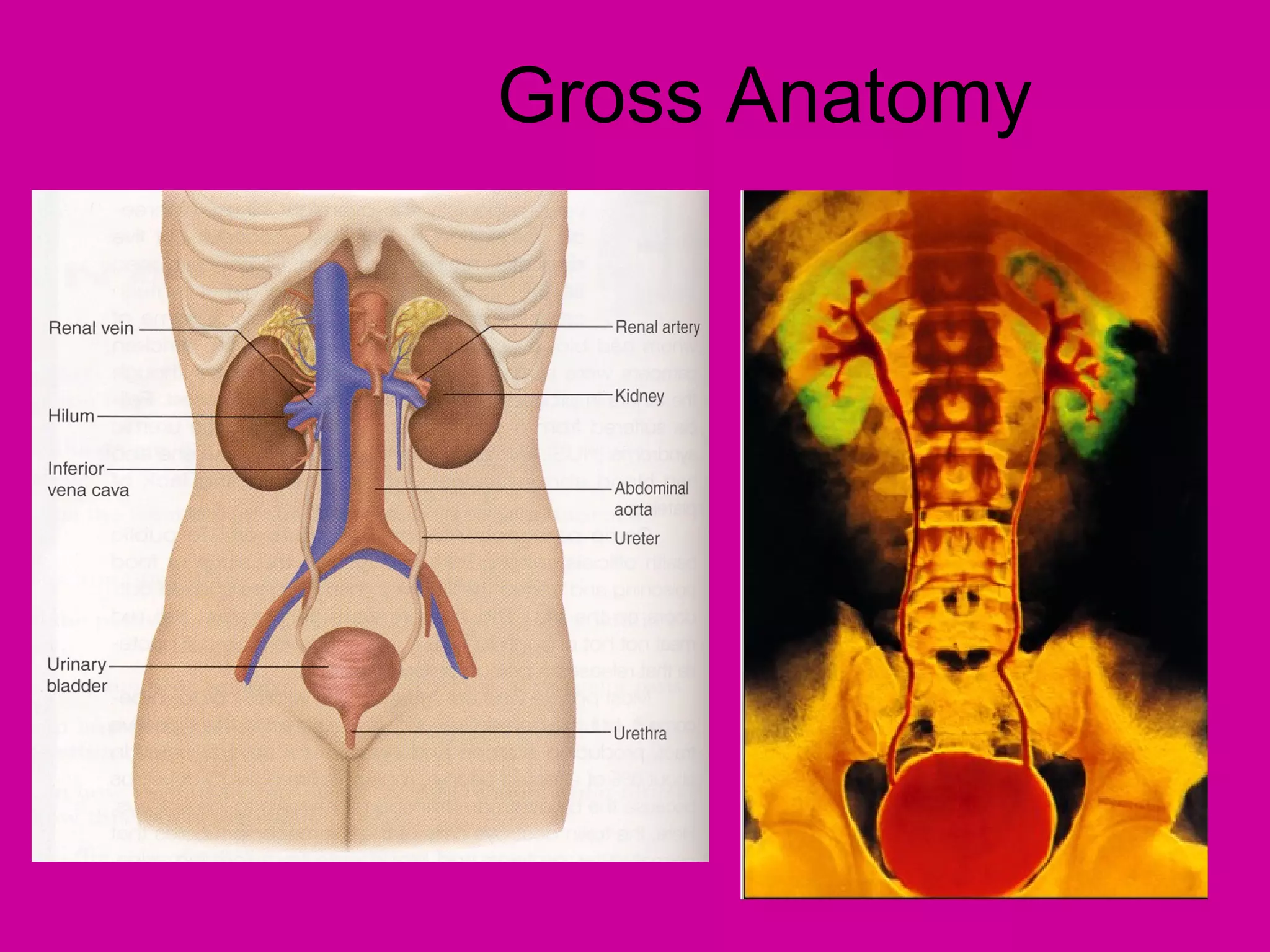
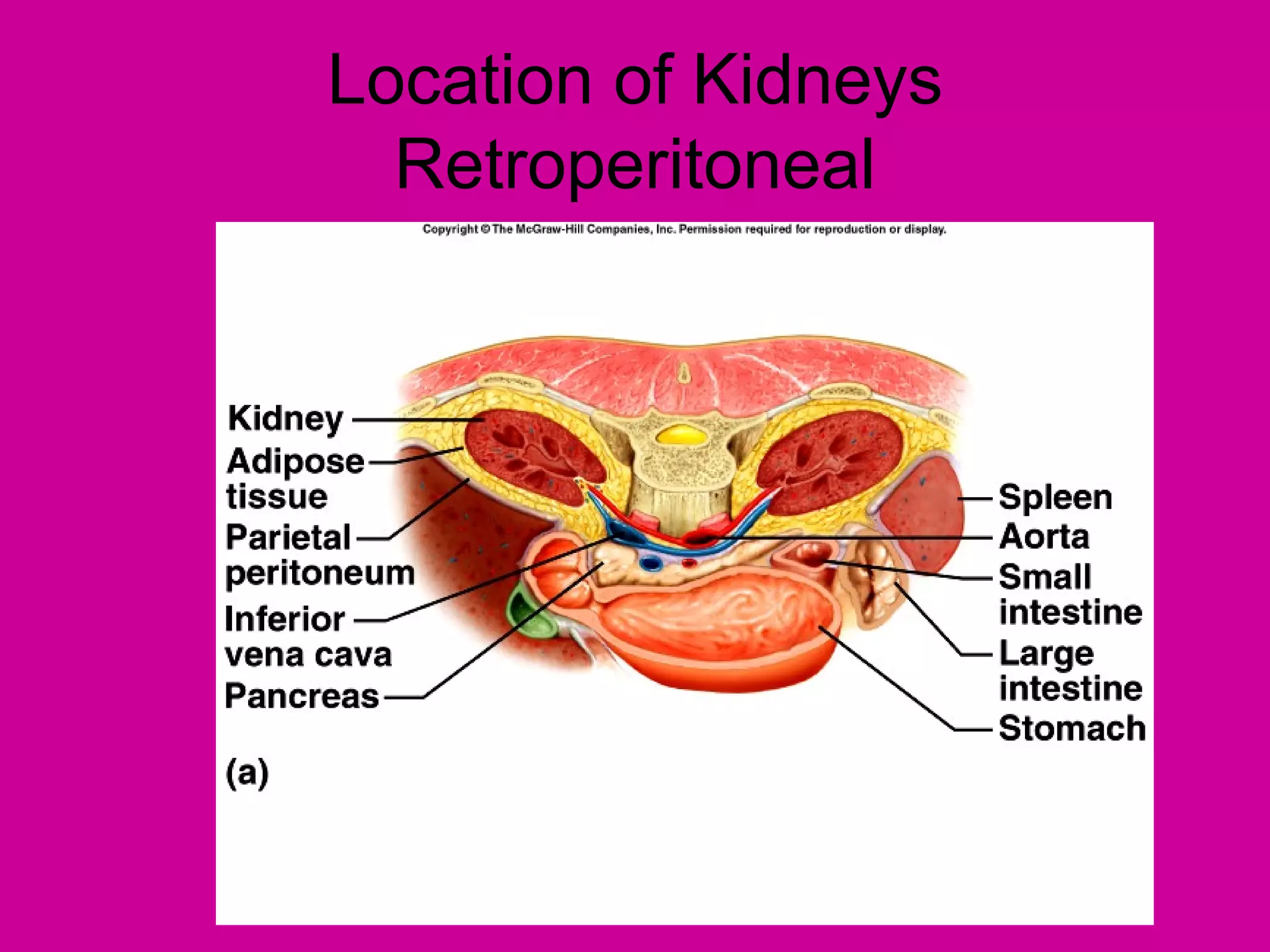
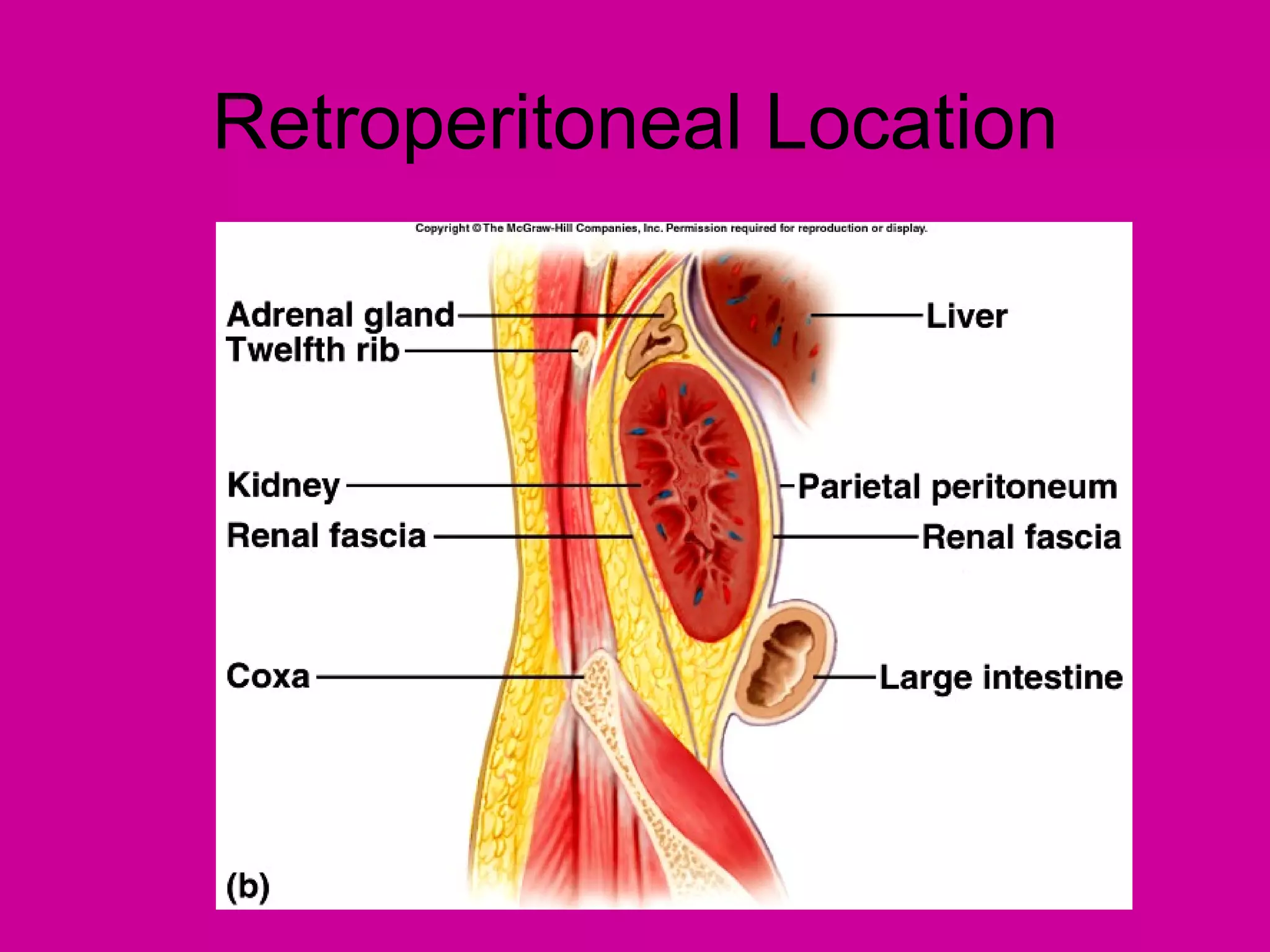
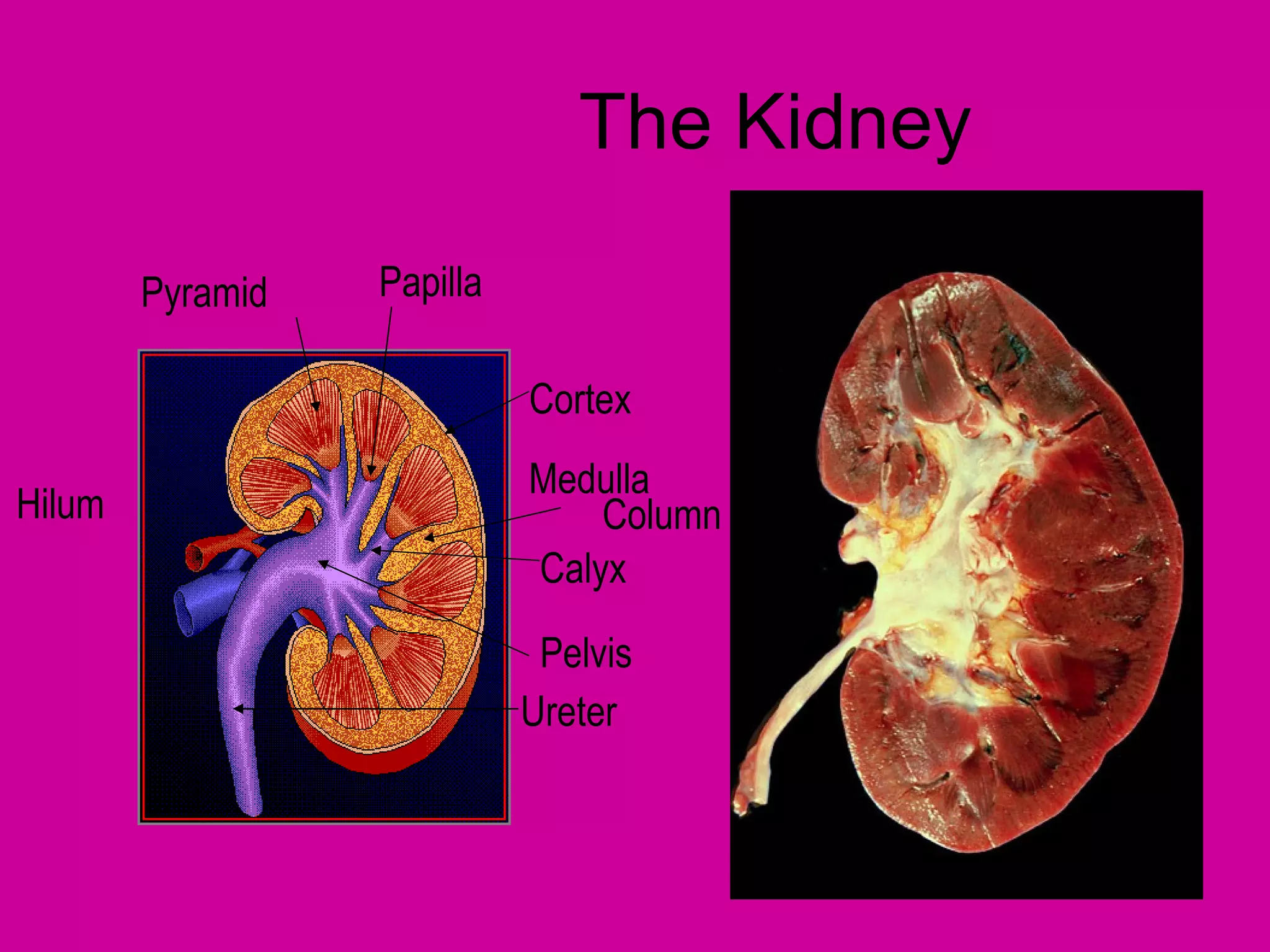
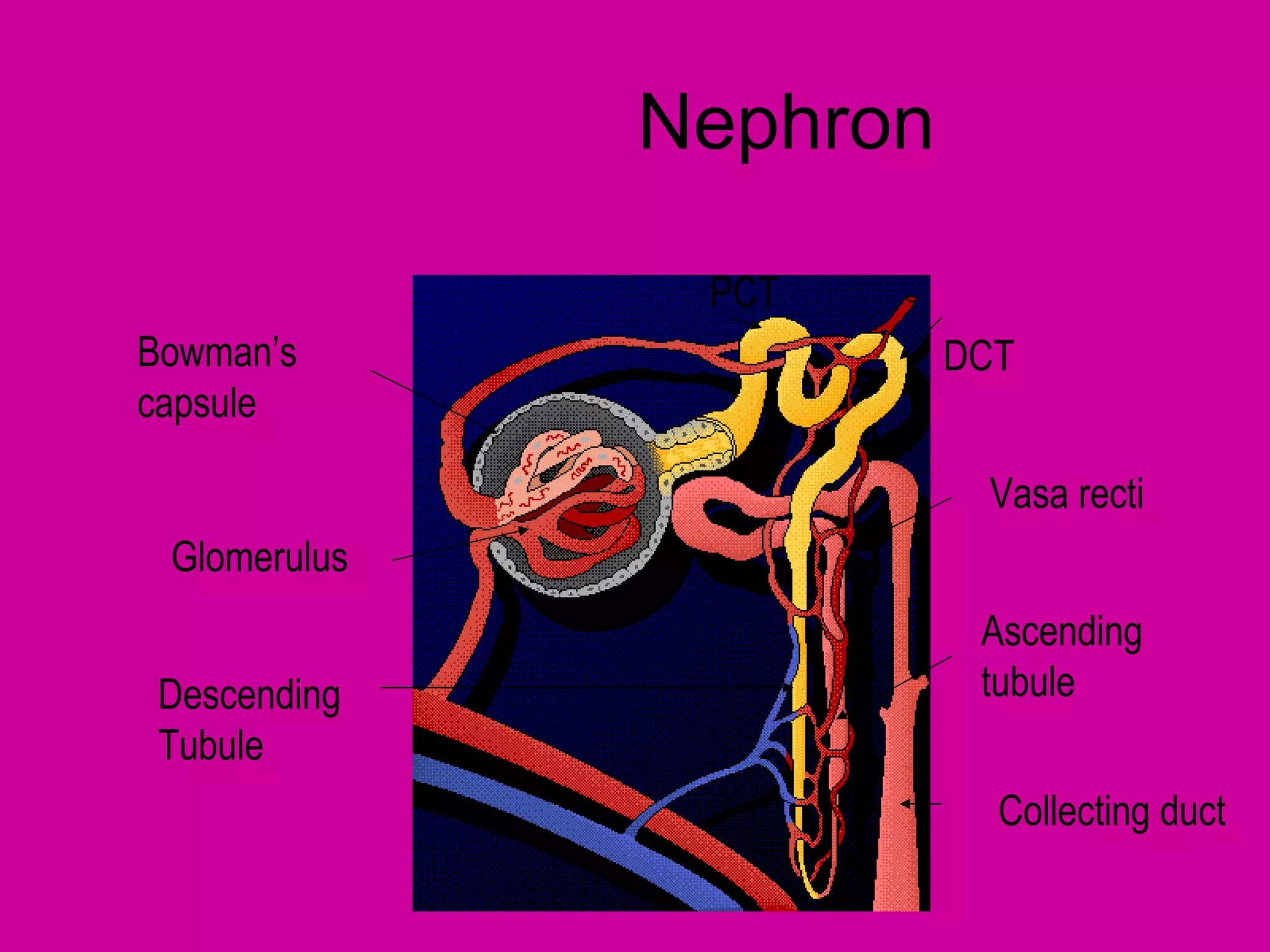
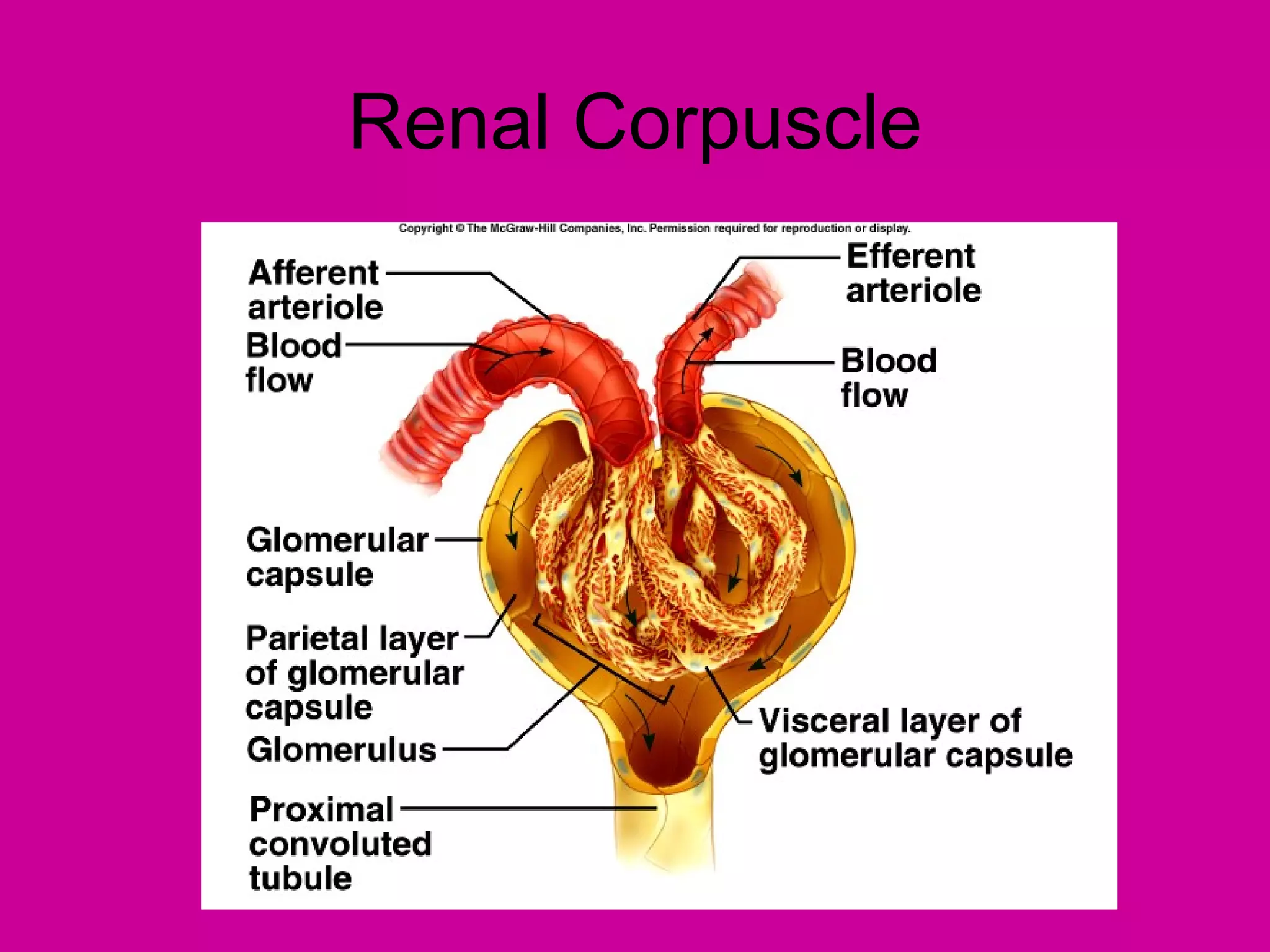
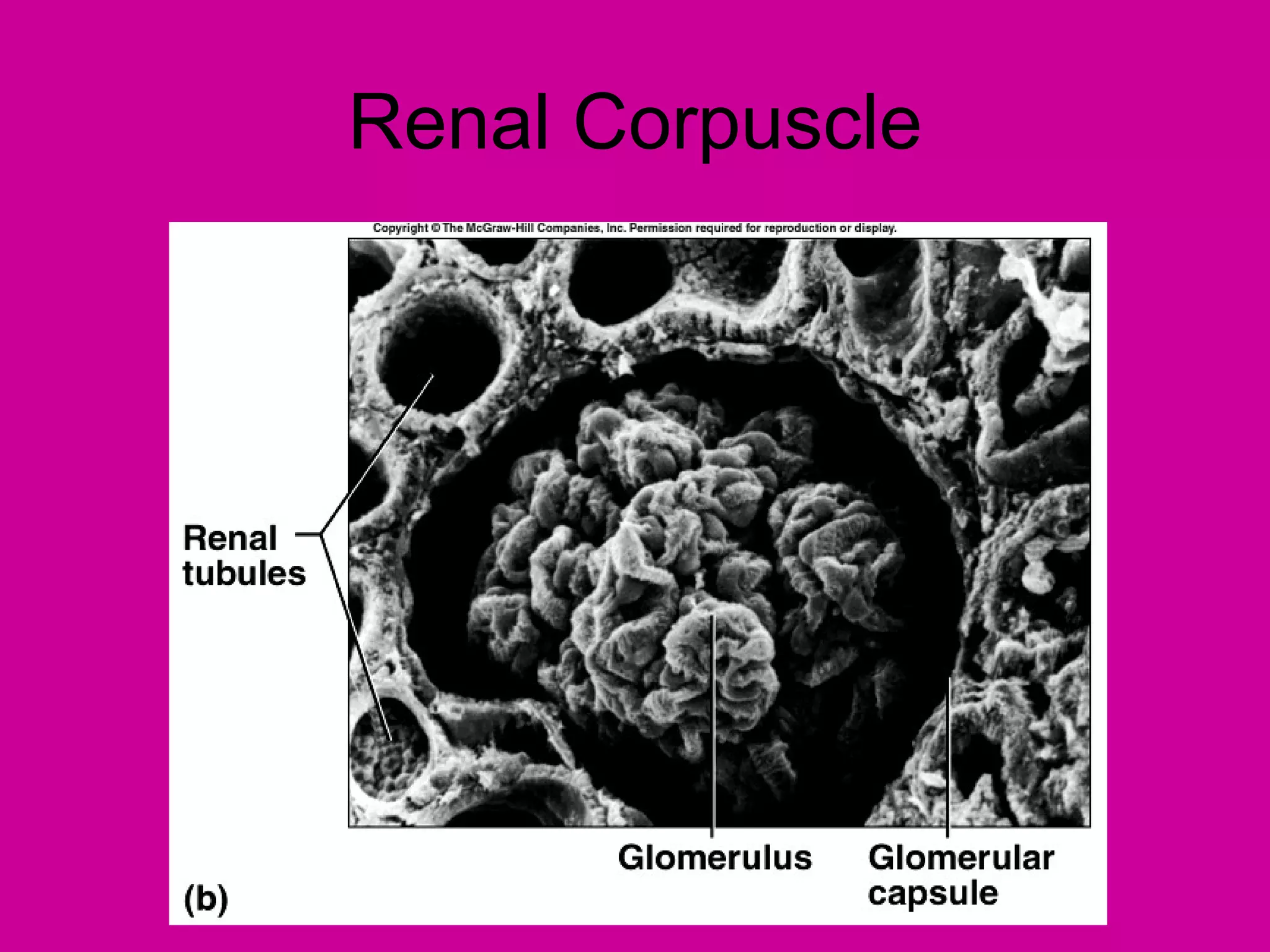
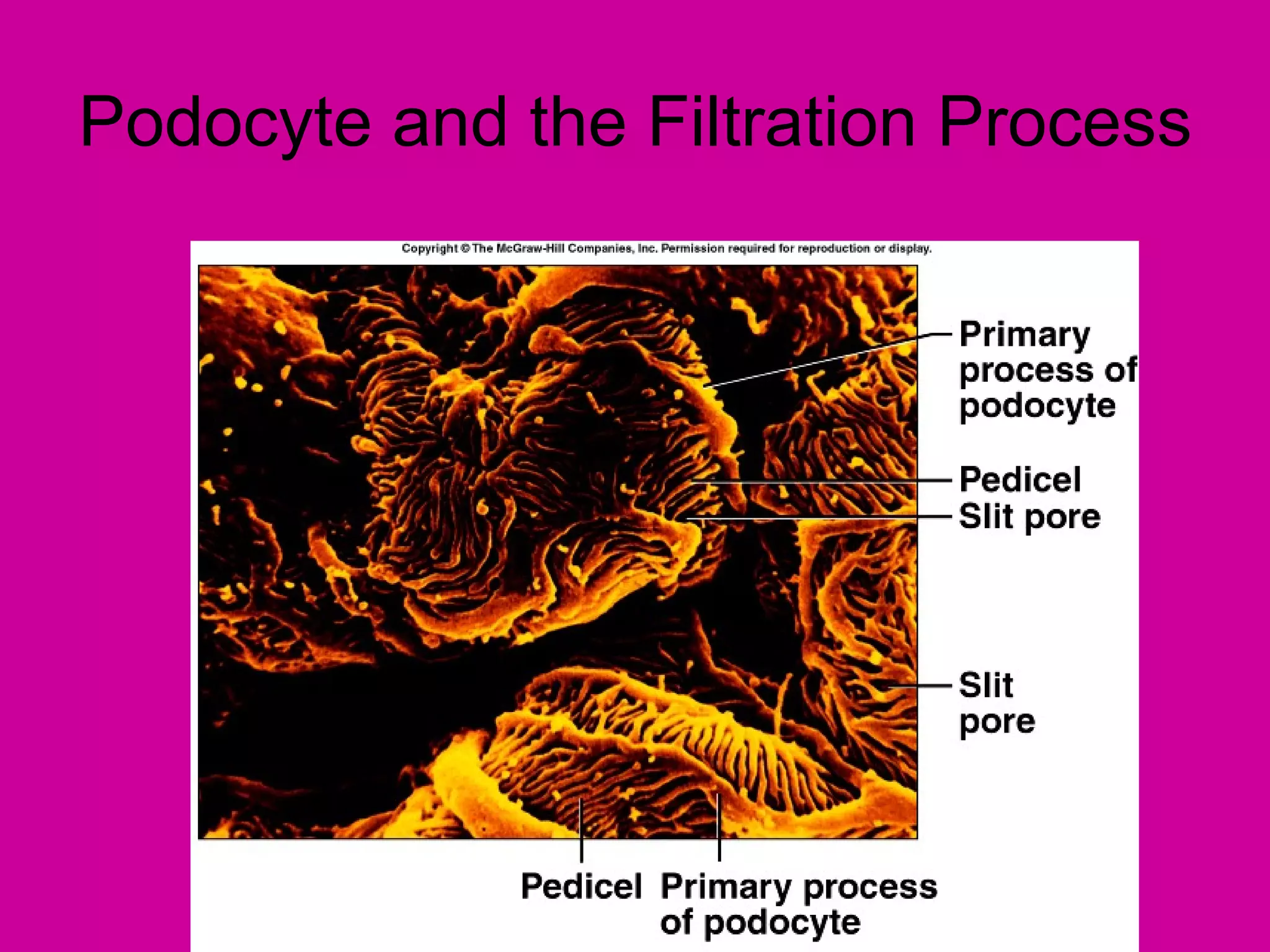
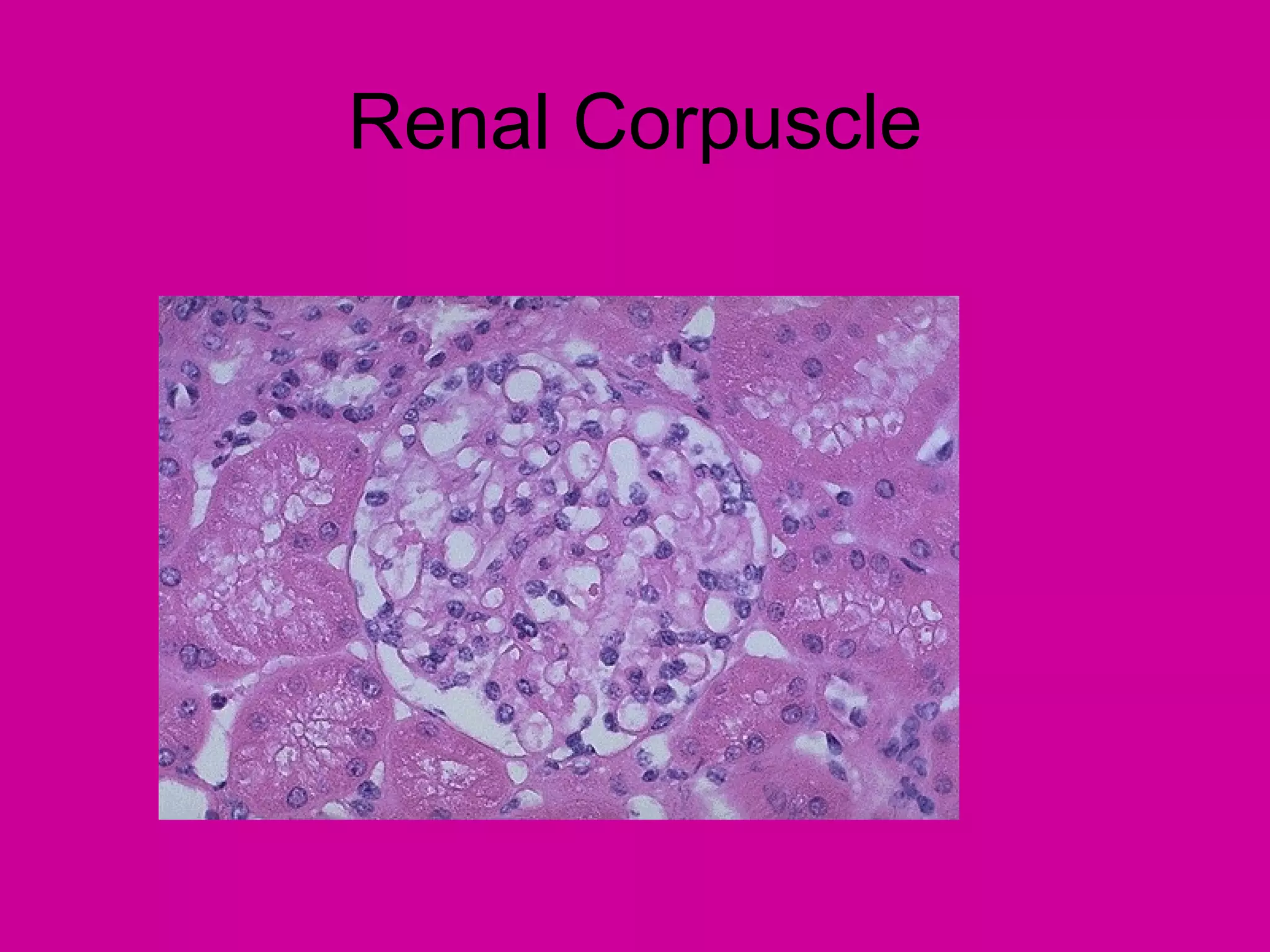
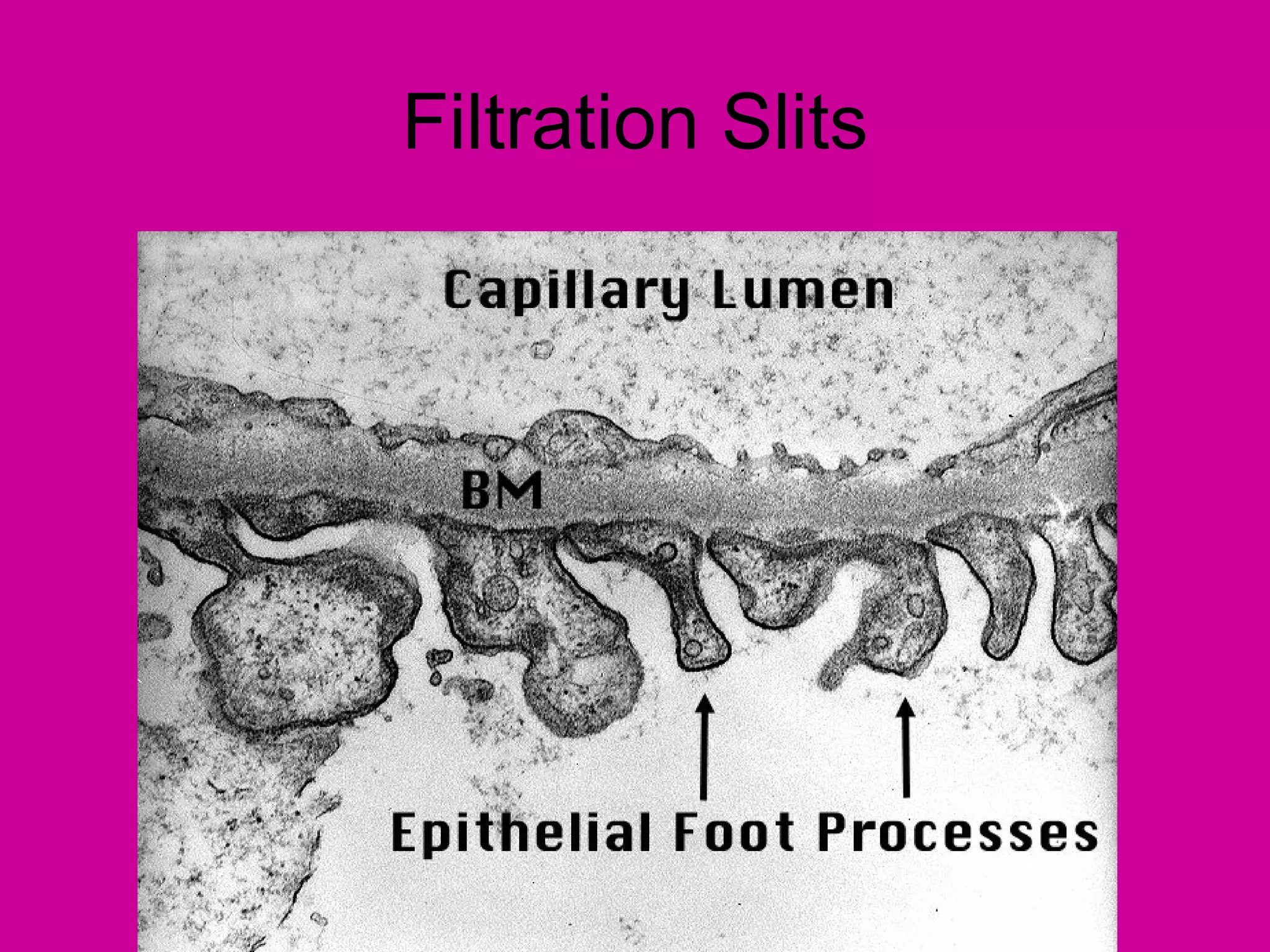
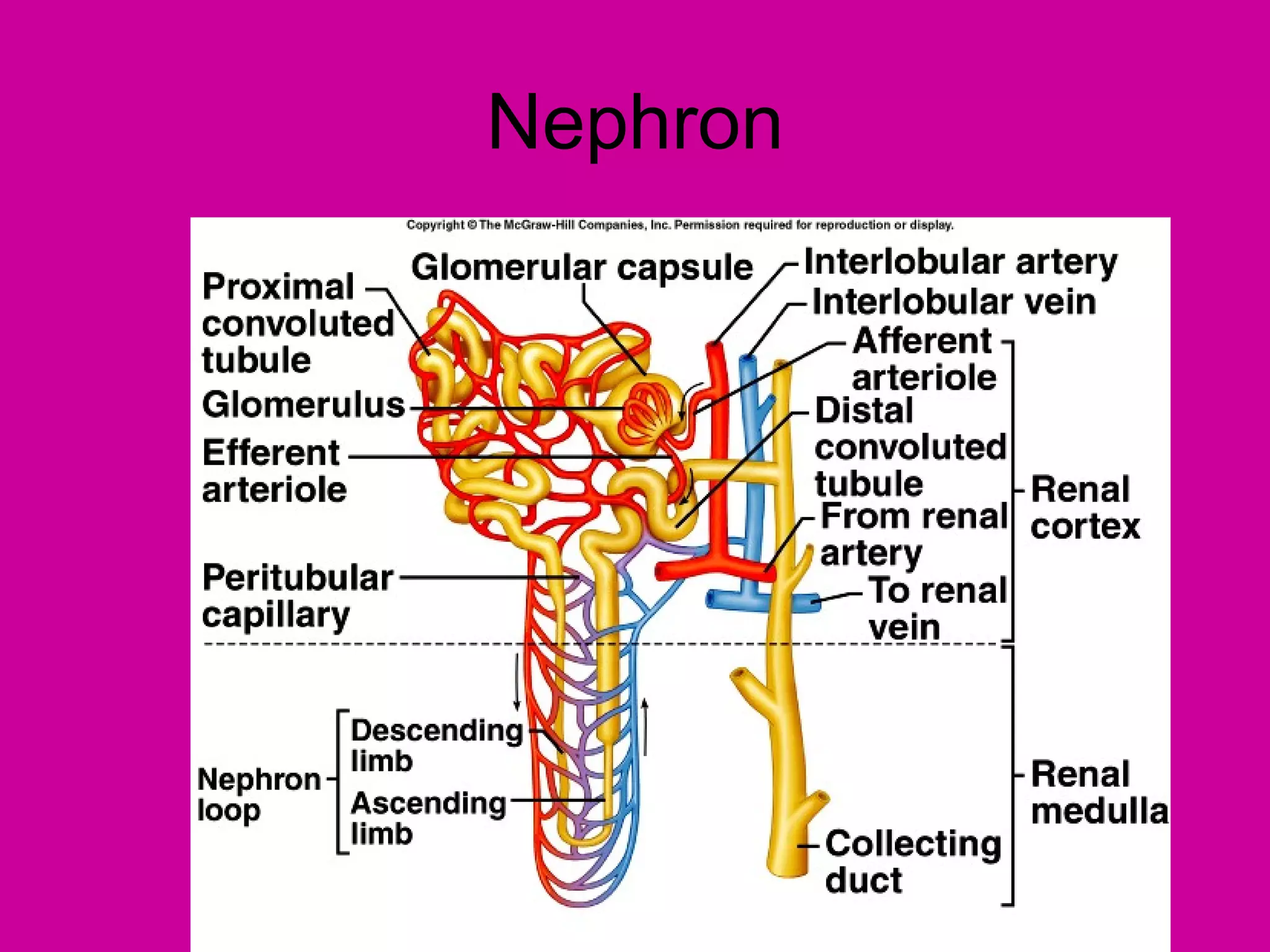
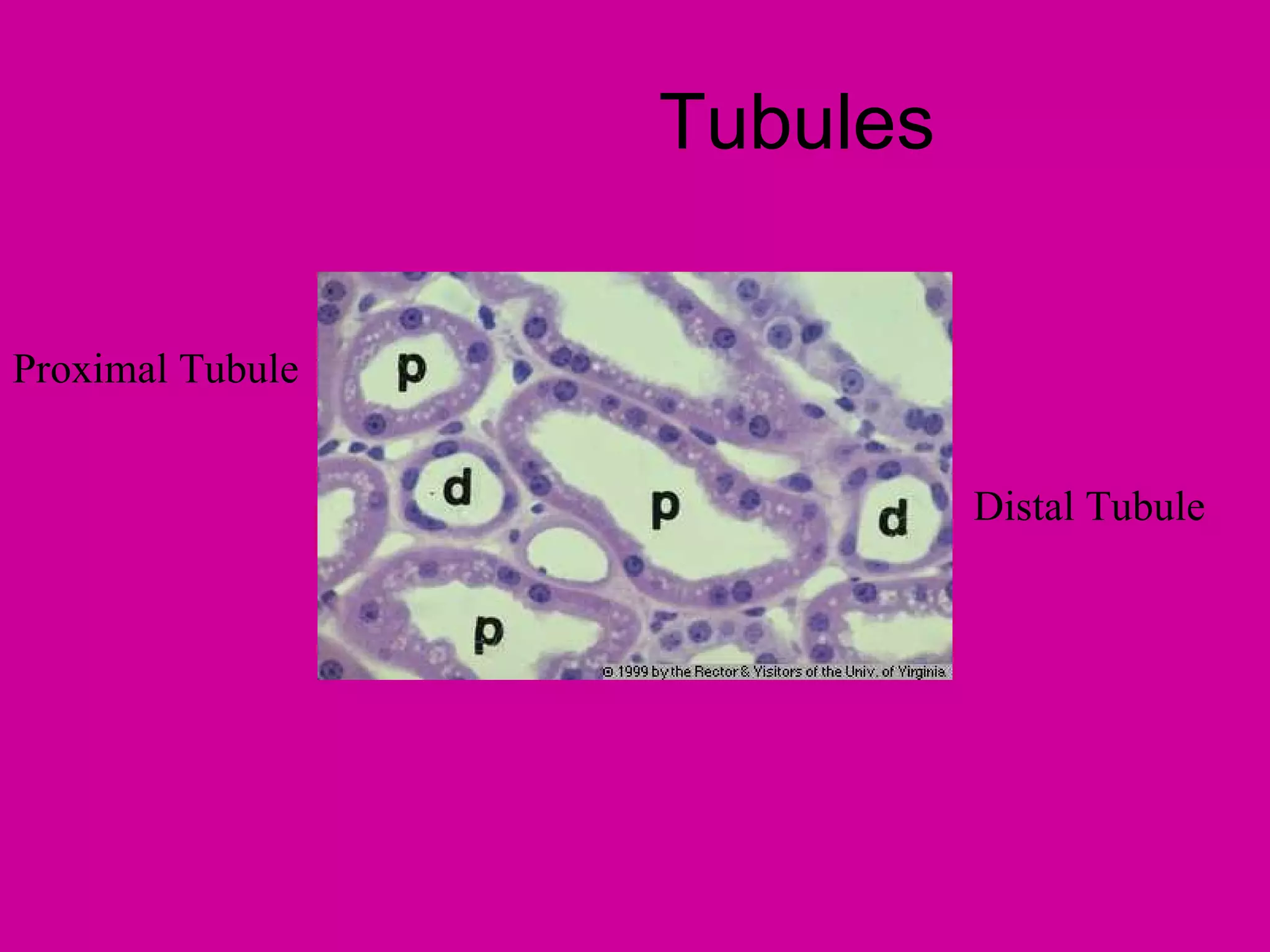
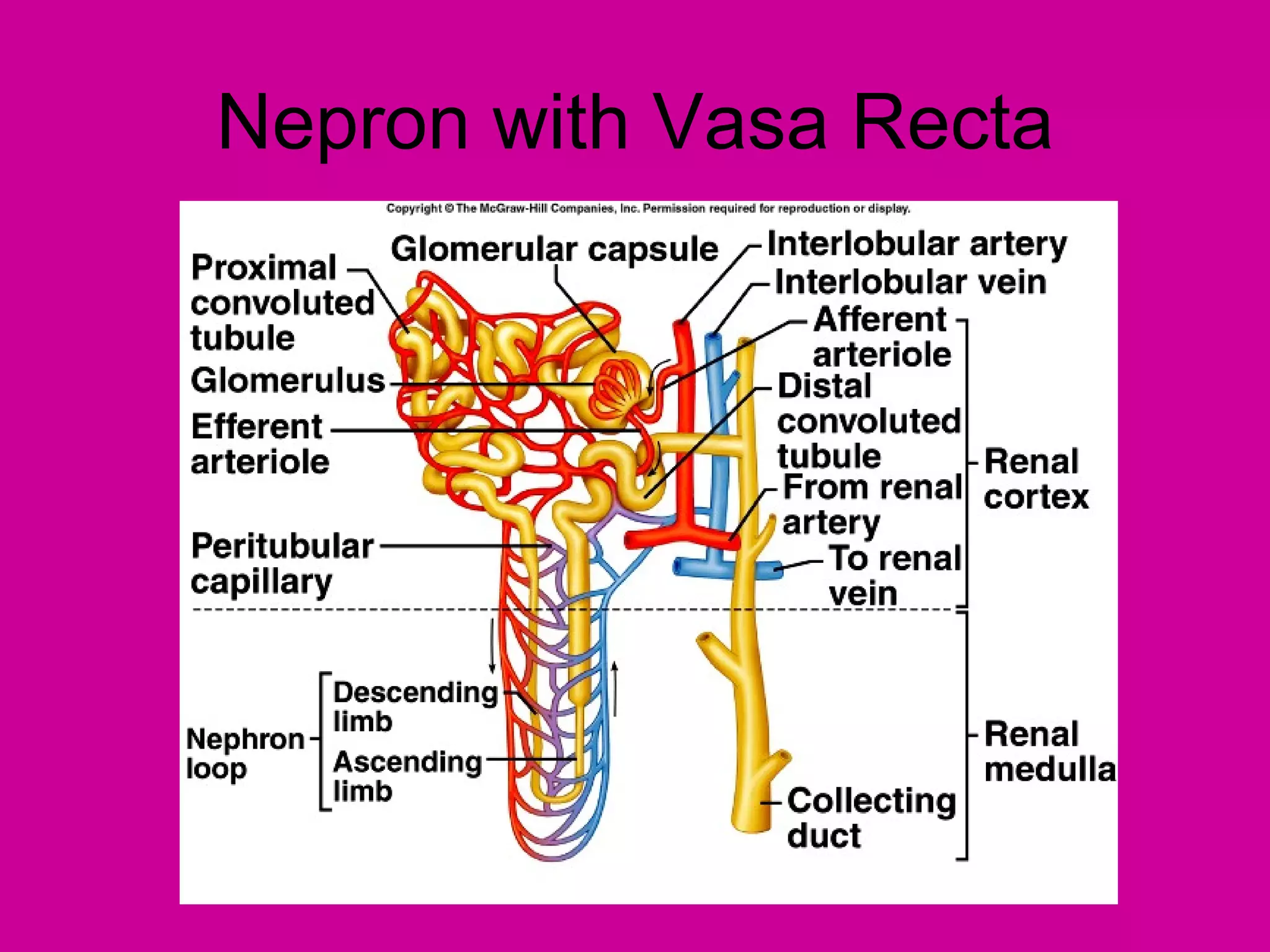
The document describes the anatomy and functions of the human excretory system. It details the major components, including the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys are retroperitoneal and contain nephrons, which are the functional units that filter blood to form urine. The nephrons contain a glomerulus for blood filtration and tubules for reabsorption and secretion. The excretory system regulates fluid balance and volume, removes waste, and controls blood pressure and red blood cell production.