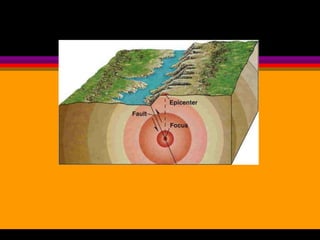
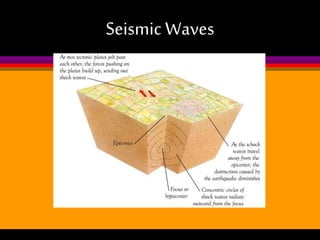
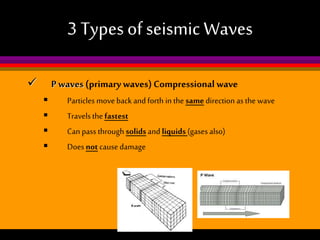
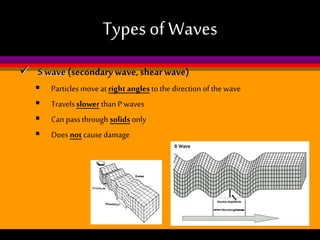
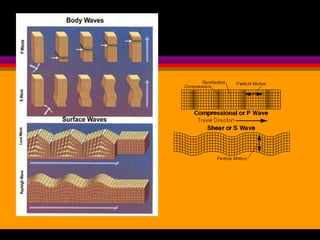
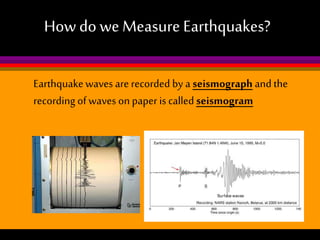
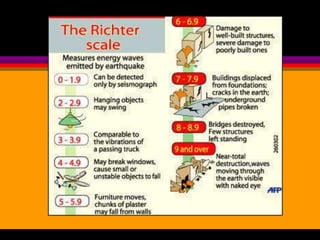
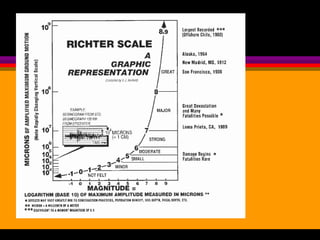
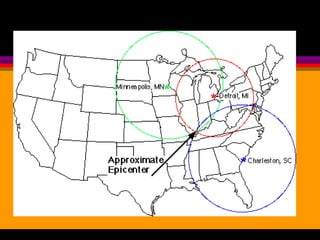
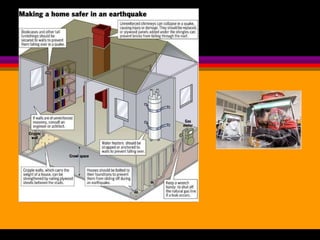
Earthquakes are caused by the sudden release of built-up energy along fault lines in the Earth's crust. When the stresses exceed the strength of the rocks, they break and seismic waves are produced. There are three main types of seismic waves - P waves, S waves, and L waves. P waves travel fastest while L waves cause the most damage. Earthquakes are measured by both magnitude, which indicates the amount of energy released, and intensity, which describes the effects at a particular location. Analyzing seismic wave arrival times at multiple stations allows scientists to determine the epicenter and focus of an earthquake. Major earthquake hazards include tsunamis, landslides, liquefaction, and falling debris.