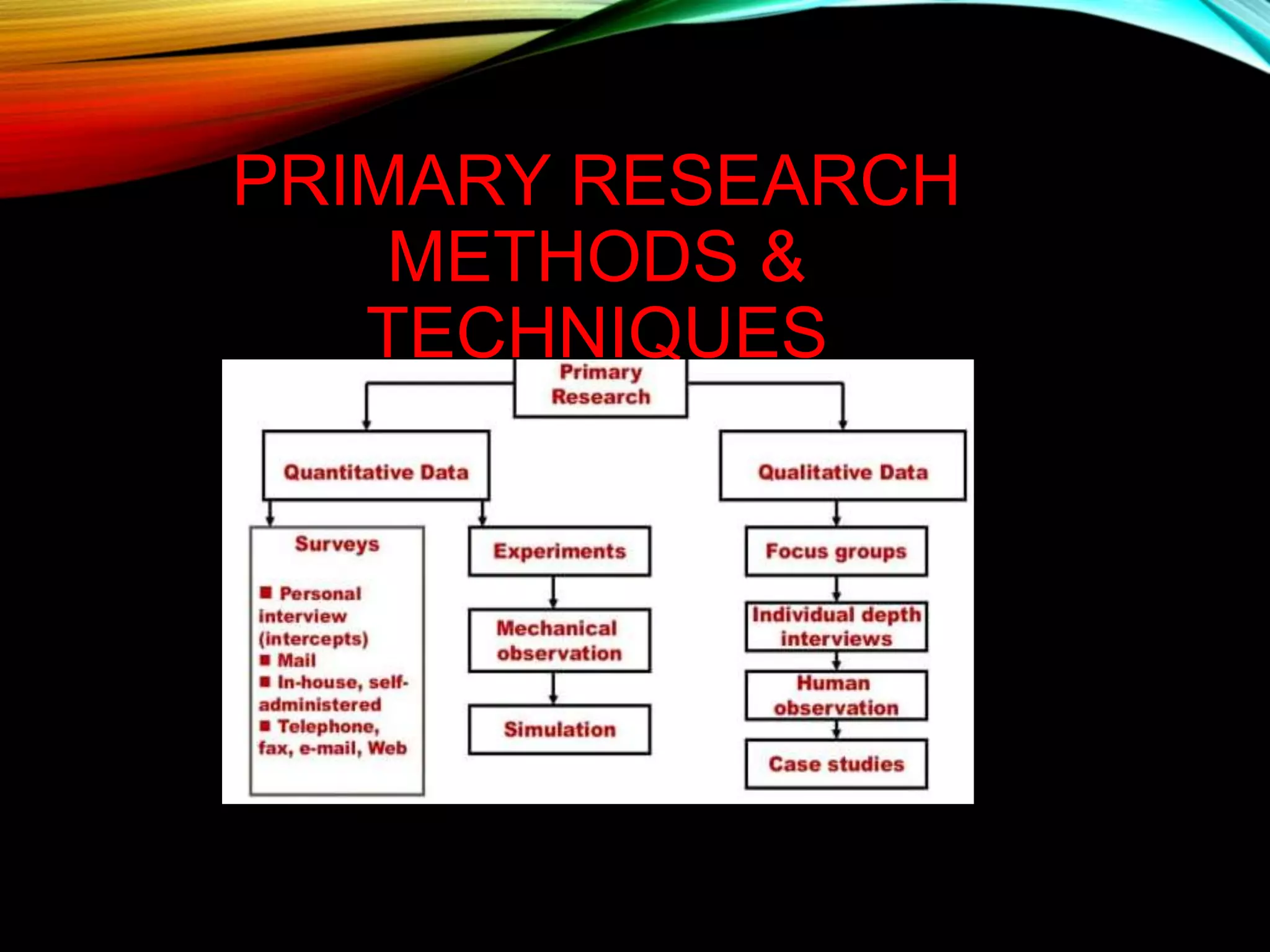
This document discusses primary and secondary data collection methods. Primary data involves directly collecting original data through methods like questionnaires. This allows for targeted issues to be addressed but is costly and time-consuming. Secondary data refers to previously collected data from sources like books, journals and internal records. It is less costly and time-consuming than primary data but may not be specific to the researcher's needs. The document outlines various primary and secondary data collection techniques and their advantages and disadvantages.