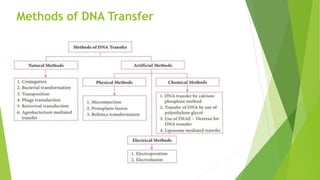
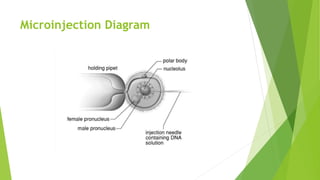
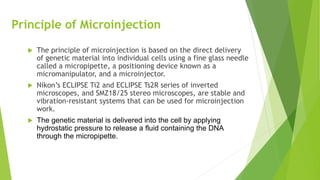
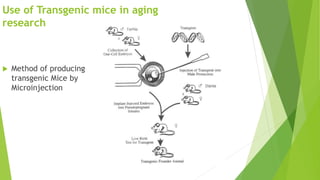
The document provides an overview of microinjection, a method of gene transfer used to introduce foreign DNA into targeted cells. It details the principles, procedures, applications, and disadvantages of microinjection, emphasizing its use in the creation of transgenic animals and cloning via somatic cell nuclear transfer. It also references historical context and includes multiple-choice questions related to the topic.