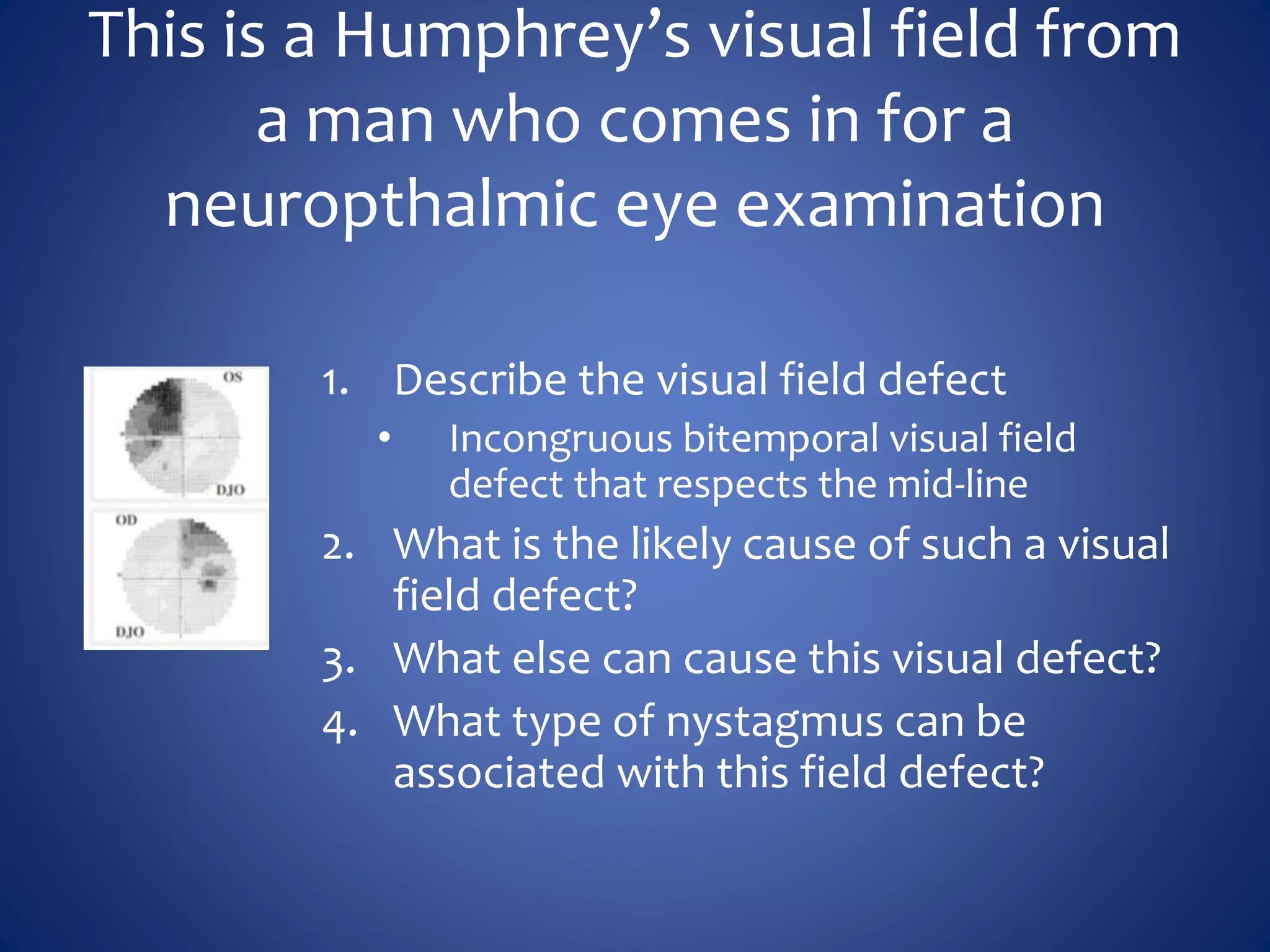
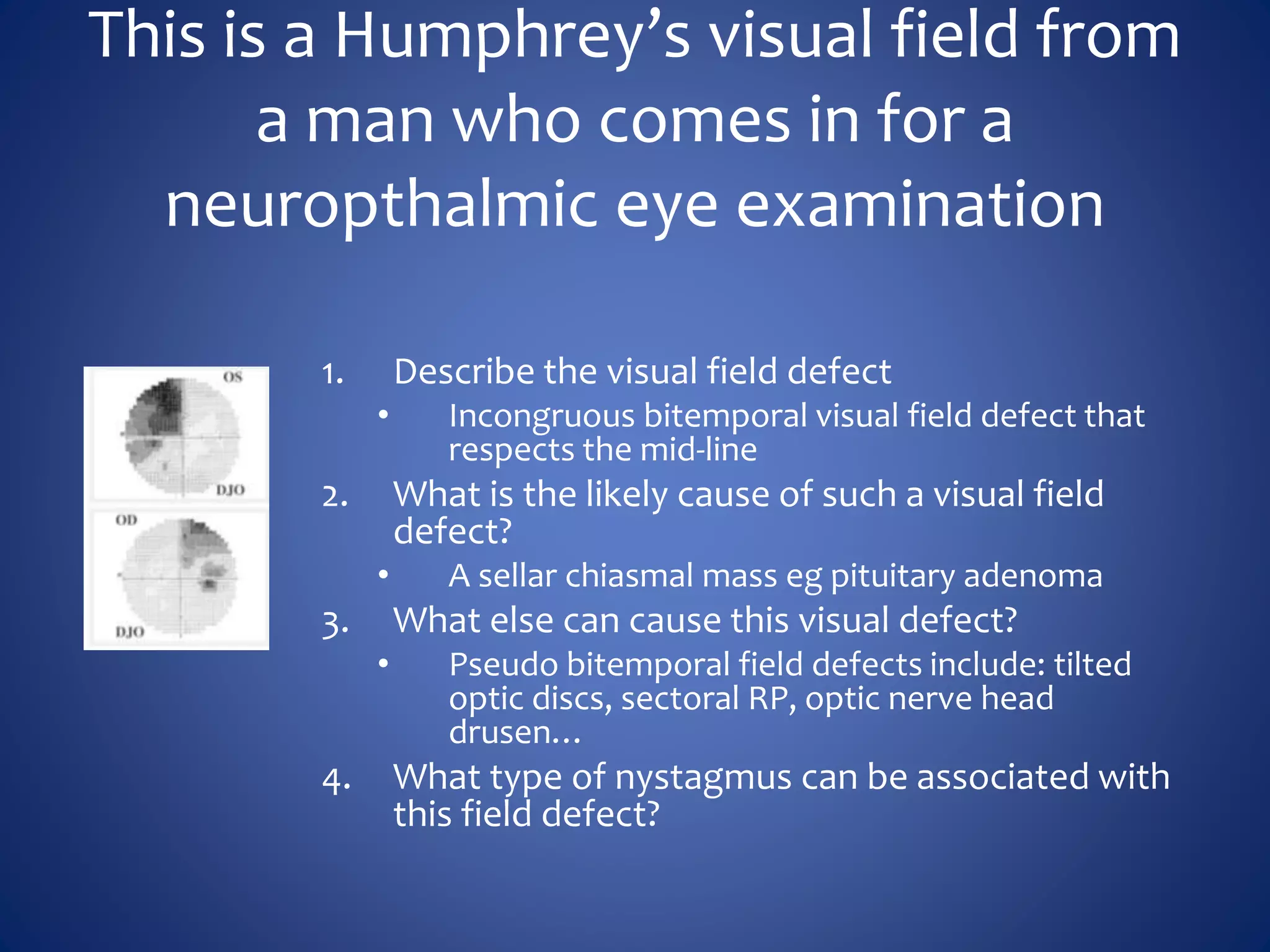
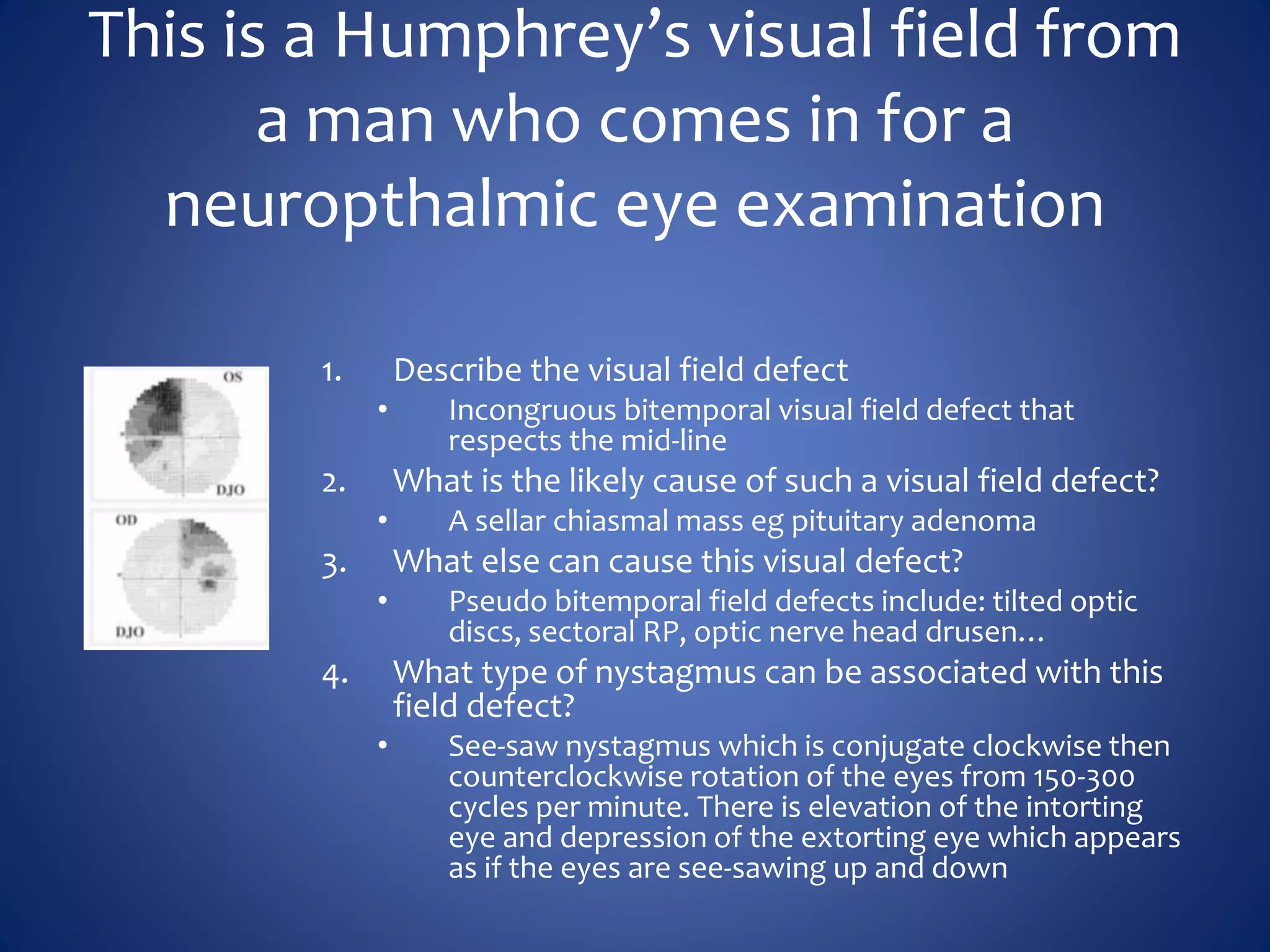
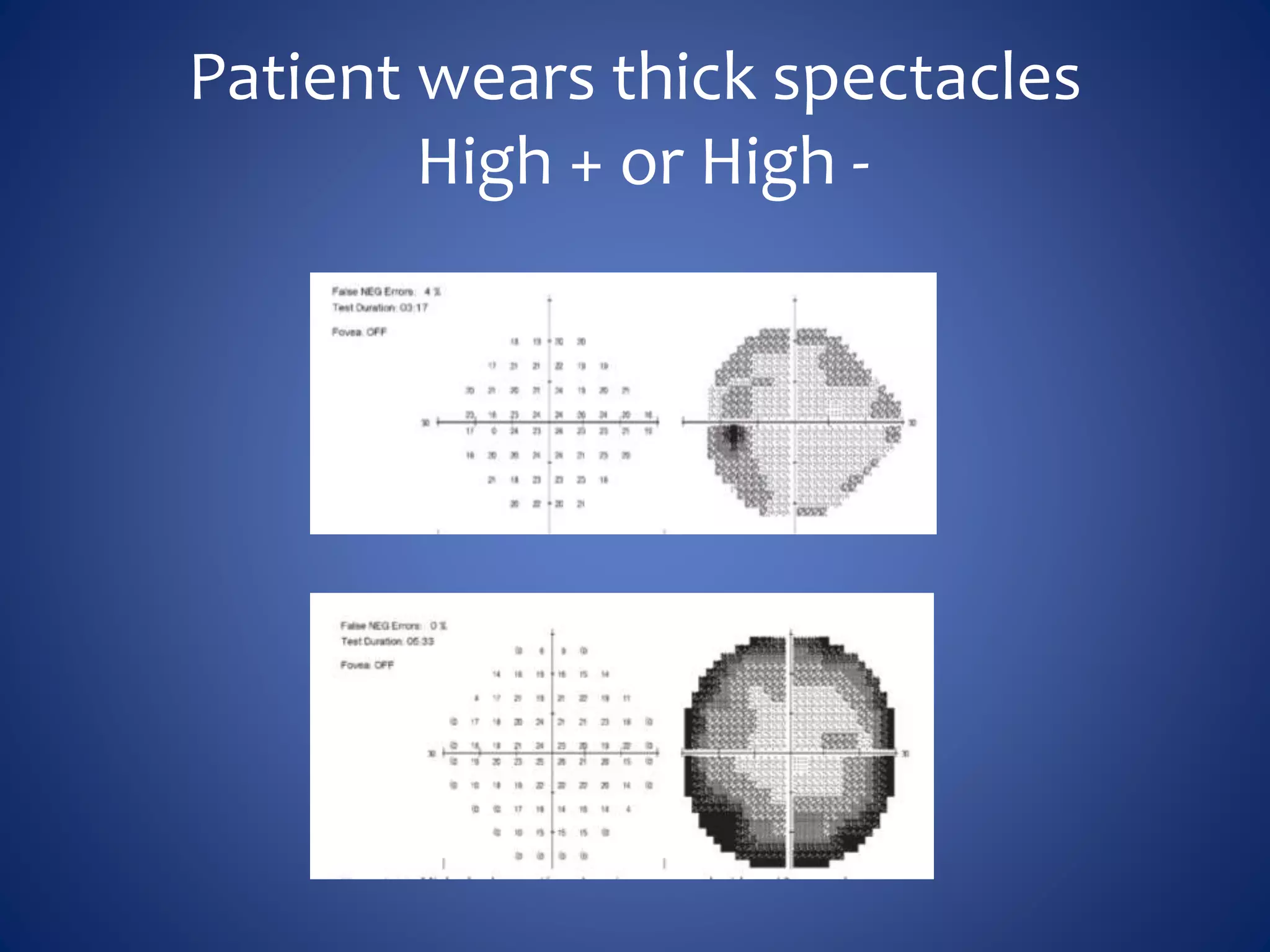
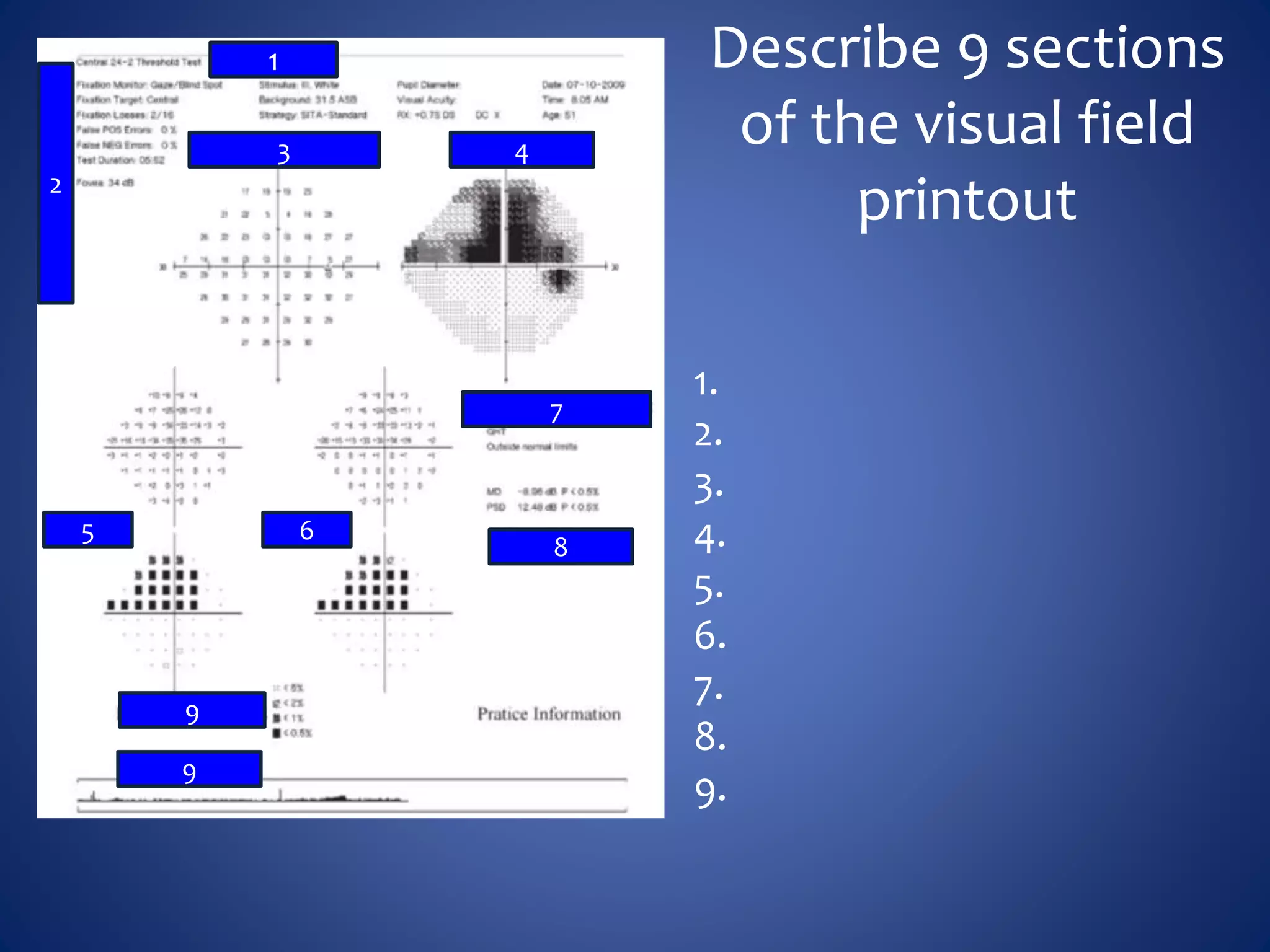
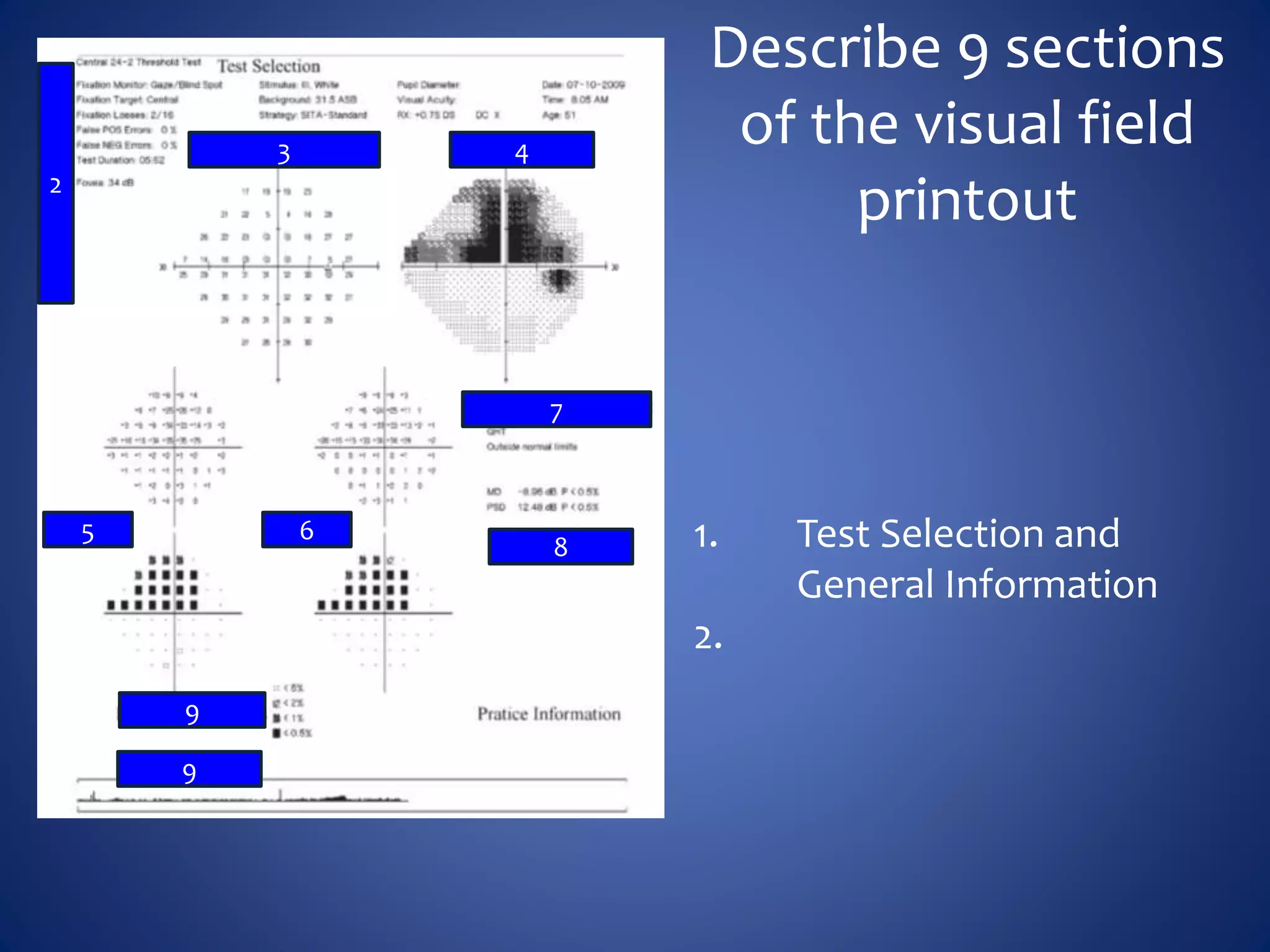
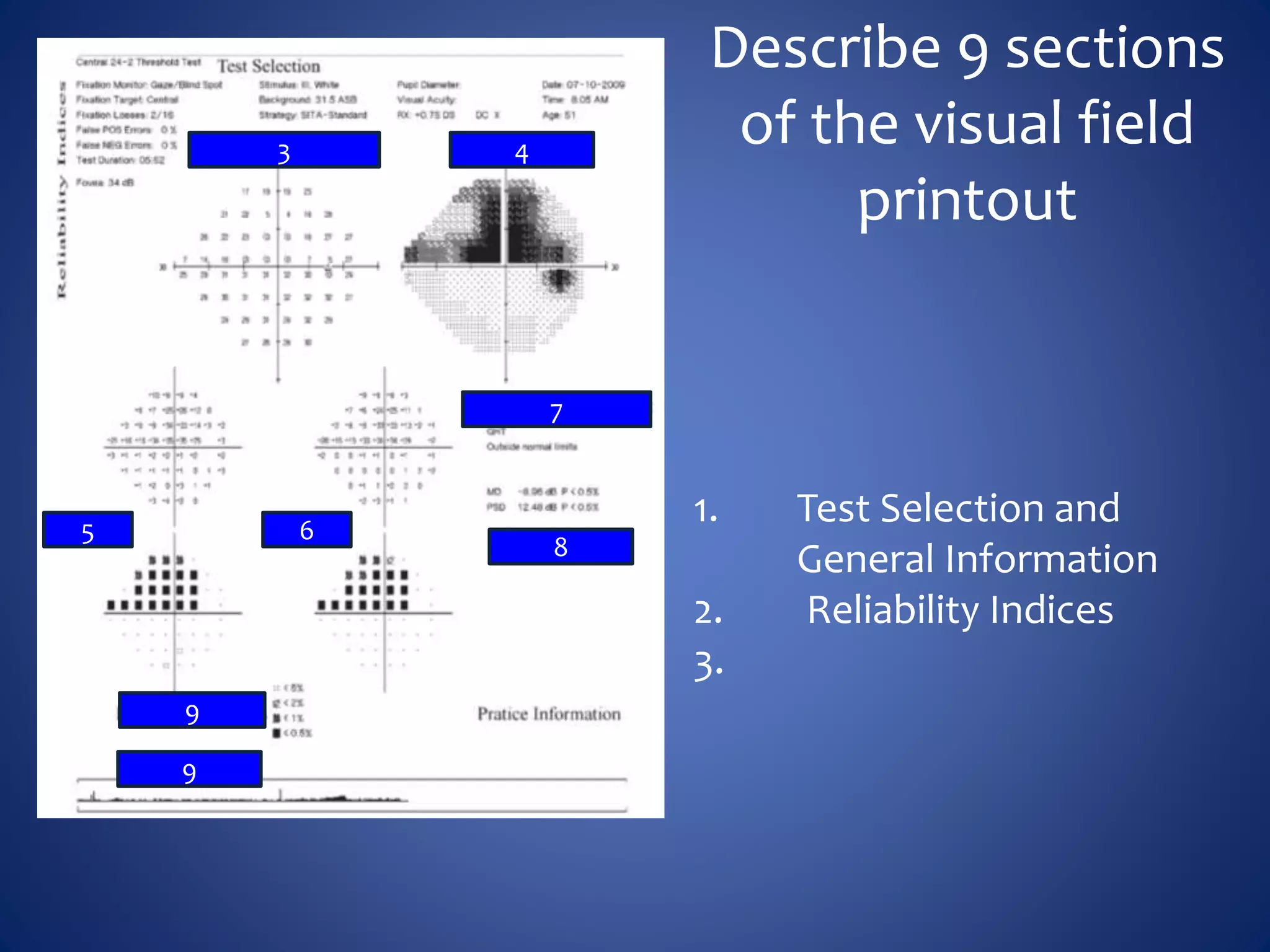
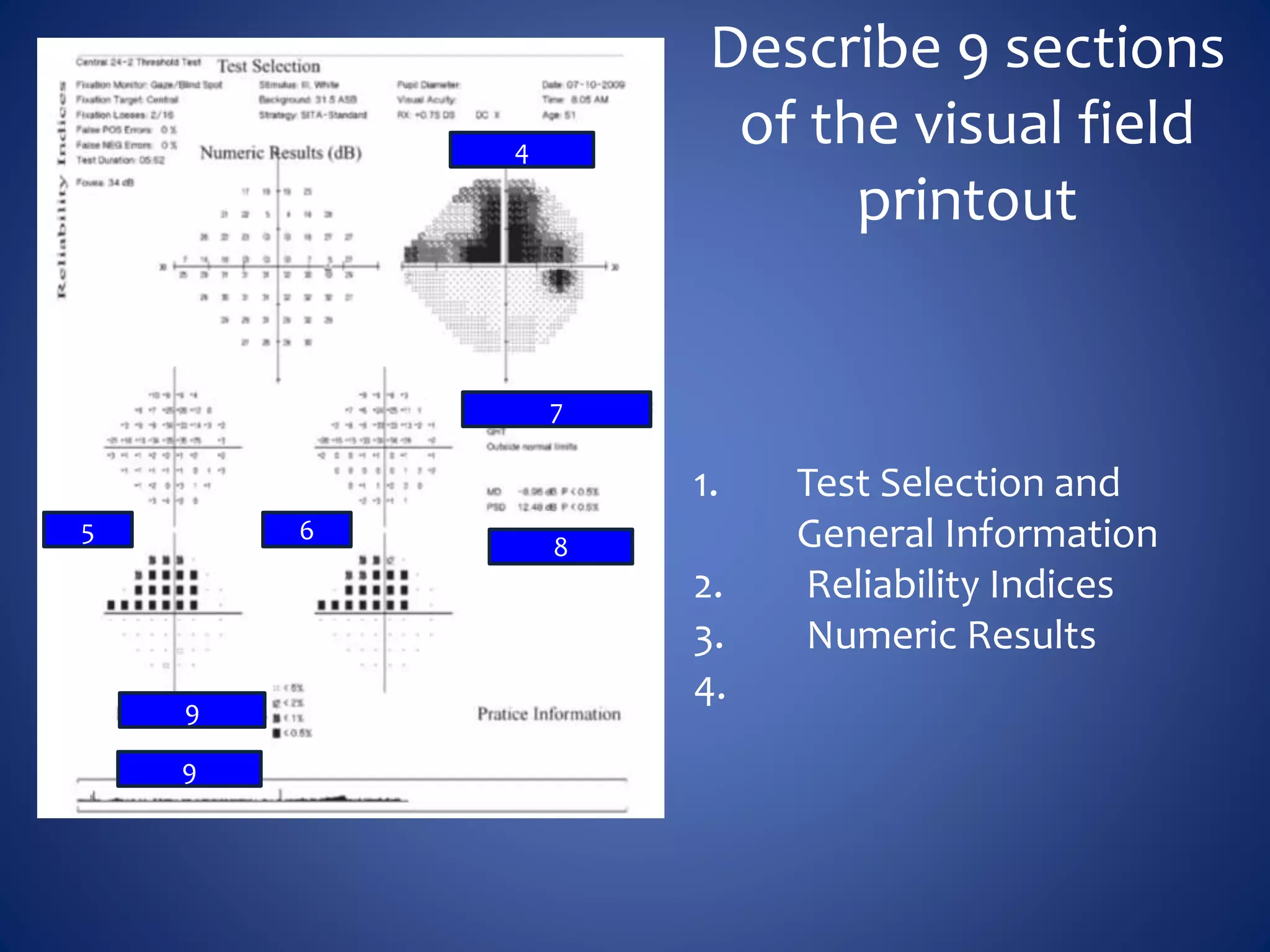
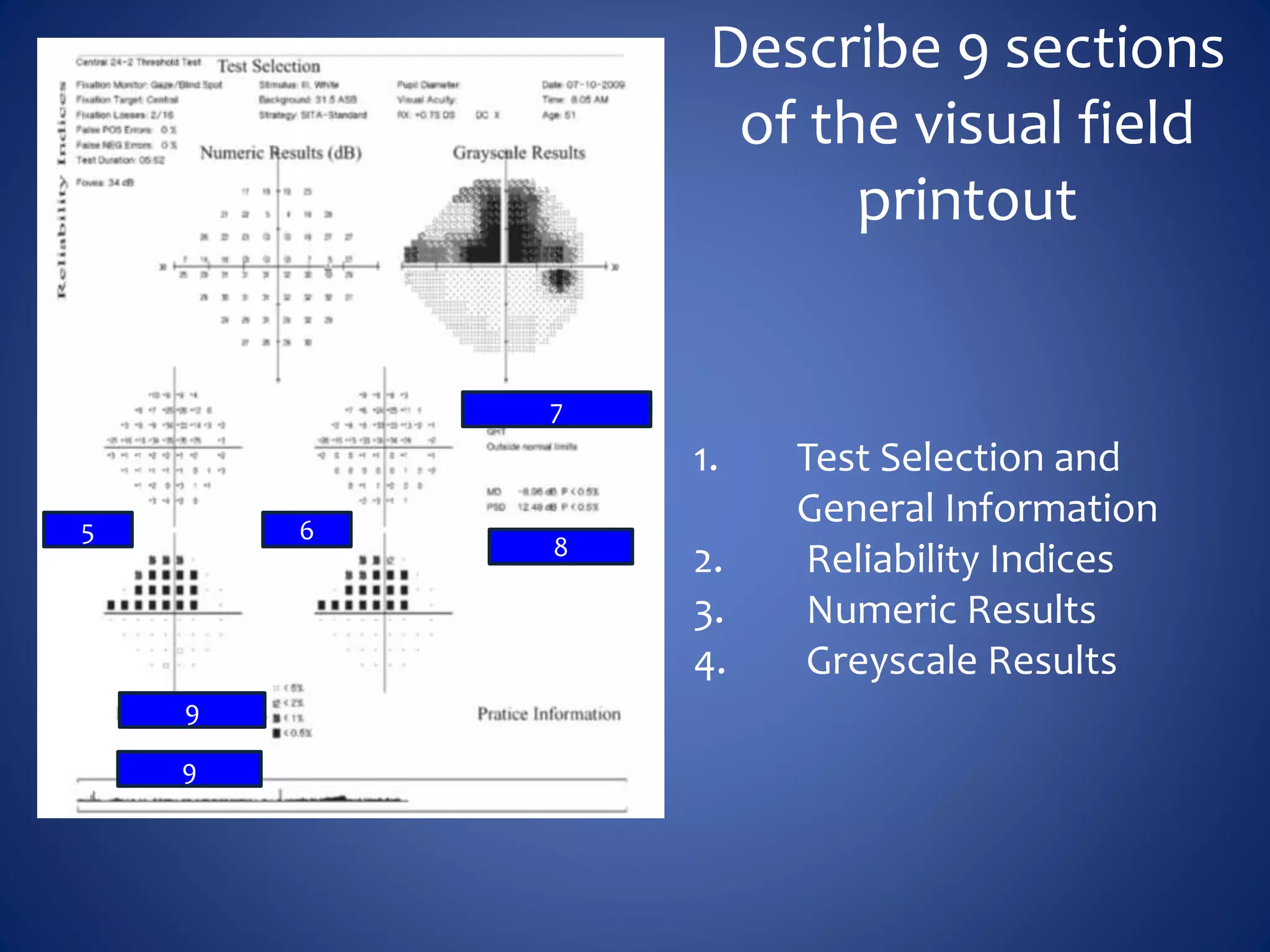
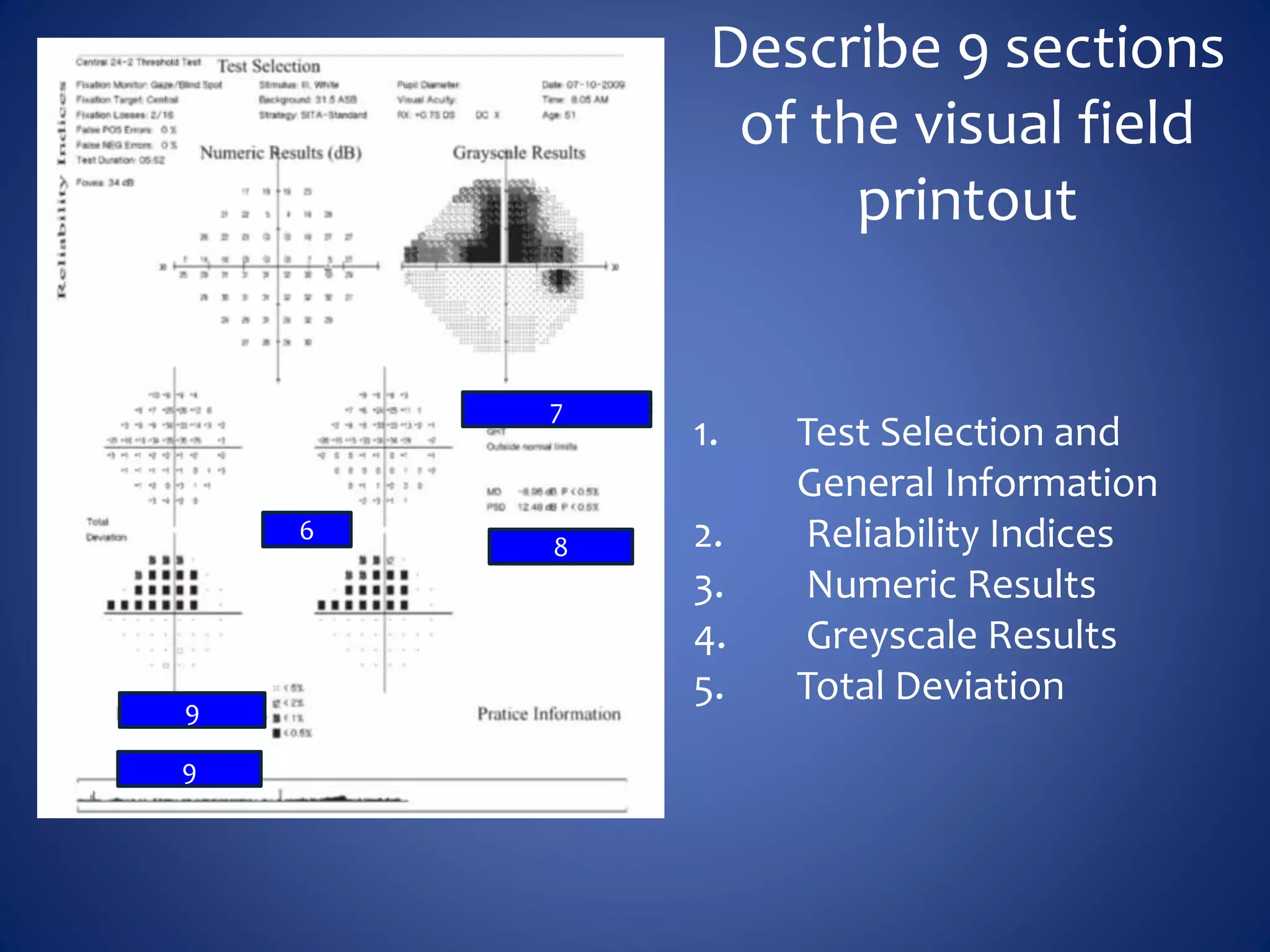
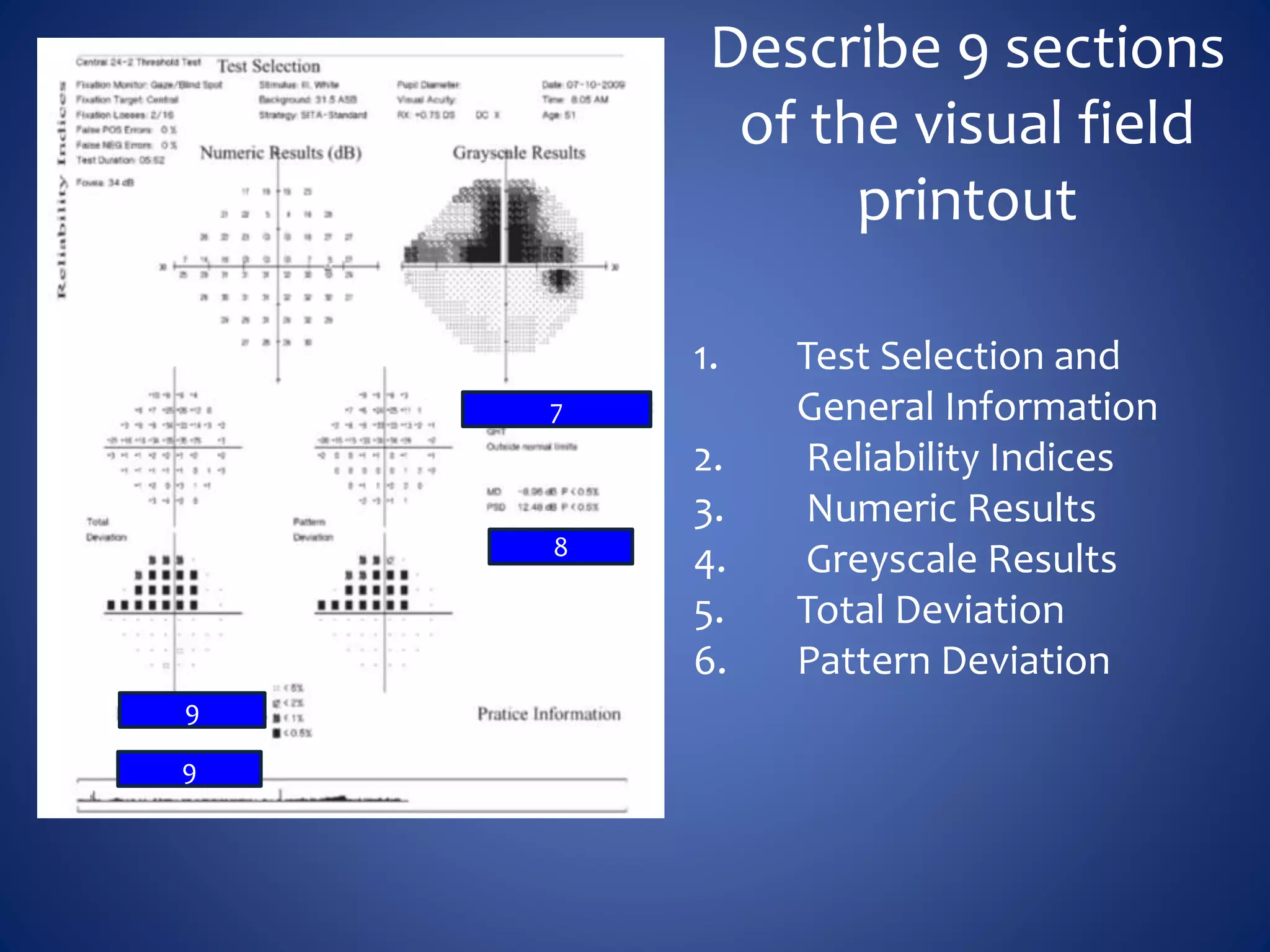
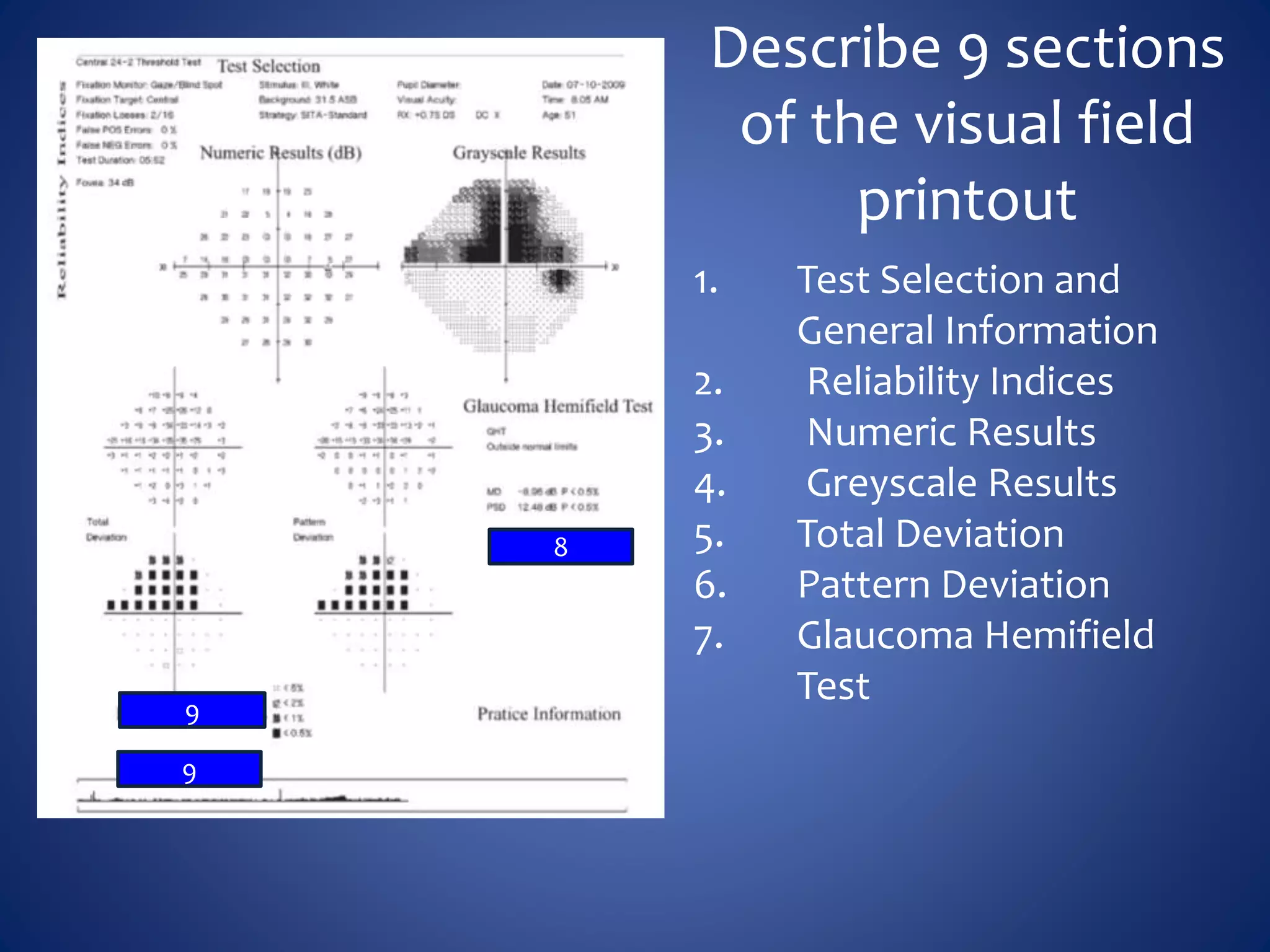
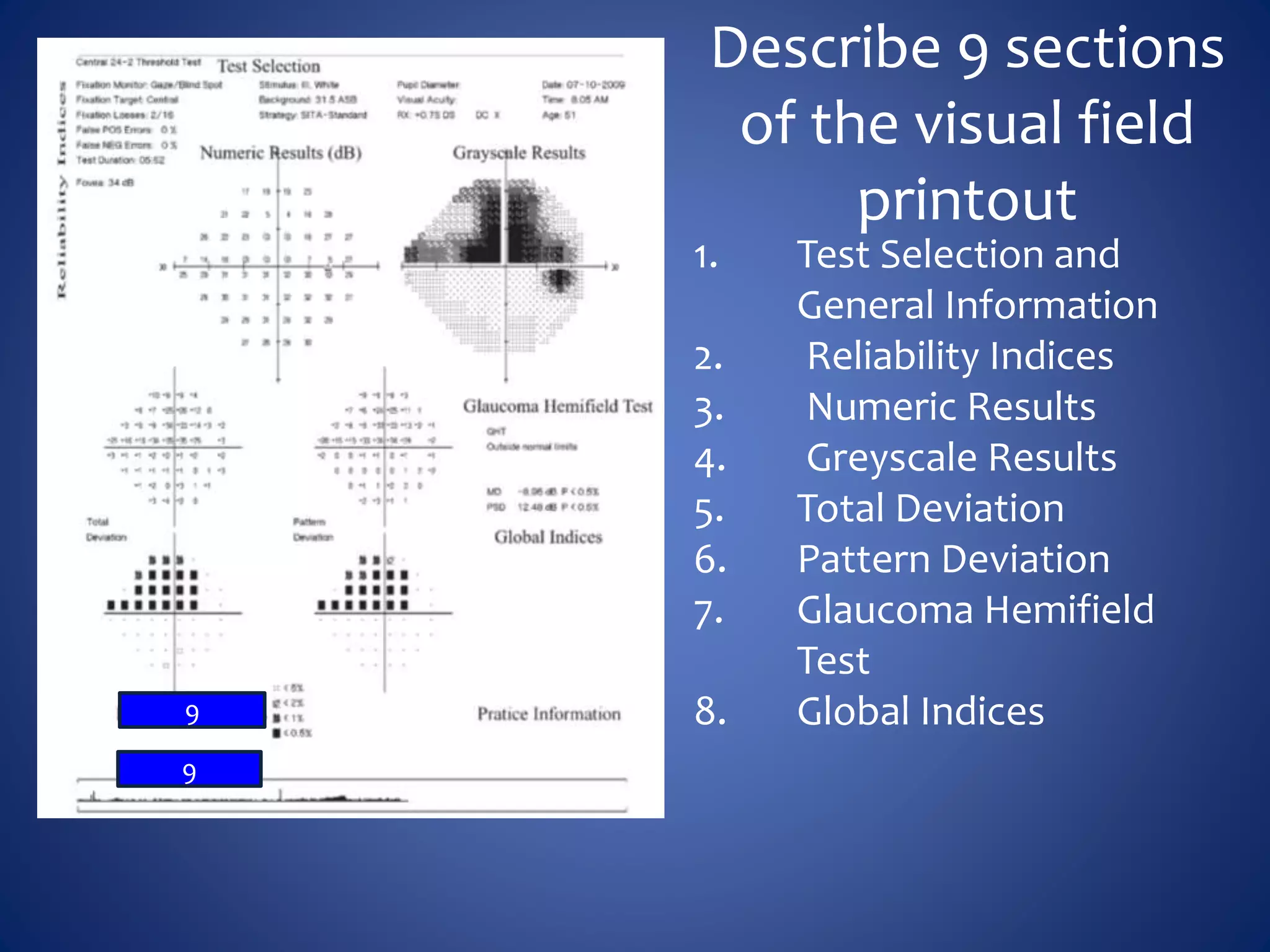
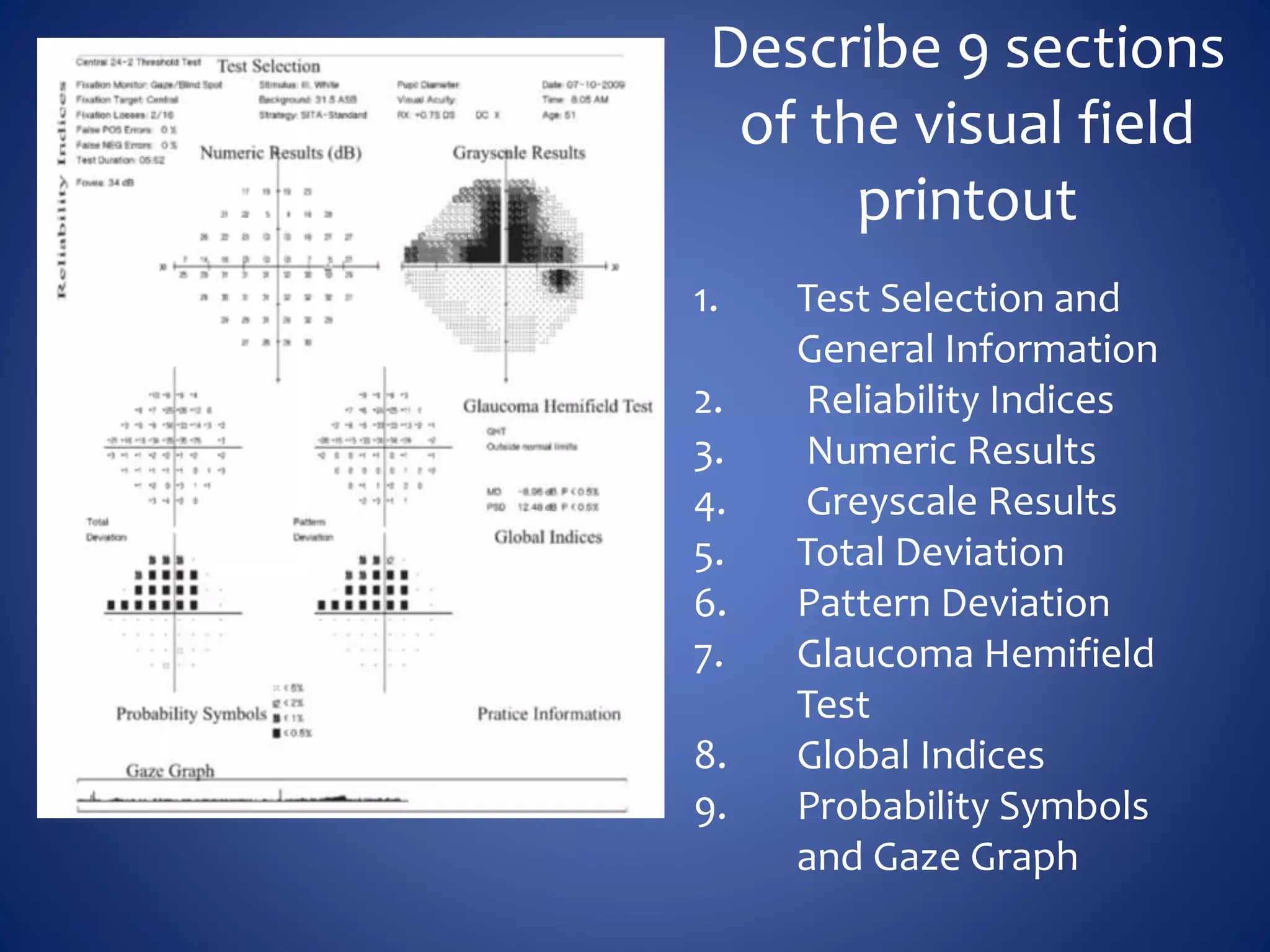
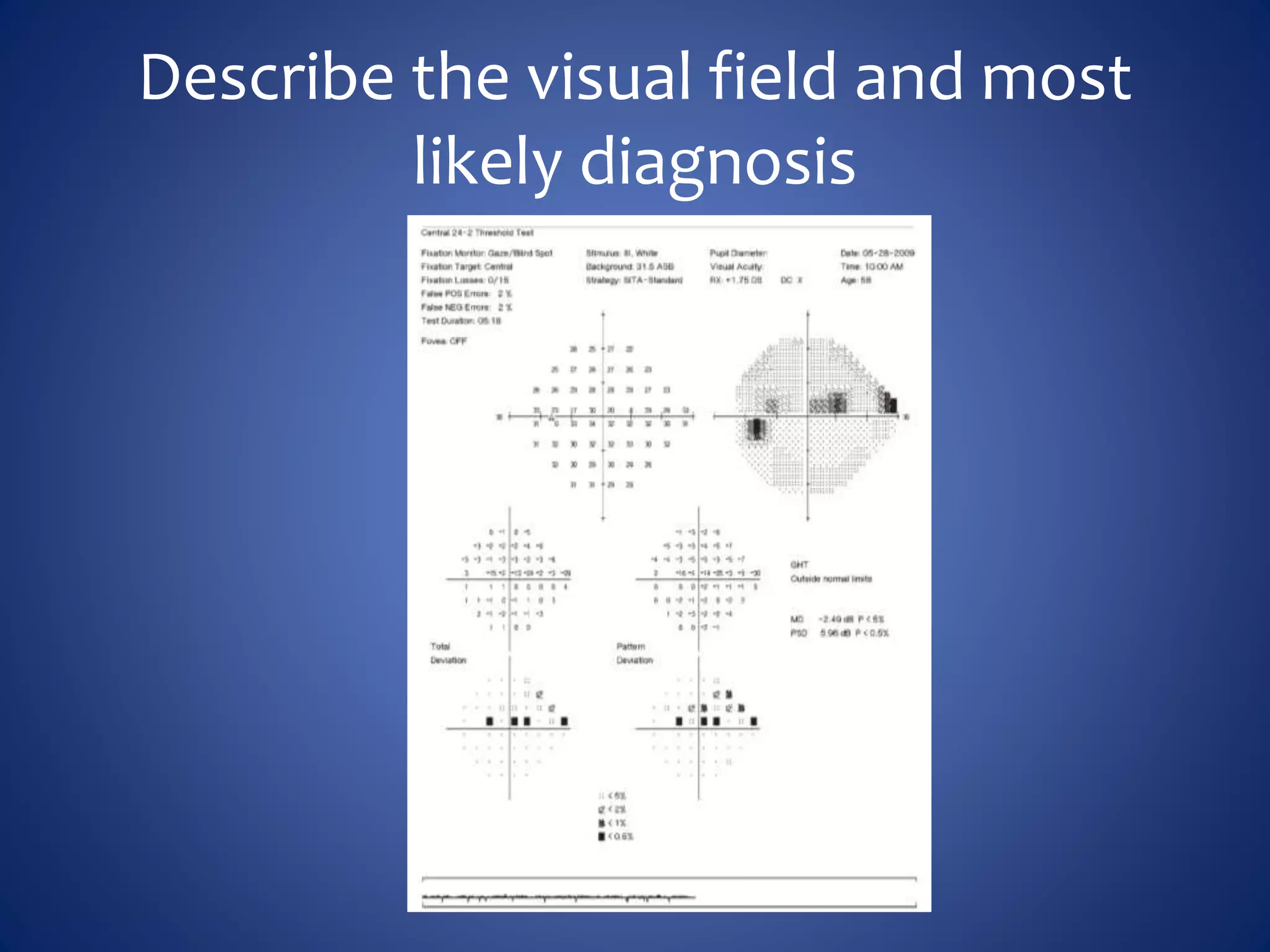
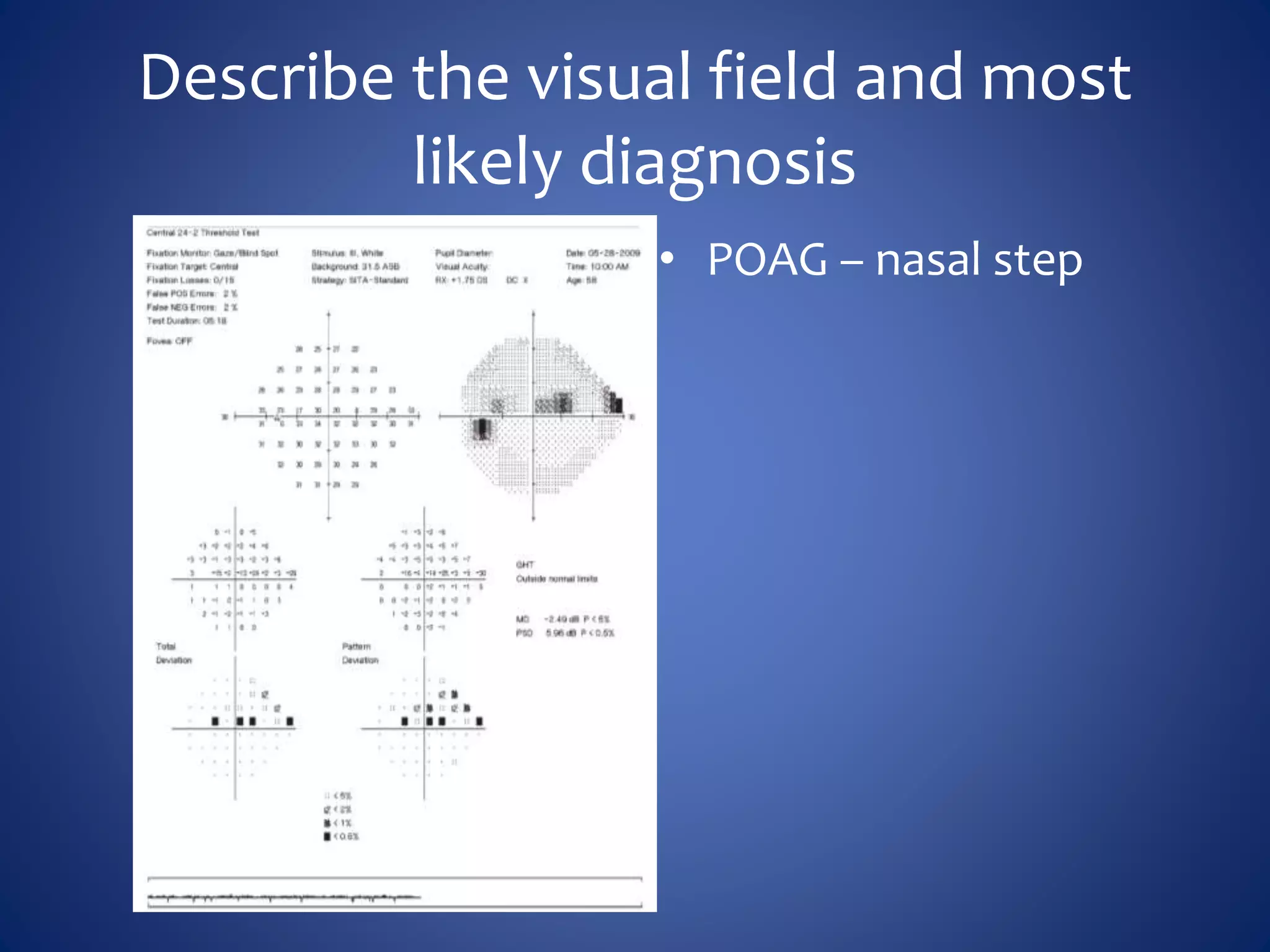
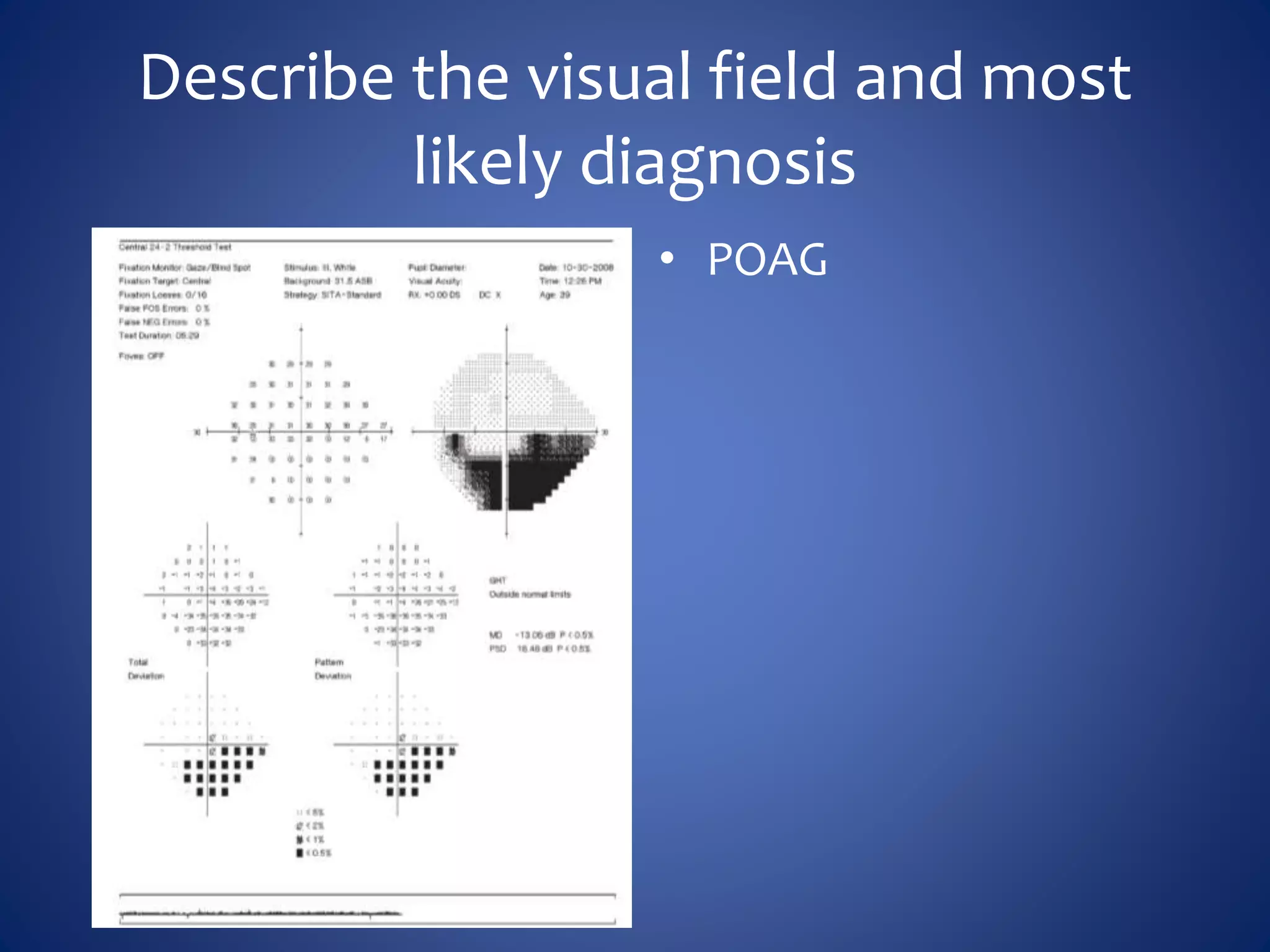
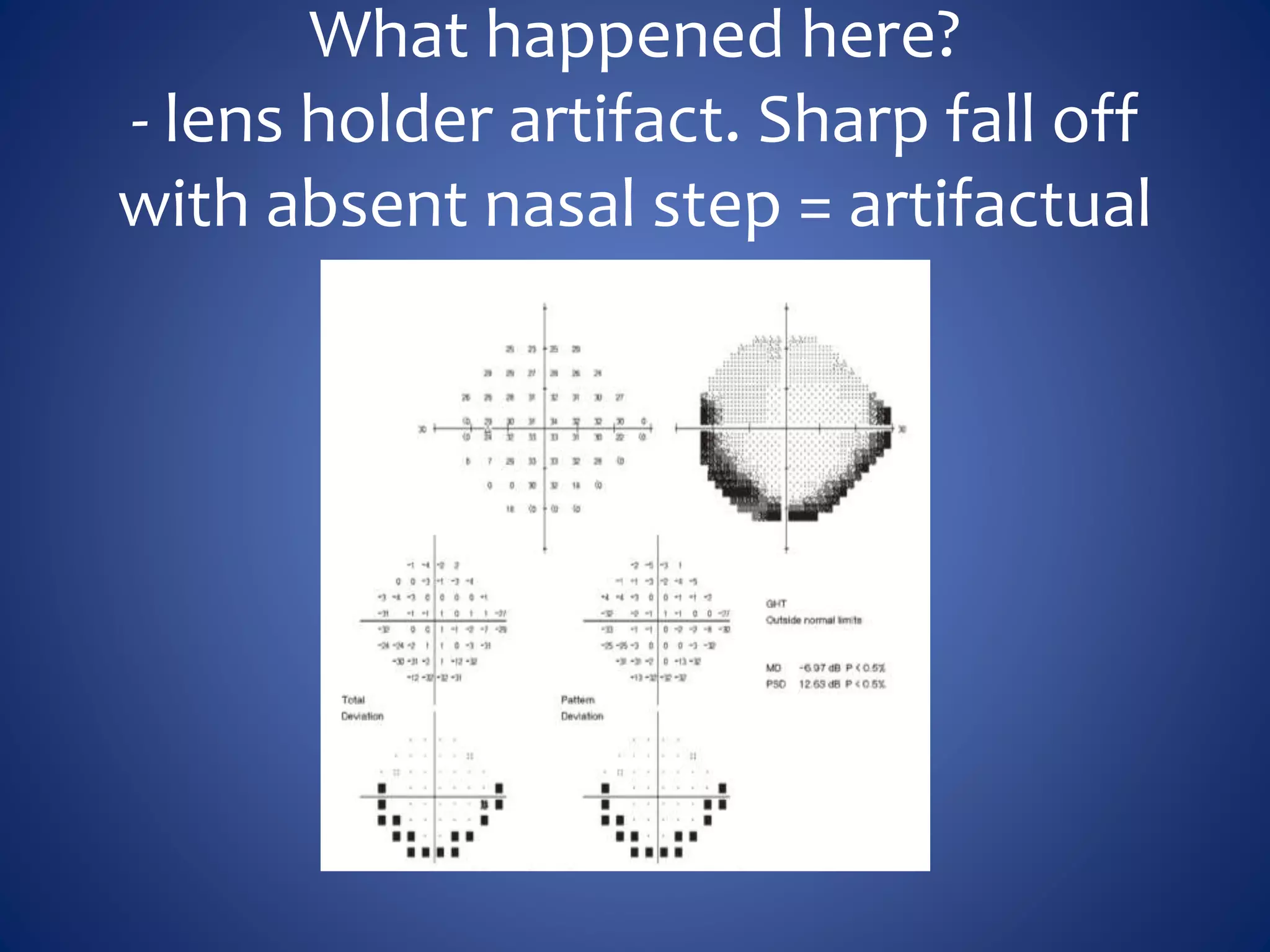
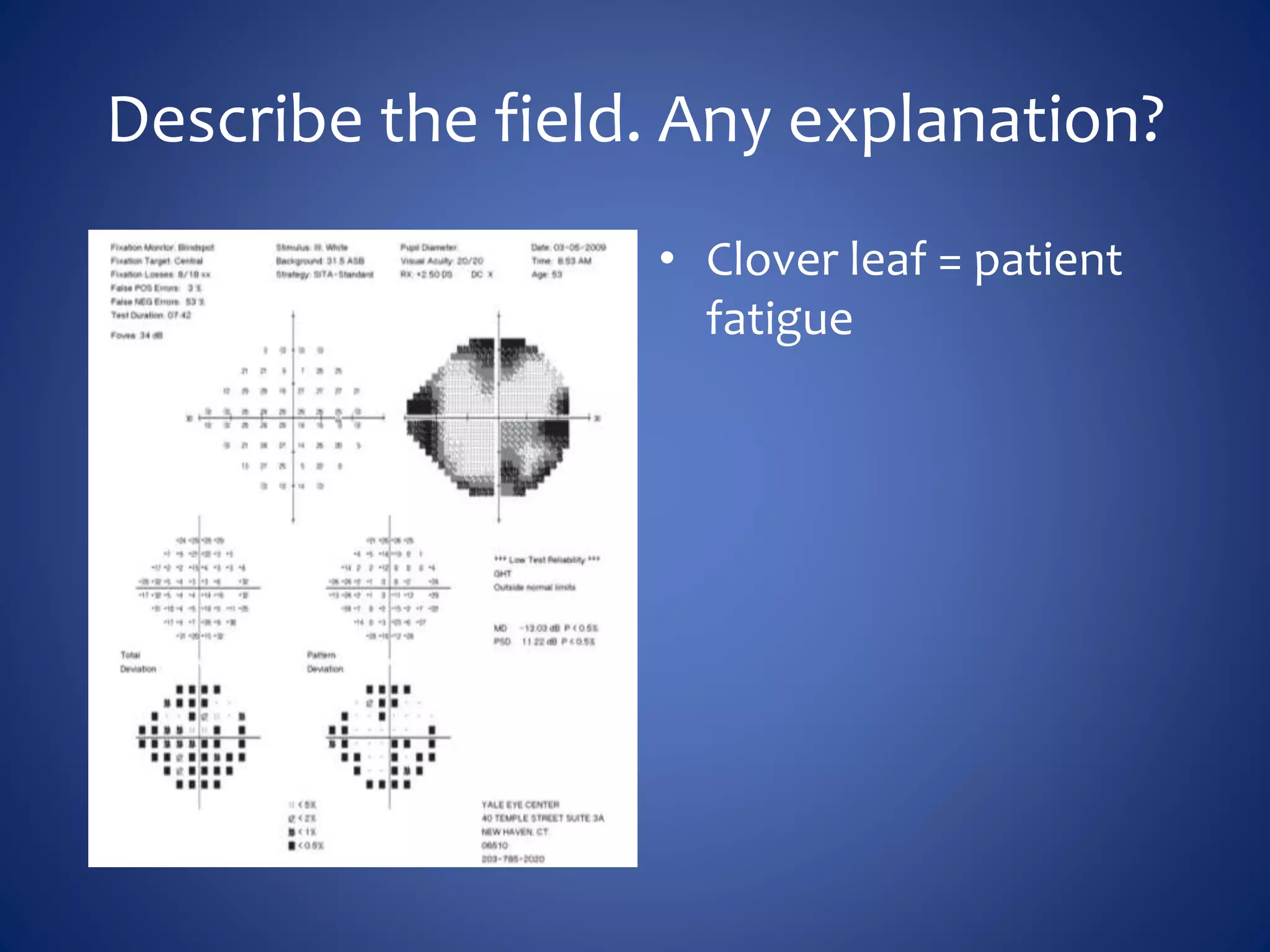
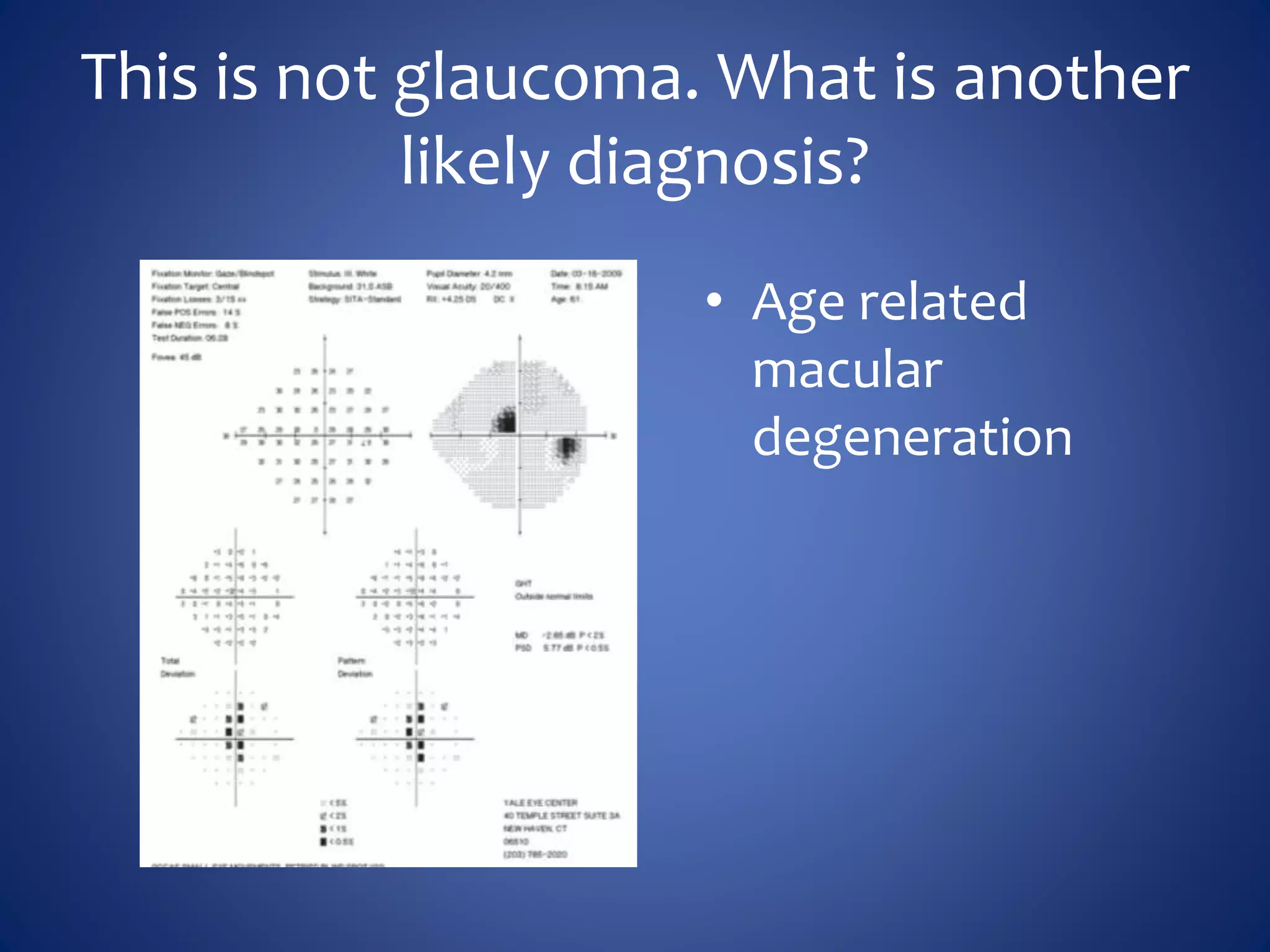
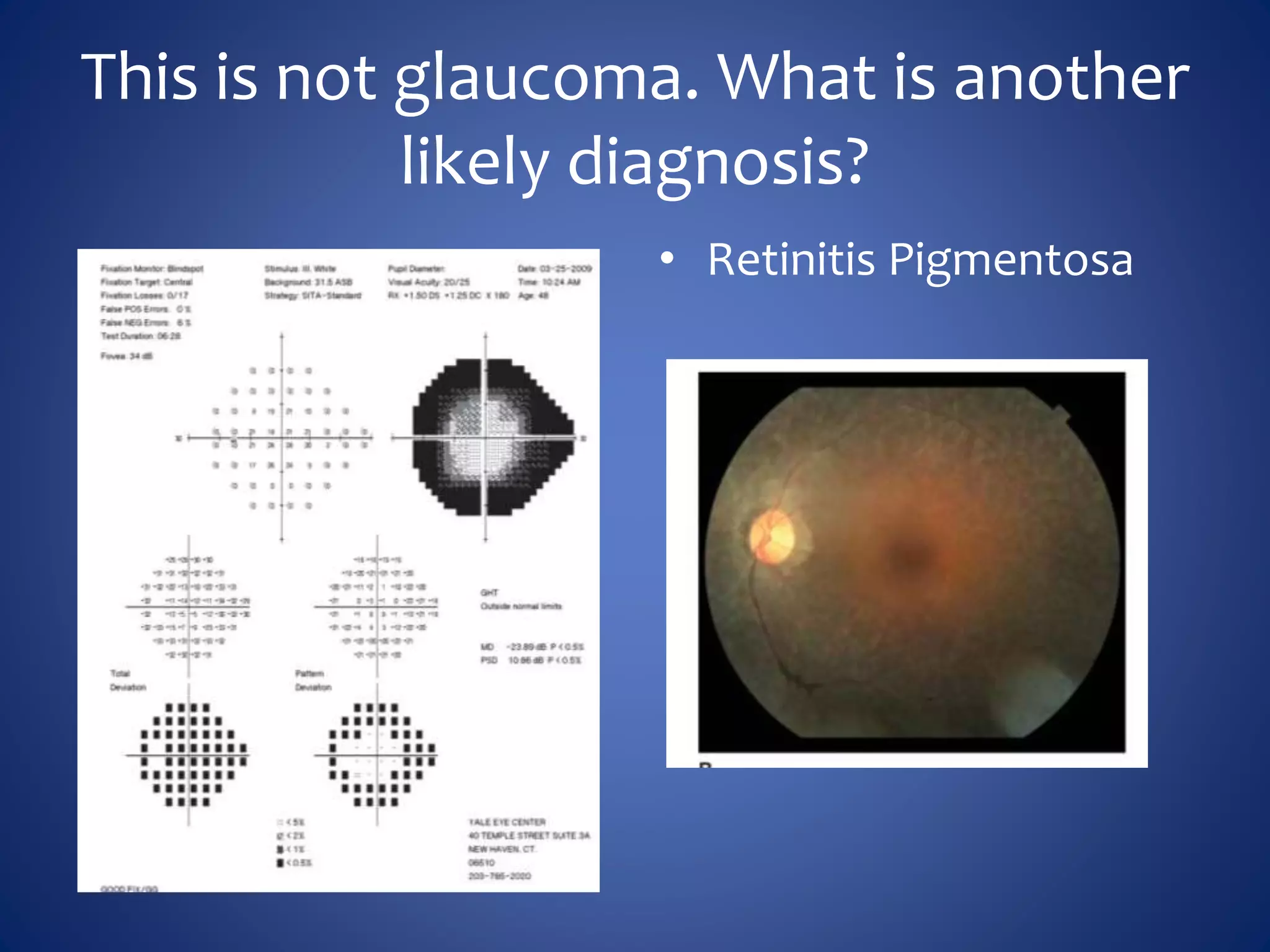
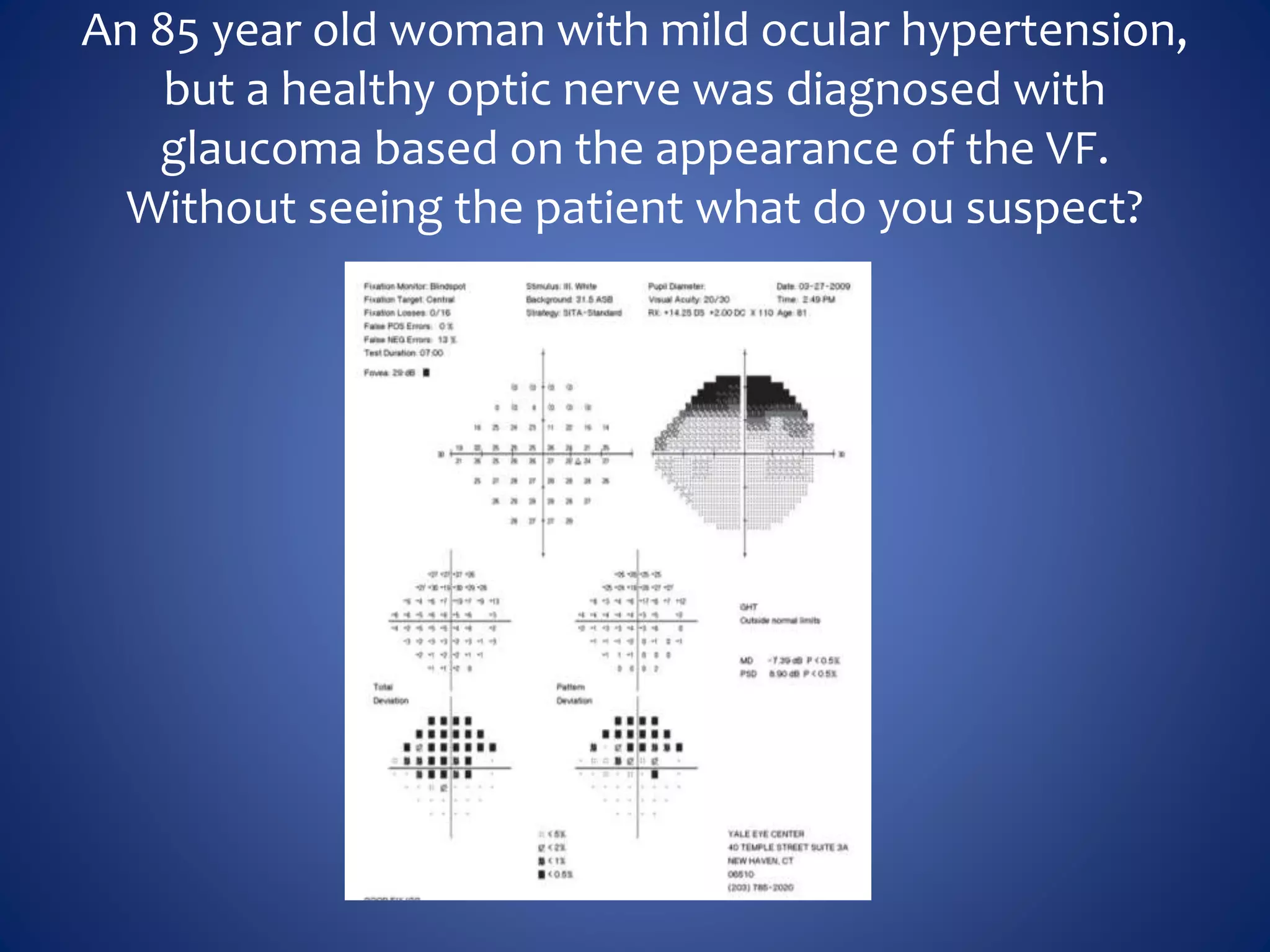
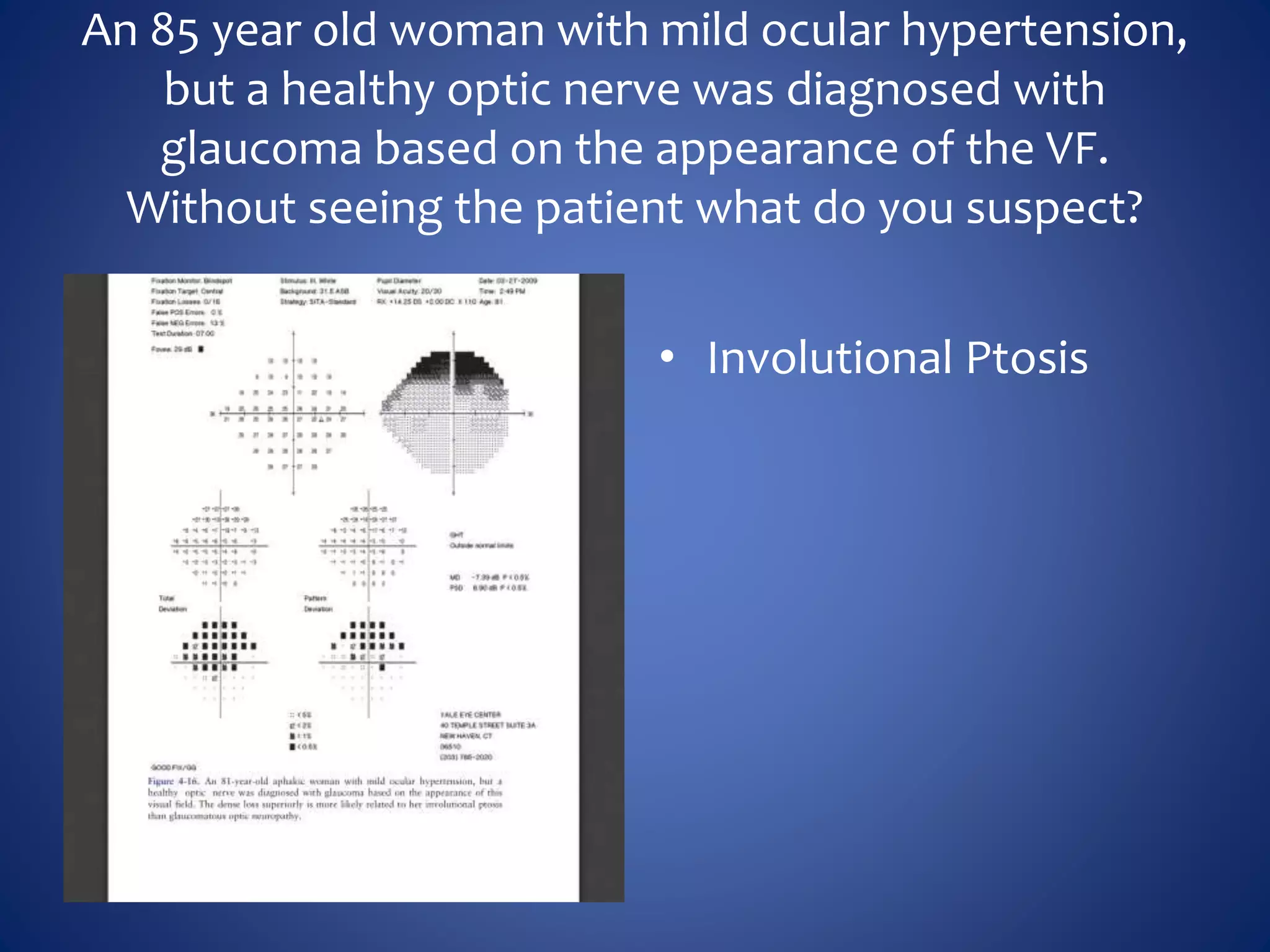
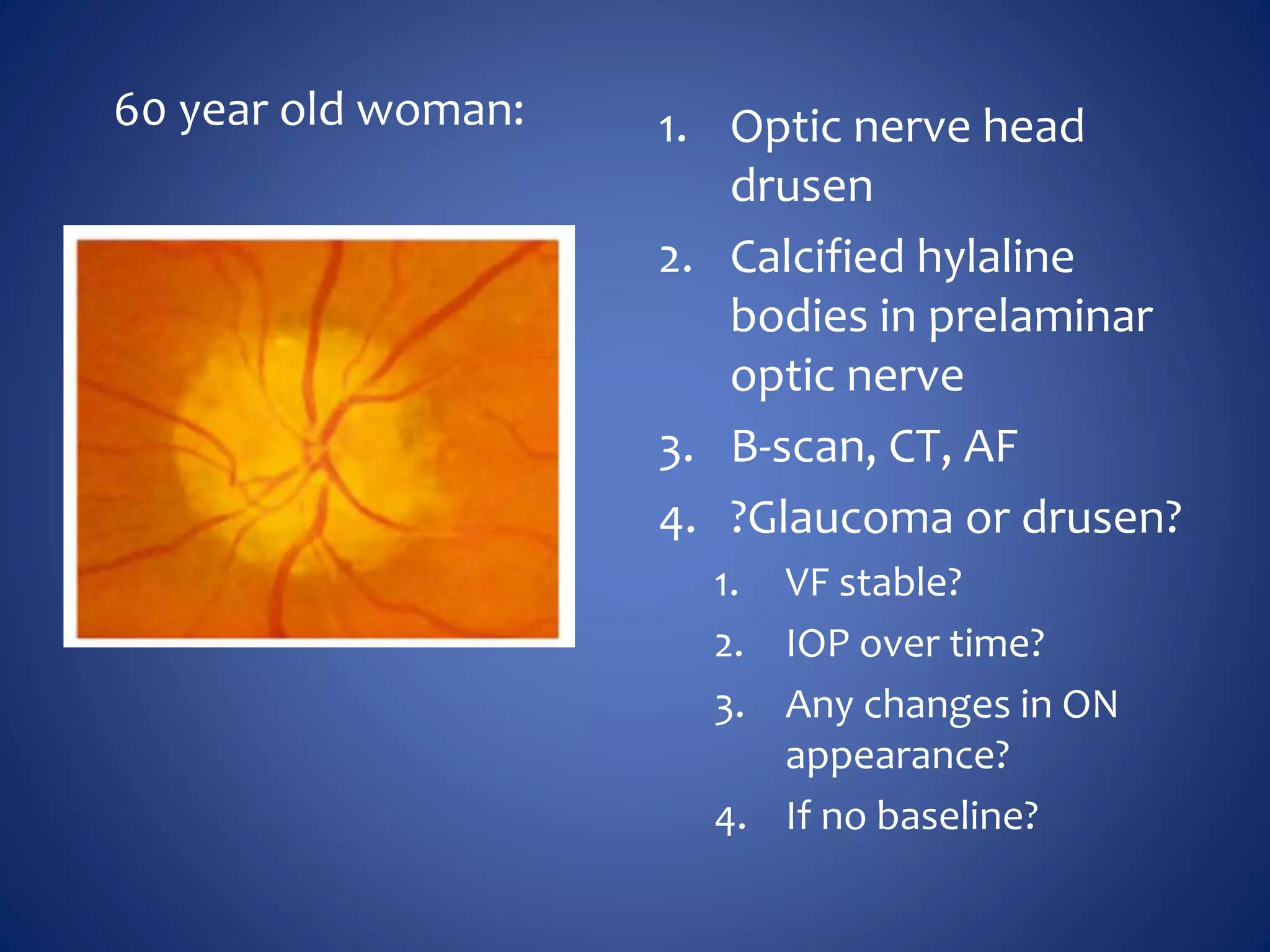
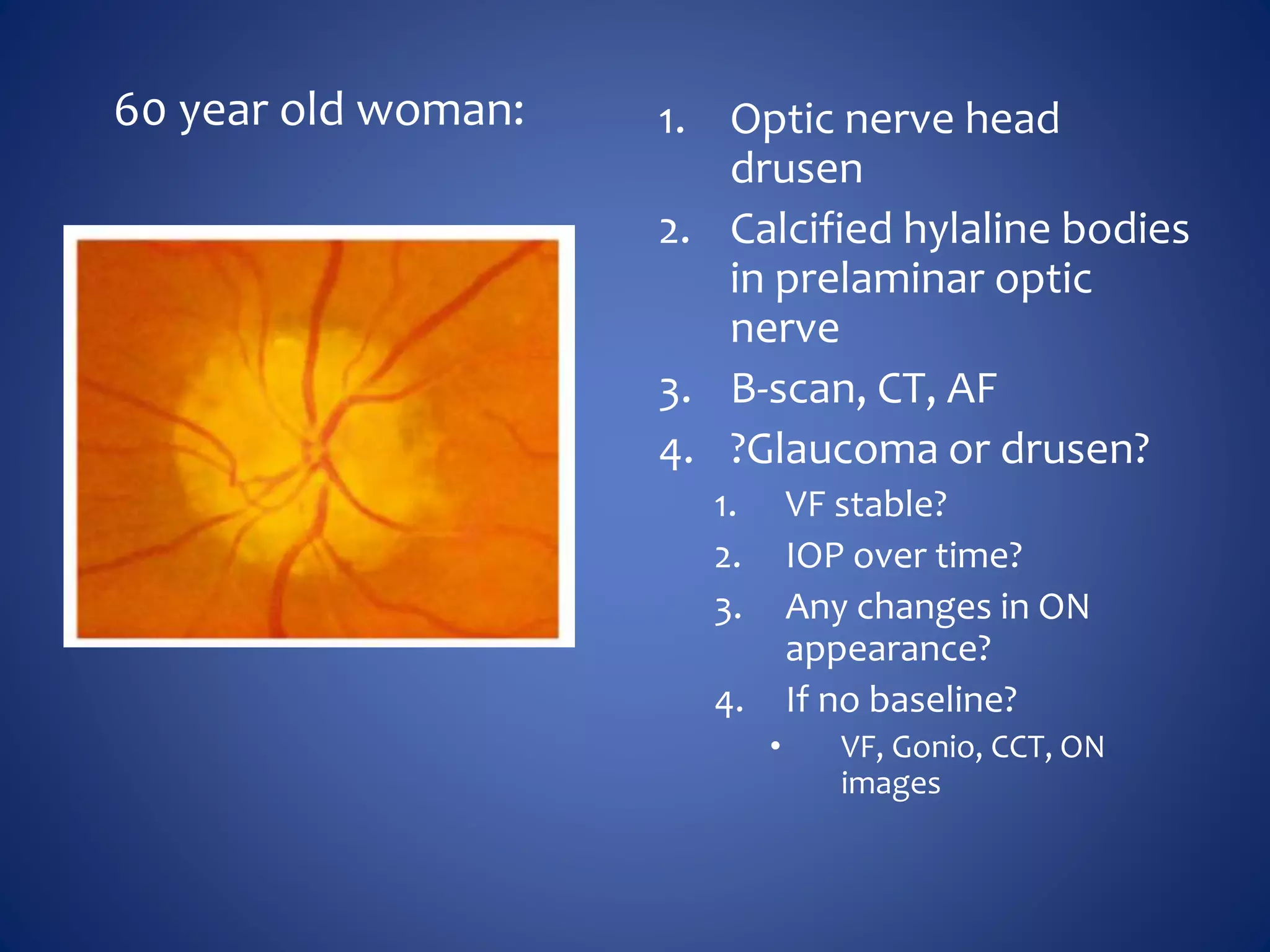
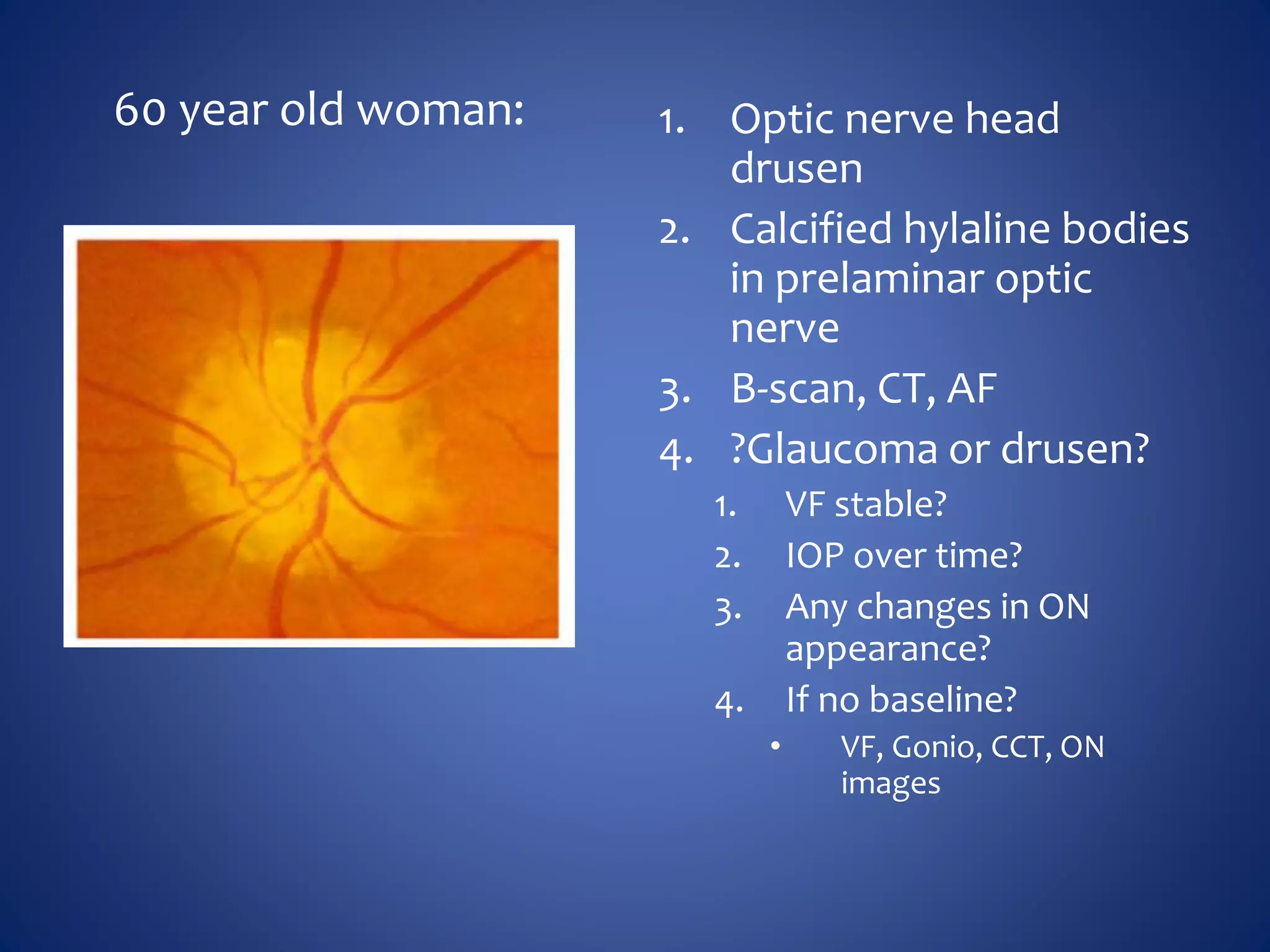
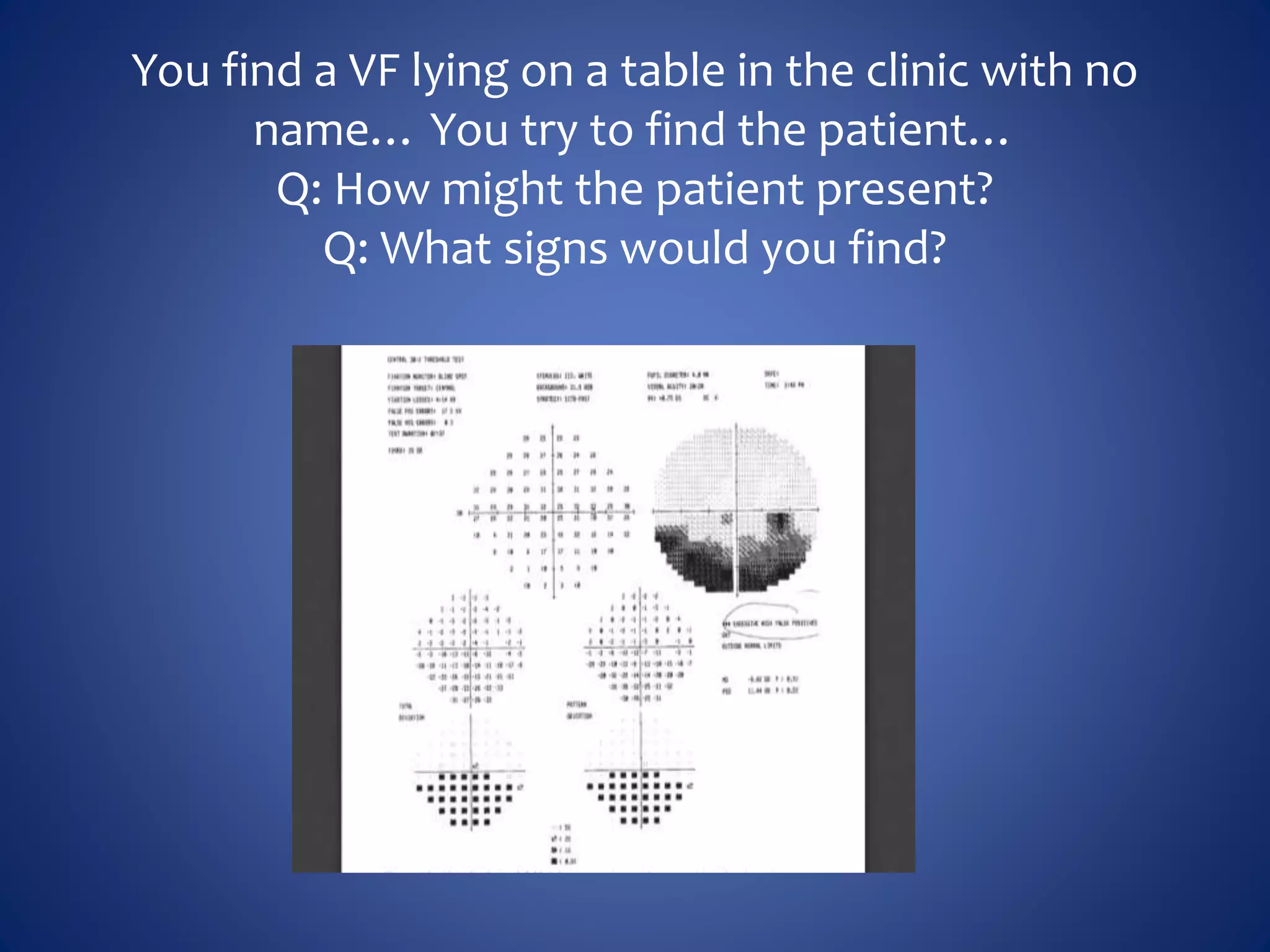
Based on the visual field series shown, it appears the patient is experiencing lens artifact on the visual fields over time. The sharp nasal step seen on earlier fields is likely not real. My management would be:
- Discontinue glaucoma treatment since visual fields are unreliable due to lens artifact
- Perform gonioscopy and review optic nerve/retinal nerve fiber layer to evaluate for glaucoma
- Consider cataract surgery to remove lens artifact on future visual fields
- Counsel patient that visual fields were unreliable due to cataract and glaucoma status cannot be determined from VF alone
The key things are to not rely solely on unreliable visual fields for glaucoma diagnosis or management, and address the underlying cause