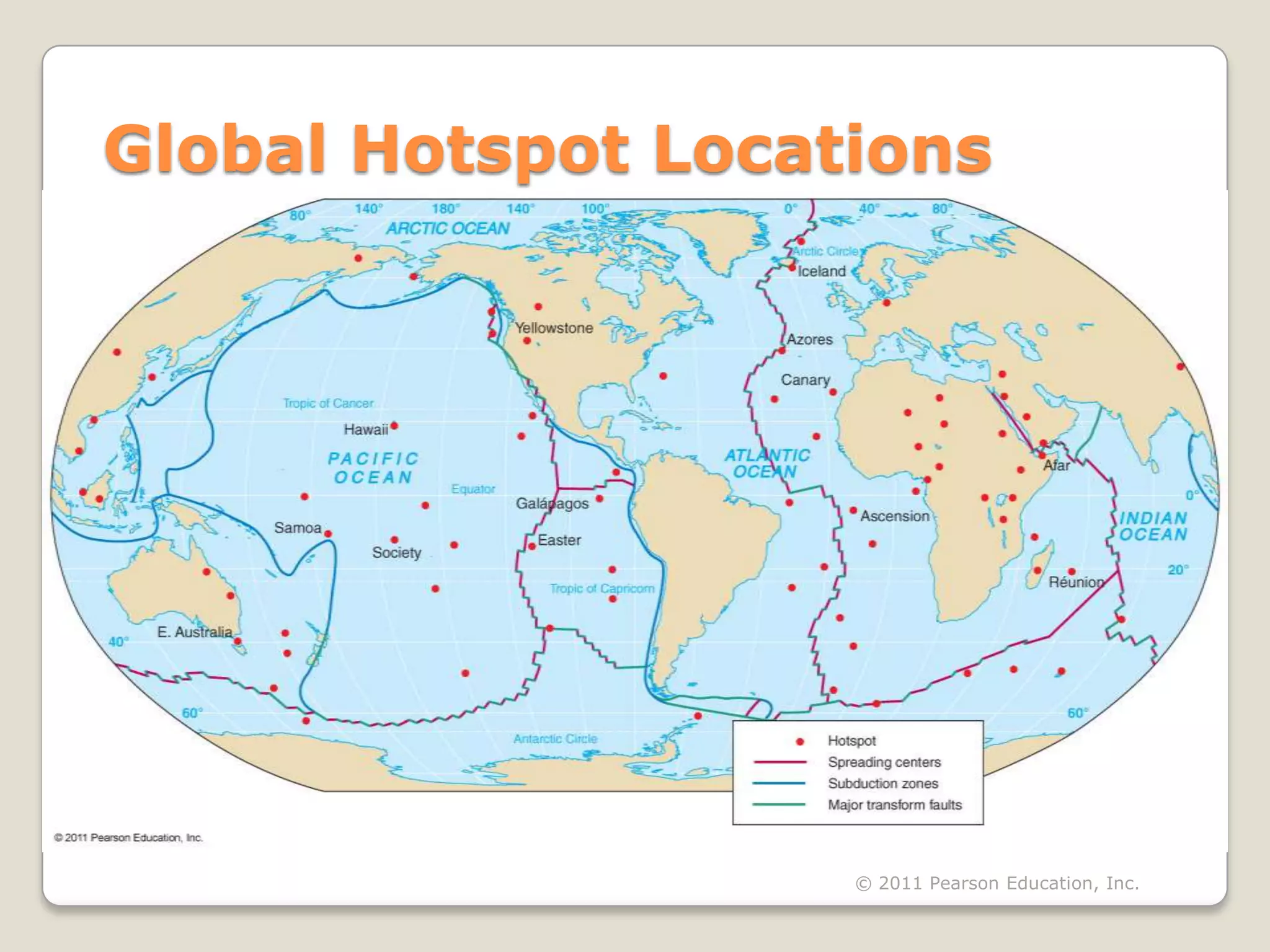
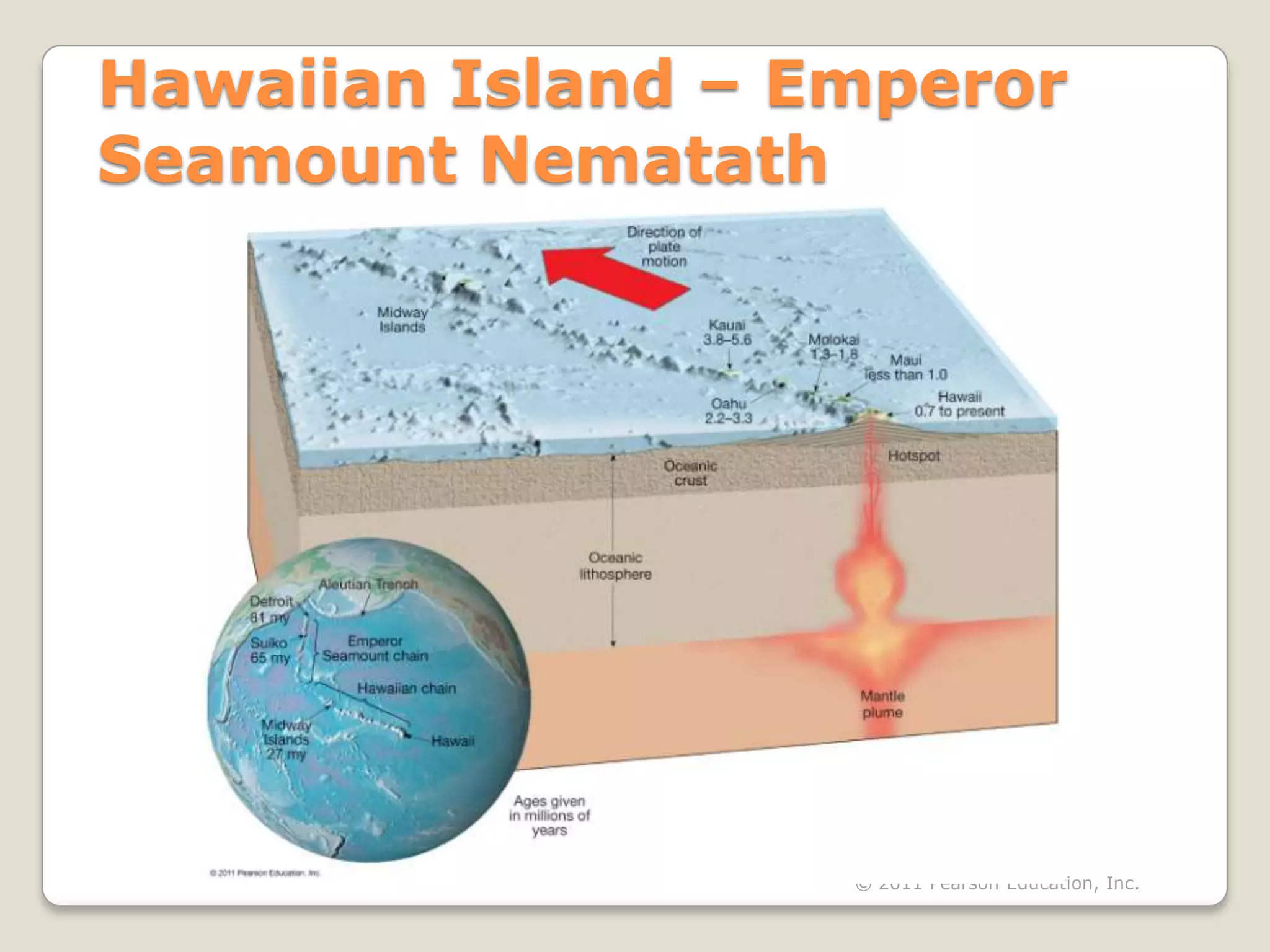
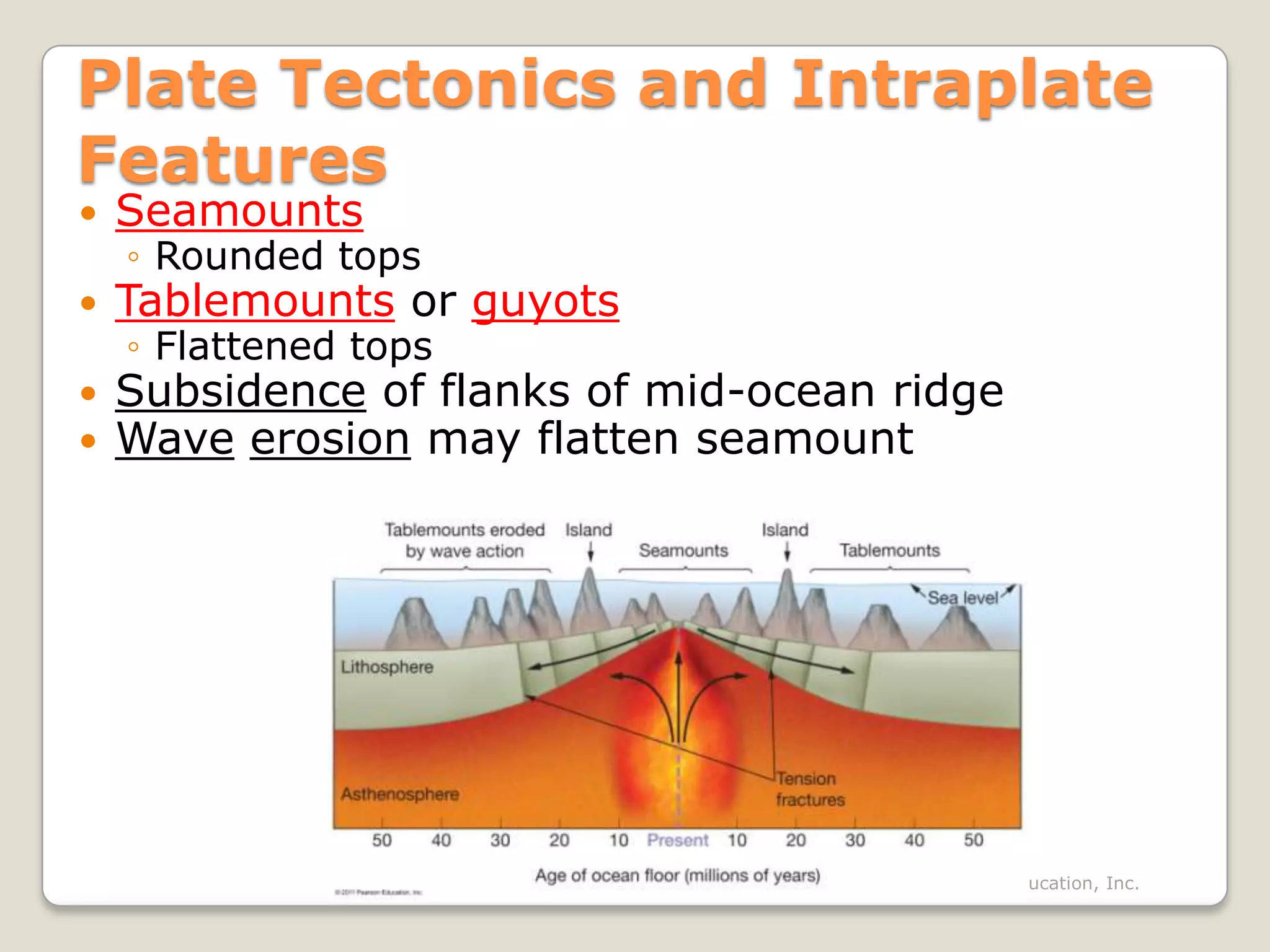
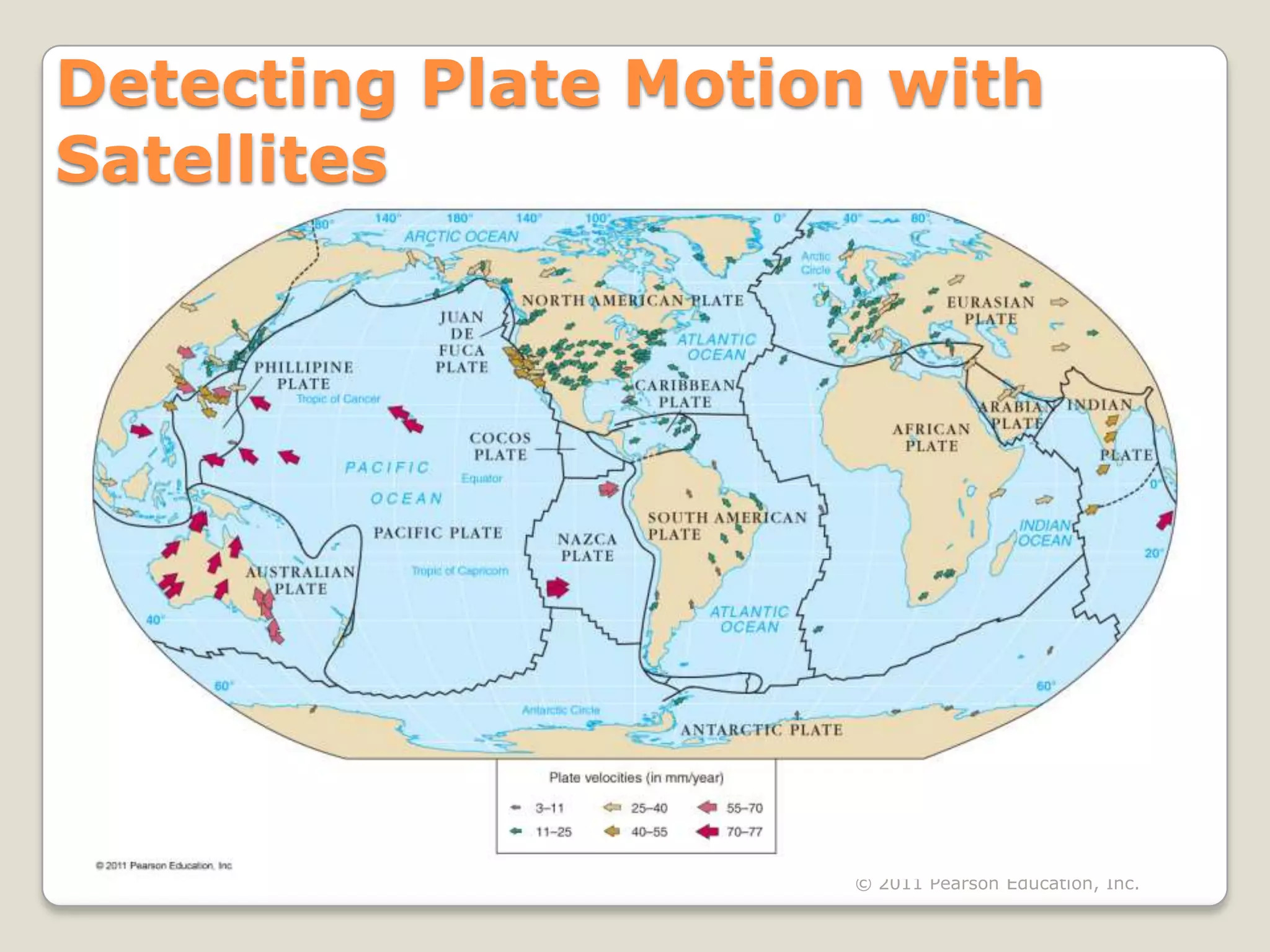
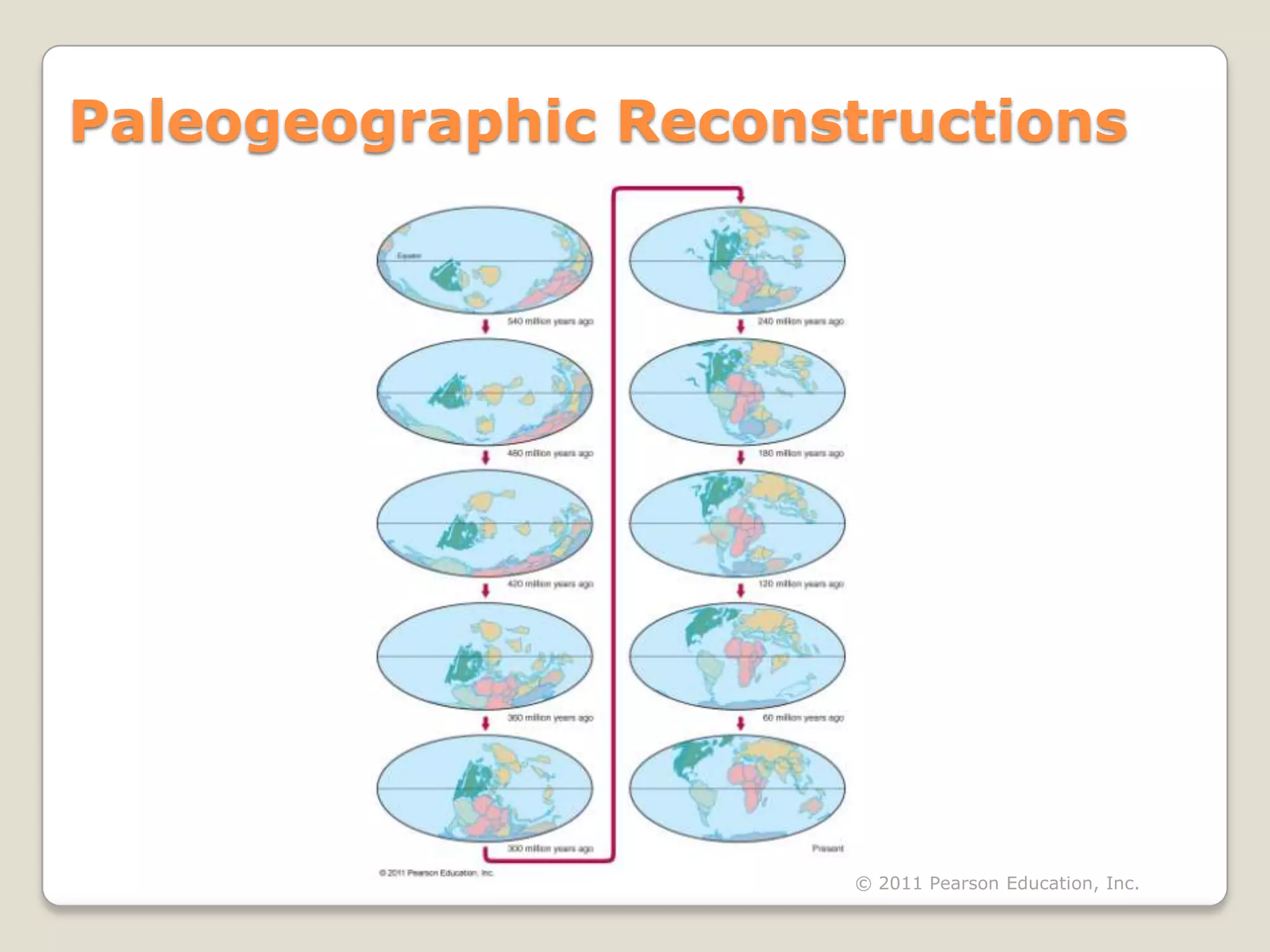
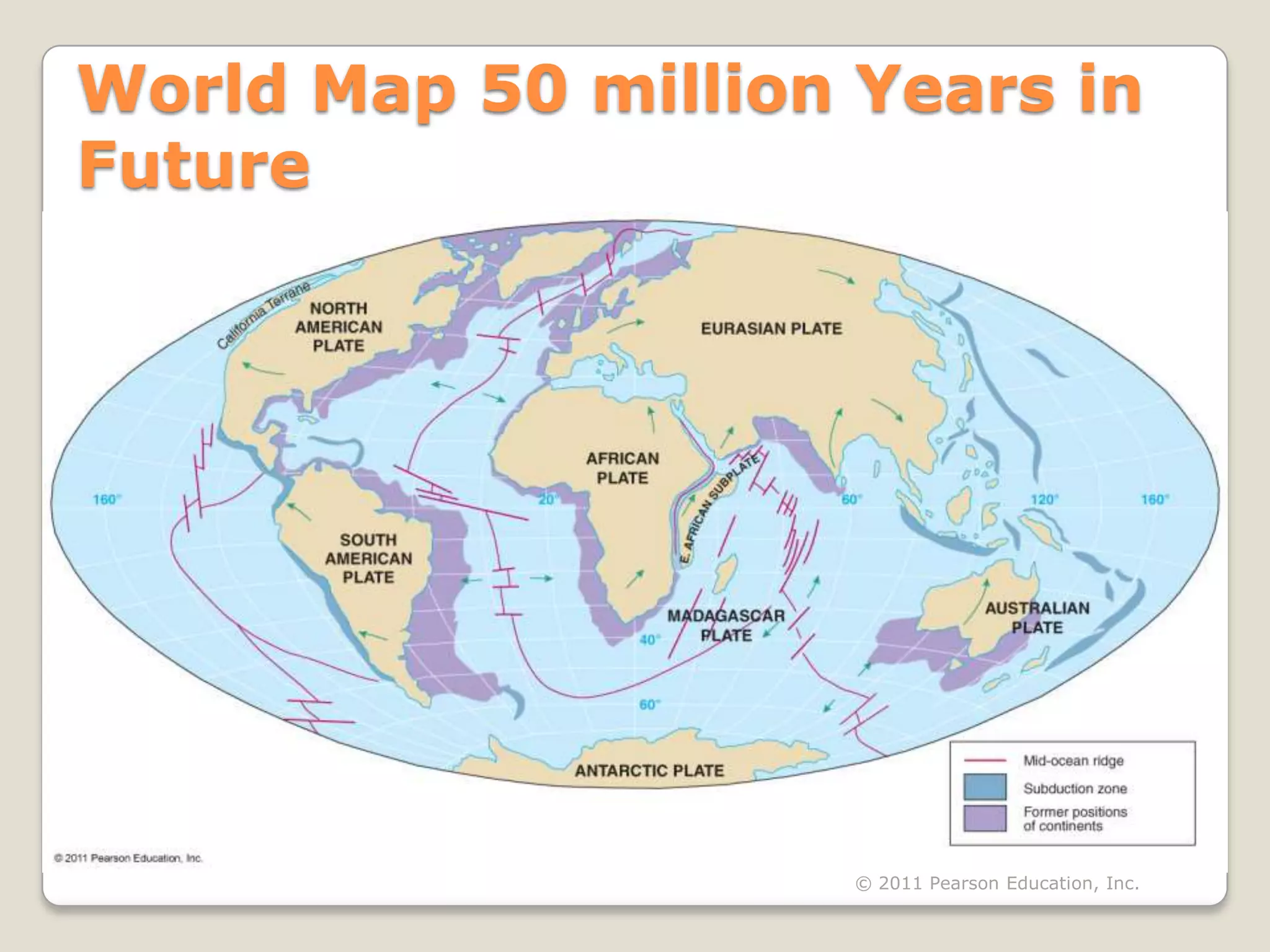
The document discusses key evidence that supports plate tectonic theory, including magnetic stripes in ocean crust that record reversals in Earth's magnetic field, the symmetrical distribution of ages of ocean floors around mid-ocean ridges with the oldest being only 180 million years old, the correlation of earthquake activity with tectonic plate boundaries, and the types of features found at different plate boundary types like transform faults. It also covers applications of plate tectonics like hotspots and mantle plumes, using hotspot tracks to determine past plate motions, and generating paleogeographic reconstructions and predictions of future continental positions.