Glycolysis Explained in 10 Steps
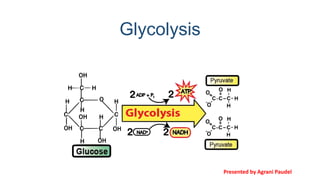
- 2. Glycolysis Glyco- glucose; lysis – breakdown 1 mole of 6-carbon glucose is broken down into 2 moles of 3-carbon pyruvate by 10 enzyme-catalyzed sequential reactions. Energy as ATP and NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide).
- 3. Glycolysis (Embden Meyerhof Parnas Pathway; EMP) • Why an important path? • common step for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration • generate several biosynthetic precursors as 3 –phosphoglycerate; (phosphoketolase pathway), Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (HMP); pyruvate • Product of other metabolism also ends in pyruvate or some product of glycolysis • glucose is the only fuel that brain uses under non starvation condition and the only fuel red blood cells can use at all
- 4. Glycolysis location : cytoplasm Various enzymes required are in cytosol and nearly all the enzymes require Mg++ Glut 2 – liver , kidney glut 4 – muscle, fat
- 5. Glycolysis – Can be divided into two phases • FIRST PHASE: Preparatory phase • Investment of 2 ATP molecules to activate glucose molecule and prepare for its cleavage • use energy in form of ATP.
- 6. Glycolysis – Can be divided into two phases • SECOND PHASE: Pay off phase • Glyceraldehyde-3- Phosphate is converted into pyruvate. • In this phase energy is produced in the form of ATP and NADH
- 7. Step 1- Phosphorylation of glucose • Glucose into Glucose-6-Phosphate (G-6-P) • Enzyme- HEXOKINASE • transfer of phosphate from the ATP(1st ATP utilized)
- 8. Step 2- Isomerization of Glucose-6-phosphate • Glucose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate • reversibly isomerized • Enzyme- phosphohexose isomerase • involves a shift of the carbonyl oxygen from C1 to C2, thus converting an aldose into a ketose.
- 9. Step 3- Phosphorylation of fructose-6-phosphate • F-6-P into Fructose 1,6- bisphosphate • enzyme -phospho-fructokinase • transferring a phosphate molecule from another ATP to form an ADP (second ATP is utilized).
- 10. Step 4- Cleavage of fructose 1, 6-diphosphate • F1,6-Bis P into : ‘GLYCERALDEHYDE 3- PHOSPHATE’(aldose) and ‘DIHYDROXYACETONE PHOSPHATE’ (ketose); 3-carbon molecules • Enzyme- ALDOLASE • The remaining steps in glycolysis involve three-carbon units, rather than six carbon units.
- 11. Step 5- Isomerization of dihydroxyacetone phosphate • dihydroxyacetone phosphate isomerized into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate • enzyme -ISOMERASE • Also, one molecule of Glucose gives two molecules so every reaction occurs twice and produce twice amount of products.
- 12. Step 6- Oxidative Phosphorylation of Glyceraldehyde 3- phosphate • G-3-P into 1,3- BISPHOSPHO GLYCERATE • Enzyme-GLYCERALDEHYDE-3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE. • addition of a phosphate group in the first position of the G-3-P by a catalyzing Required: A co- enzyme, NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) which is reduced into NADH • requires an inorganic phosphate group. • two NADH are generated in this step. (2) (2) (2) (2) (2) (2)
- 13. Step 7- Transfer of phosphate from 1, 3-diphosphoglycerate to ADP • 1,3-bisphospho glycerate - 3- PHOSPHOGLYCERATE • enzyme -PHOSPHO GLYCERATE KINASE • Here an ADP is converted to generate an ATP. • Since two moles of 1, 3-bisphosphoglycerate are formed from one mole of glucose, two ATPs (substrate level phosphorylation) (2) (2) (2) (2)
- 14. Step 8- Isomerization of 3-phosphoglycerate • 3-phosphoglycerate into 2- PHOSPHOGLYCERATE, simple rearrangement reaction • Enzyme -PHOSPHOGYCERATE MUTASE • This is a reversible isomerization reaction. (2) (2)
- 15. Step 9- Dehydration 2-phosphoglycerate • 2-phosphoglycerate dehydrated to phosphoenolpyruvate. • enzyme -enolase (phosphopyruvate hydratase) • irreversible reaction ;two moles of water are lost. • MAGNESIUM ION. (2) (2) (2)
- 16. Step 10- Transfer of phosphate from phosphoenolpyruvate • second energy-generating • Phosphonenol pyruvate into PYRUVATE • enzyme -PYRUVATE KINASE. • enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a phosphoryl group from phosphoenolpyruvate to ADP, thus forming ATP.(substrate level phosphorylation) (2) (2) (2) (2)
- 17. FIRST PHASE: Energy is consumed -2ATP SECOND PHASE: Energy is produced -4ATP Net reaction: C6H12O6 (Glucose) + 2ADP + 2Pi + 2NAD+ → 2C3H4O3 (Pyruvate) + 2H2O + 2ATP + 2NADH + 2H+ Glucose is oxidized into pyruvate. NAD+ is reduced to NADH. ADP is phosphorylated into ATP.
- 18. Fates of Pyruvate •In conditions where the oxygen is insufficient, like in the skeletal muscle cells, the pyruvate cannot be oxidized due to lack of oxygen. •In some microbes like brewer’s yeast, the pyruvate formed from glucose is converted anaerobically into ethanol and CO2.
- 20. Regulation of Glycolysis • In metabolic pathways, the enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are potential sites of control • Three irreversible kinase reactions primarily drive glycolysis forward • Hexokinase Or Glucokinase • Phosphofructokinase • Pyruvate kinase • Each of them serves as a control site
- 21. Hexokinase • Phosphorylation of glucose • Glucose 6-phosphate • High concentration of this molecule signal that the cell no longer requires glucose for energy and the glucose will be left in the blood (hexokinase is inhibited)
- 22. Phosphofructokinase • rate limiting for glycolysis • An allosteric regulatory enzyme • Inhibitors: ATP and citrate • Both indicate high energy availability • Activators: ADP,AMP, low energy • Fructose 2,6 bisphosphate is very important regulator
- 23. Pyruvate kinase • Inhibitors: ATP; acetyl coA and fatty acids(alternative fuels for TCA cycle) • Activator: fructose 1,6- bisphosphate( “feed- forward”) • Phosphorylation by glucagon (inactive form) and dephosphorylation (active form) by insulin under hormone control