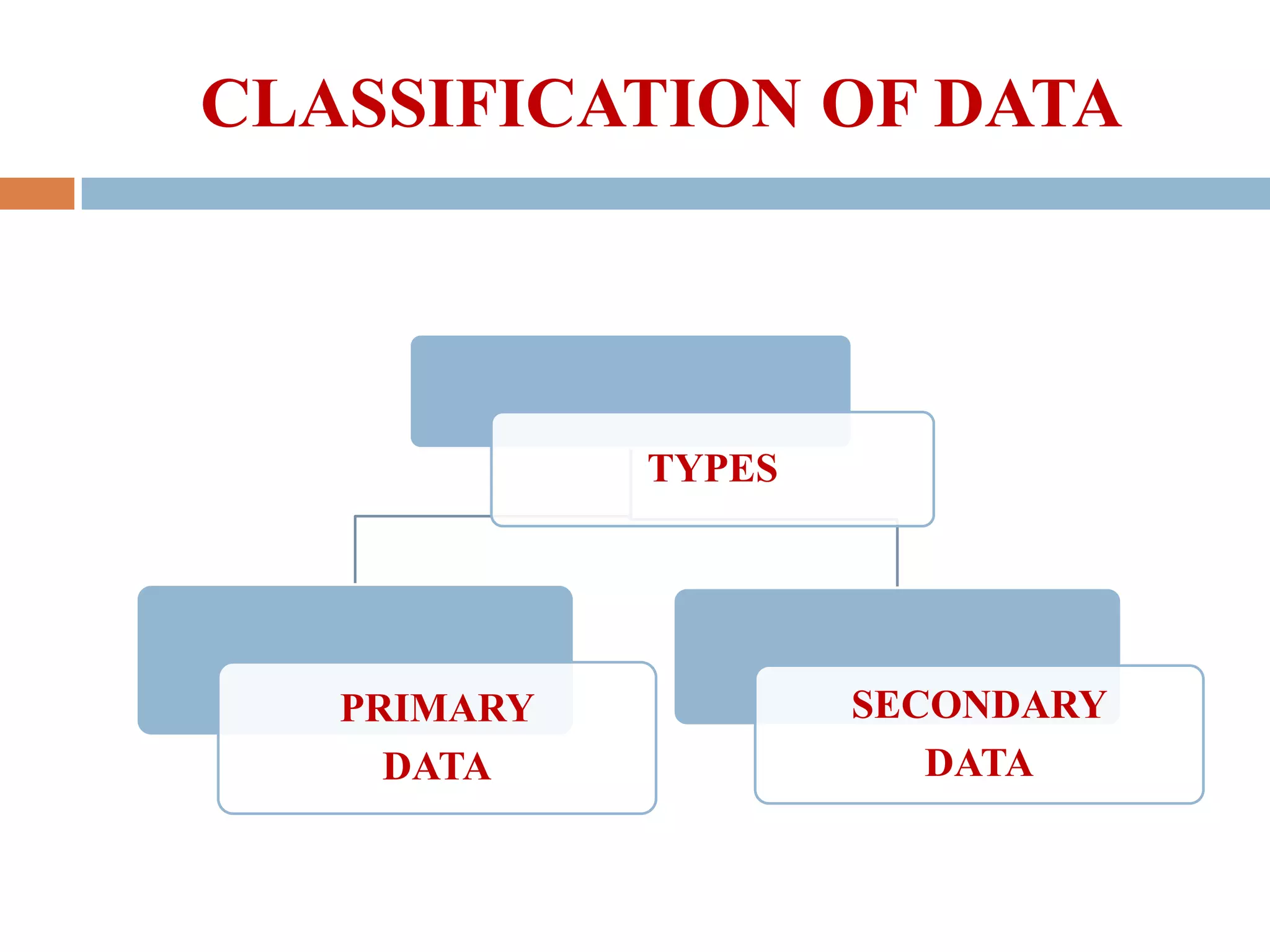
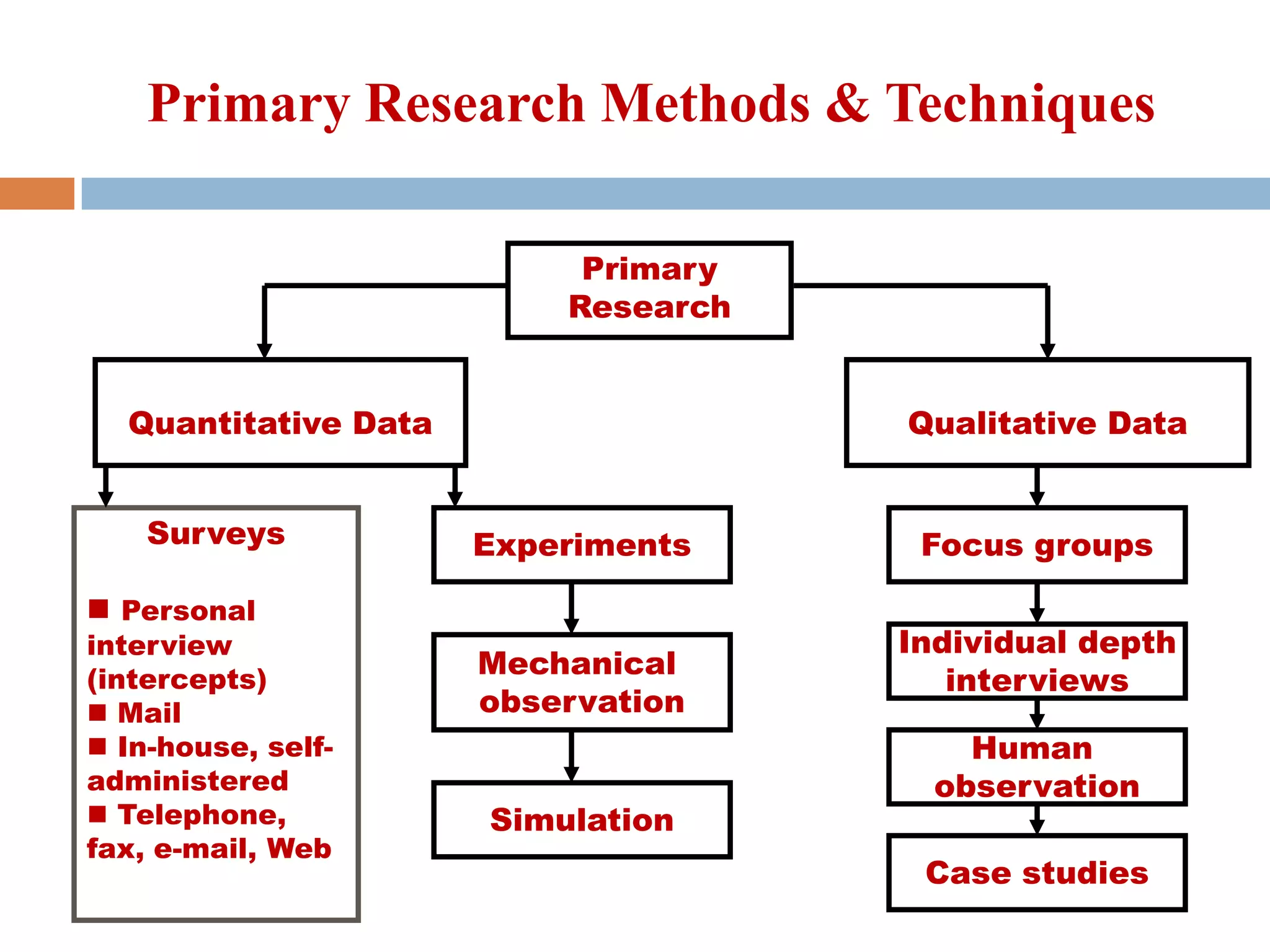
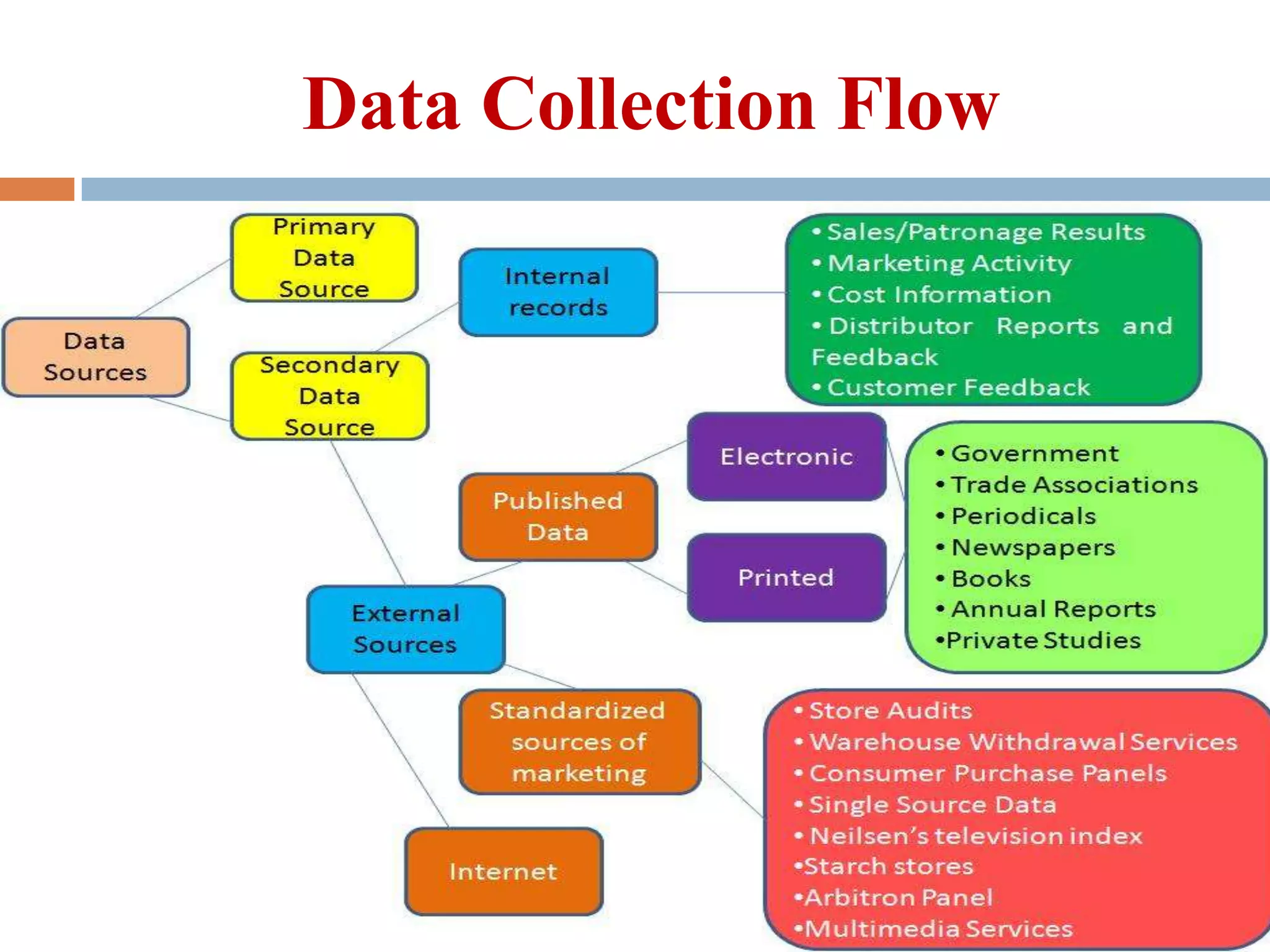
This presentation discusses primary and secondary data collection methods. It begins by defining primary data as original data collected specifically for the research purpose, such as through surveys and interviews. Secondary data refers to data previously collected by others, such as published sources. Both data types are useful but have tradeoffs - primary data directly addresses the research question while secondary data is easier to obtain but may not be specific. The presentation provides examples of primary and secondary data collection techniques and their respective advantages and disadvantages.