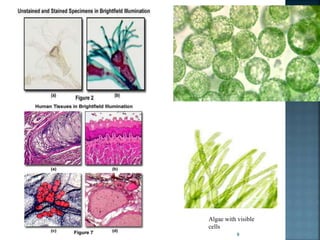
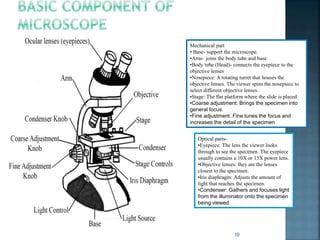
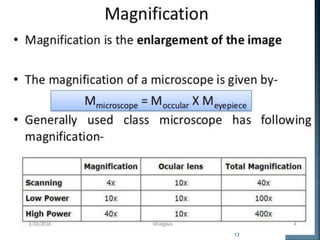
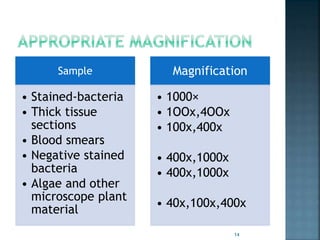
This document discusses the basics of light microscopy. It begins with a brief history, noting that the first compound microscope was created in 1590, while Antonie van Leeuwenhoek discovered microorganisms and sperm cells using a simple microscope in the 1630s. The basic components of light microscopes are described, including the objective lenses, eyepieces, stage, and condenser. Brightfield microscopy is explained in more detail, noting that it uses transmitted white light and staining to increase contrast. Applications include viewing stained bacteria, tissue sections, and algae. While brightfield microscopy is simple to use, its disadvantages include low contrast and an inability to see transparent, unstained samples clearly.