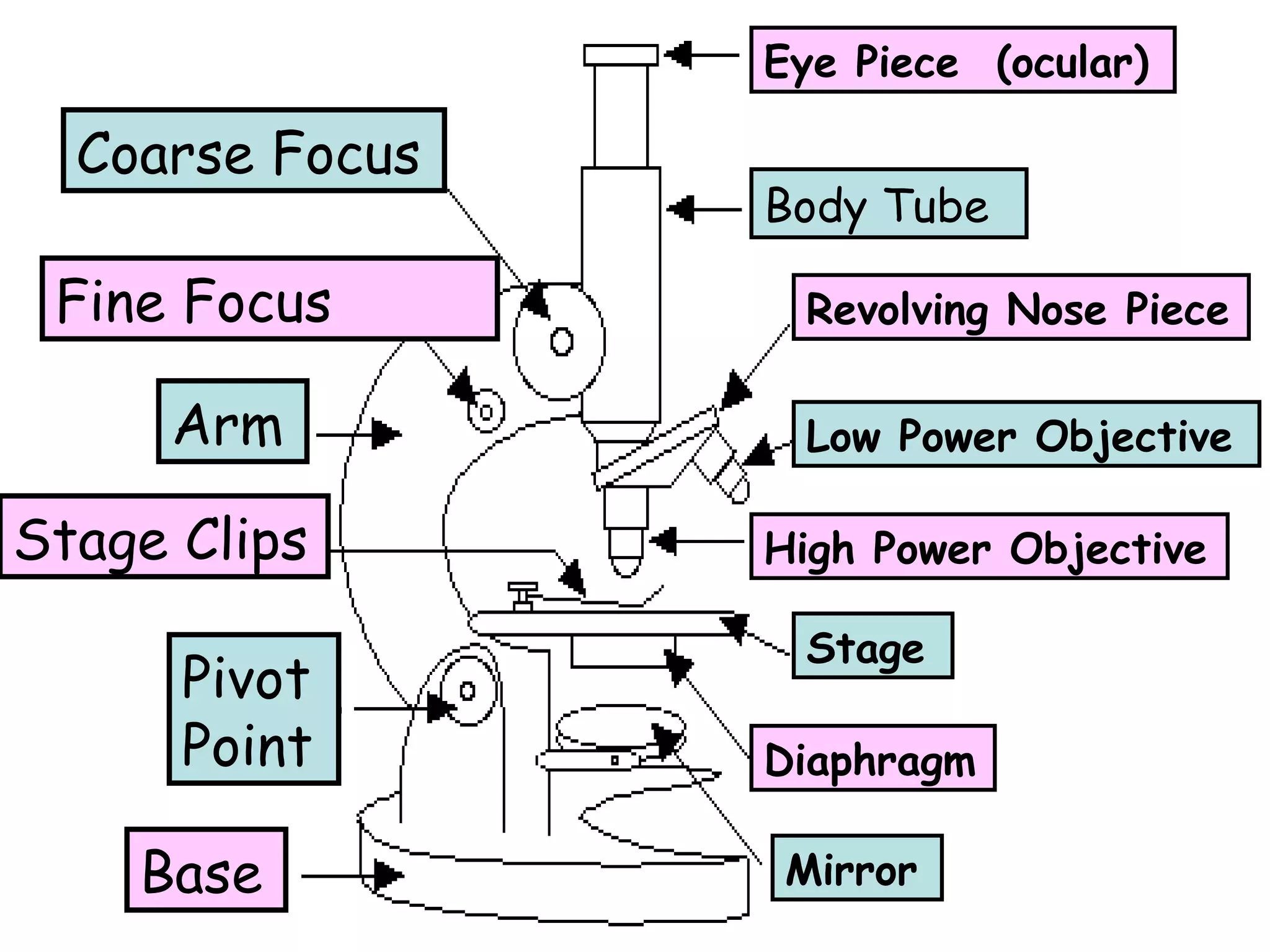
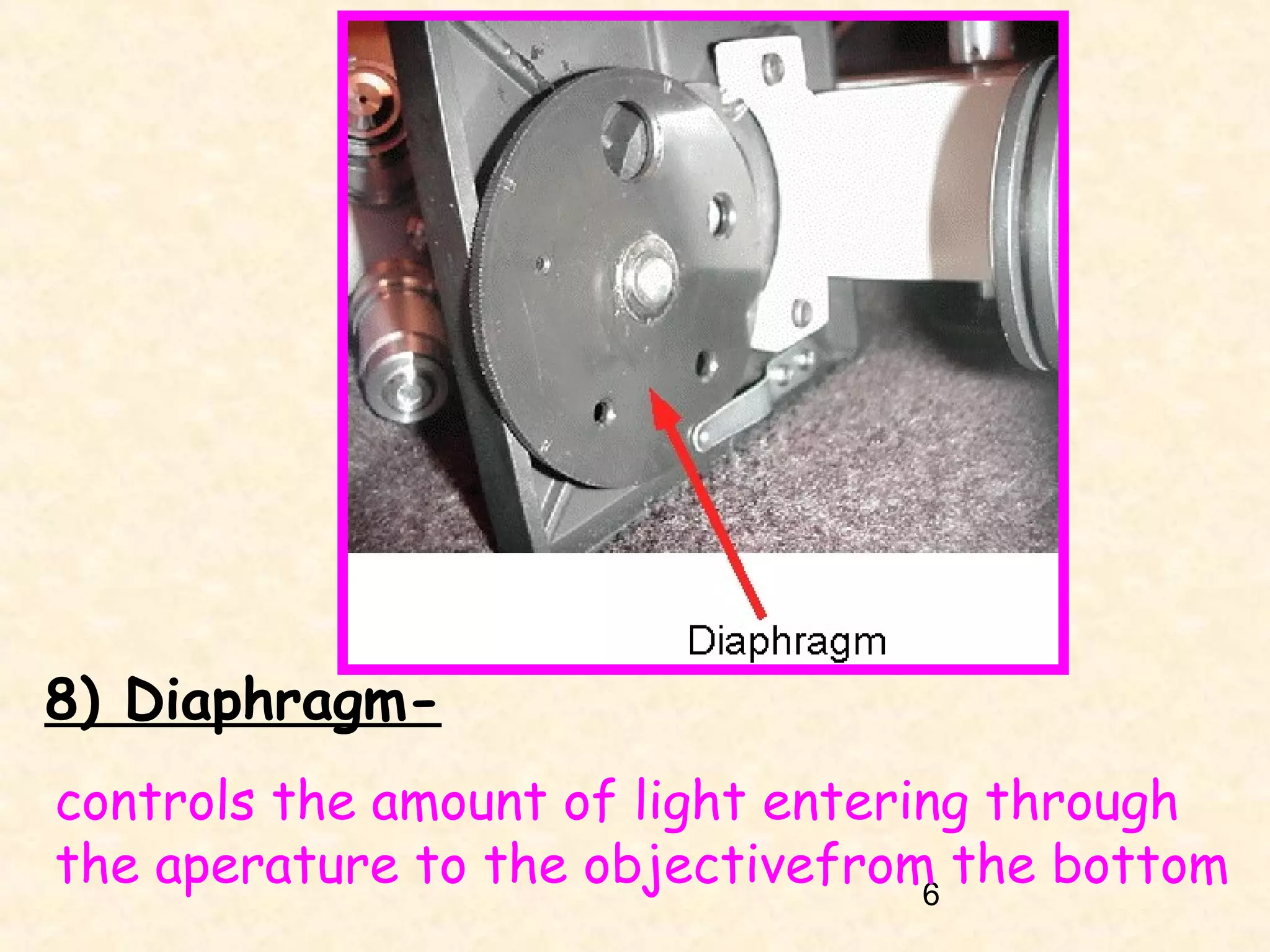
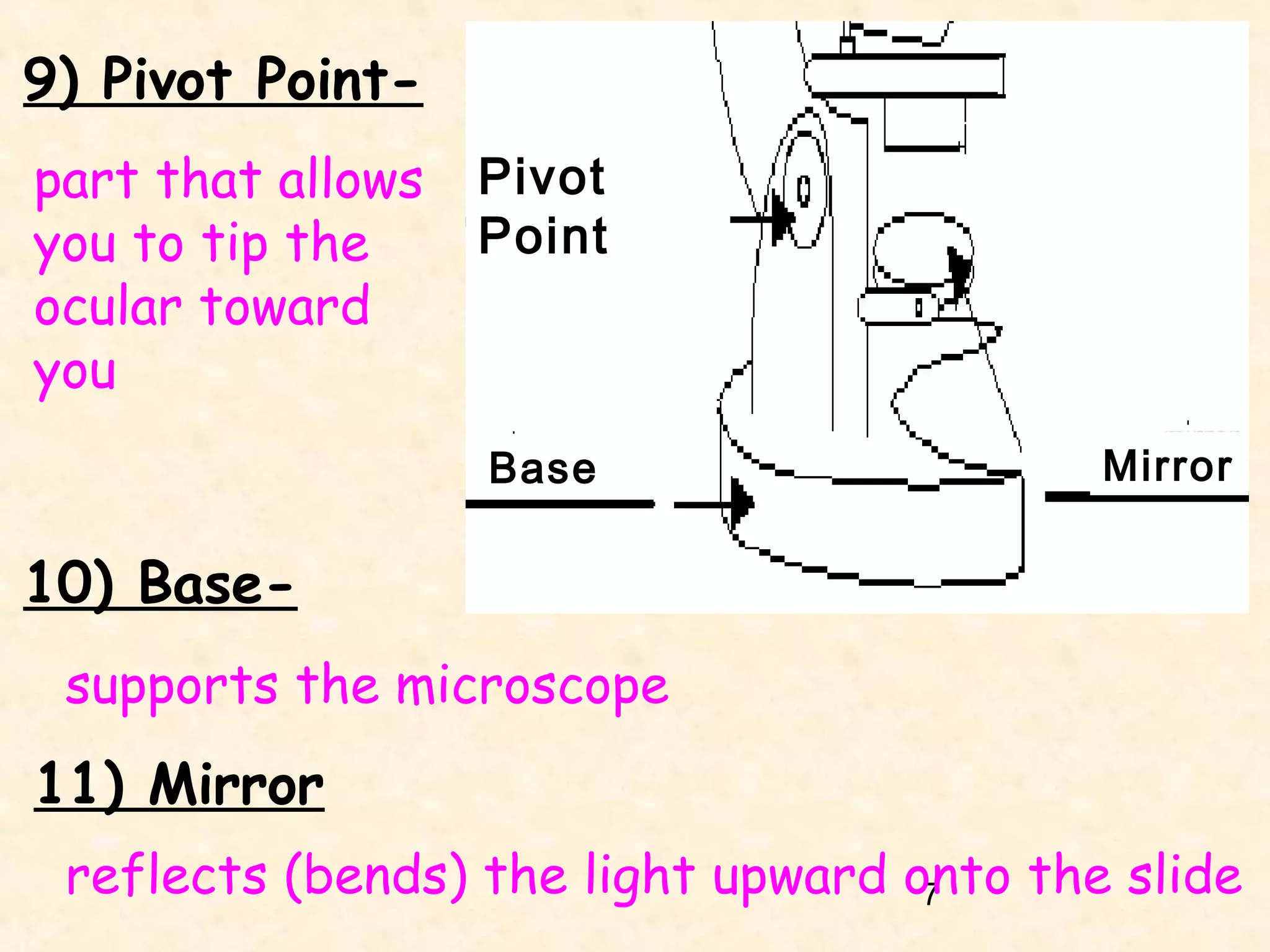
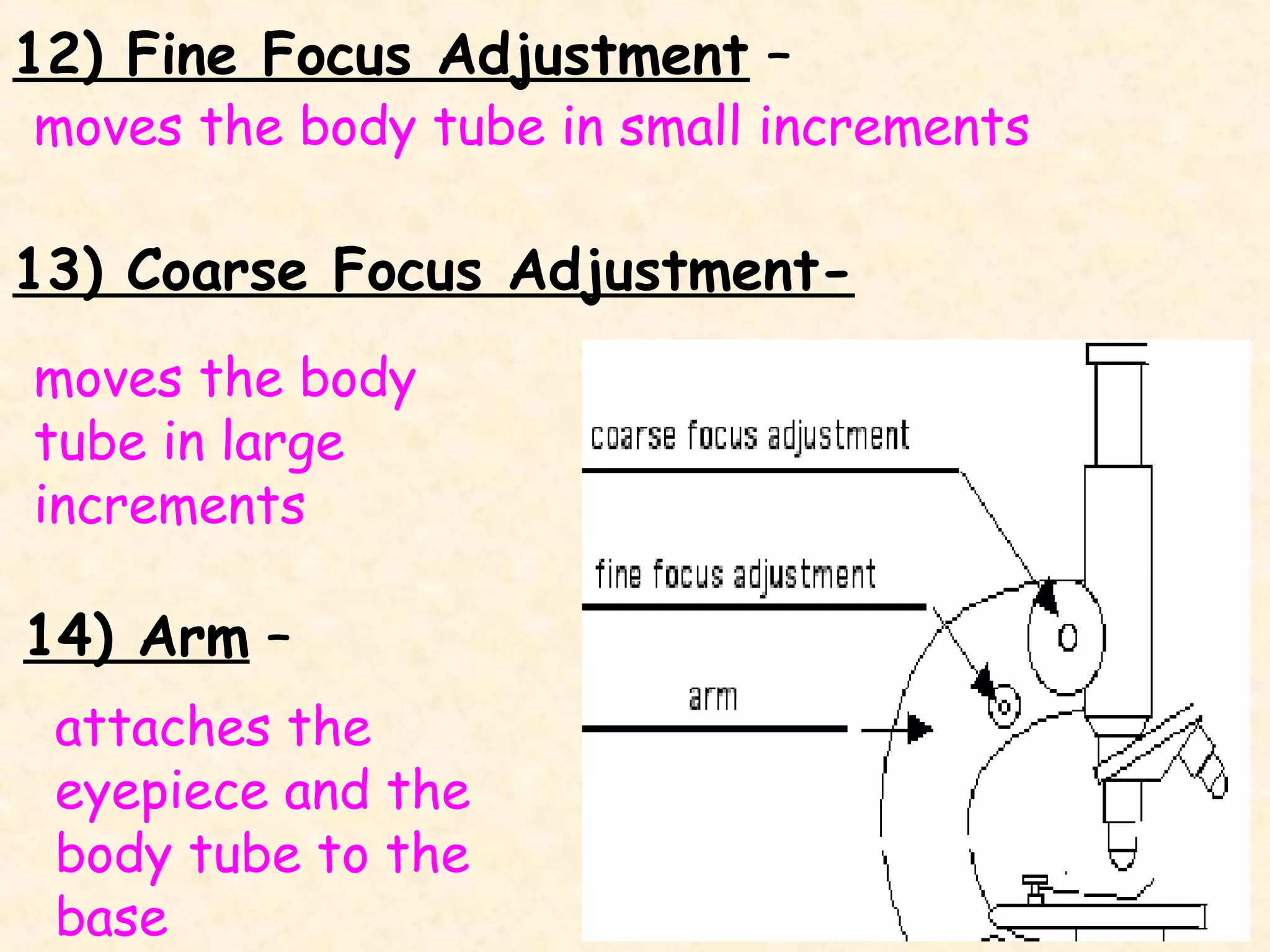
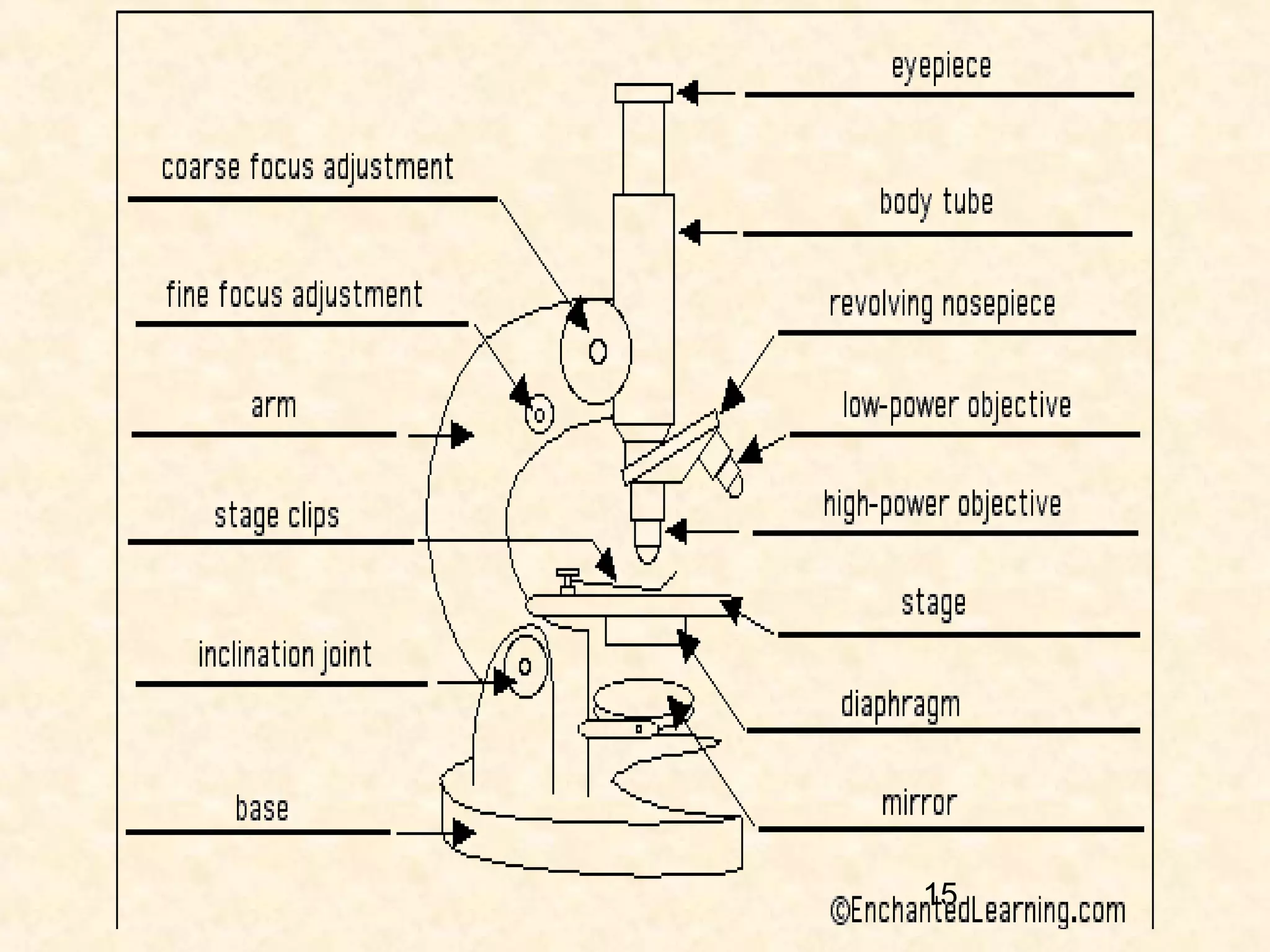
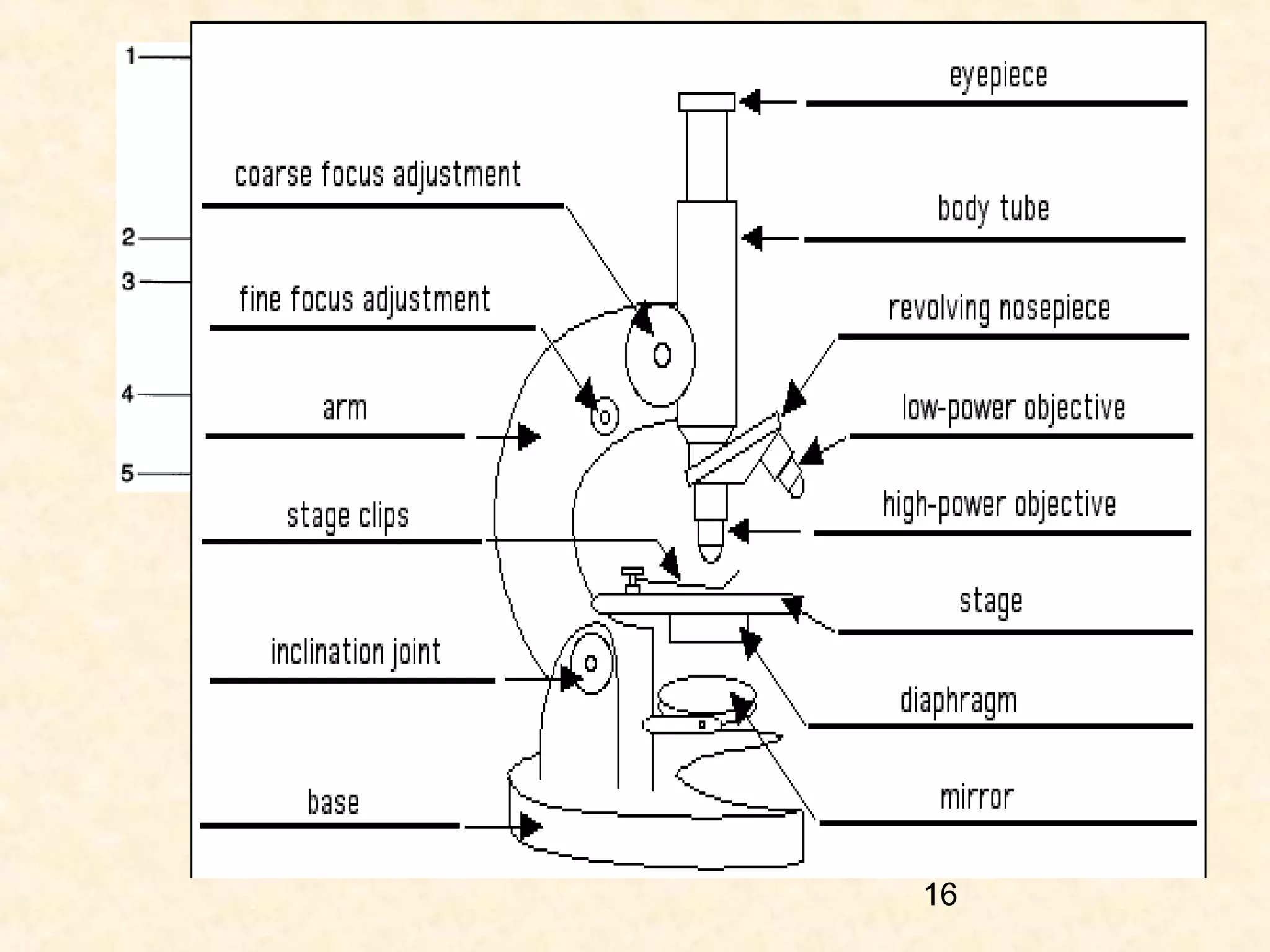
The document describes the main components of a light microscope and their functions. It includes:
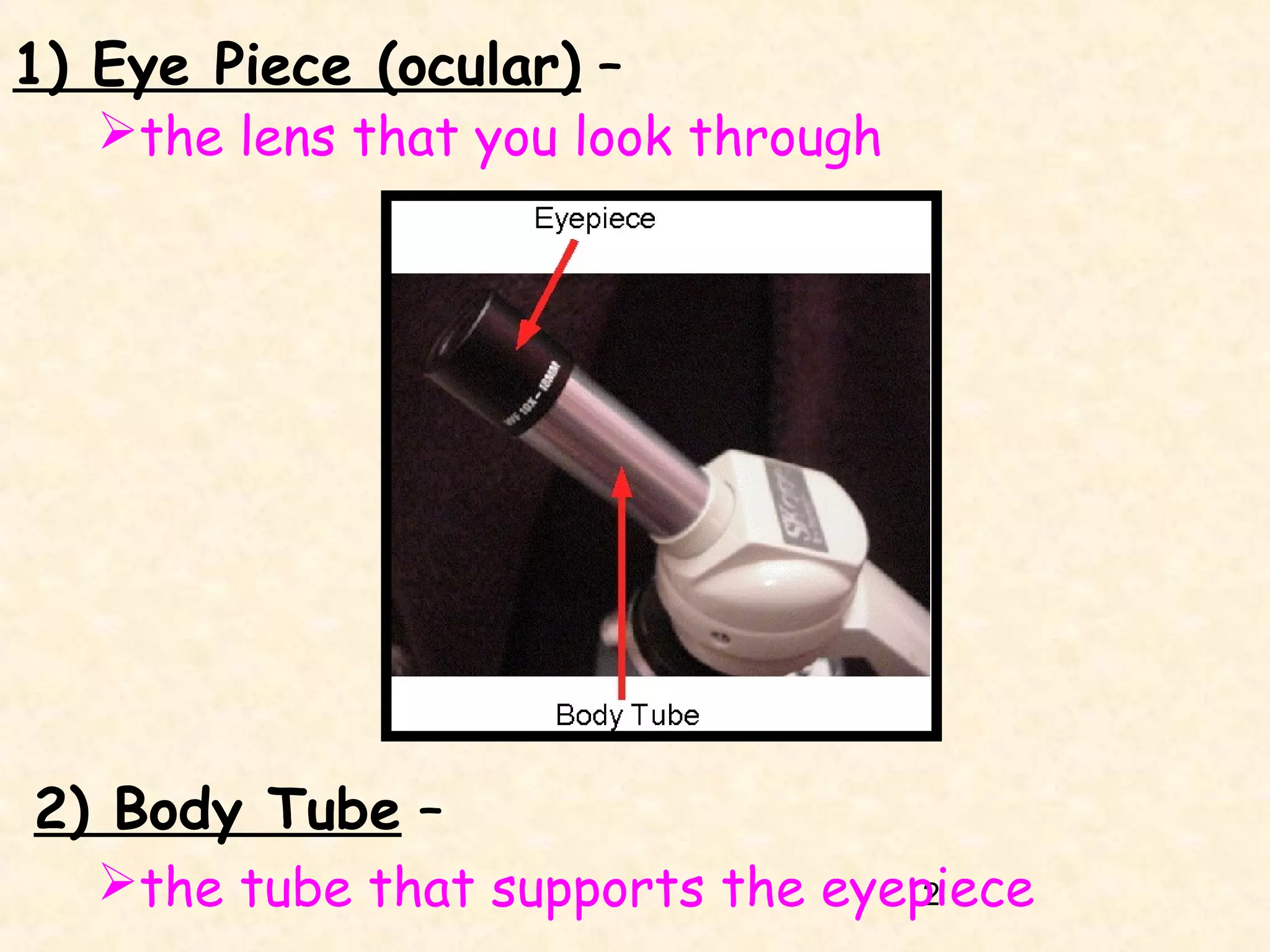
1) The eye piece or ocular, which is the lens used to view the specimen.
2) The body tube, which supports the eyepiece.
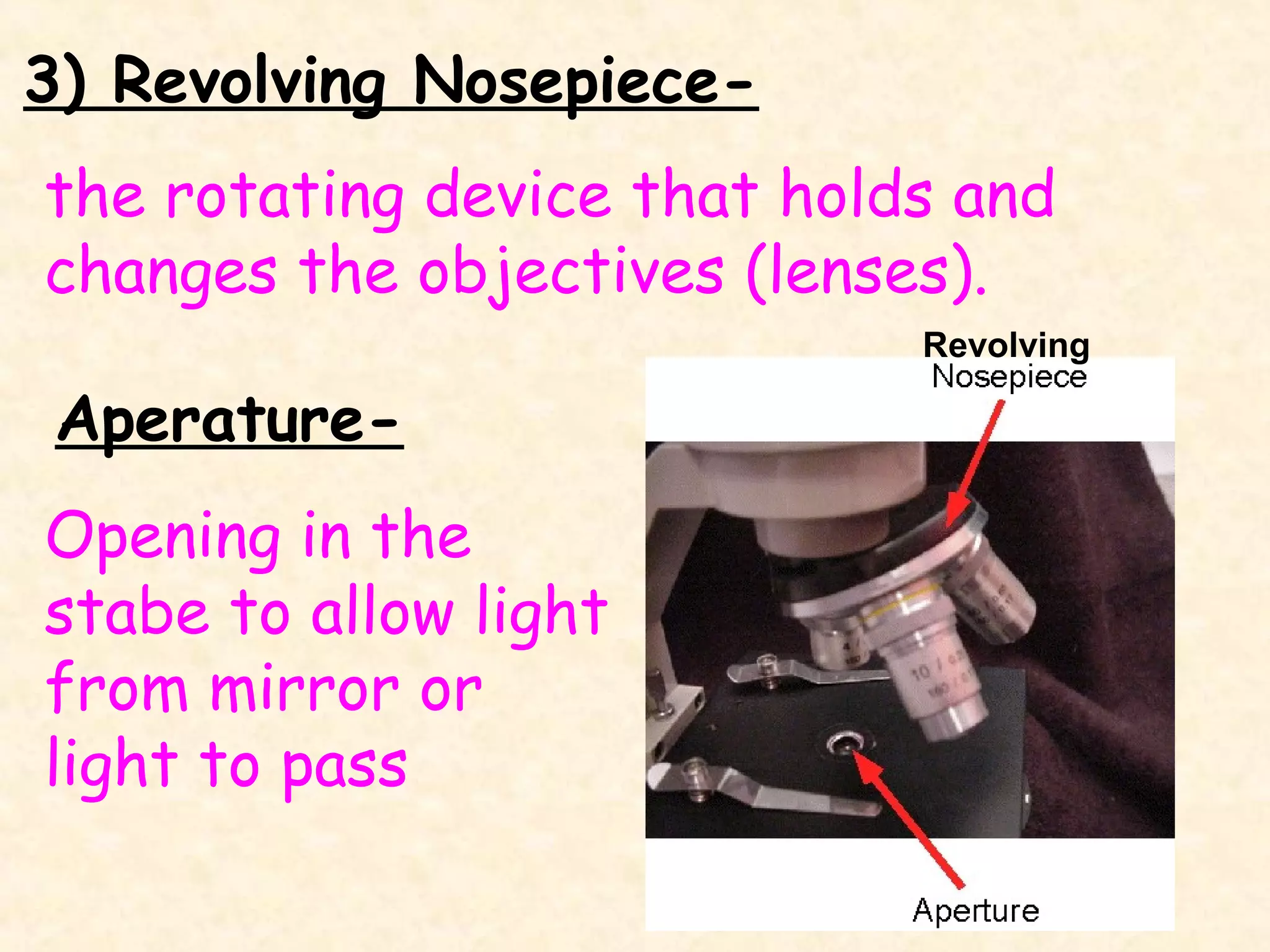
3) The revolving nosepiece, which holds the objective lenses and allows them to be changed.
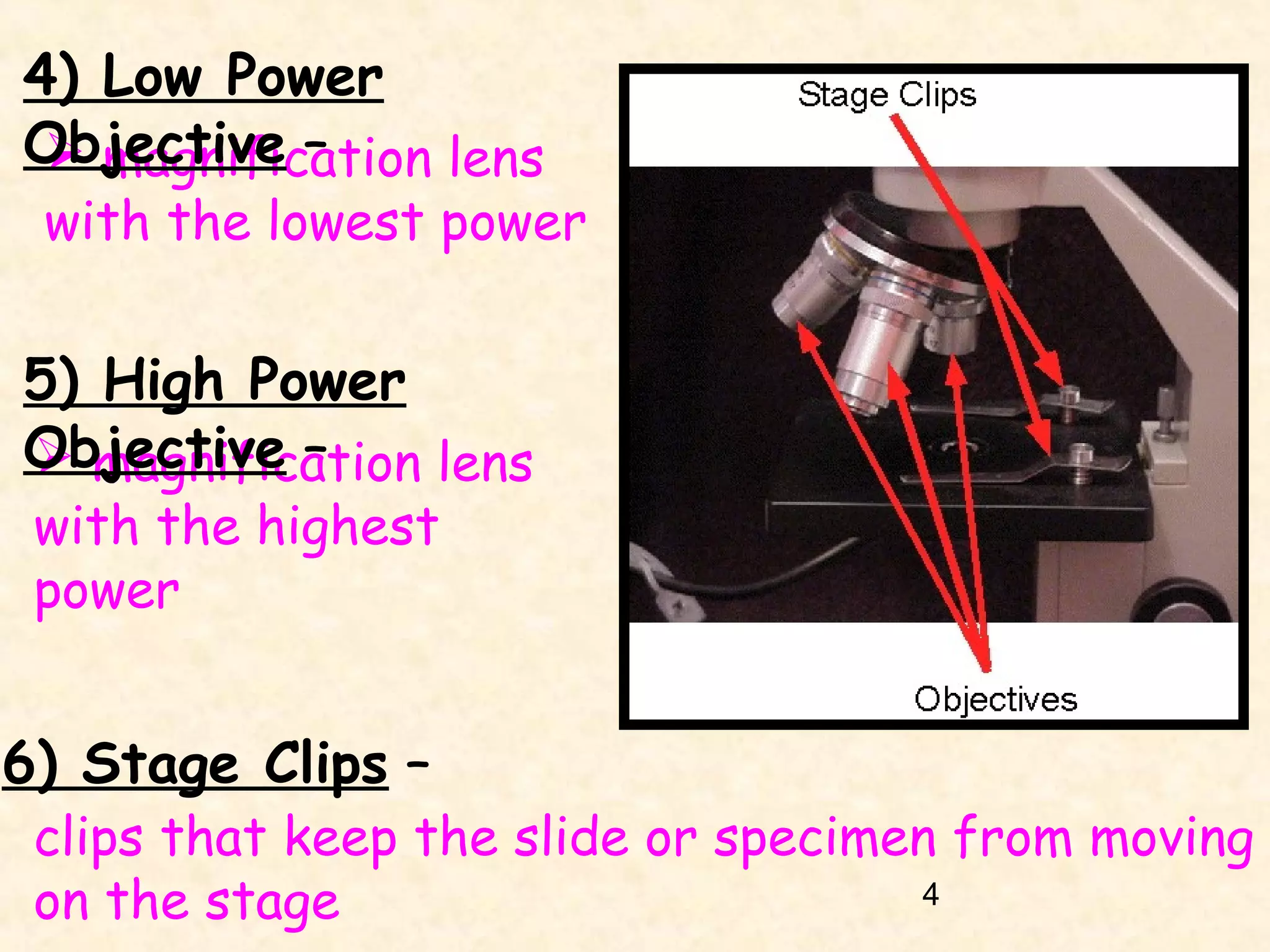
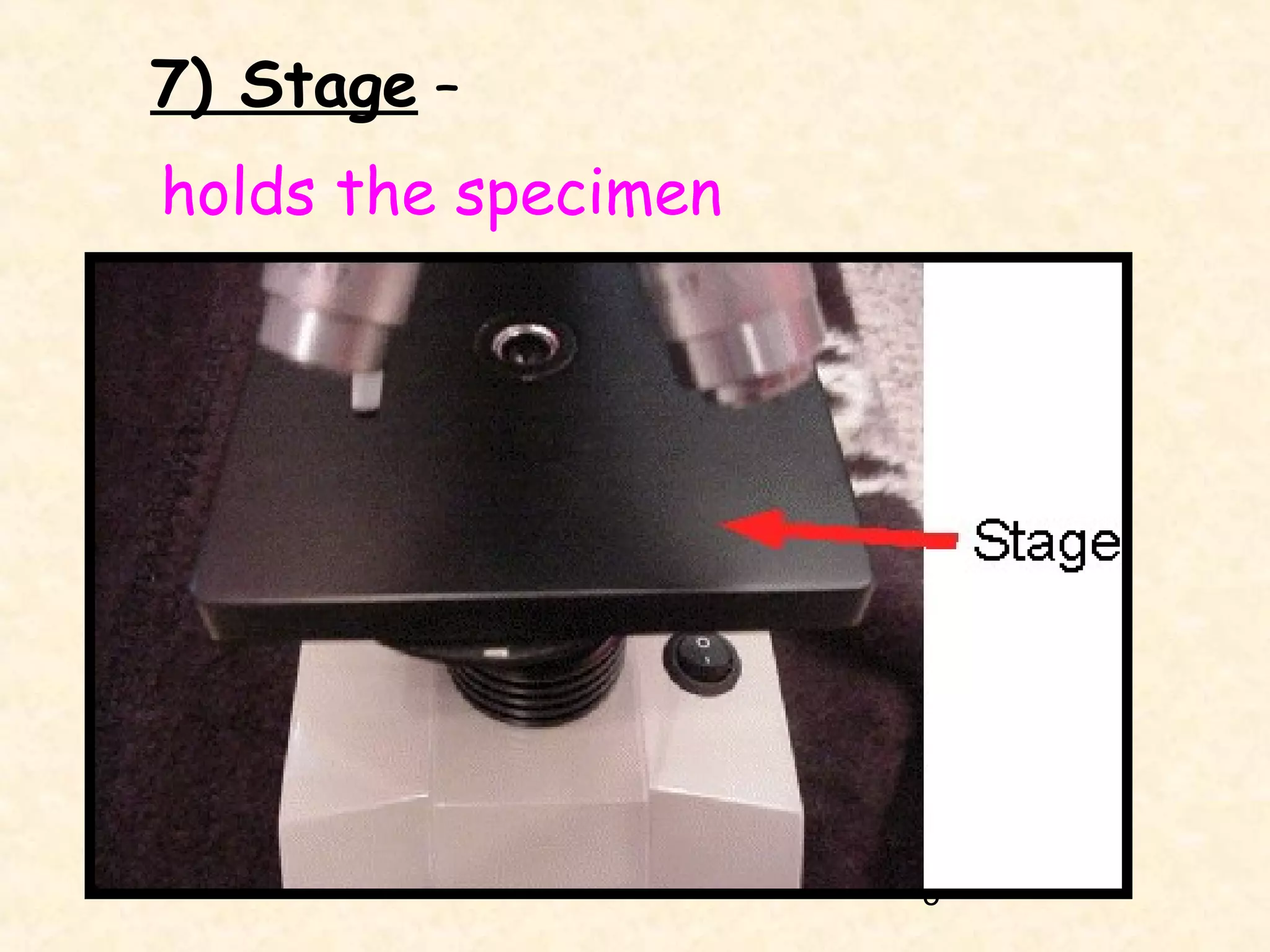
4) The stage, which holds the specimen in place under the objectives.