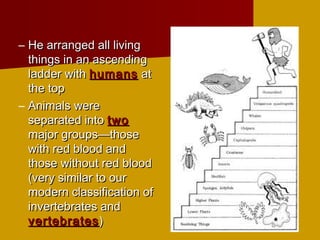
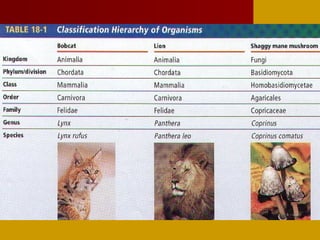
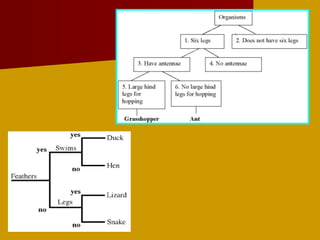
This document discusses biological classification and taxonomy. It begins by explaining why biologists classify organisms and provides a brief history of classification from Aristotle to Linnaeus establishing the modern 7-level system. The 7 levels are kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. An example classification of a housecat is given from kingdom to species. Scientific names are introduced as the standardized naming system. The document concludes by mentioning dichotomous keys which help identify organisms based on distinguishing characteristics.