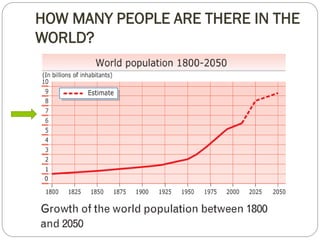
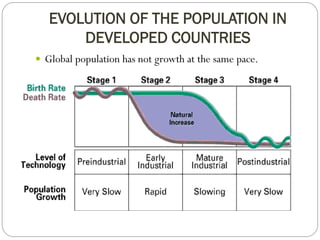
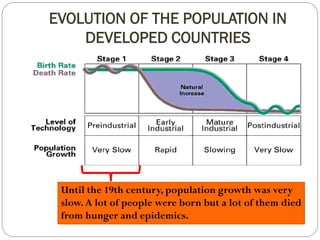
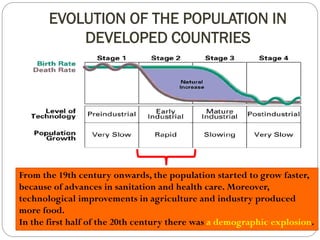
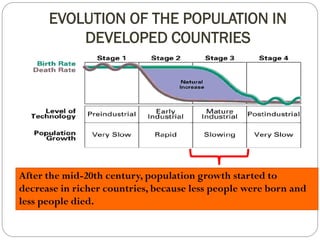
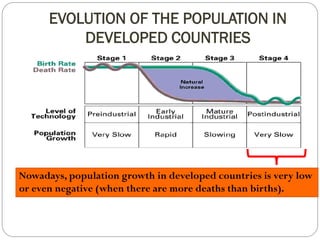
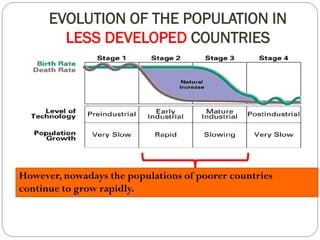
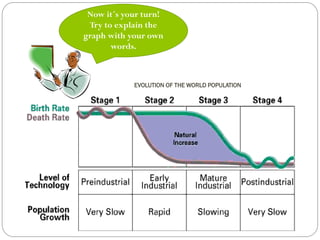
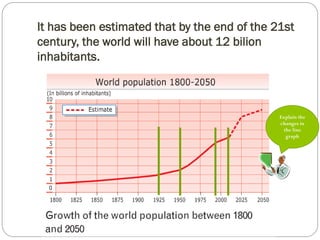
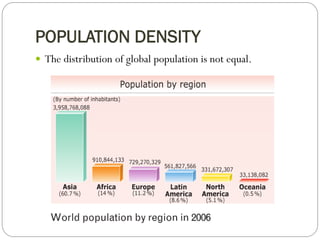
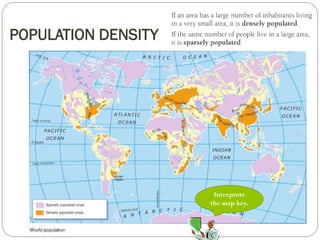
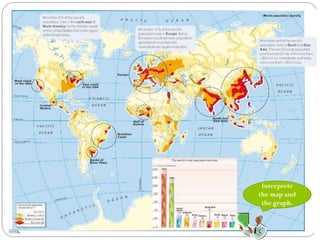
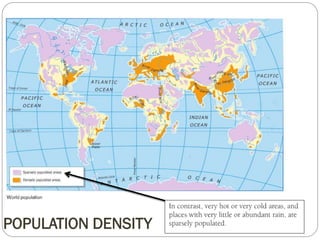
The document discusses population trends in developed and developing countries. It states that until the 19th century, population growth was slow in developed nations due to high mortality rates. From the 19th century onward, population growth increased due to advances in health care and agriculture. The population experienced rapid expansion in the early 20th century. After mid-century, population growth declined in developed nations as birth rates decreased and life expectancy increased. Currently, population growth is low or even negative in developed countries, while less developed countries continue to see rapid population increases. The world population is projected to reach 12 billion by 2100.