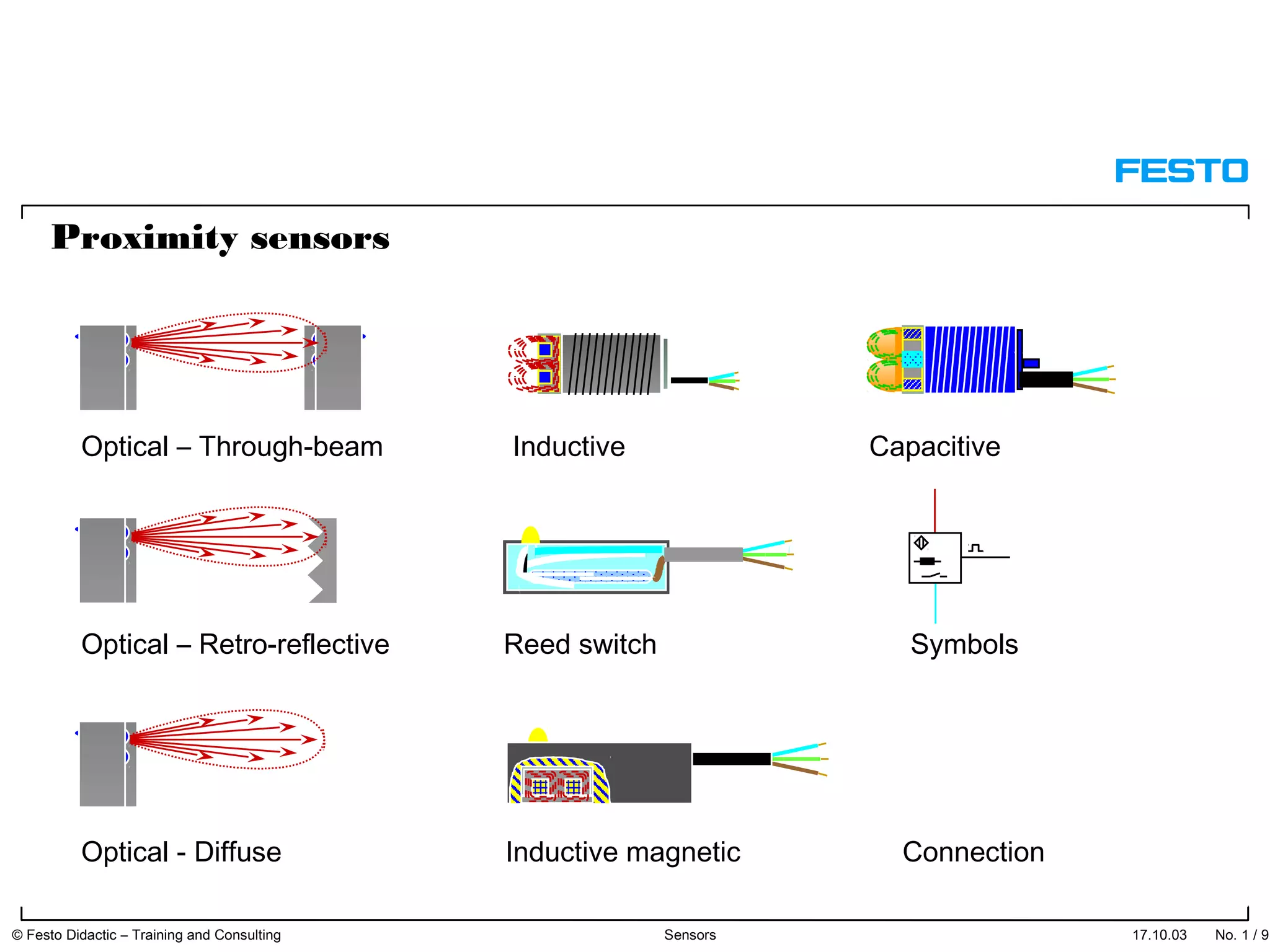
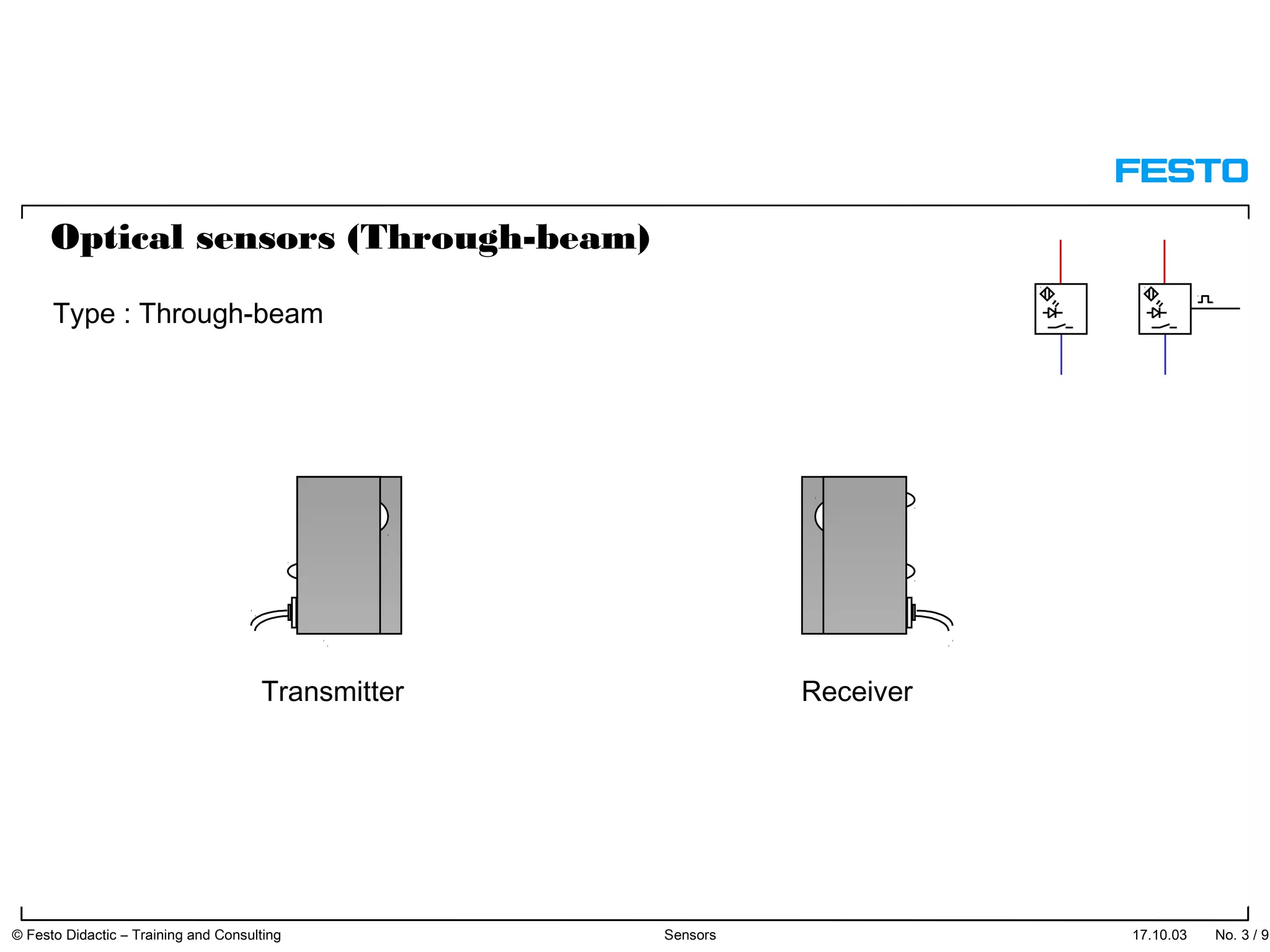
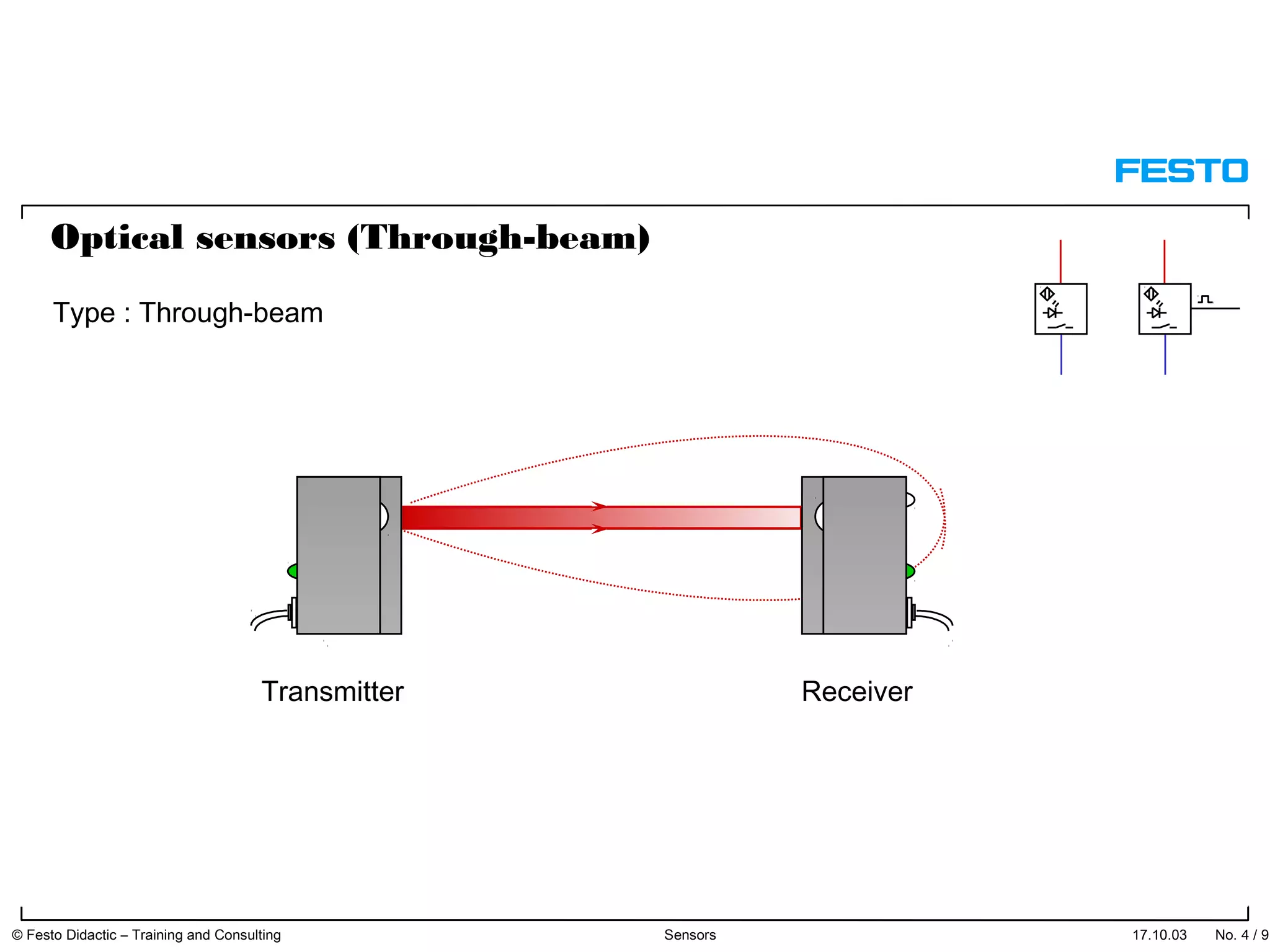
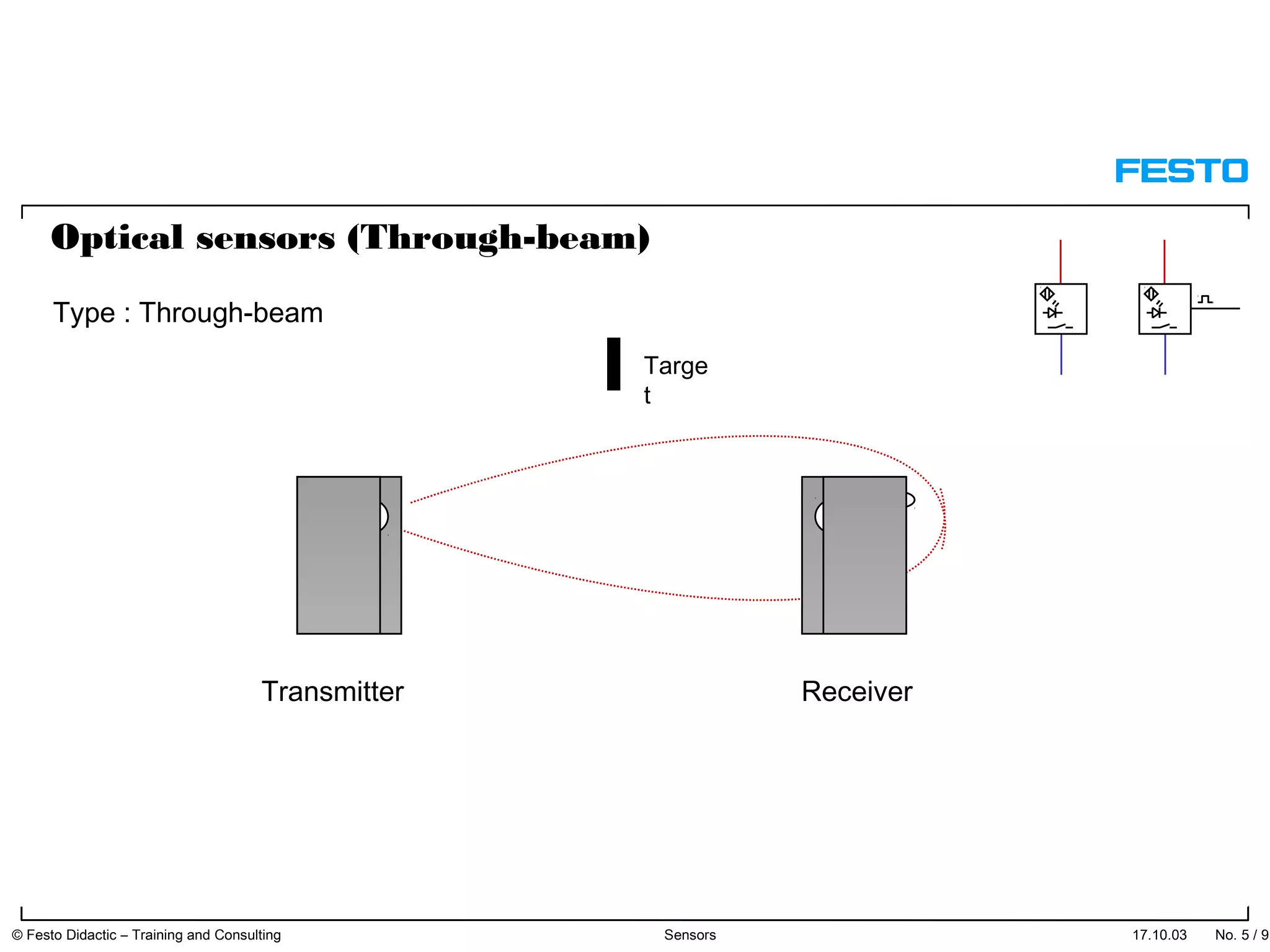
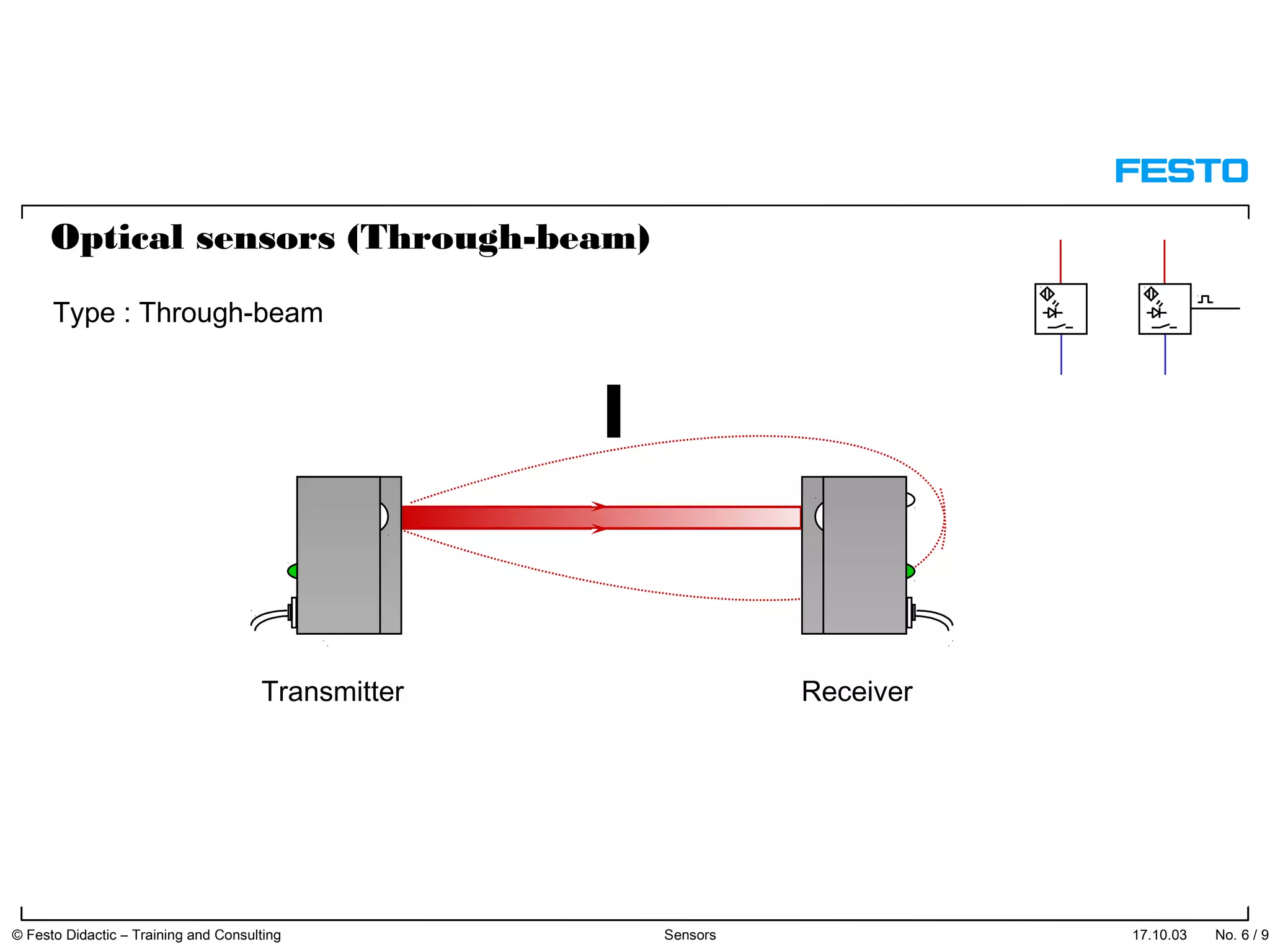
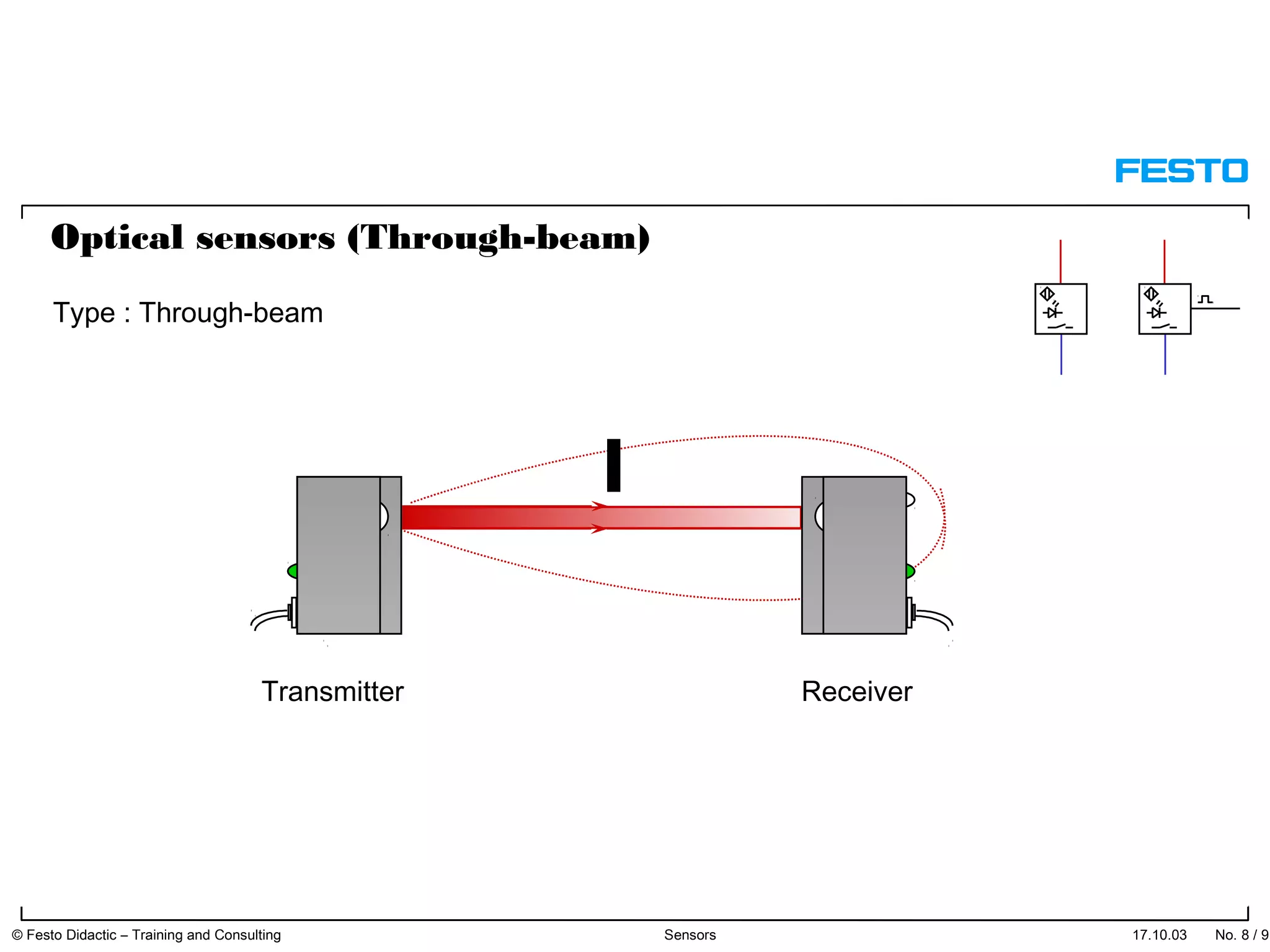
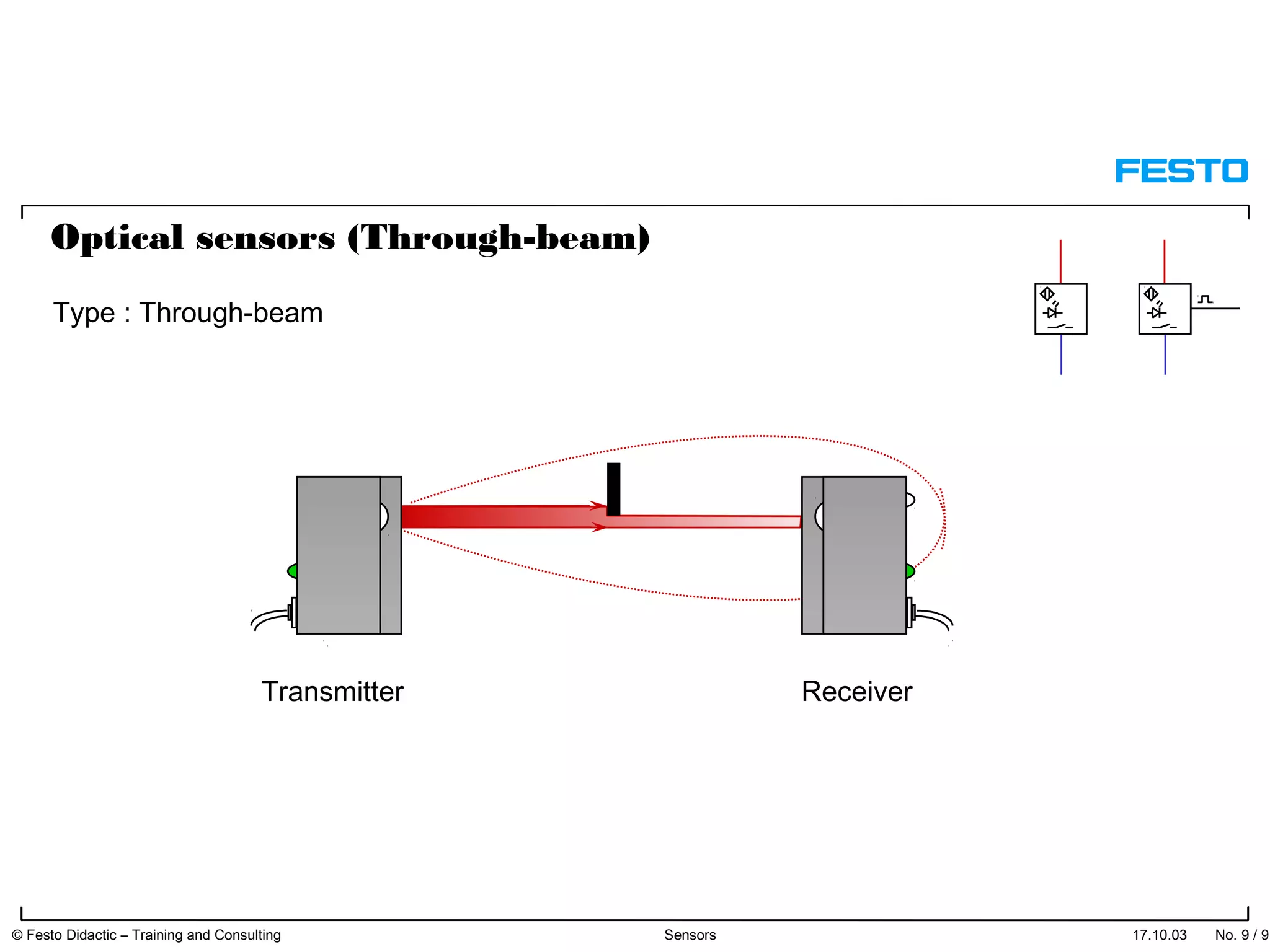
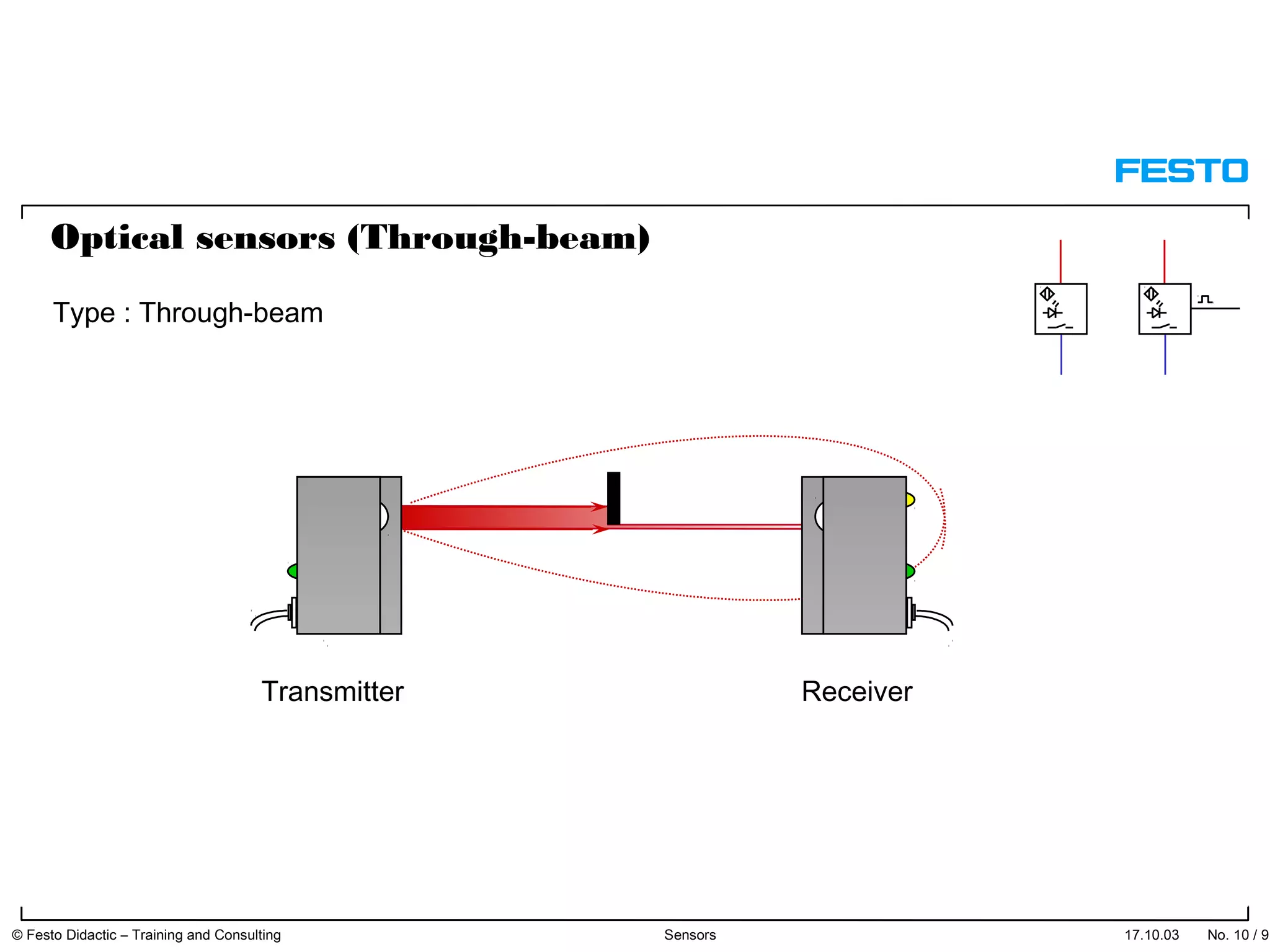
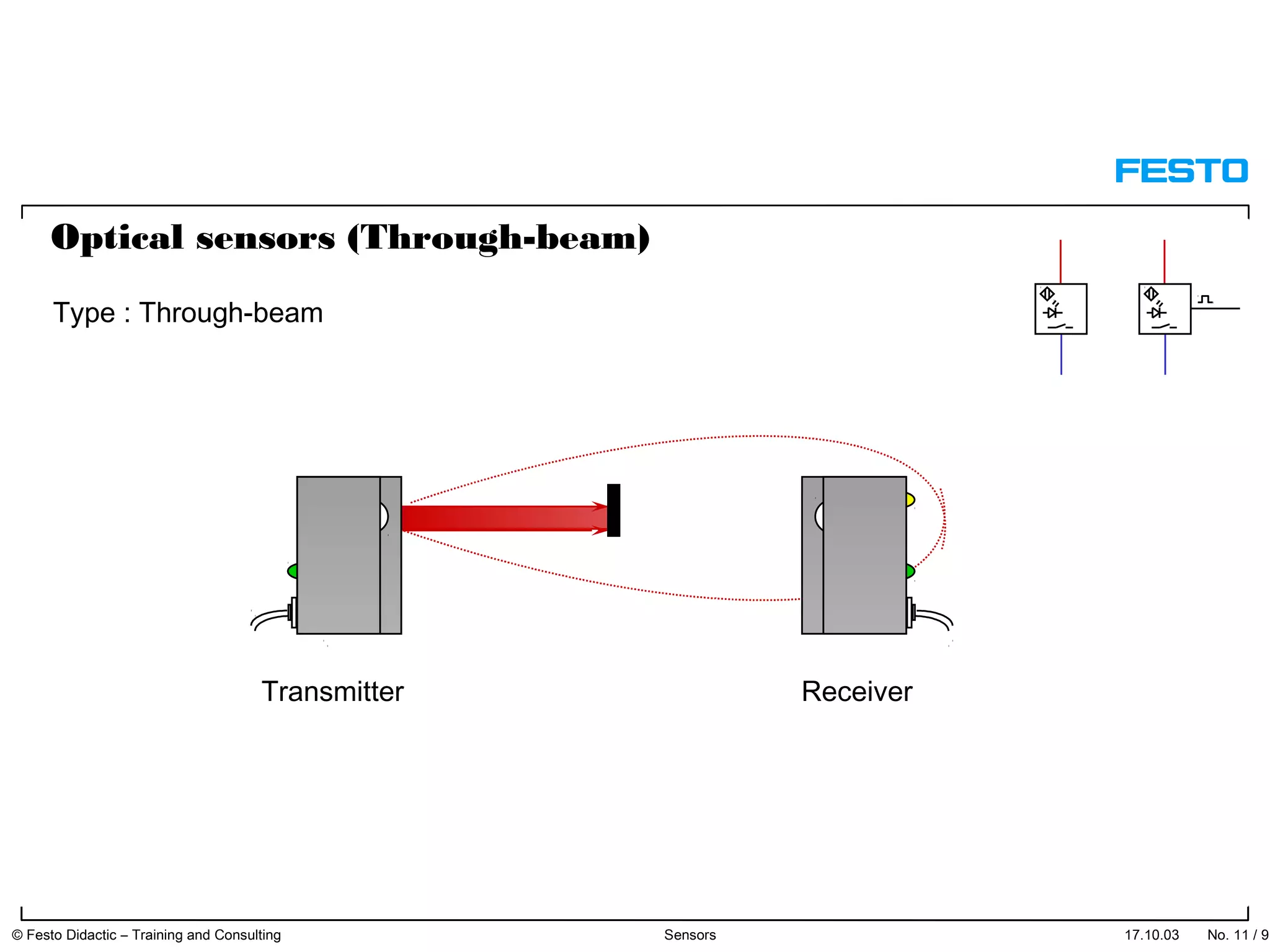
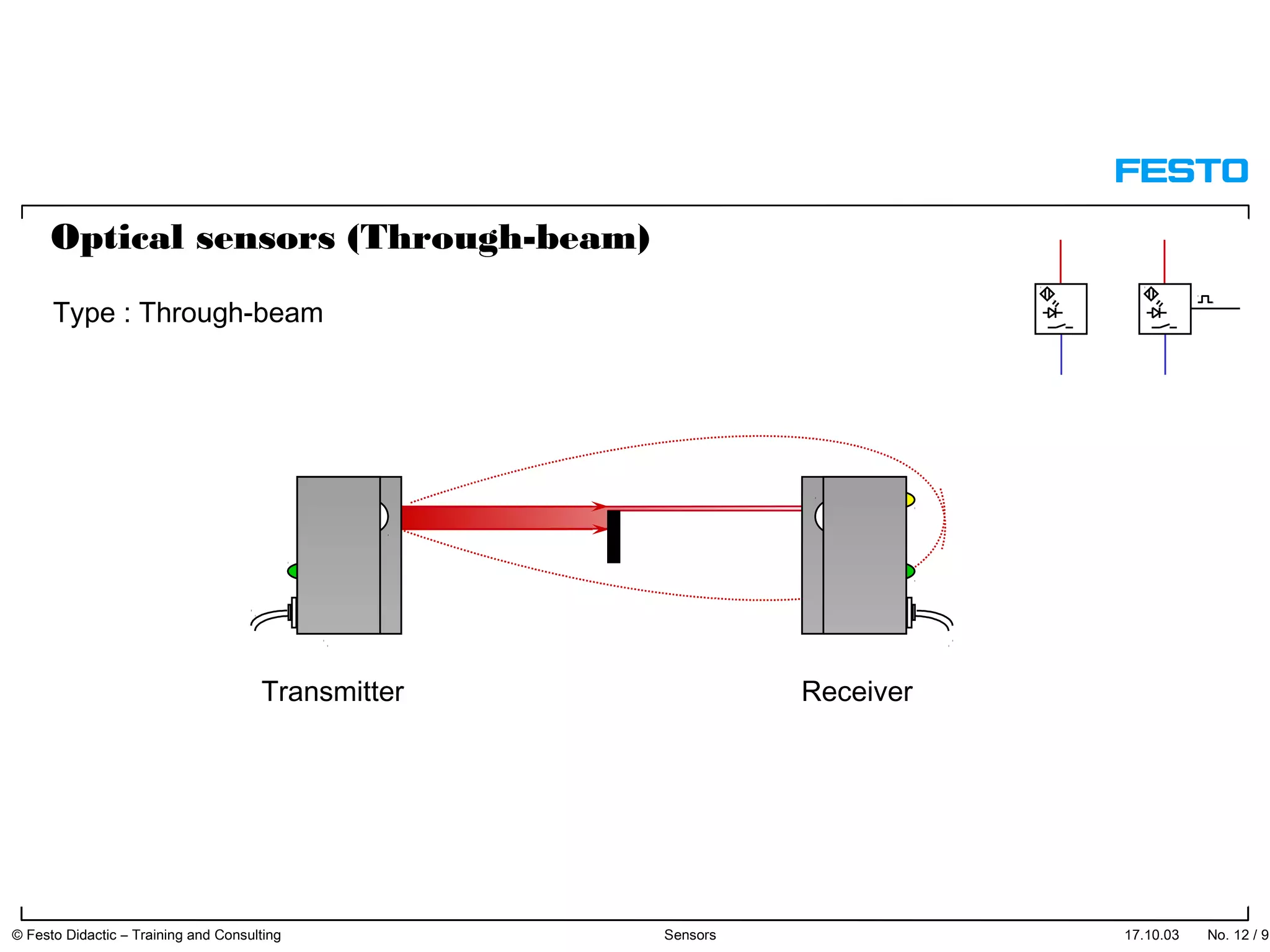
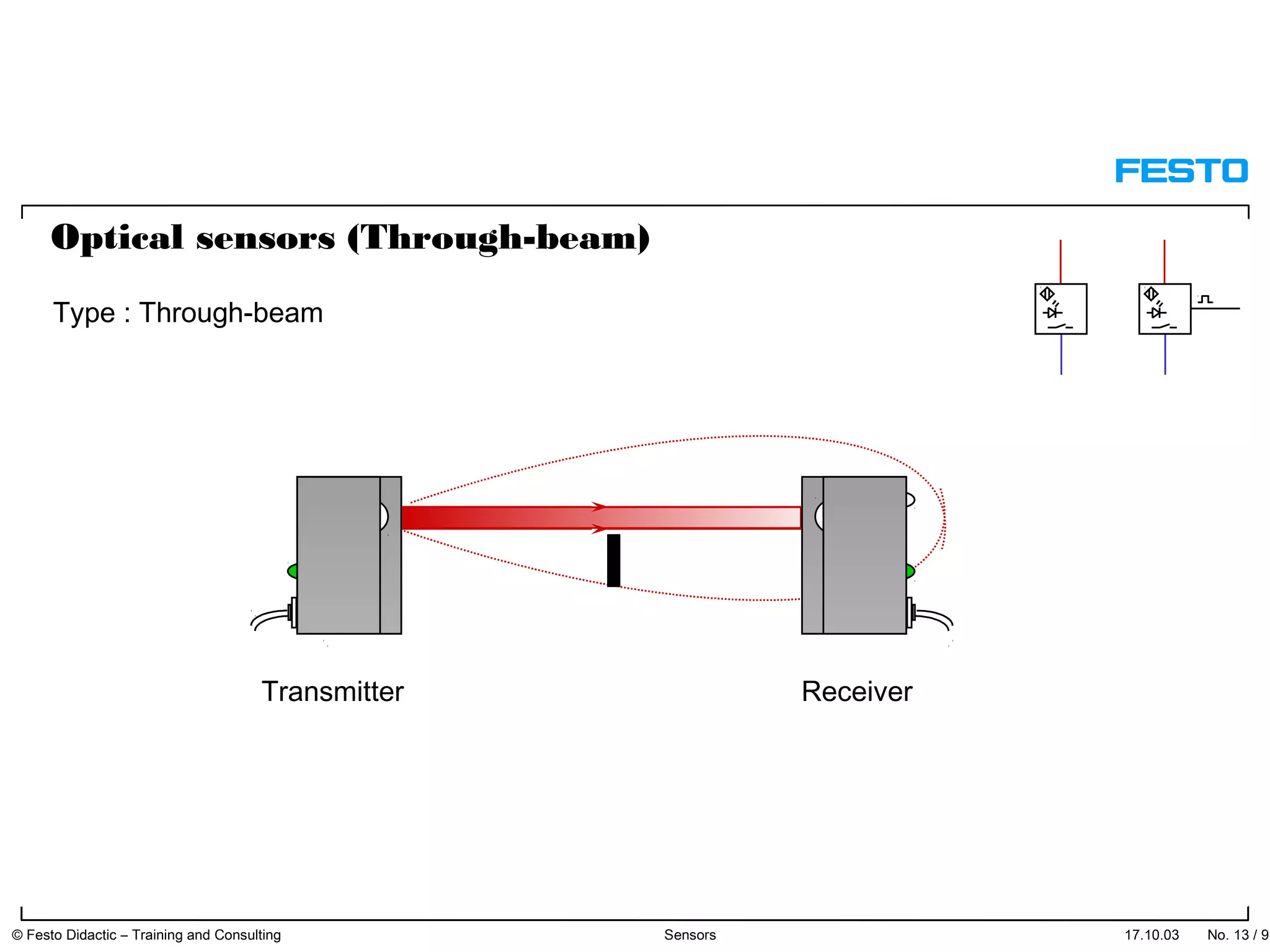
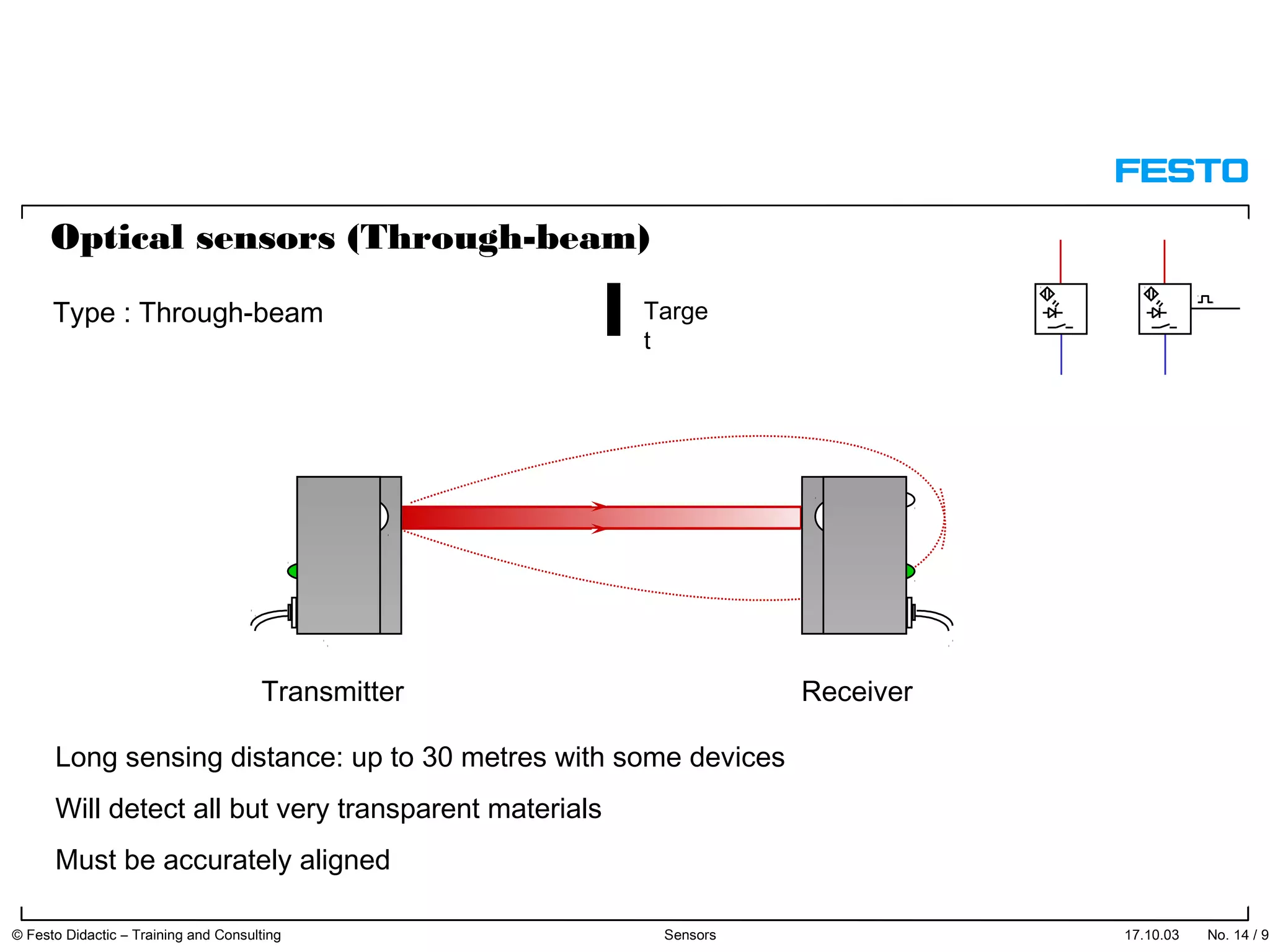
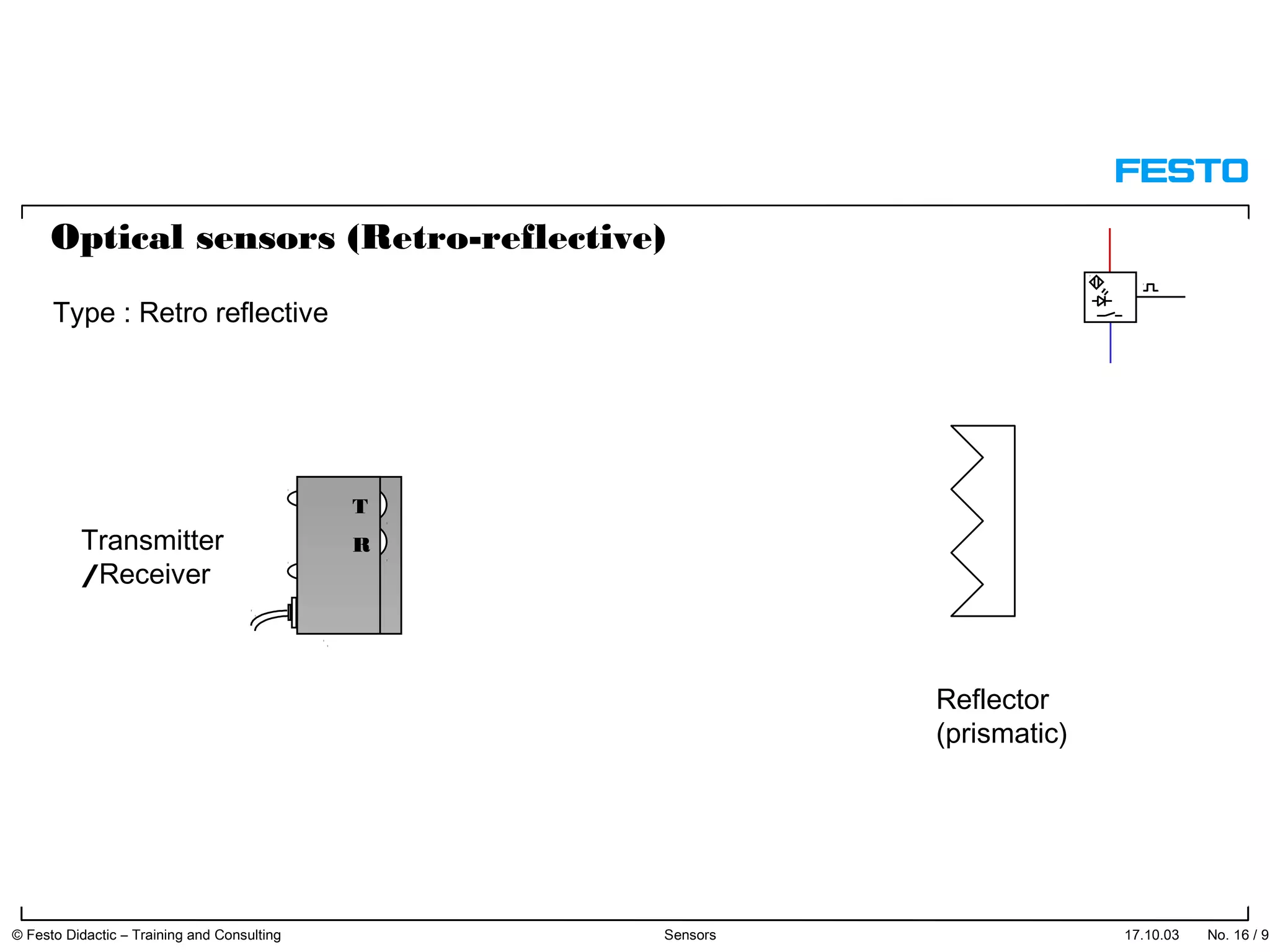
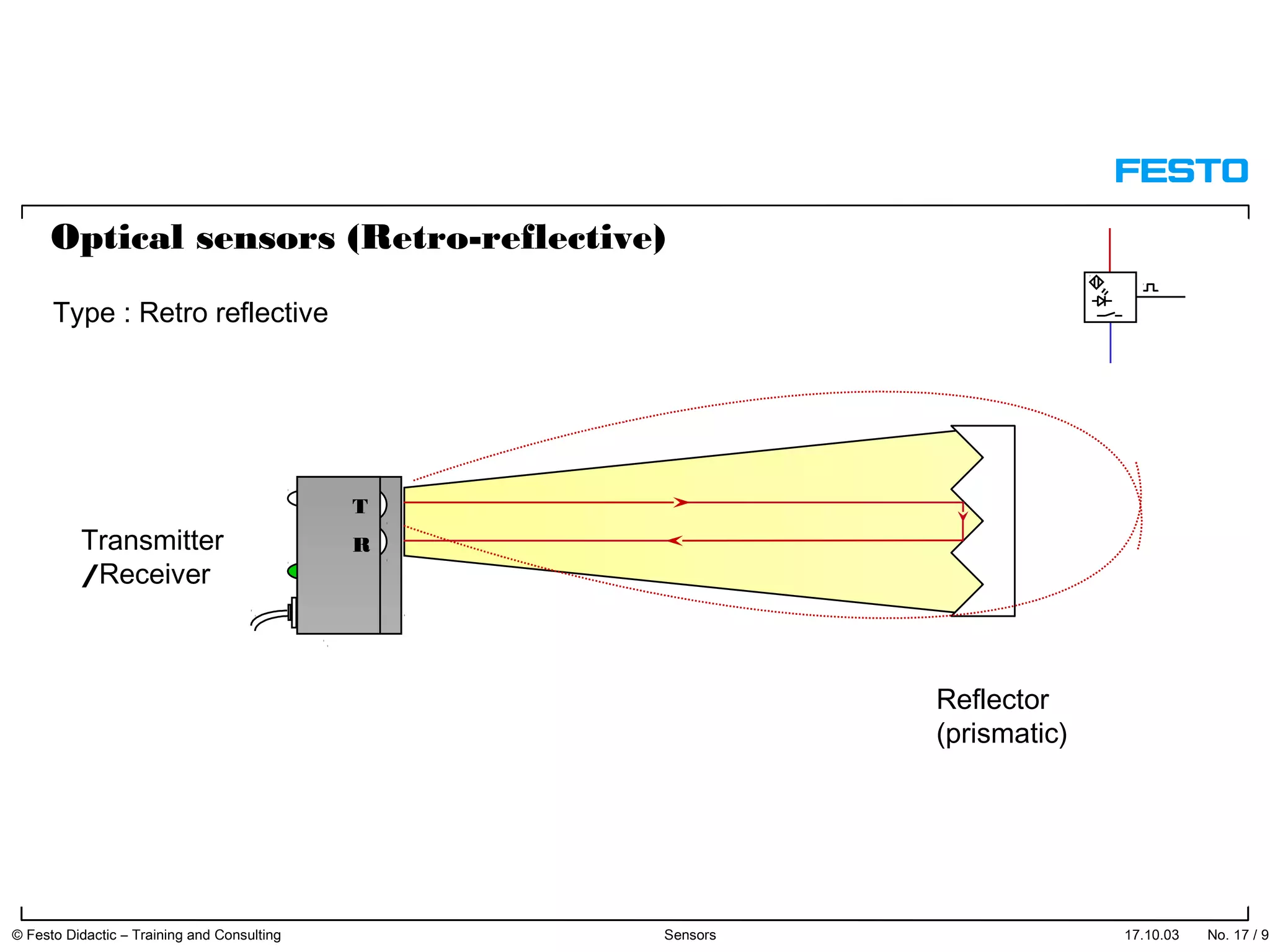
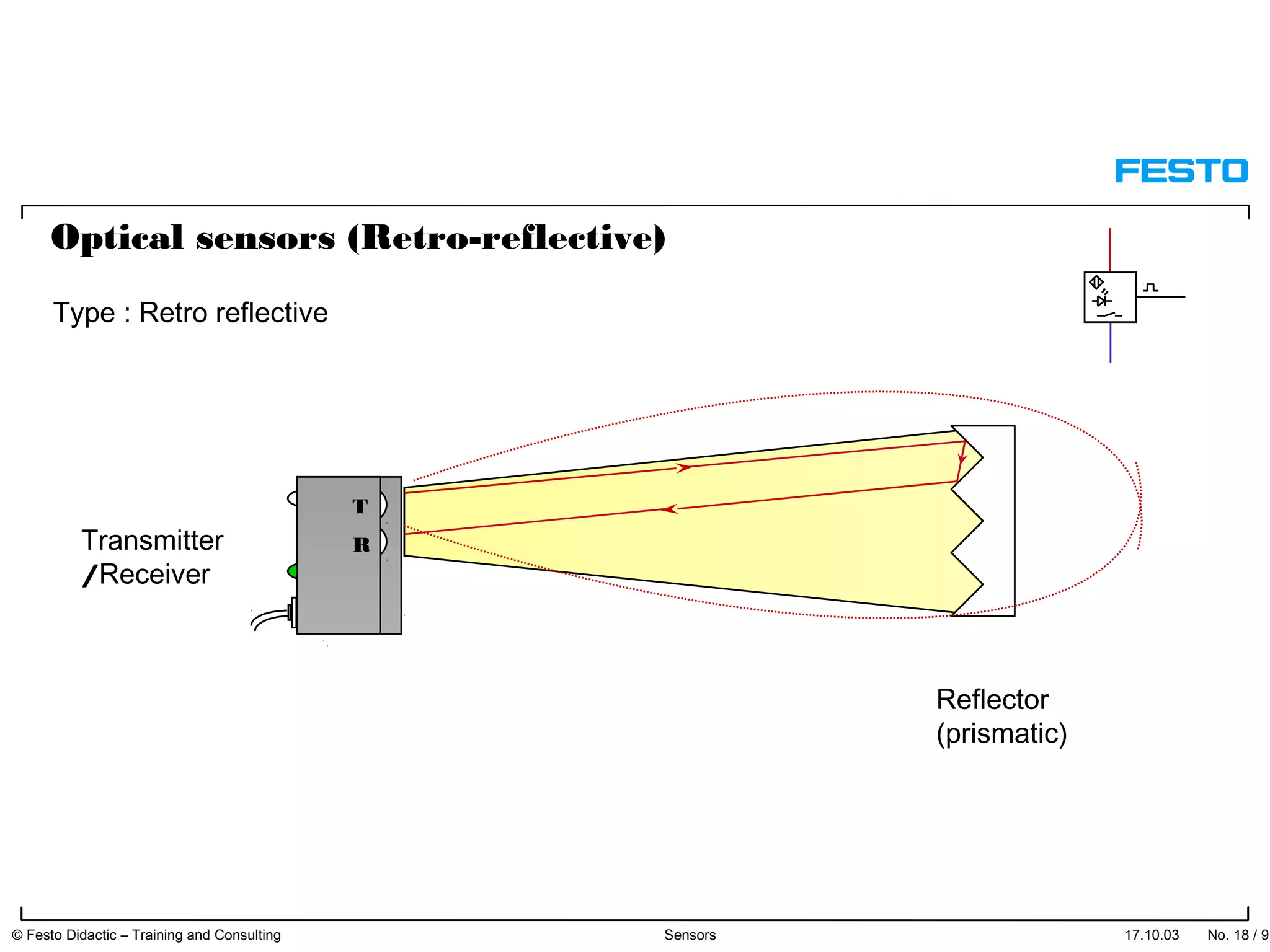
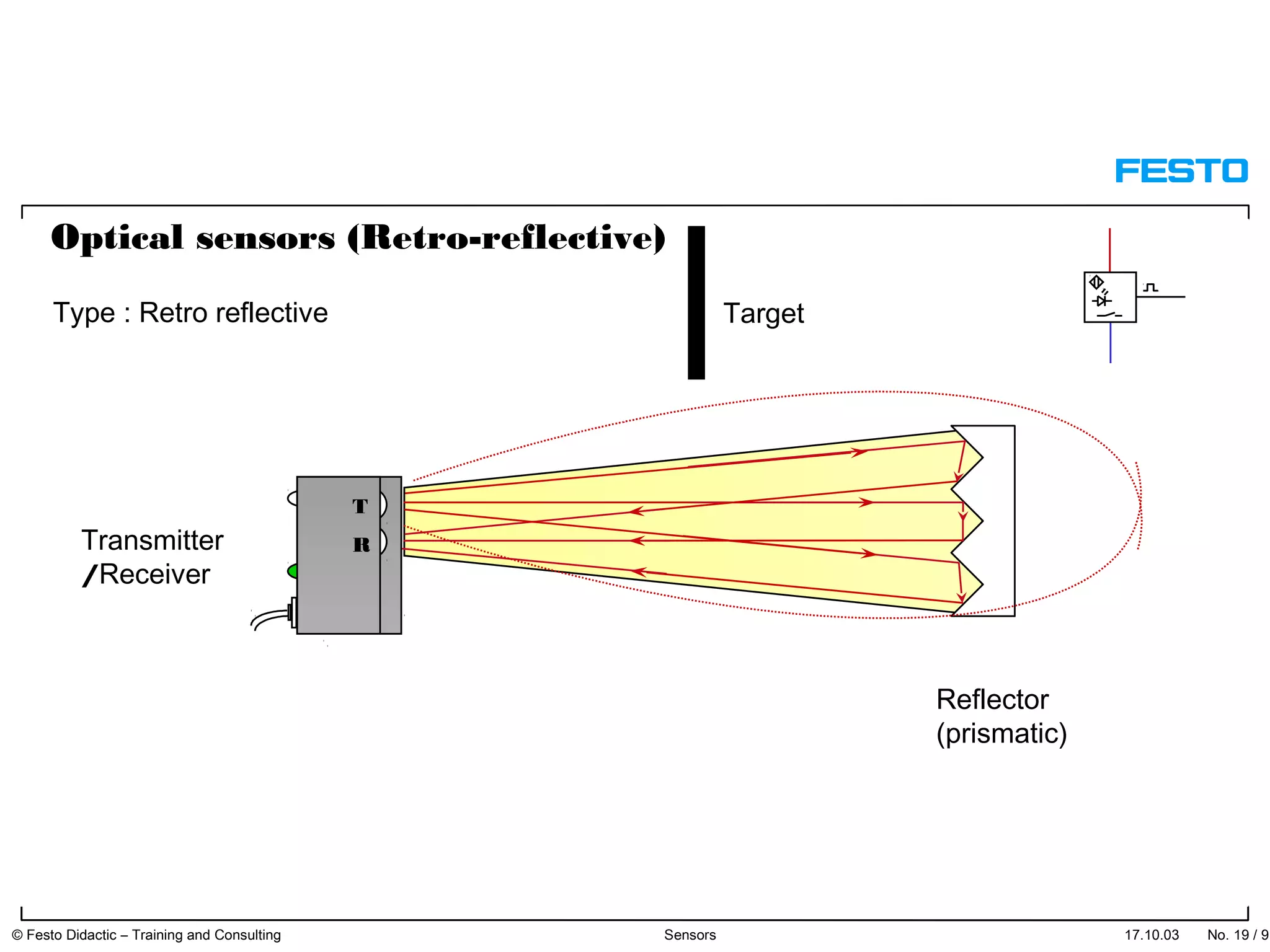
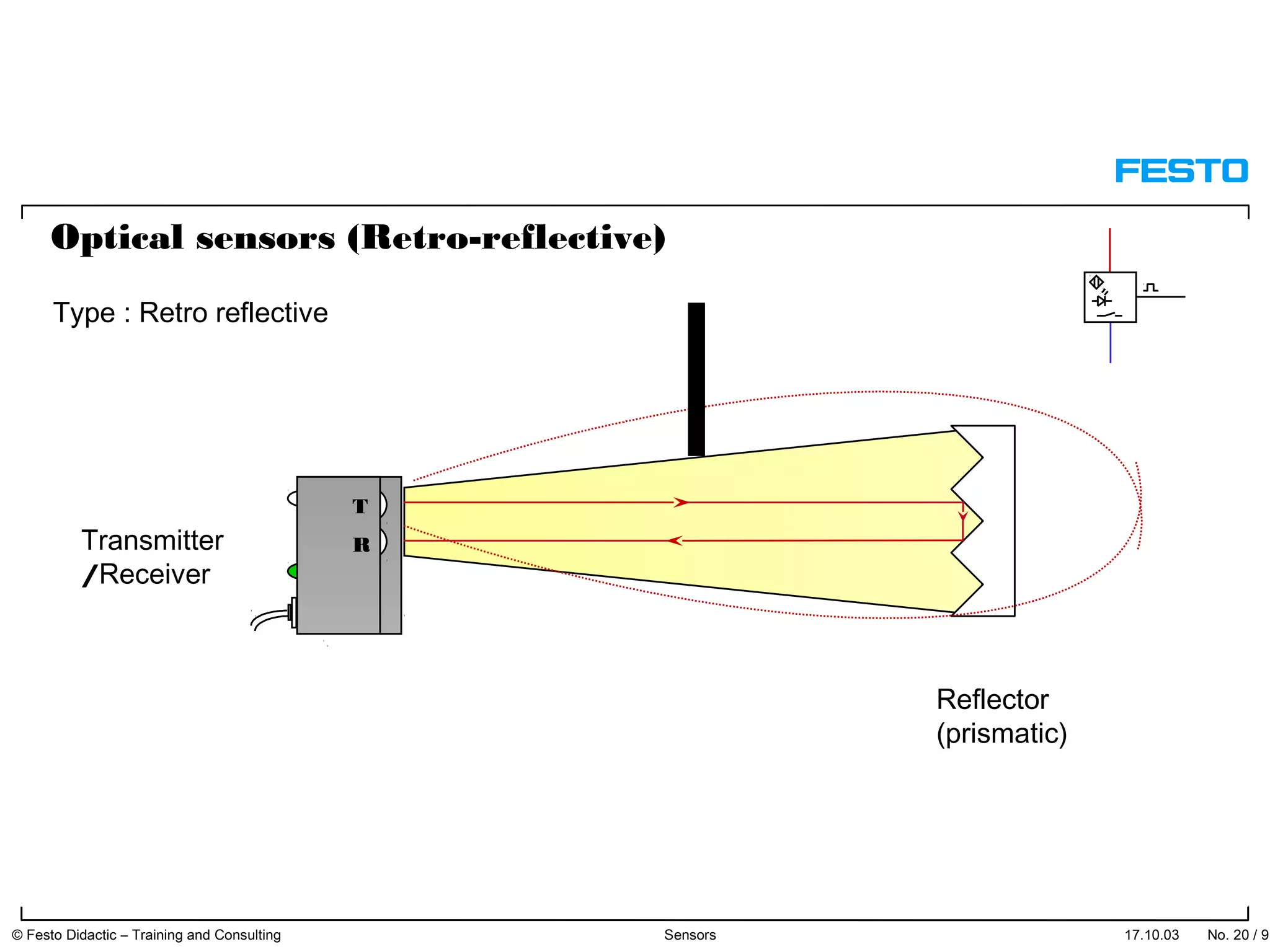
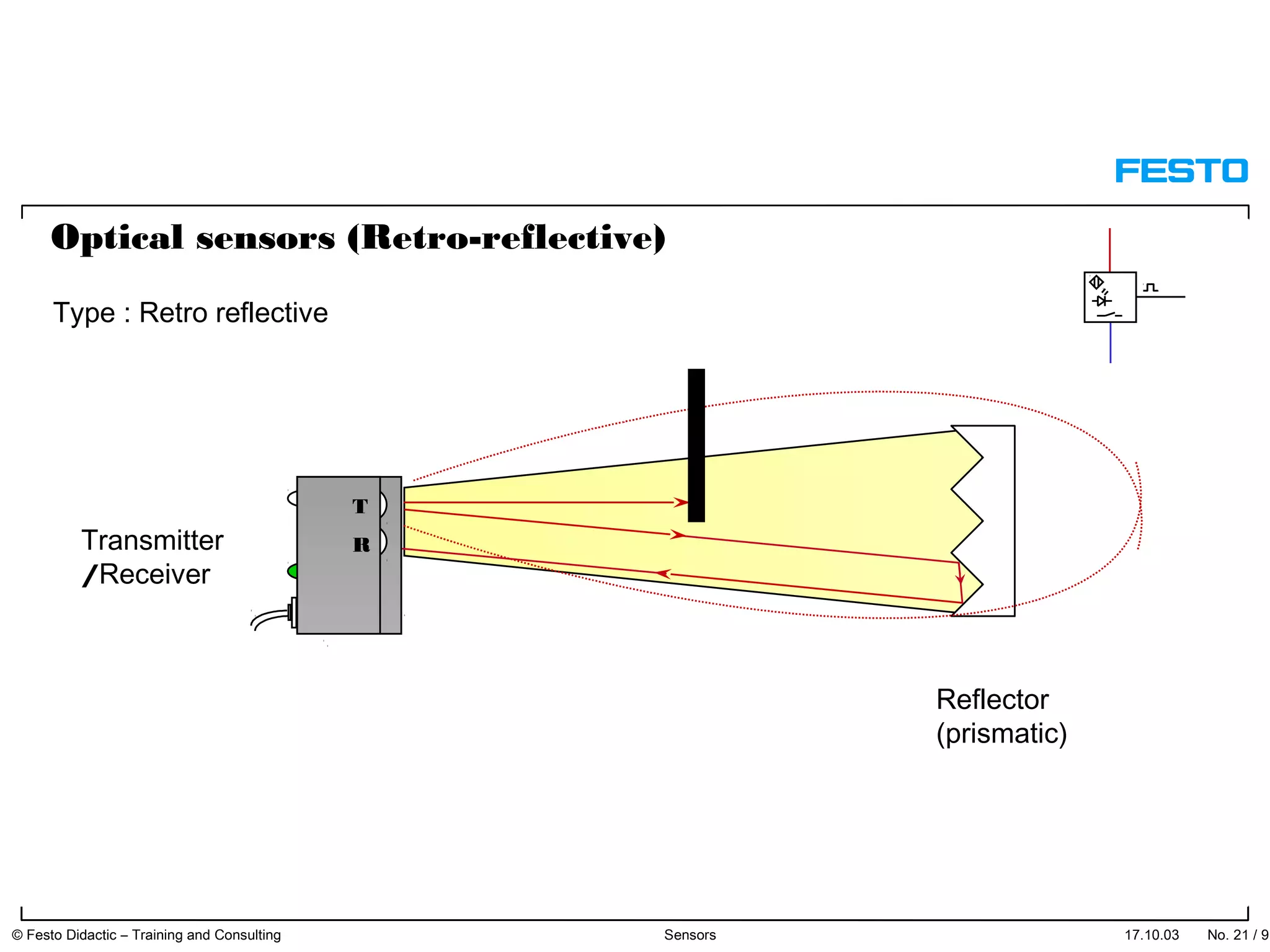
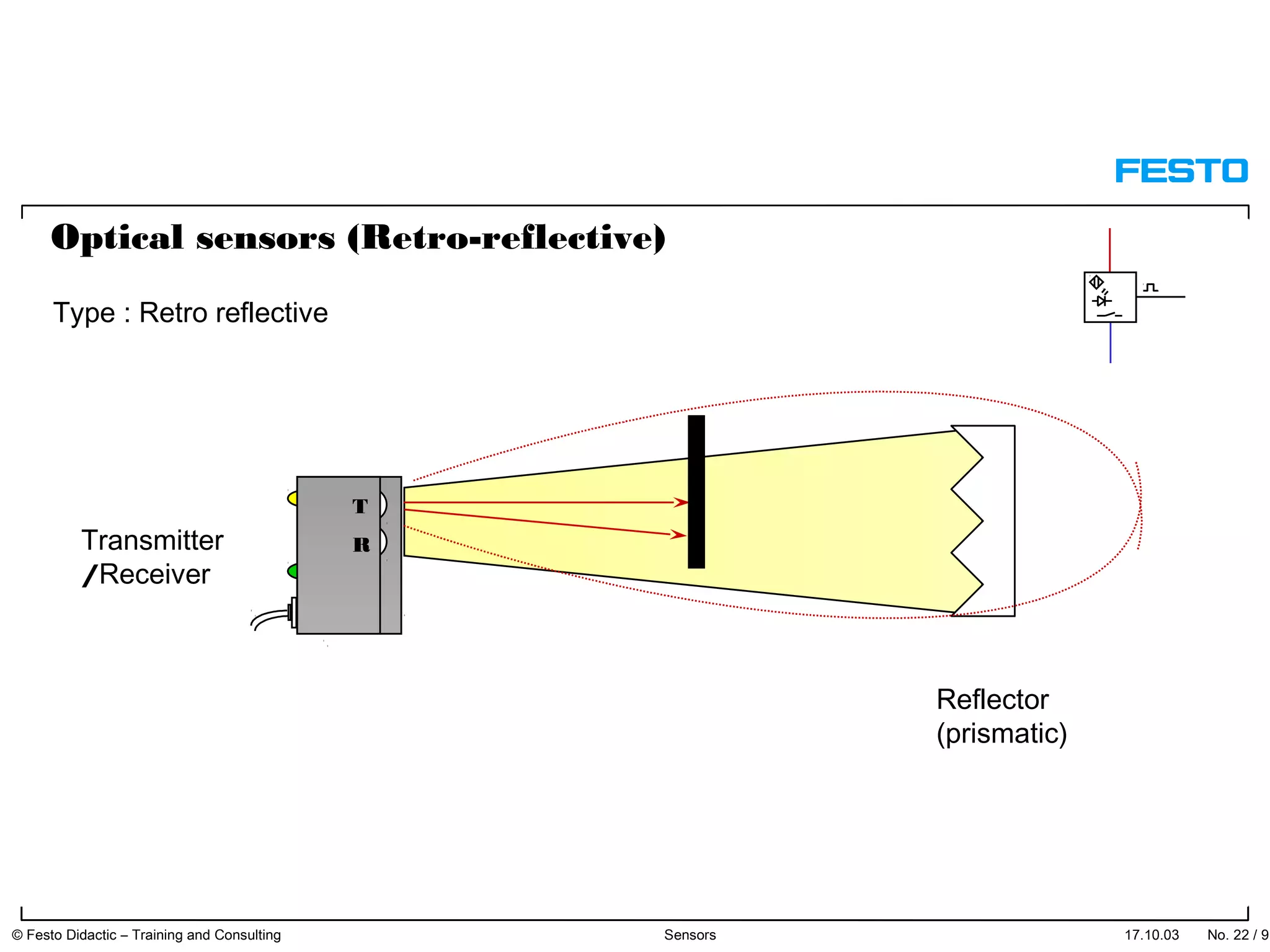
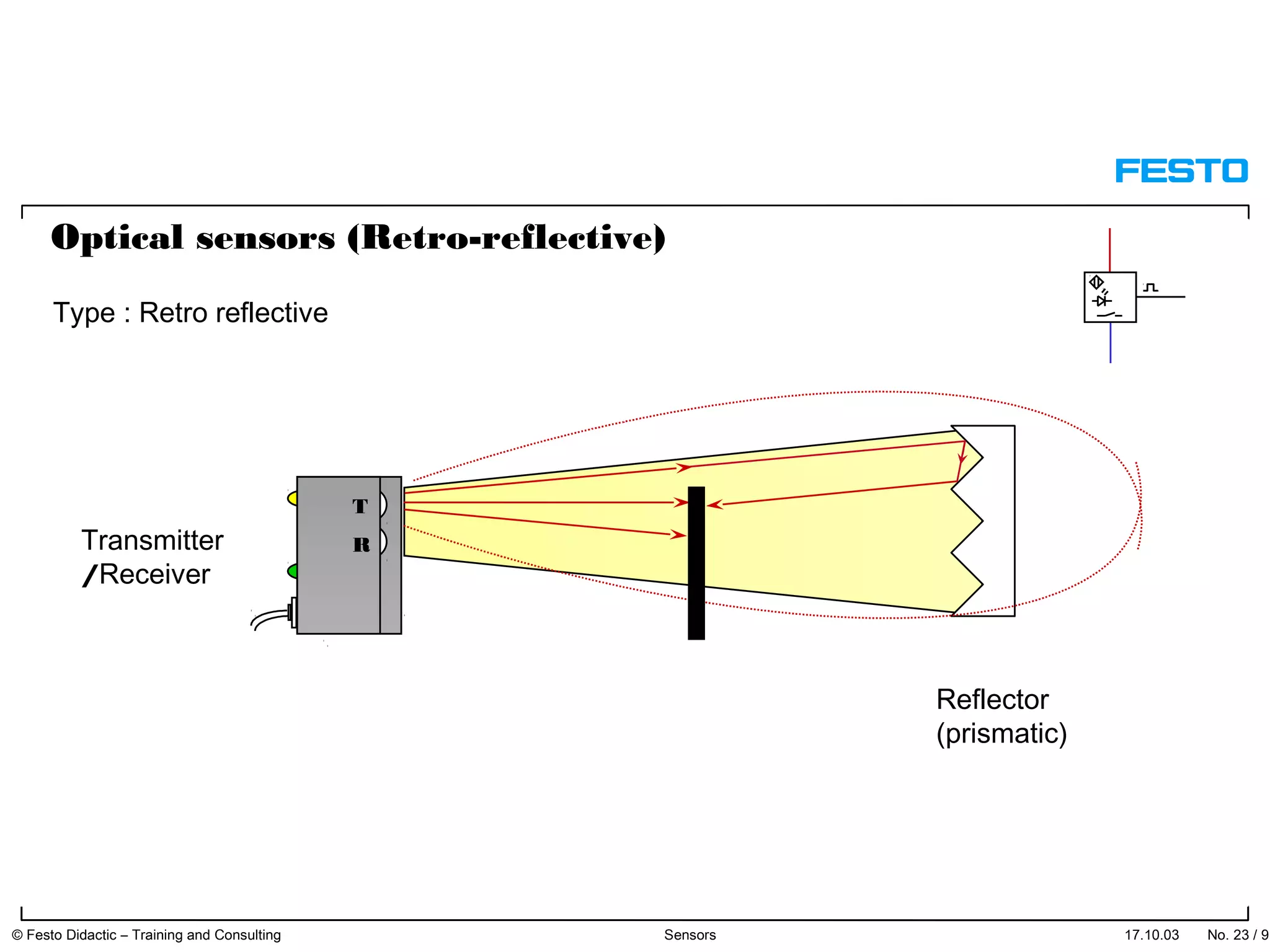
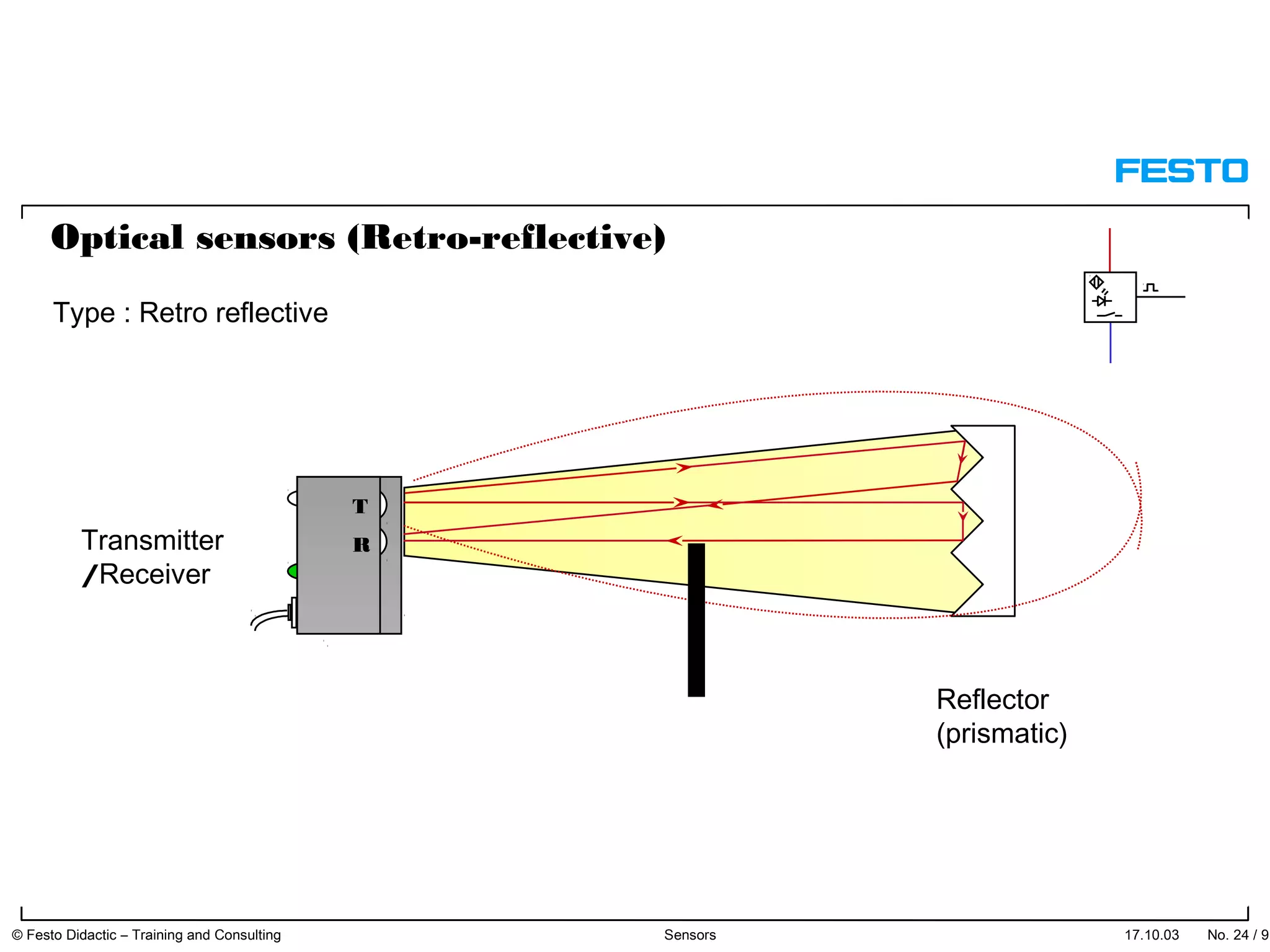
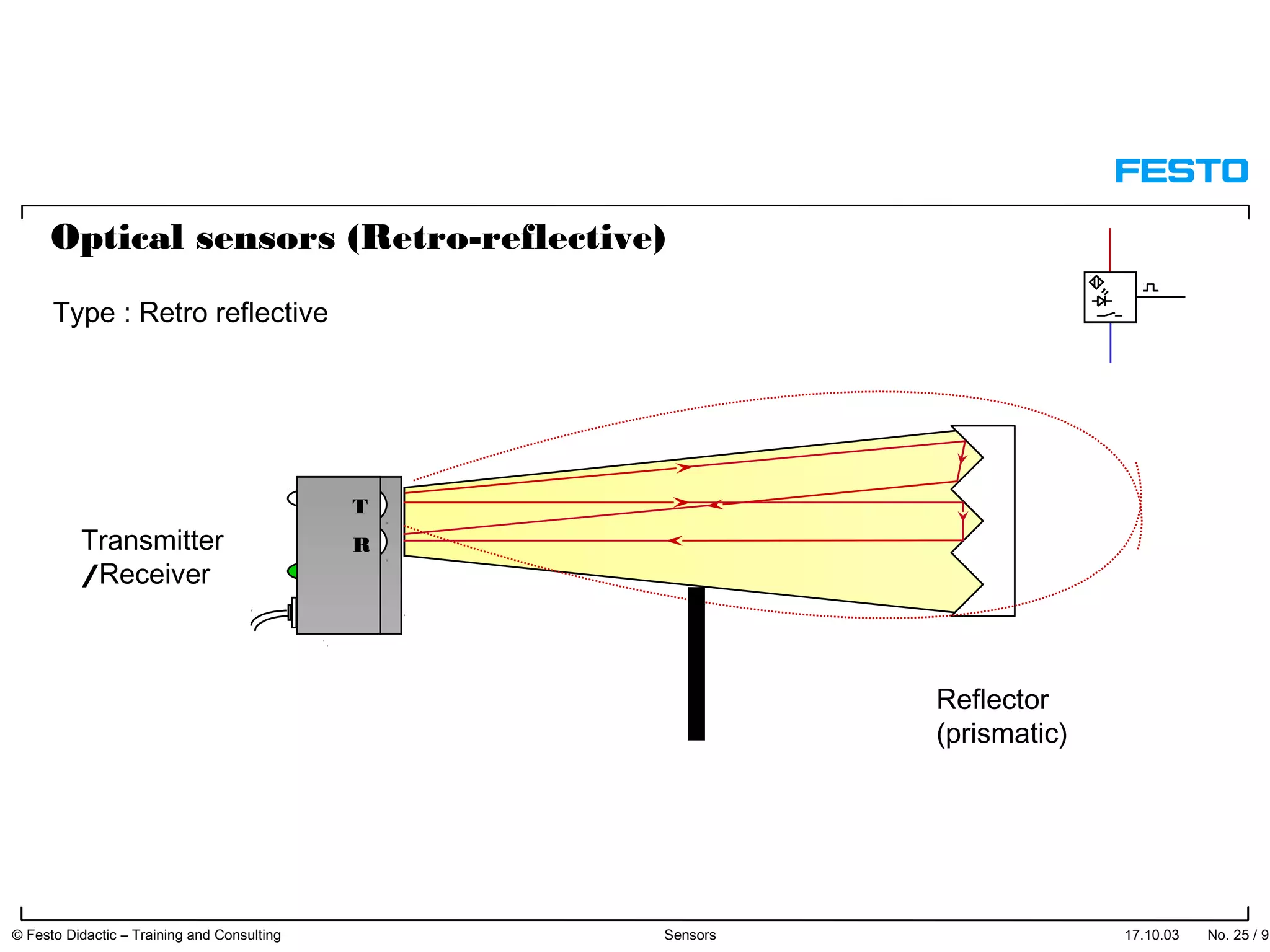
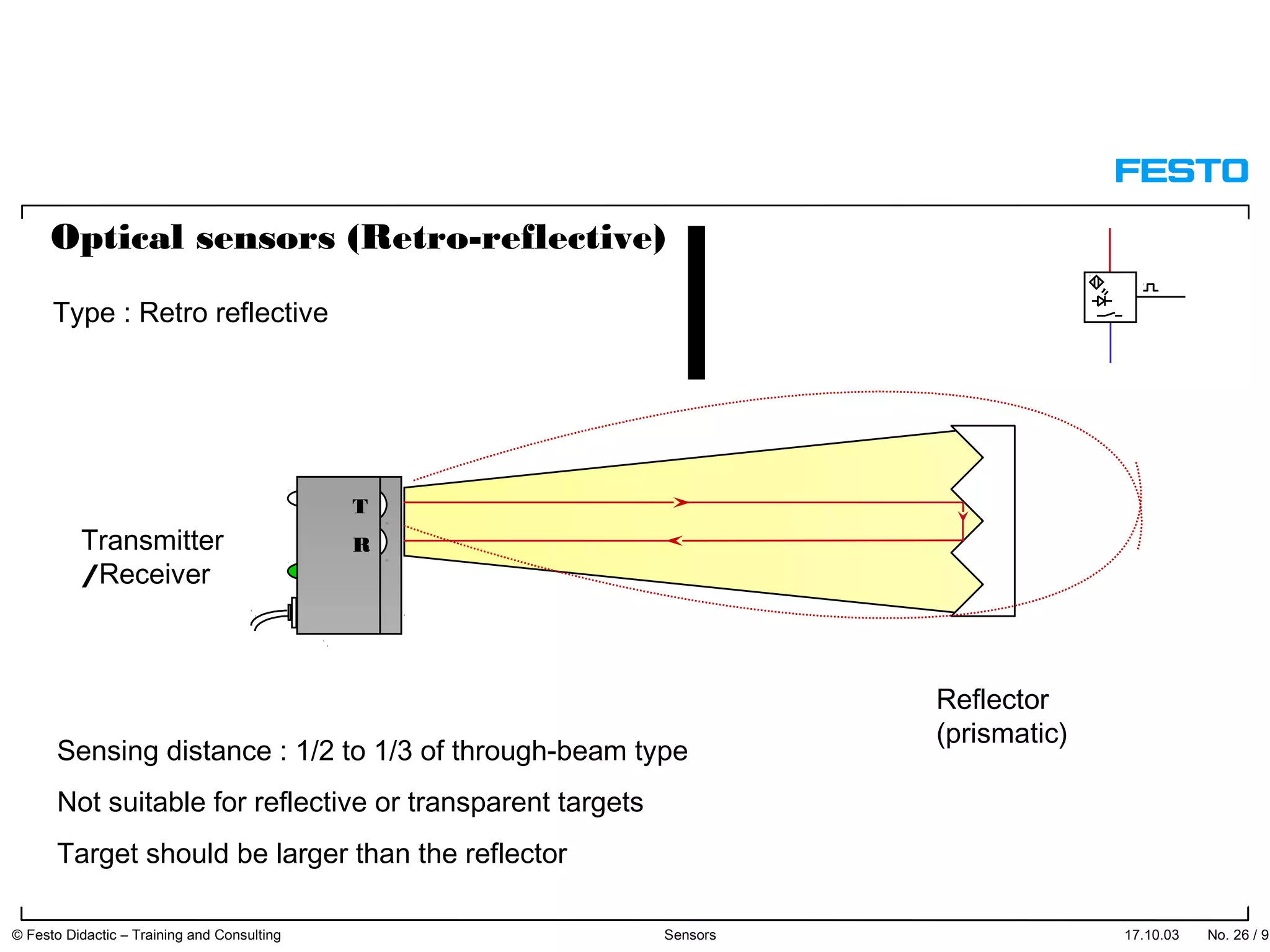
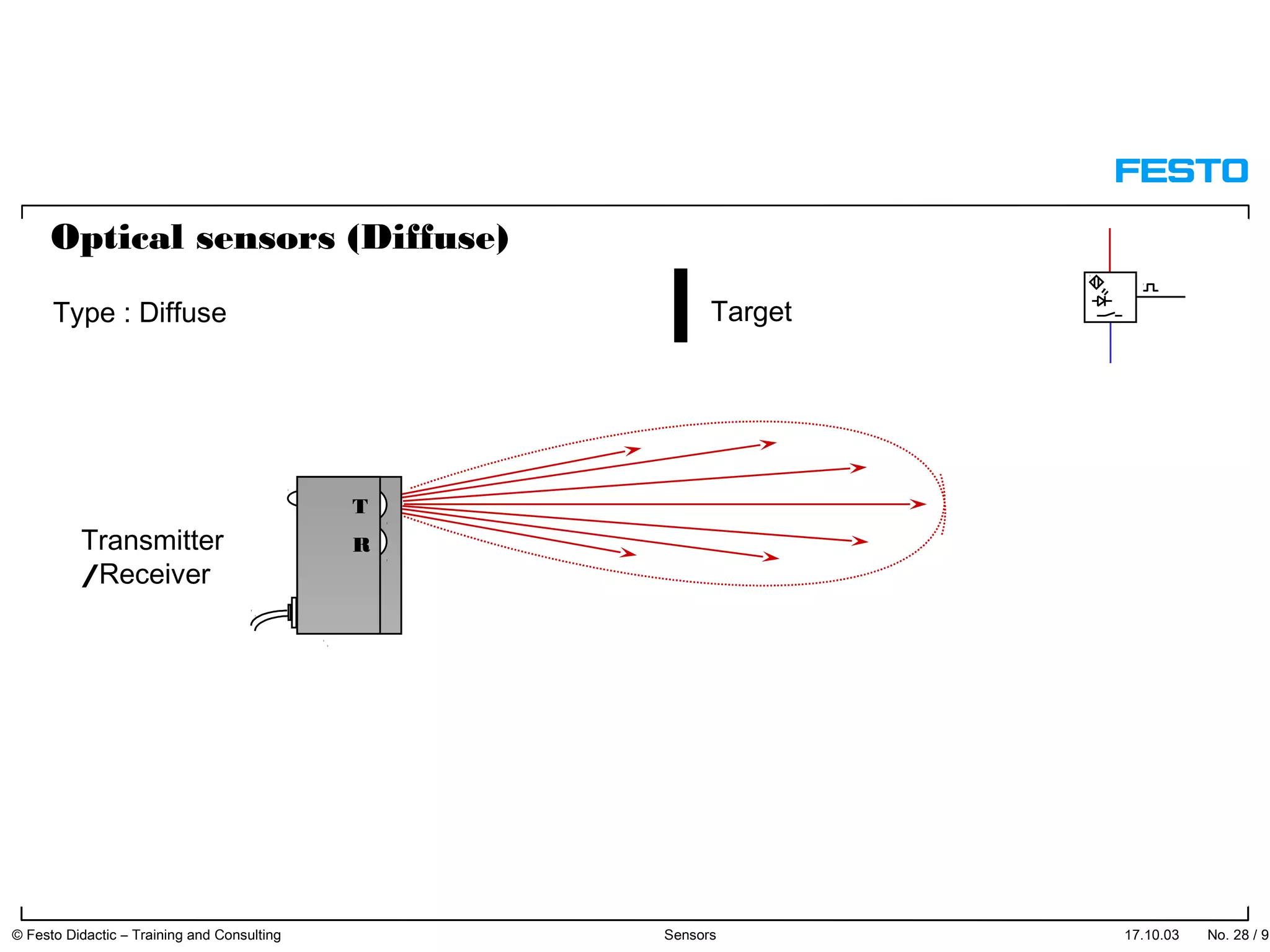
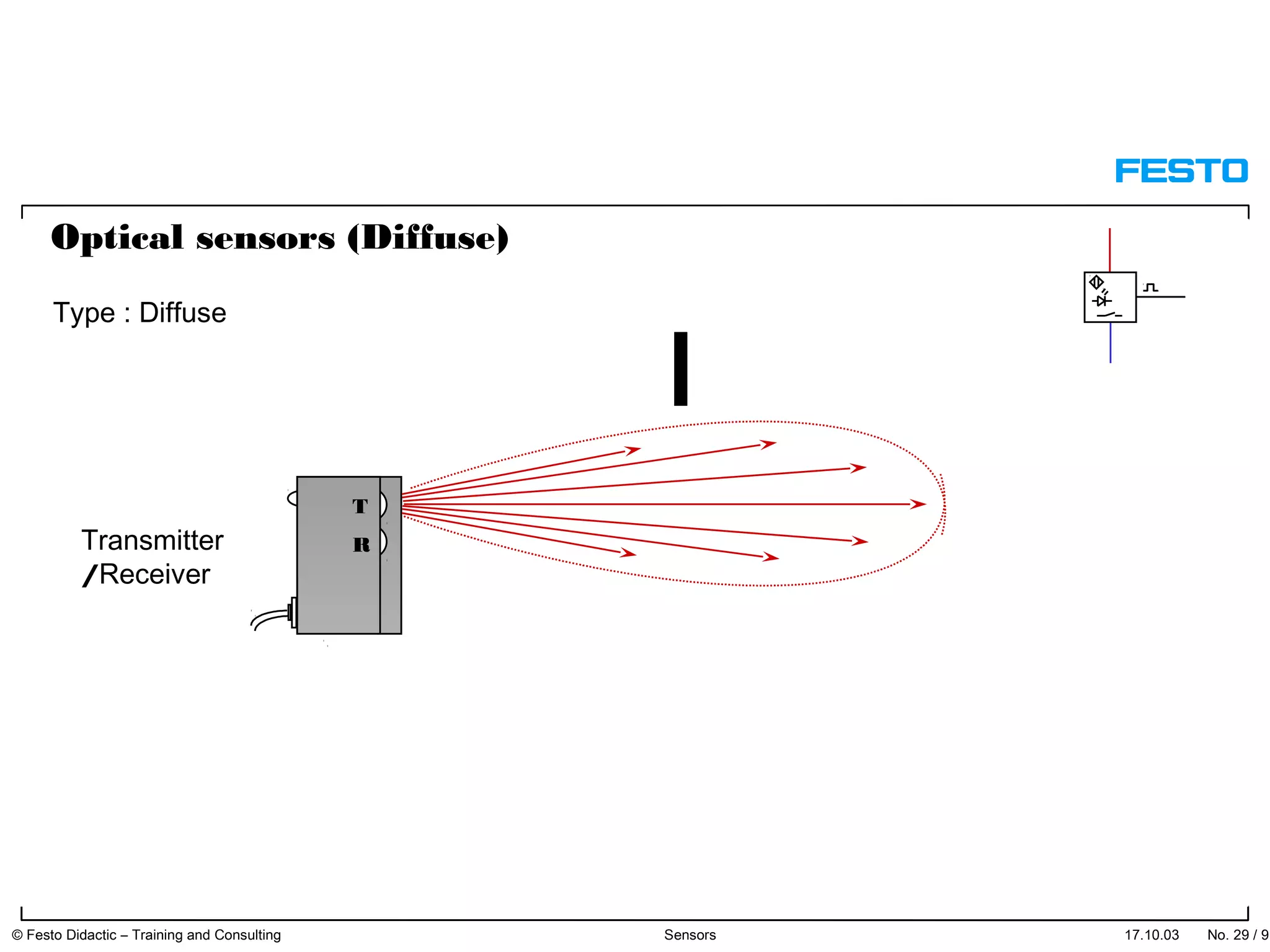
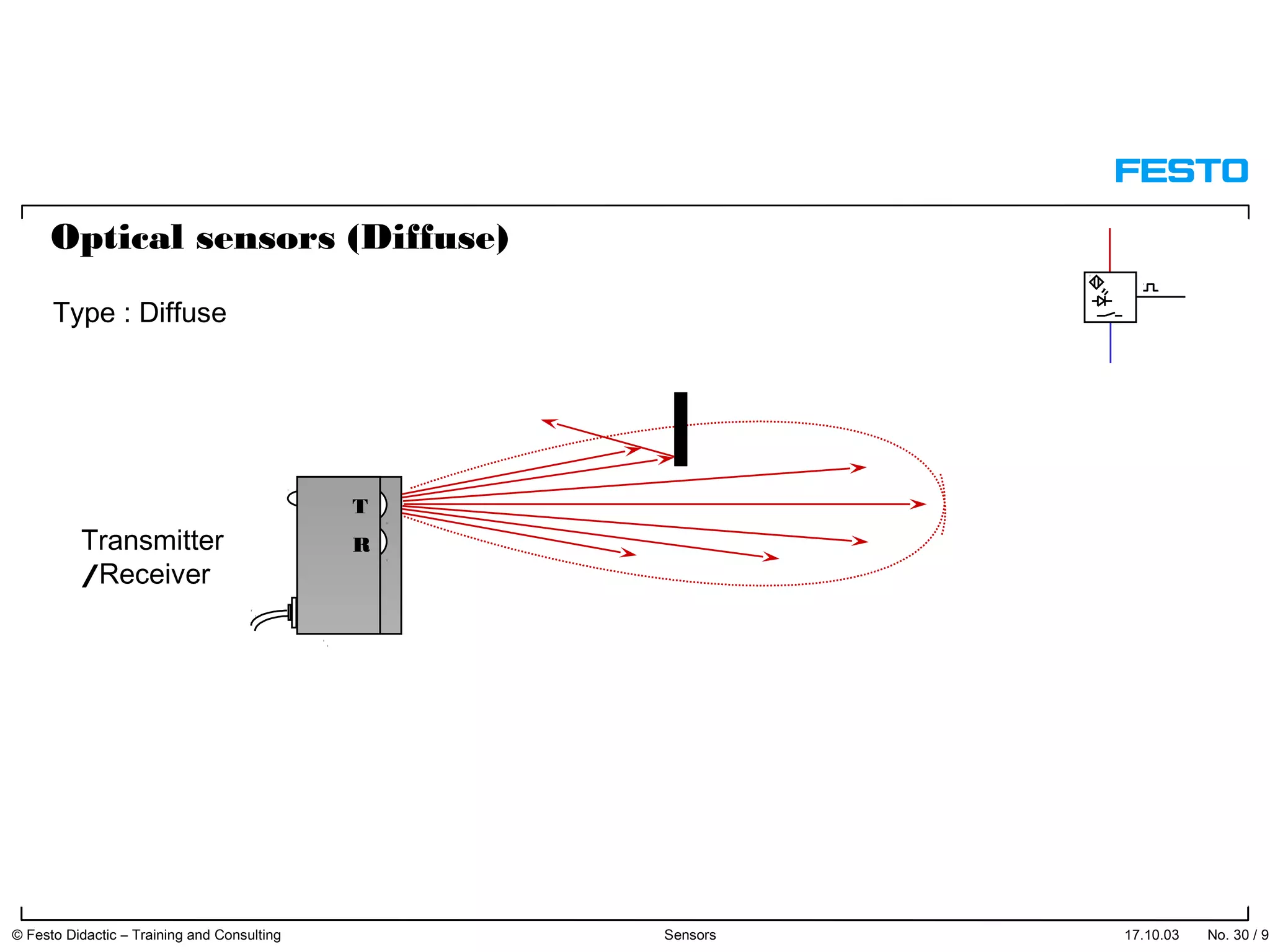
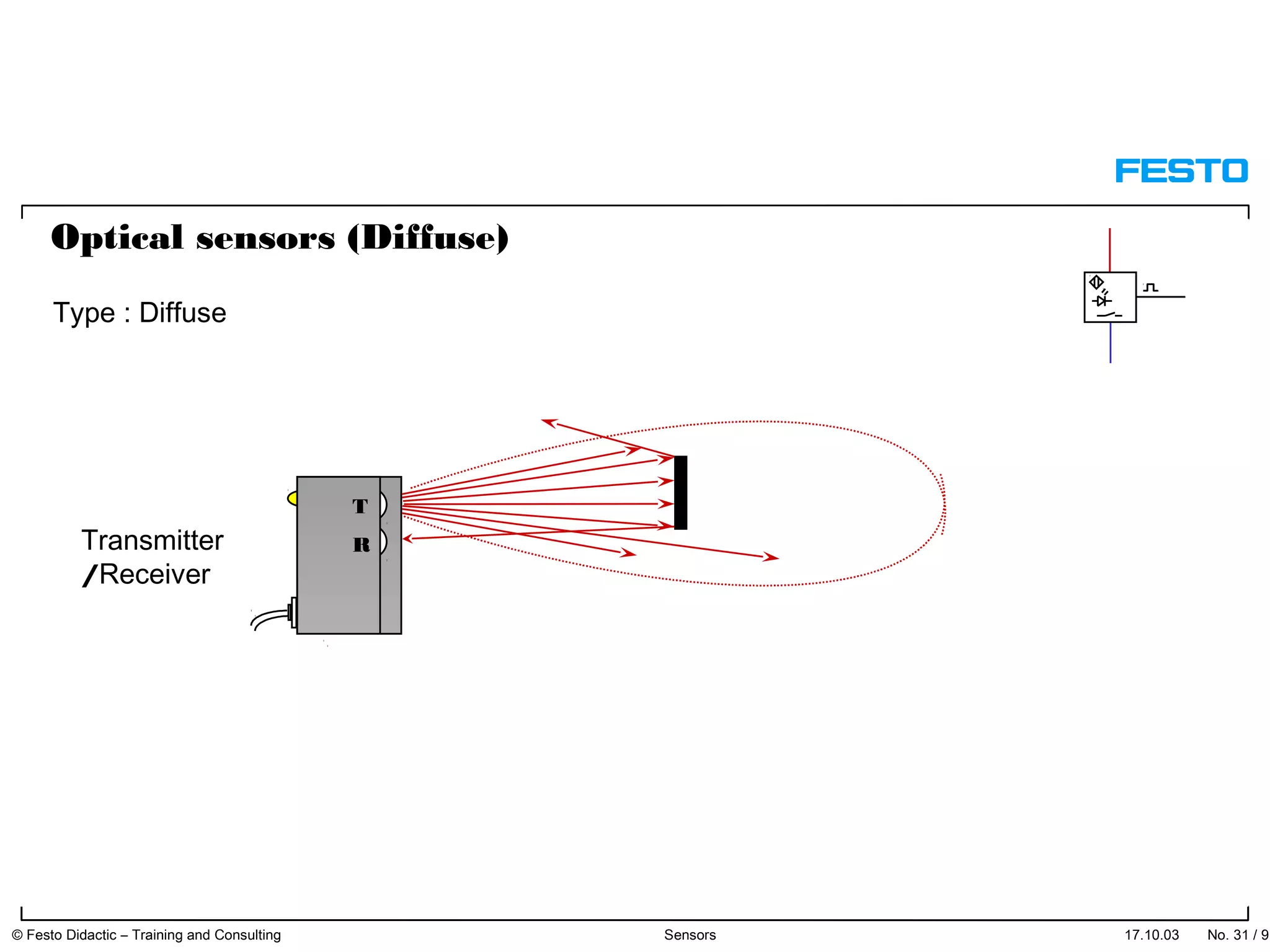
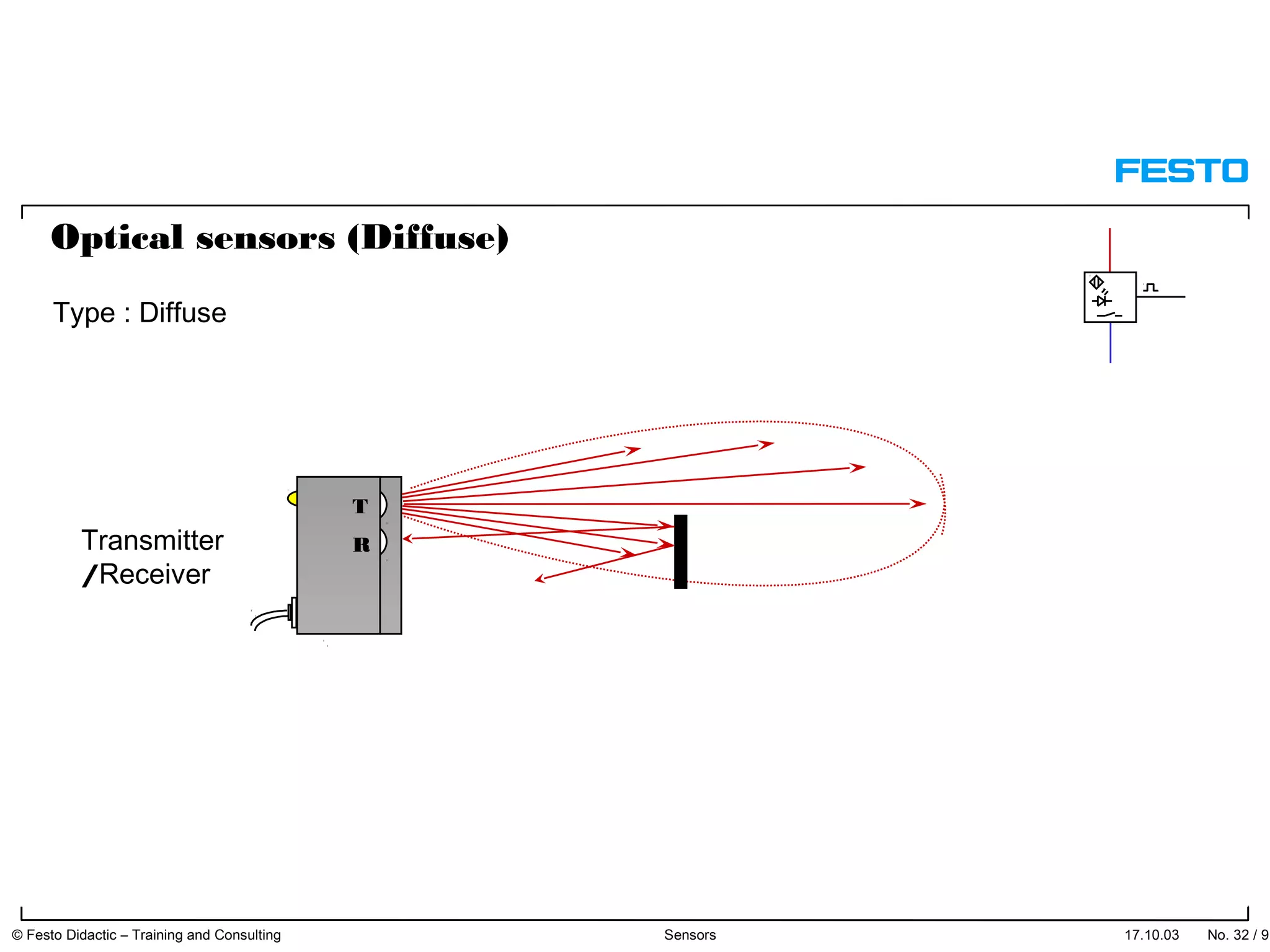
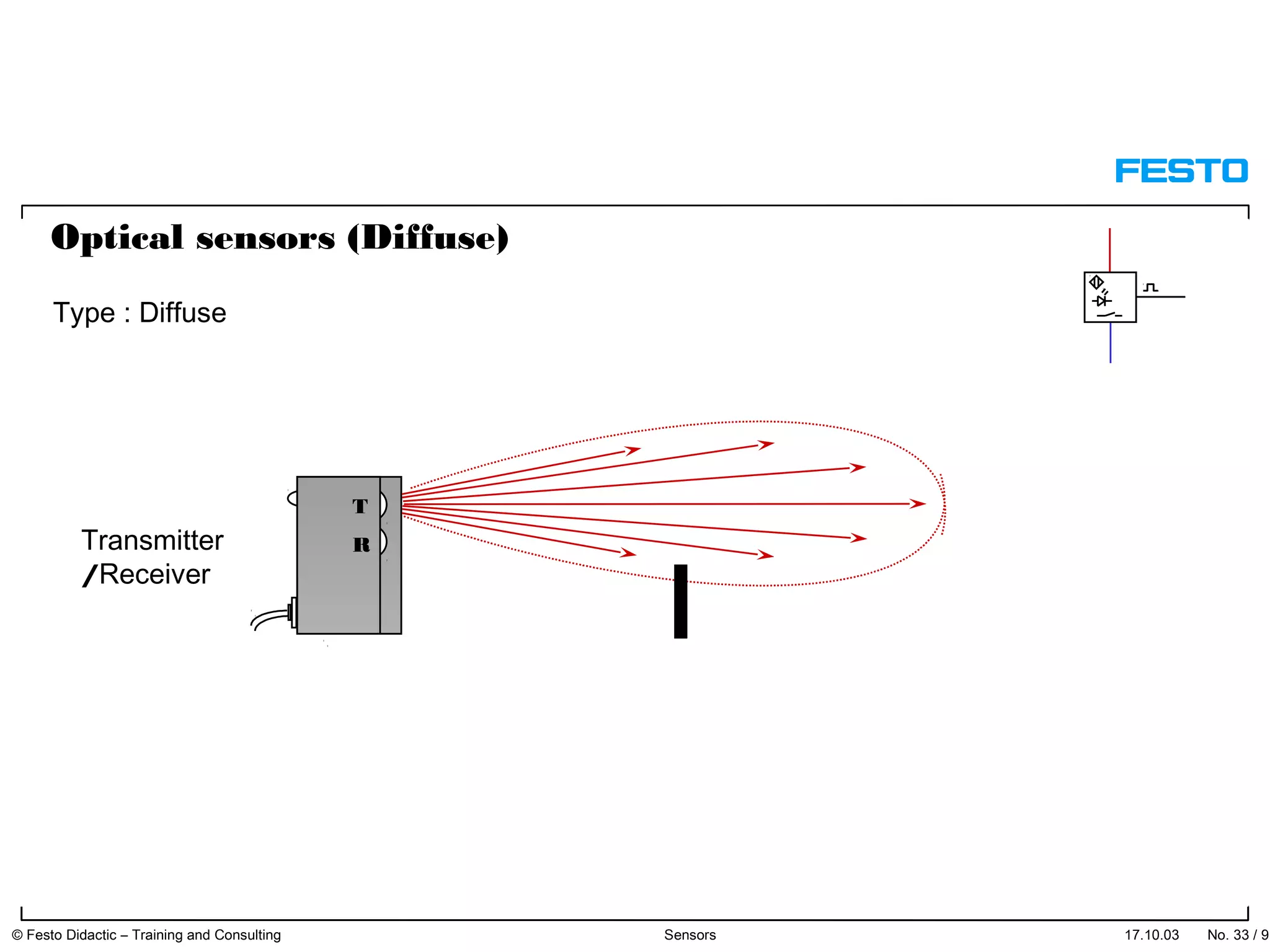
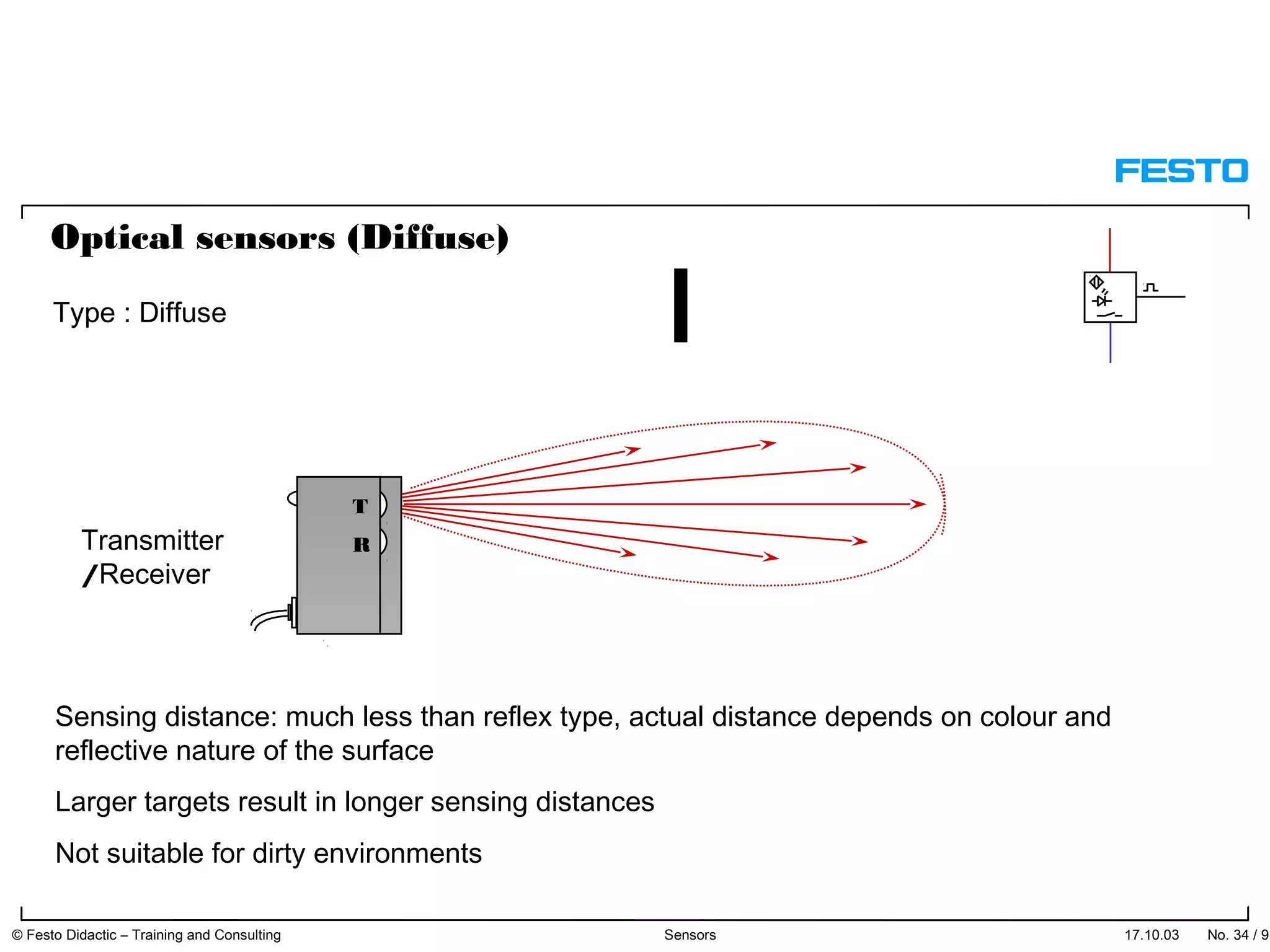
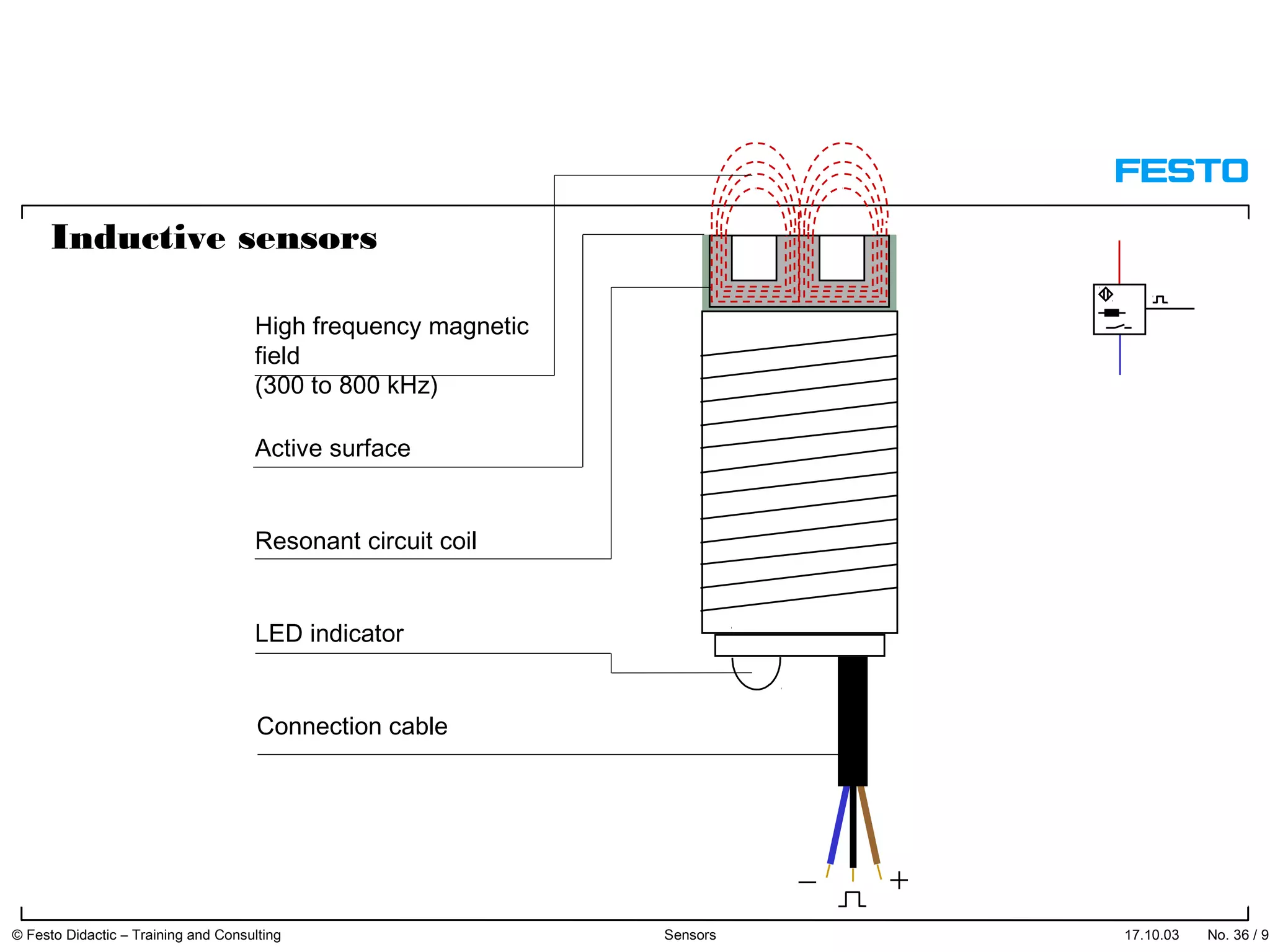
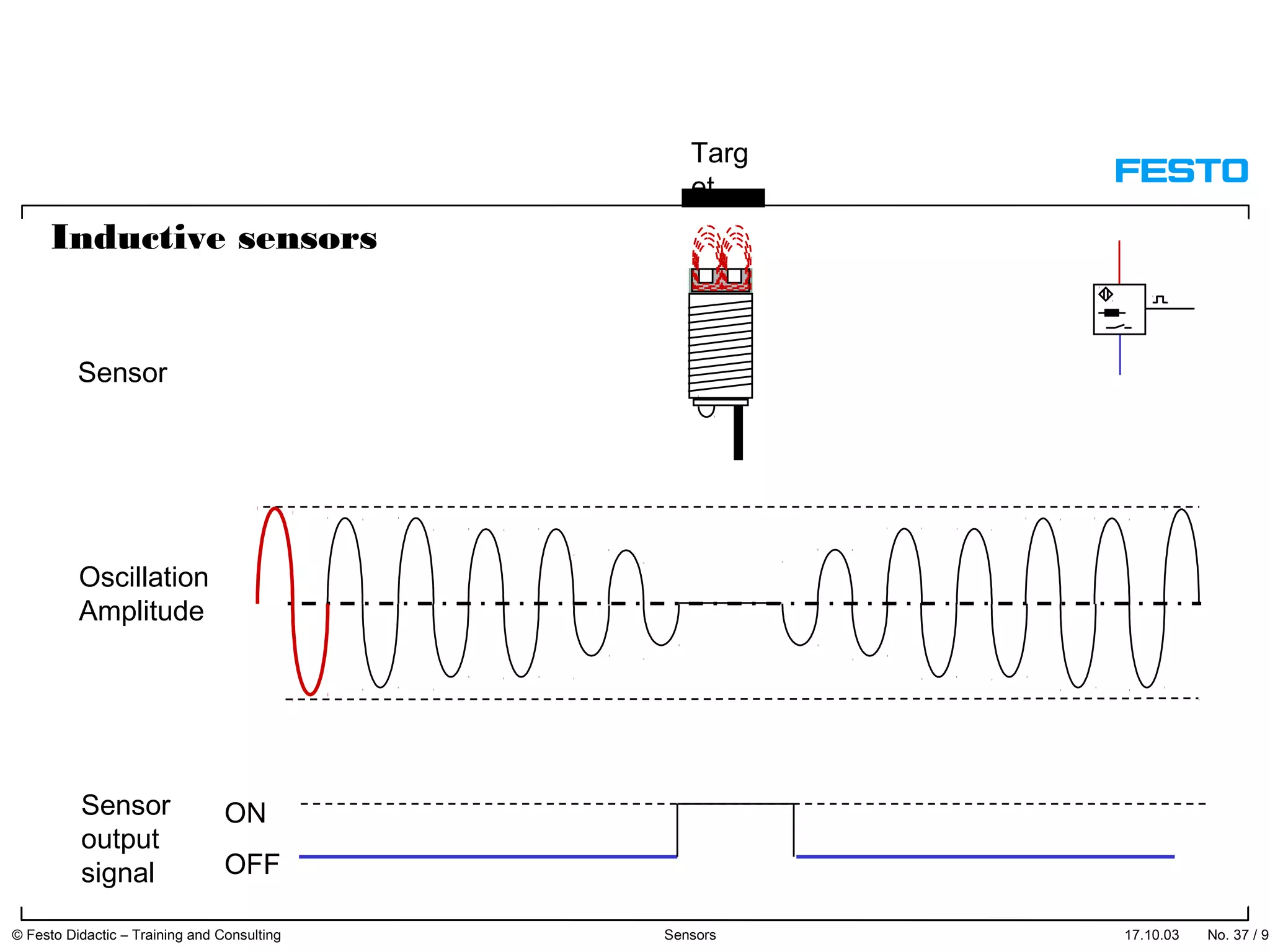
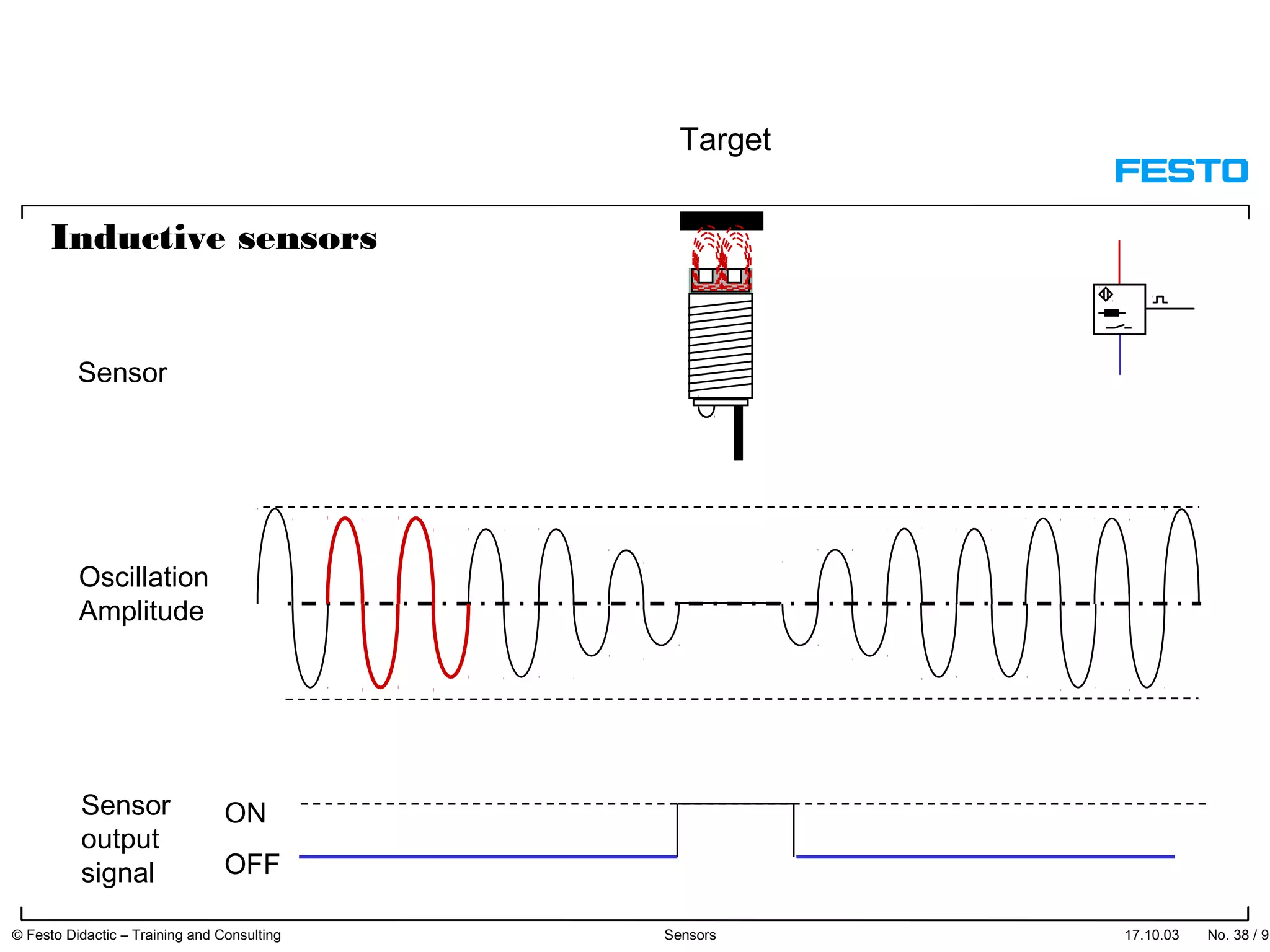
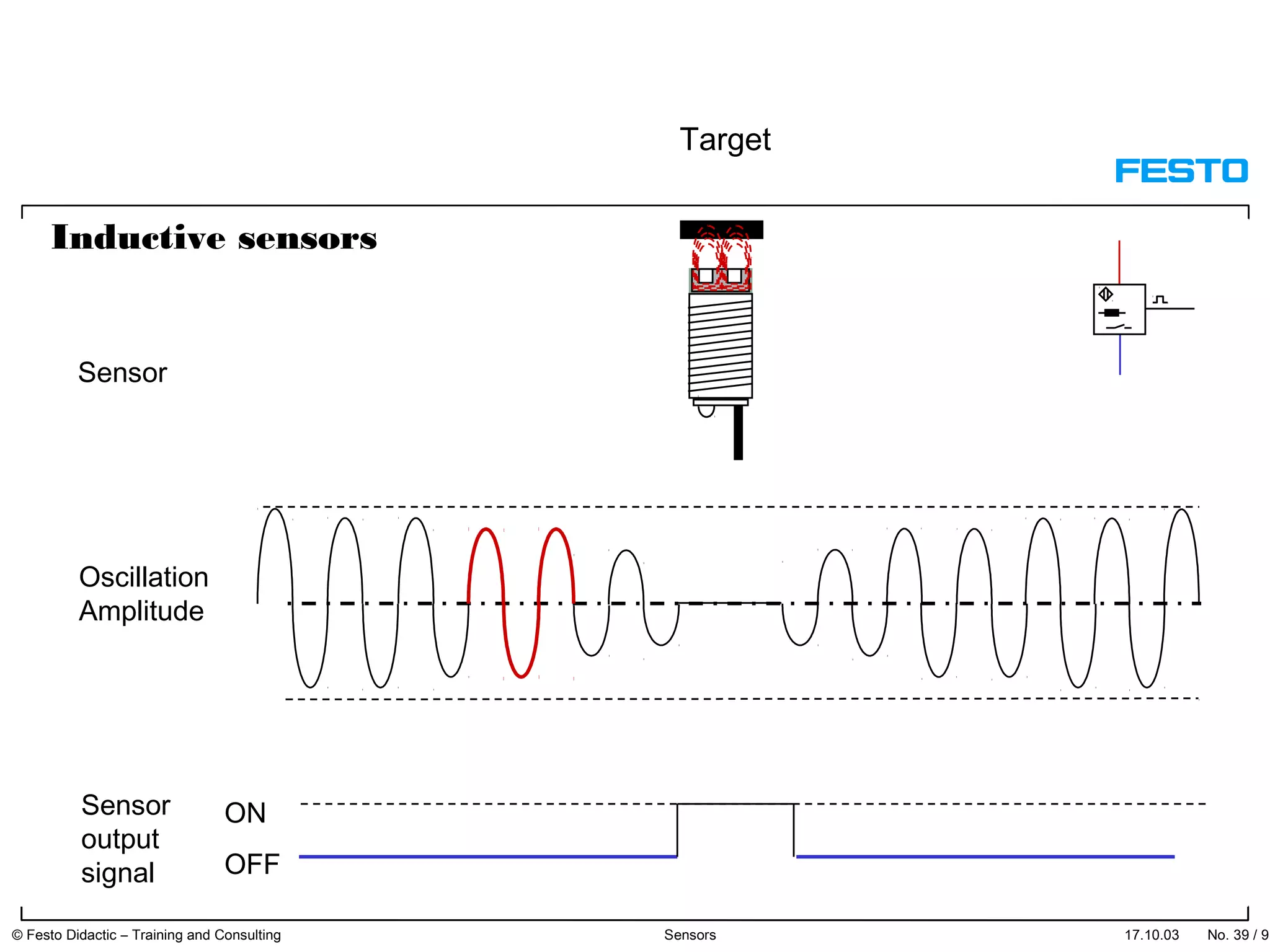
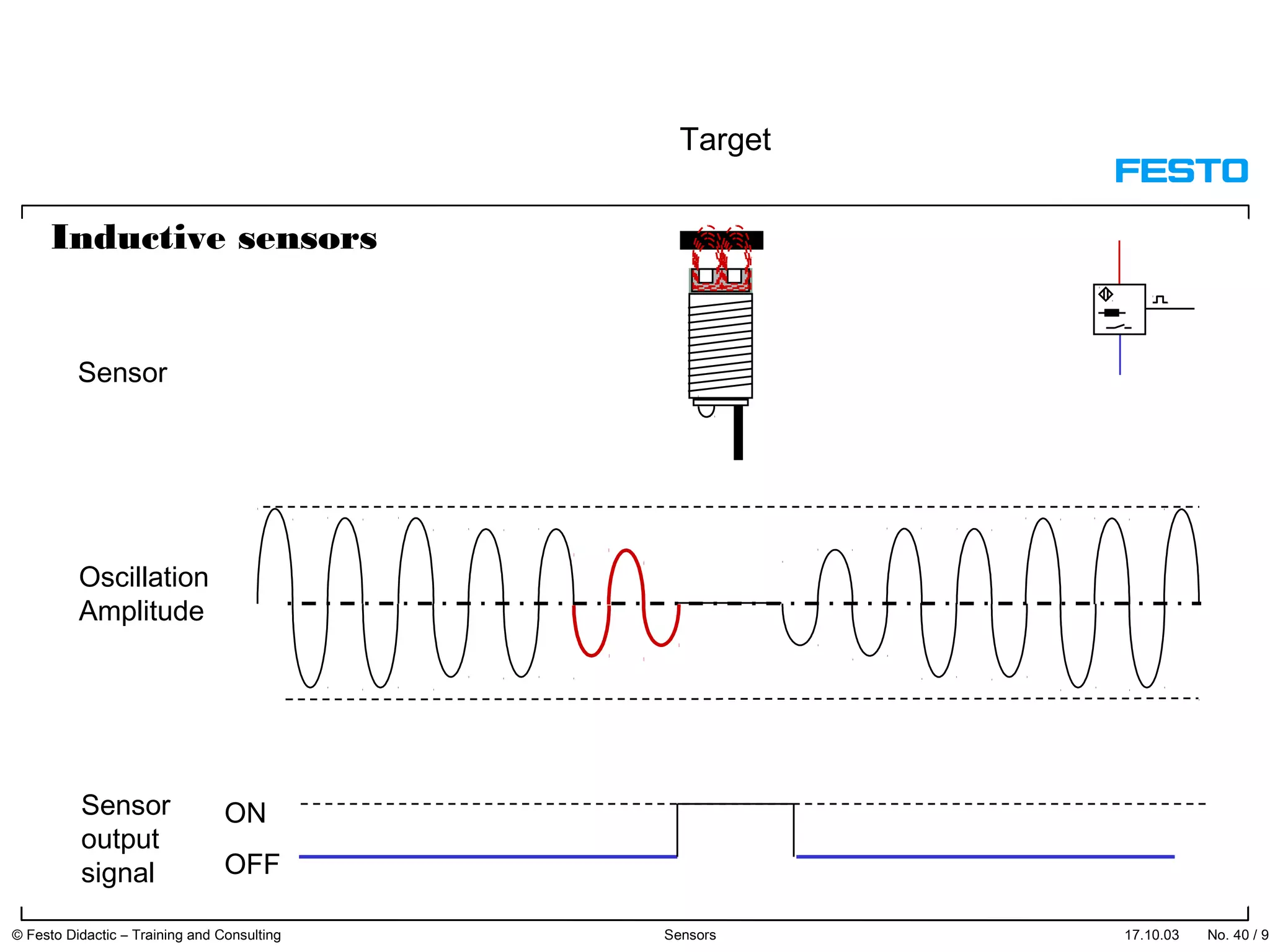
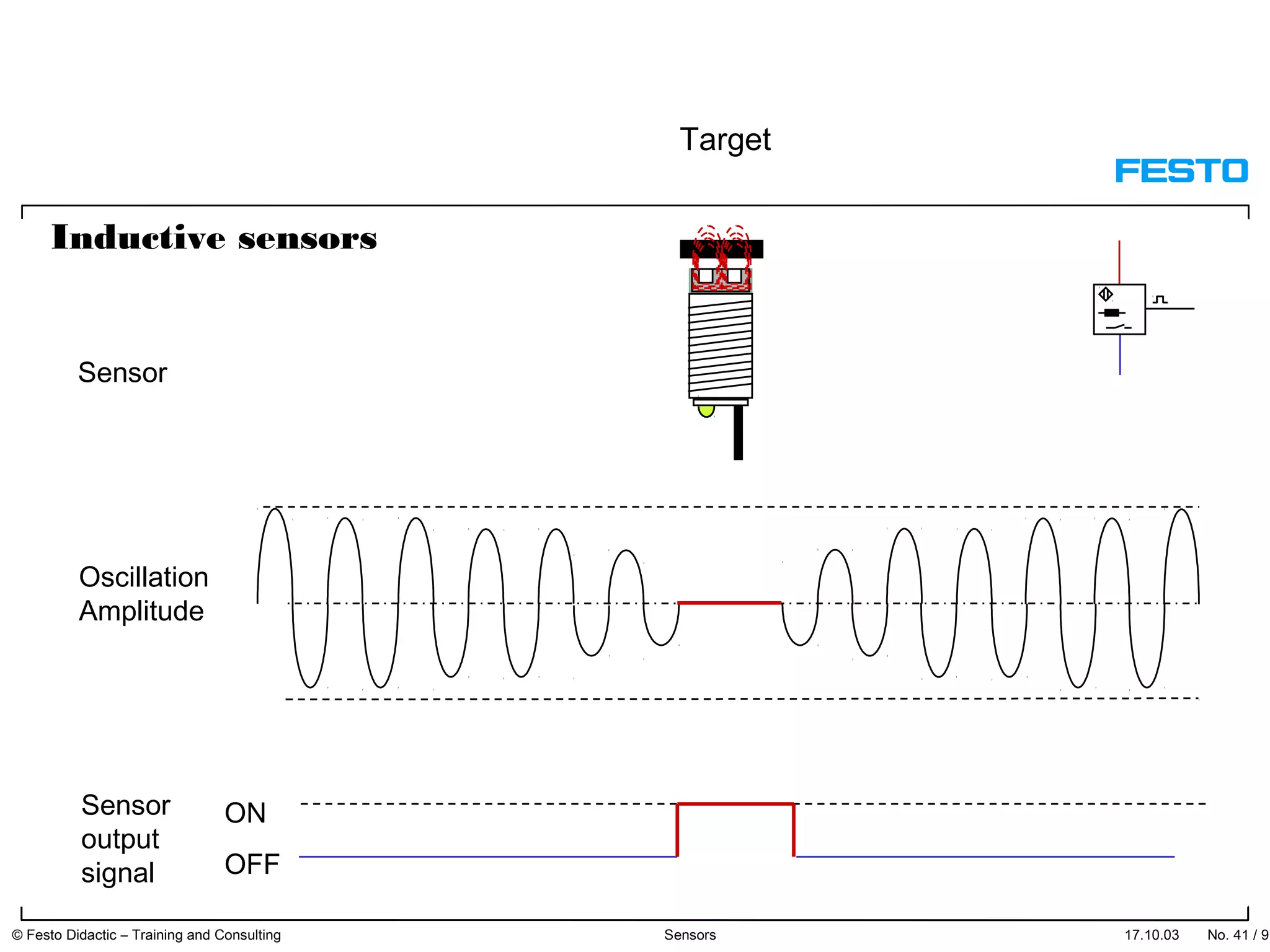
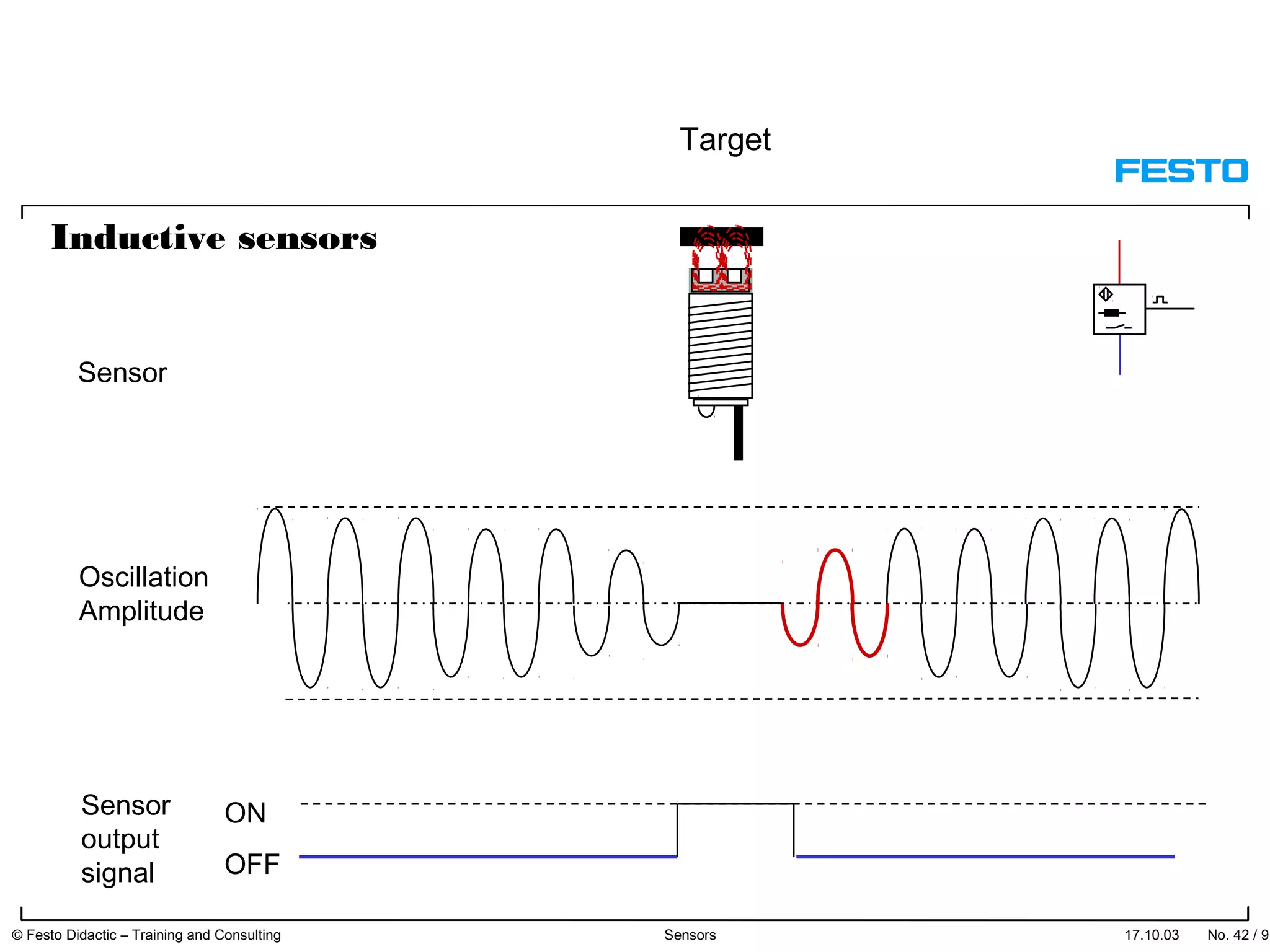
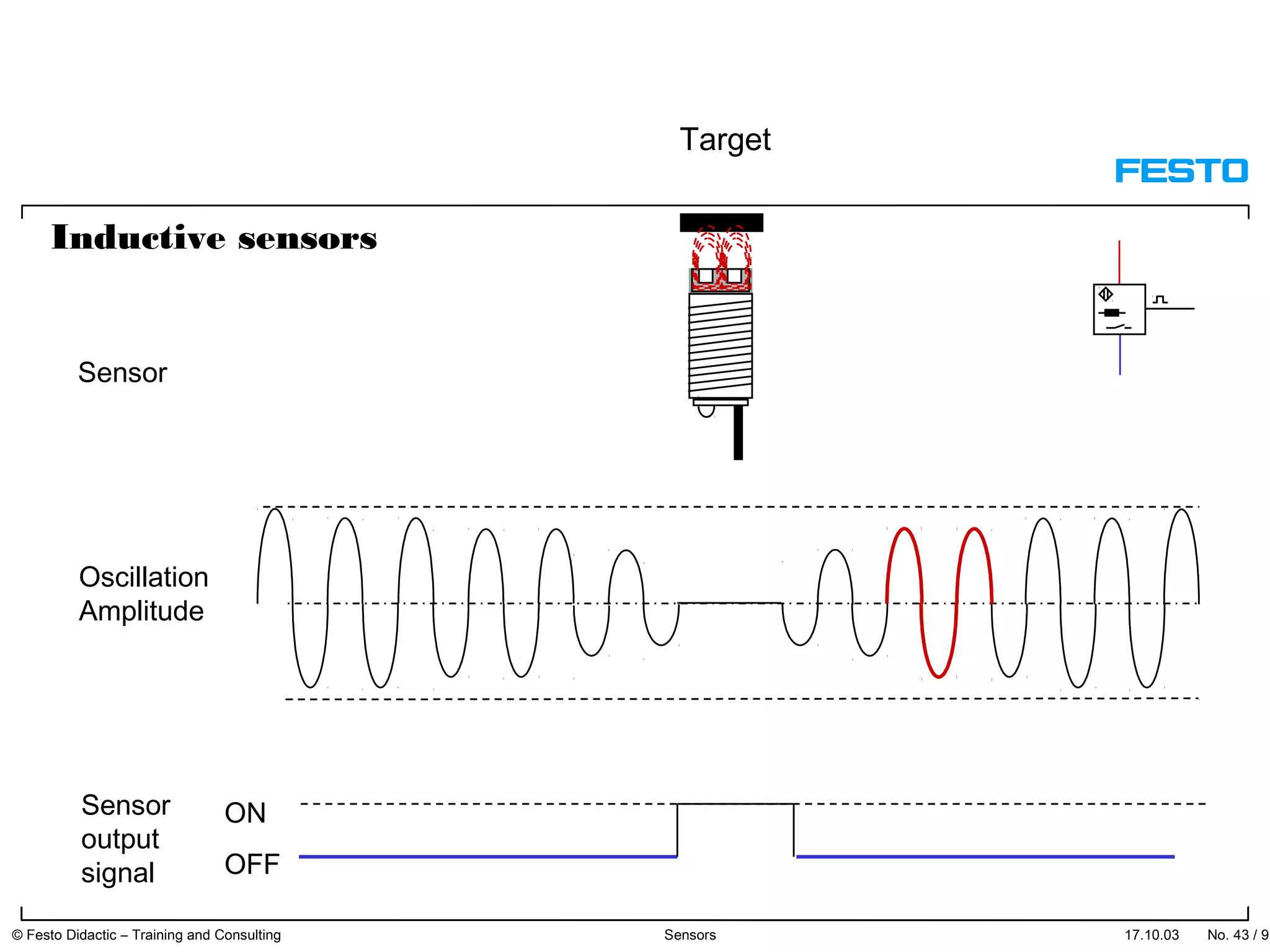
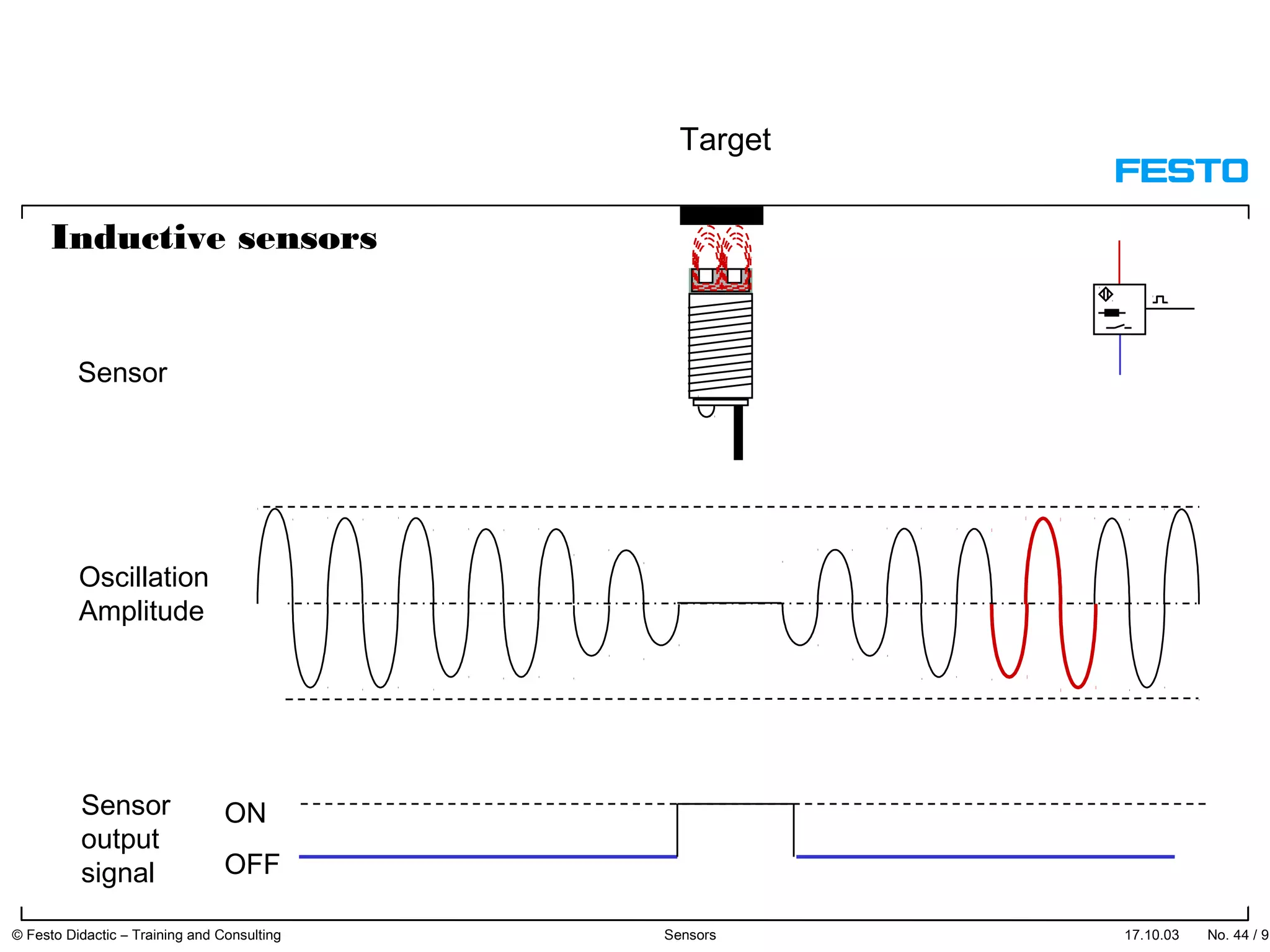
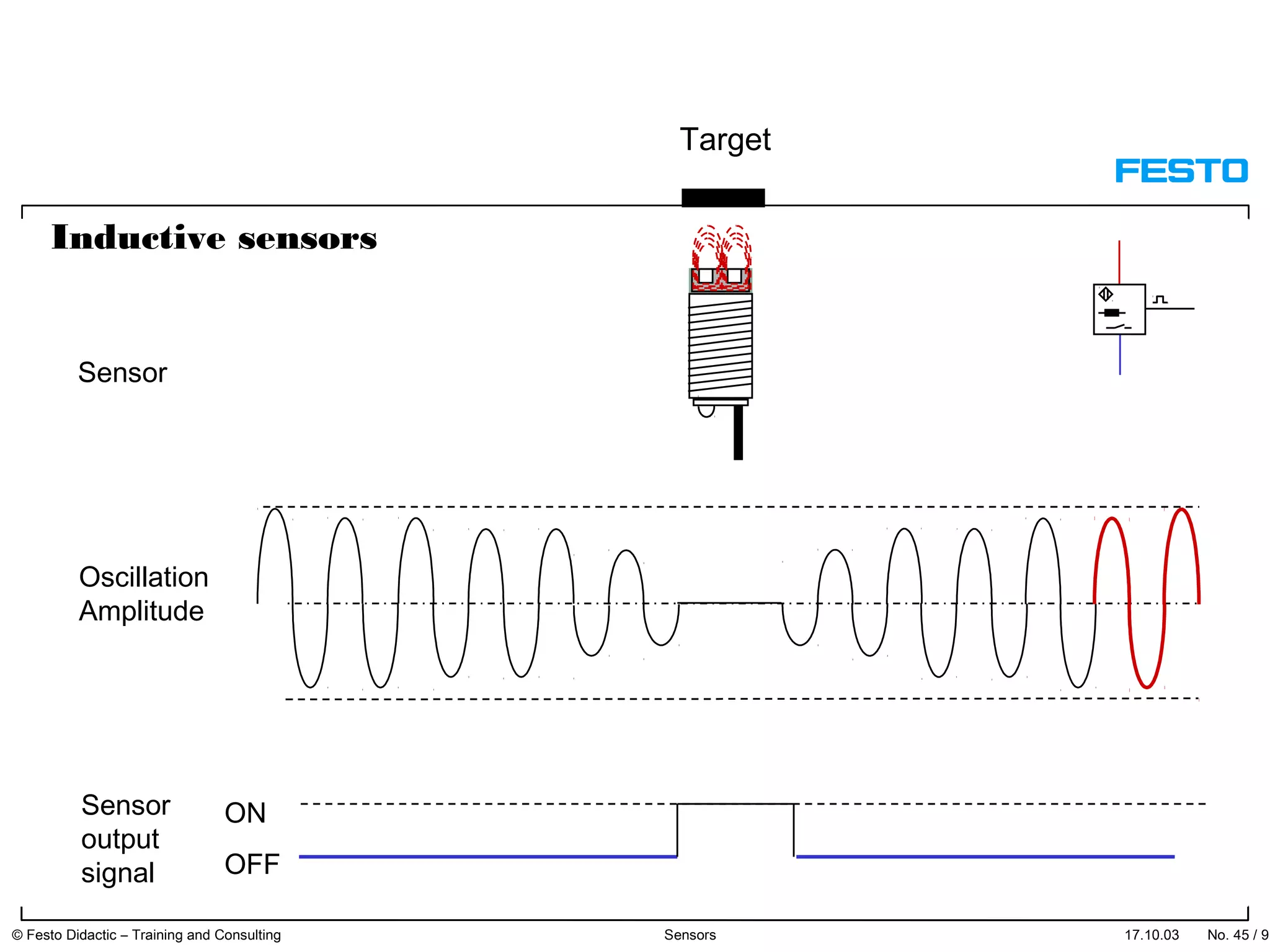
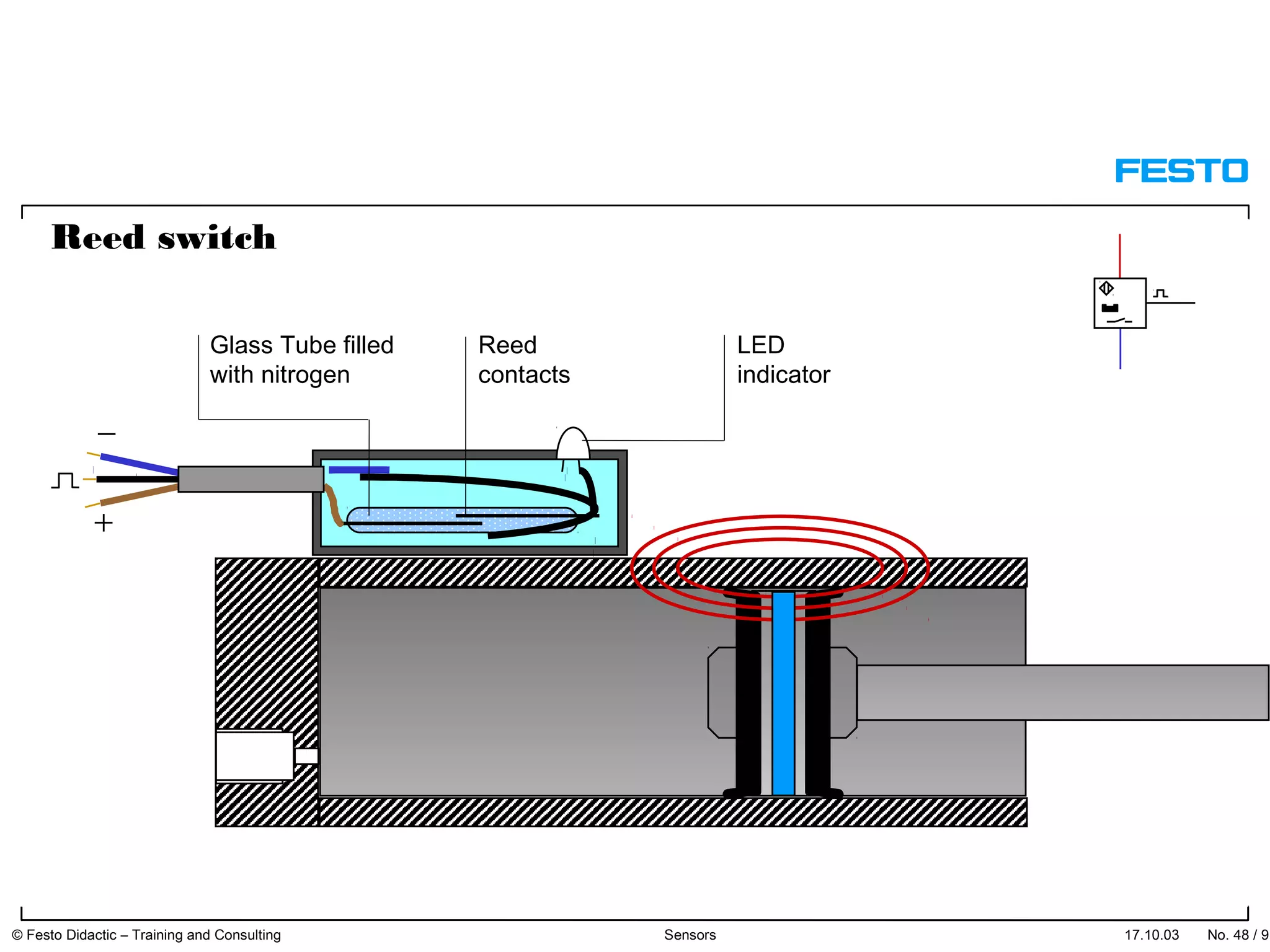
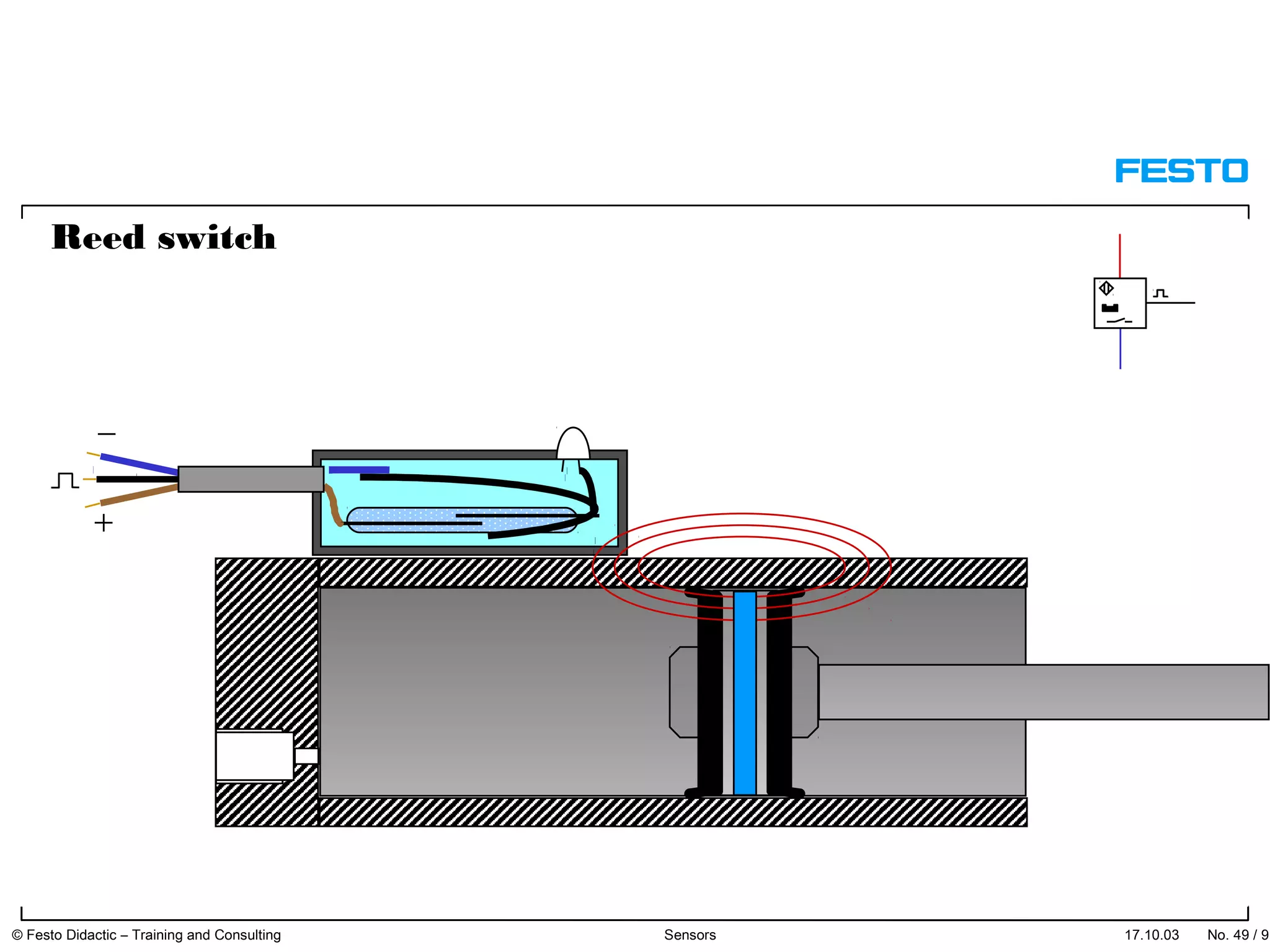
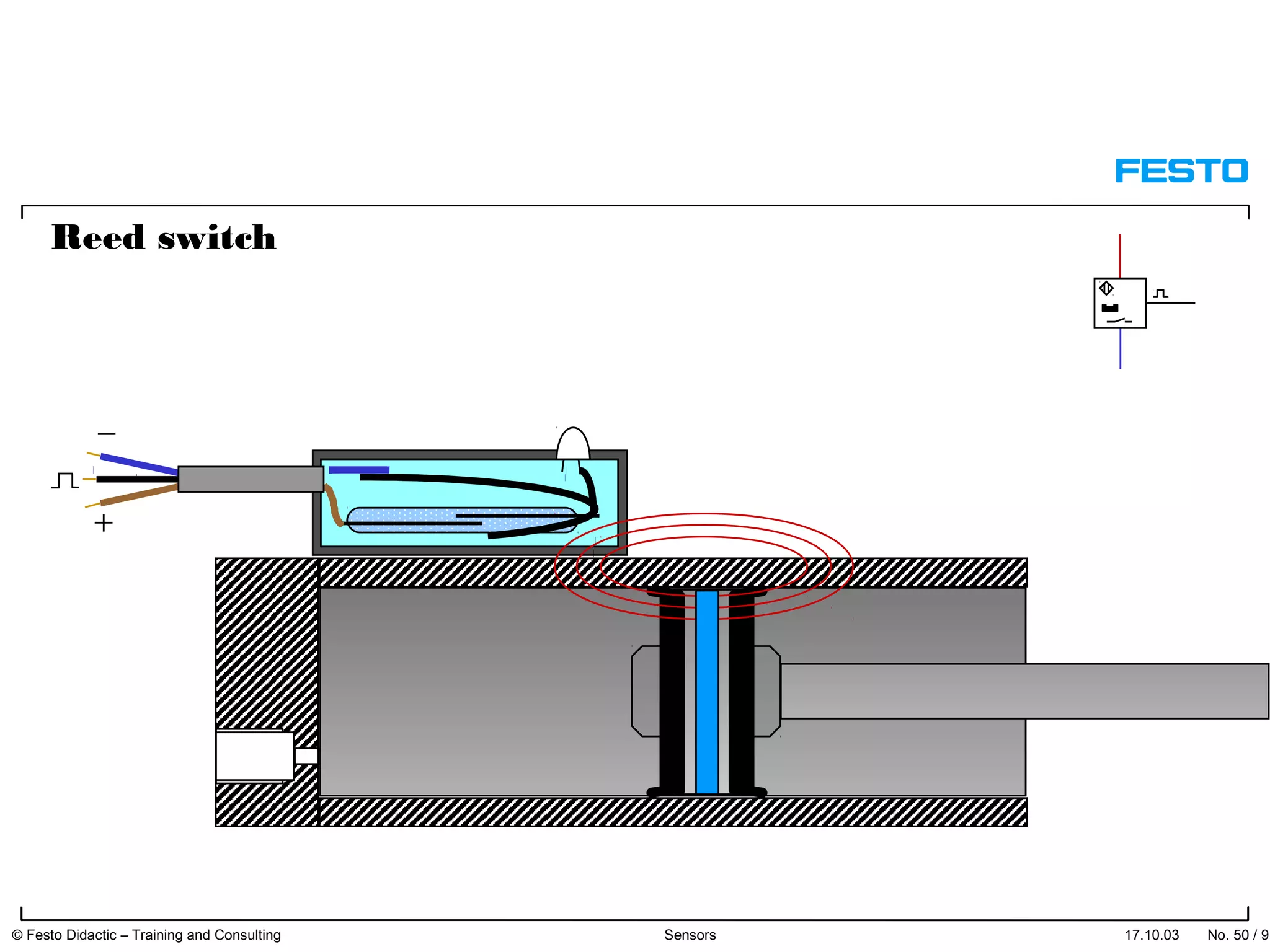
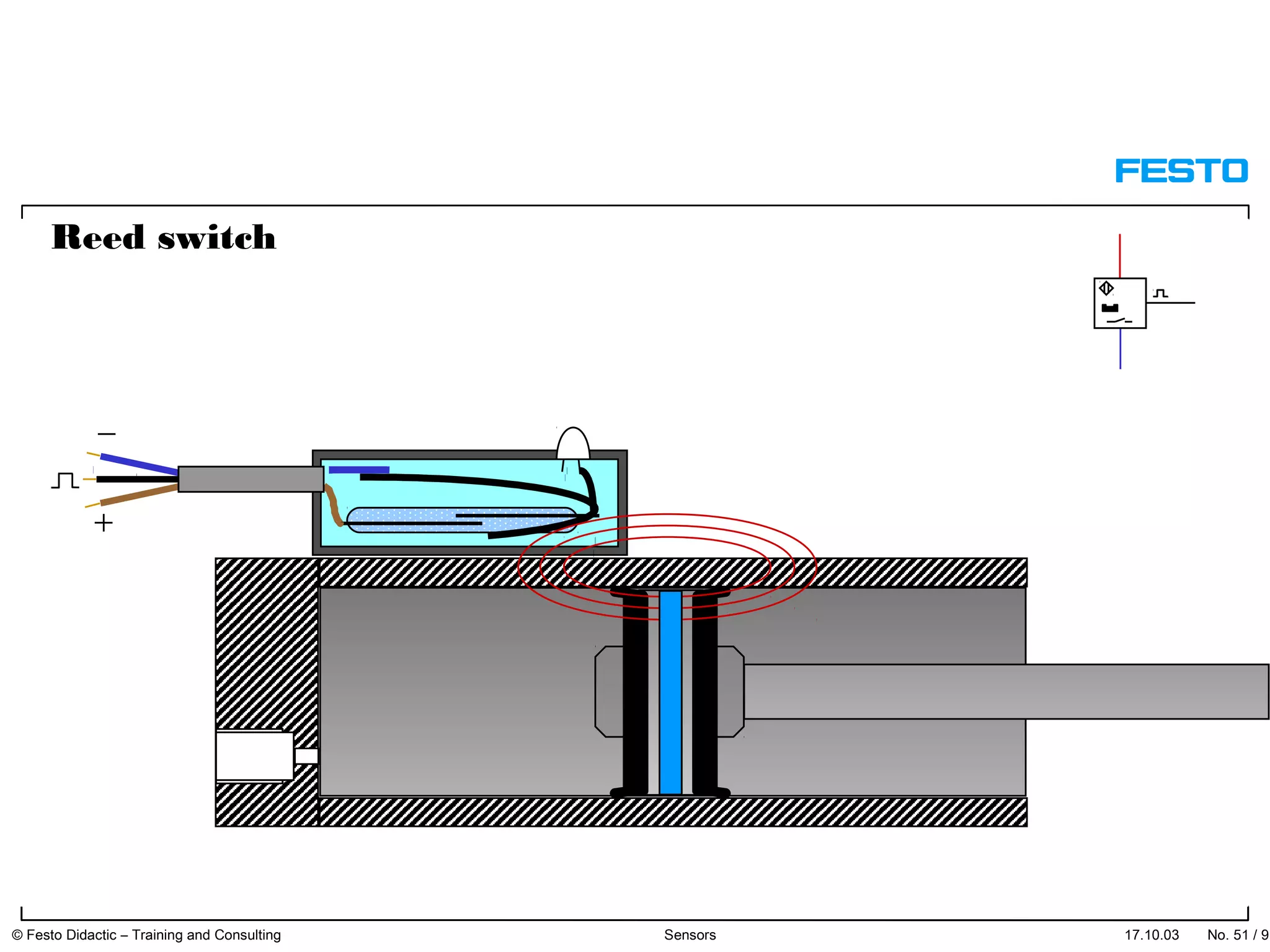
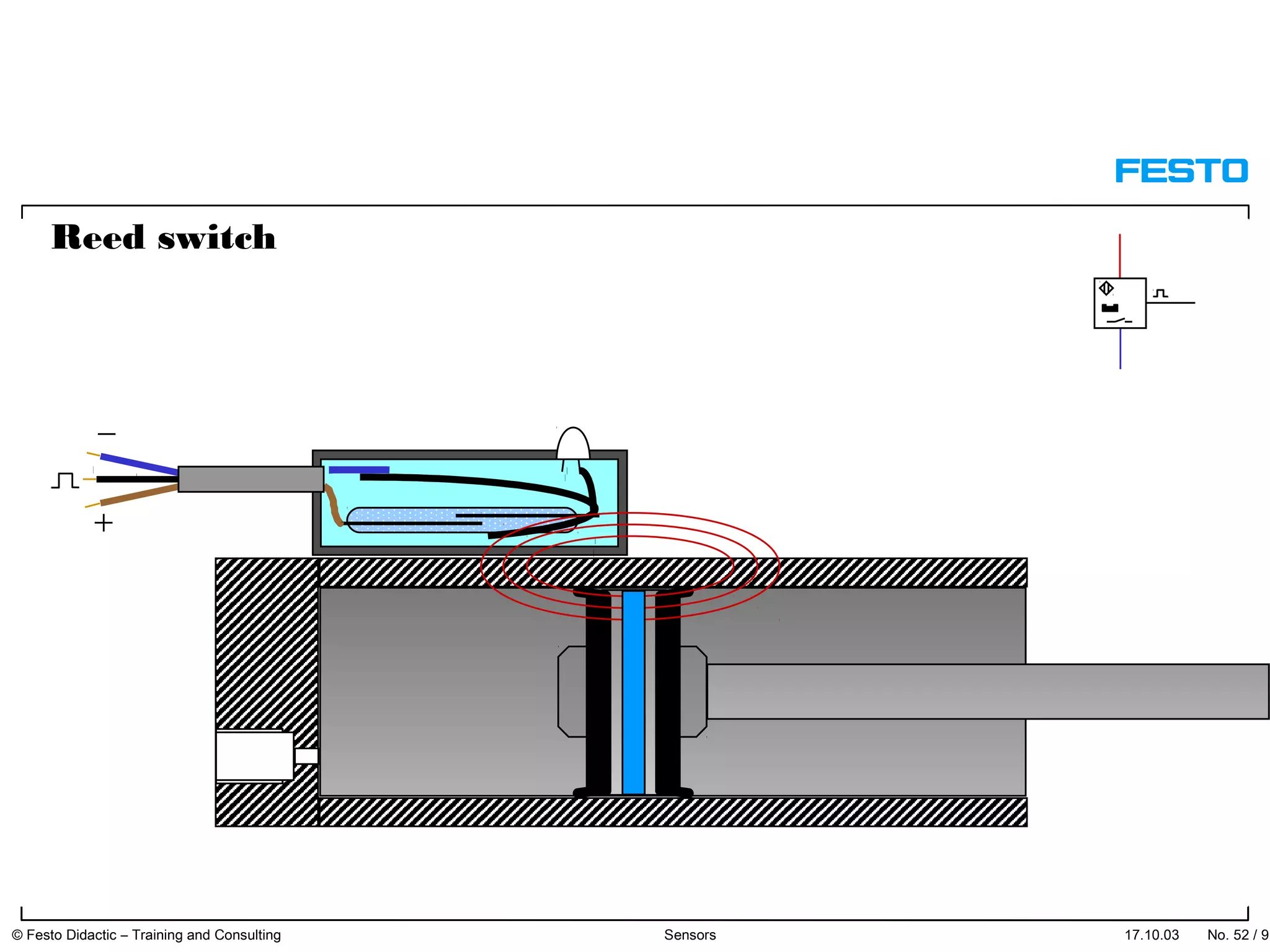
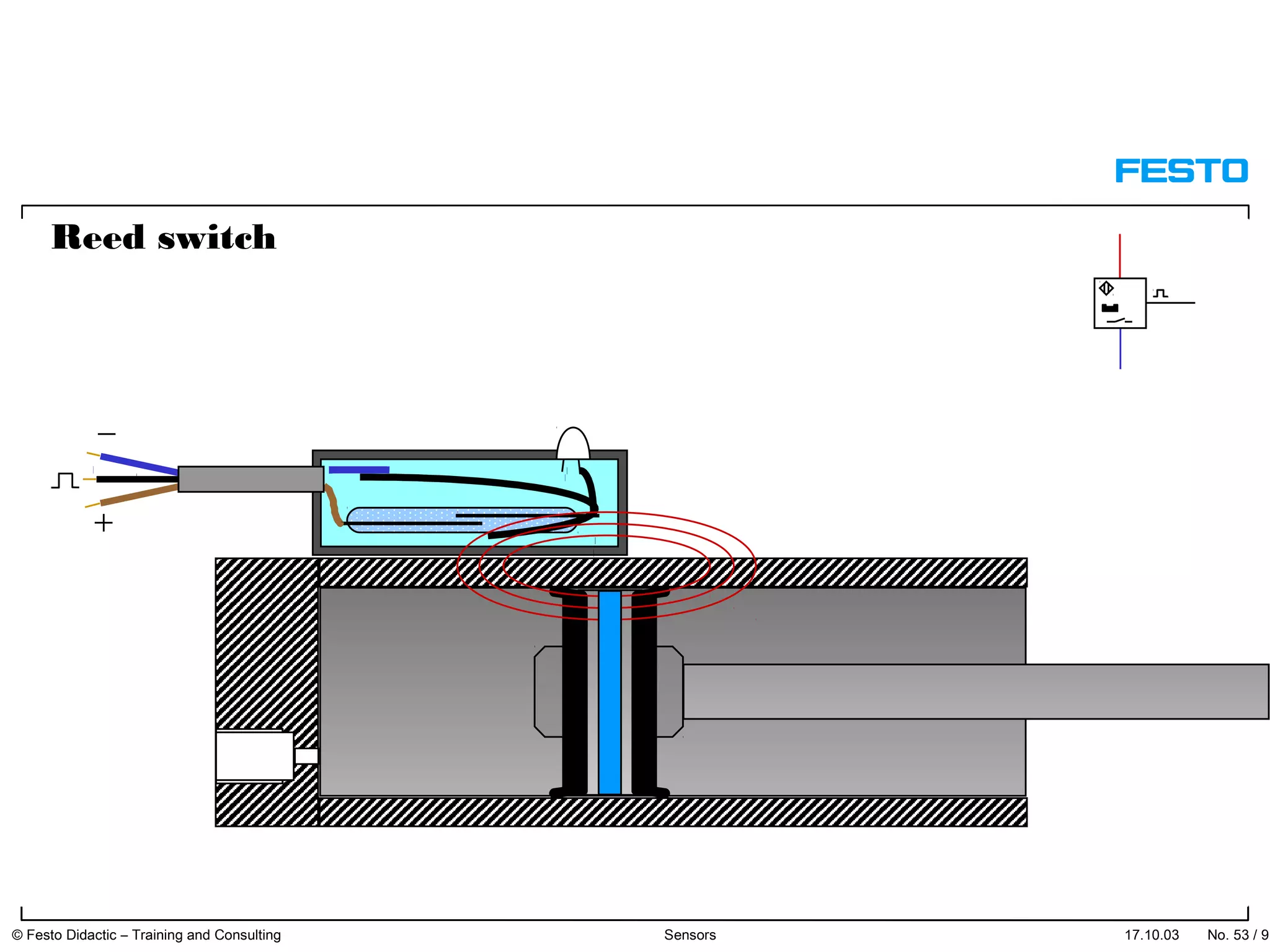
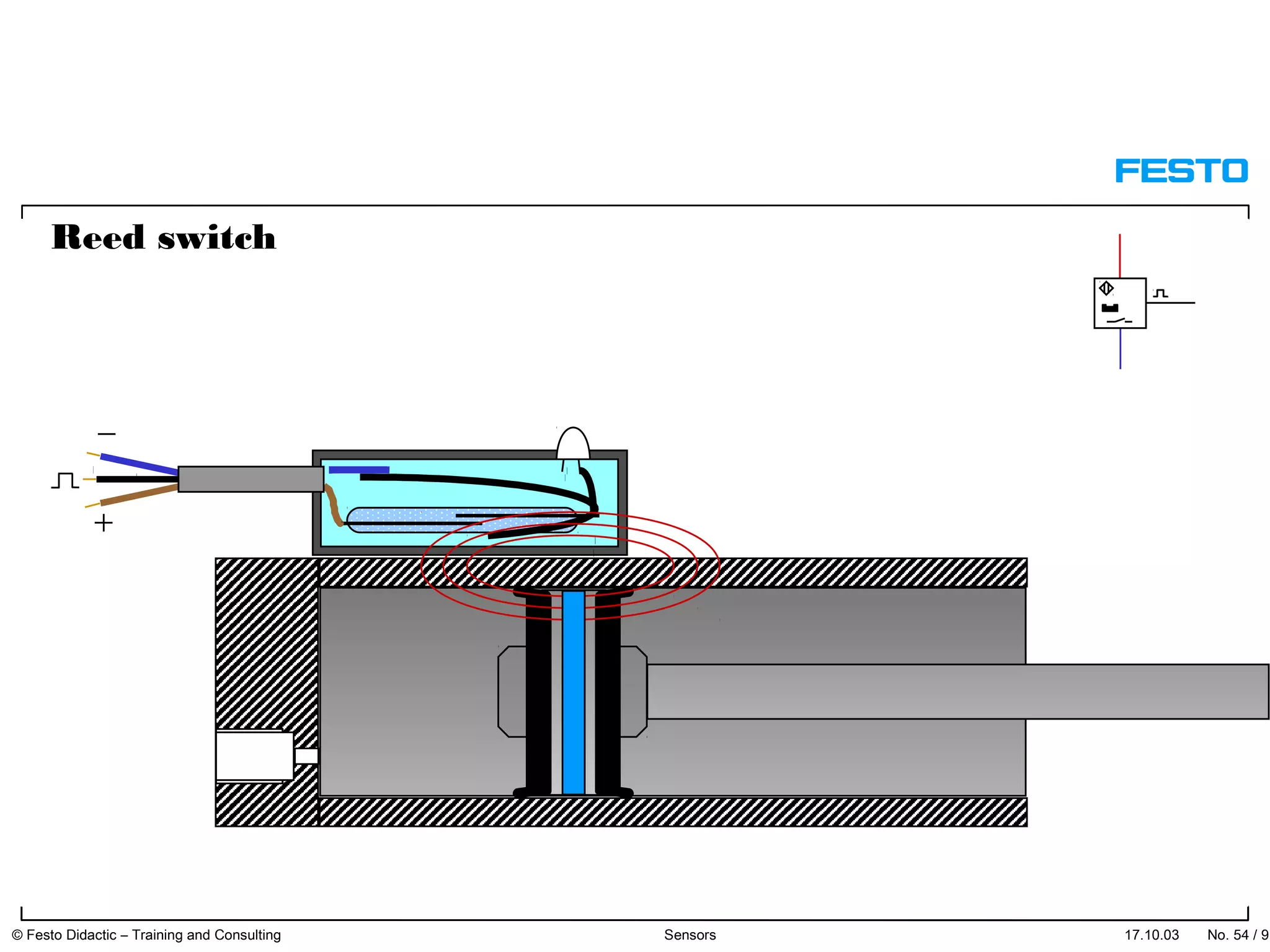
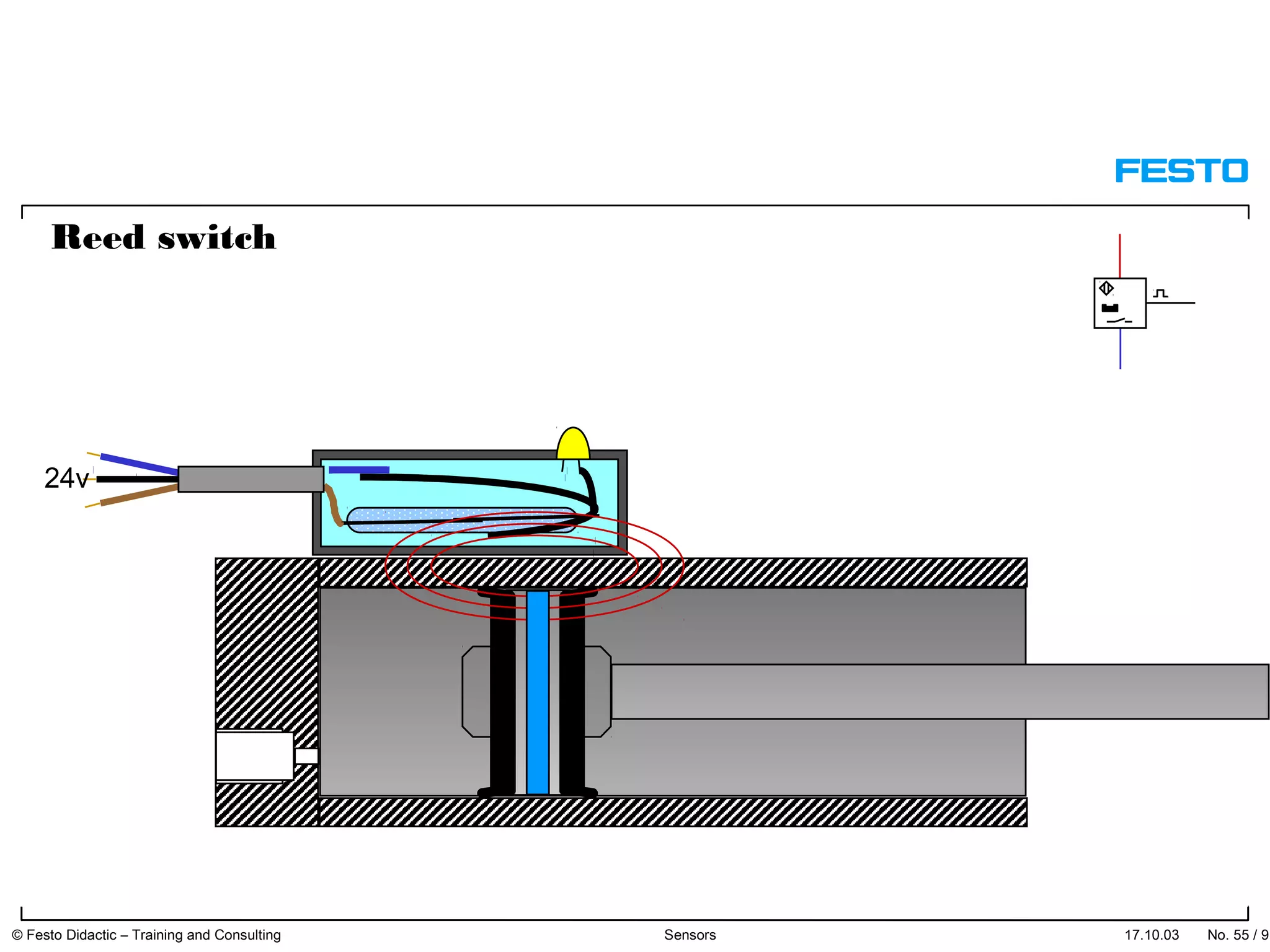
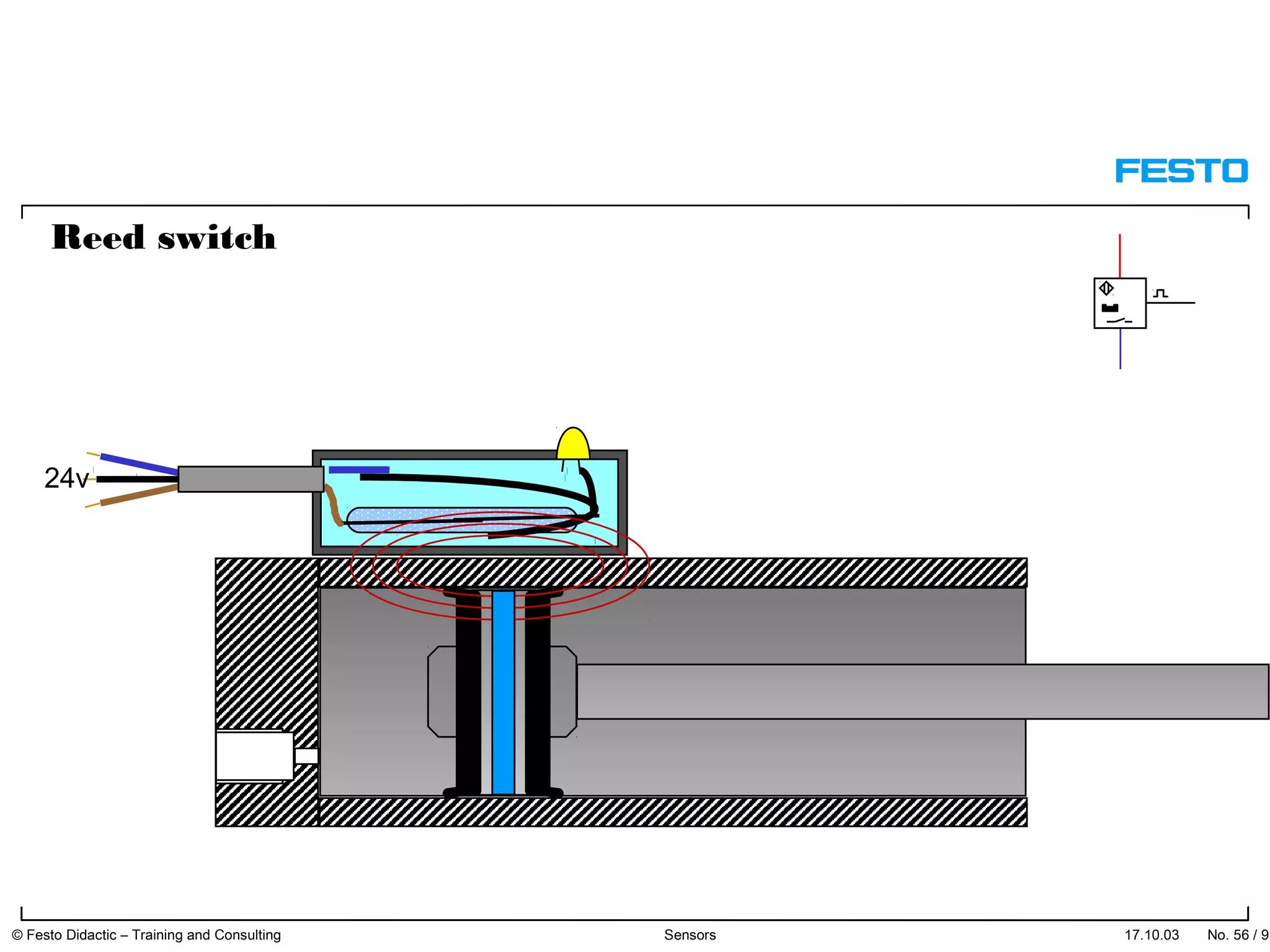
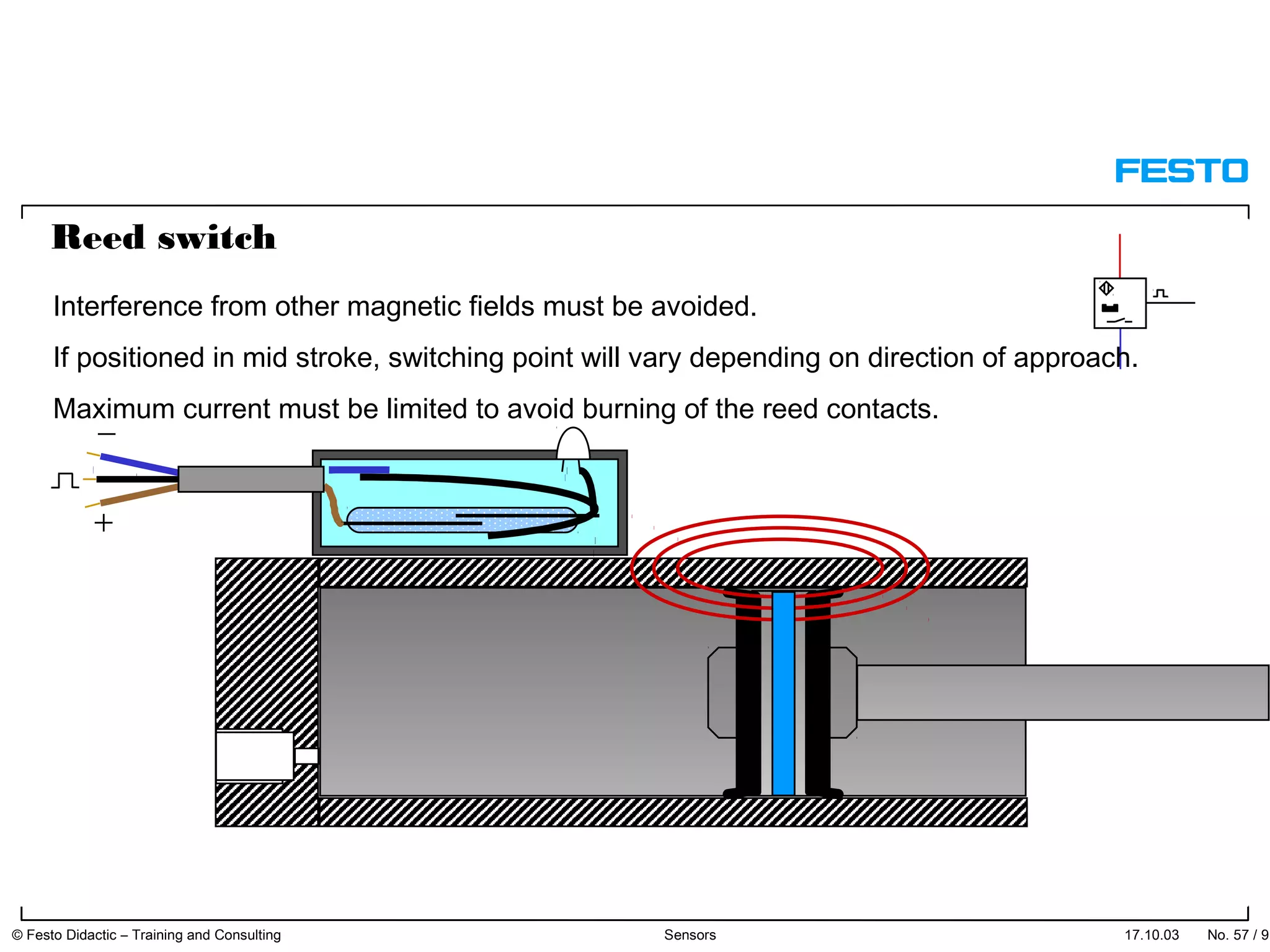
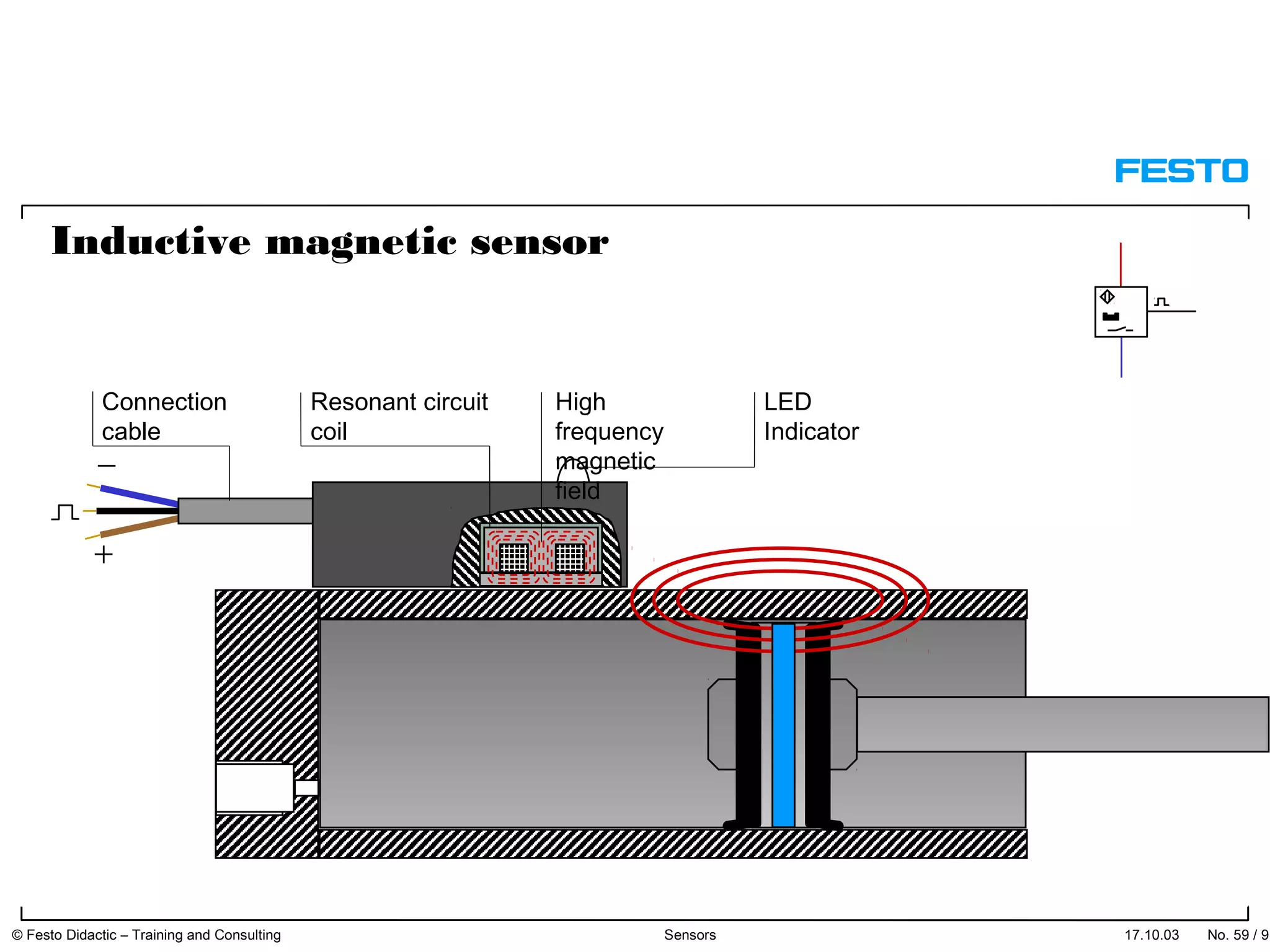
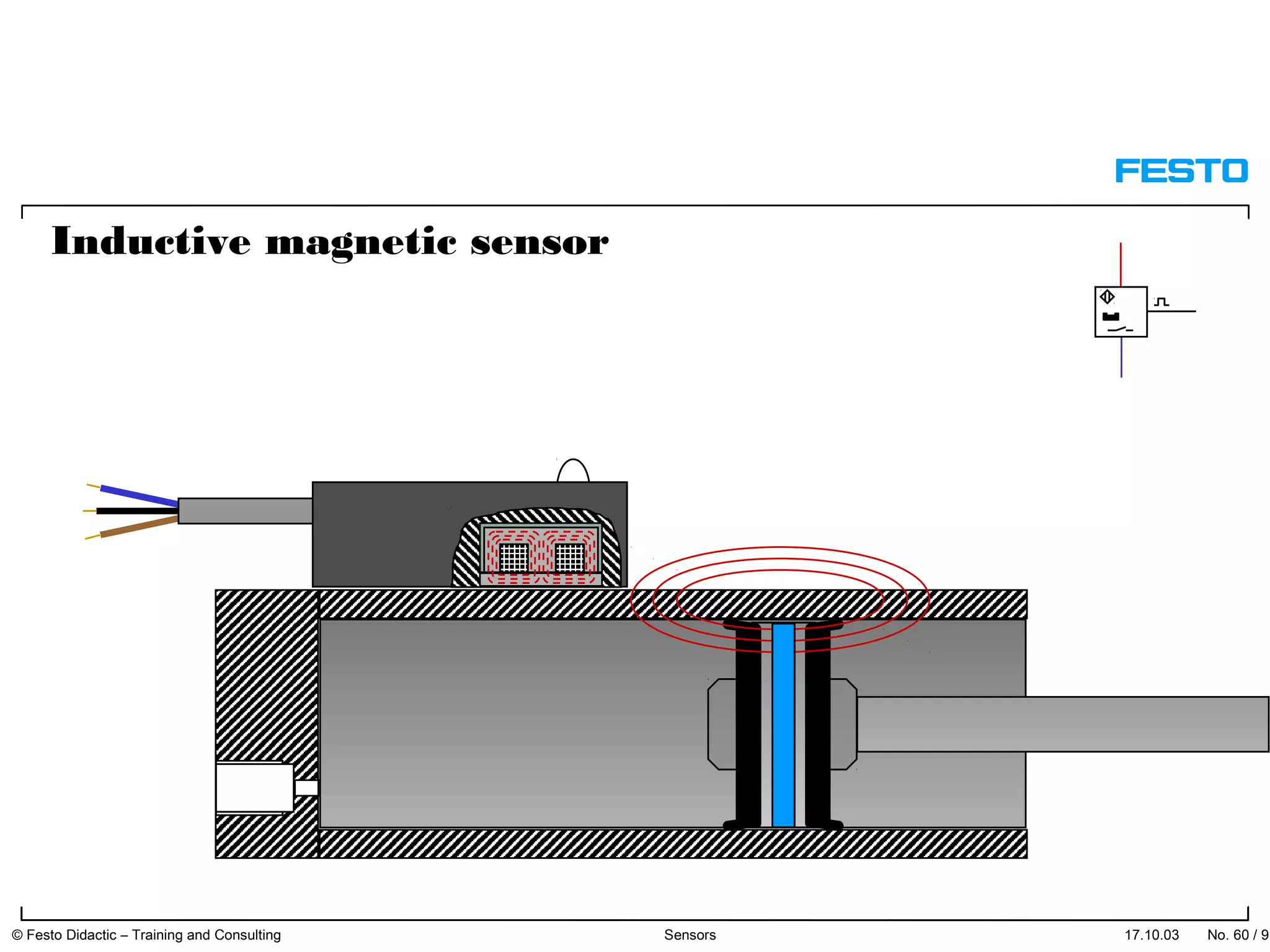
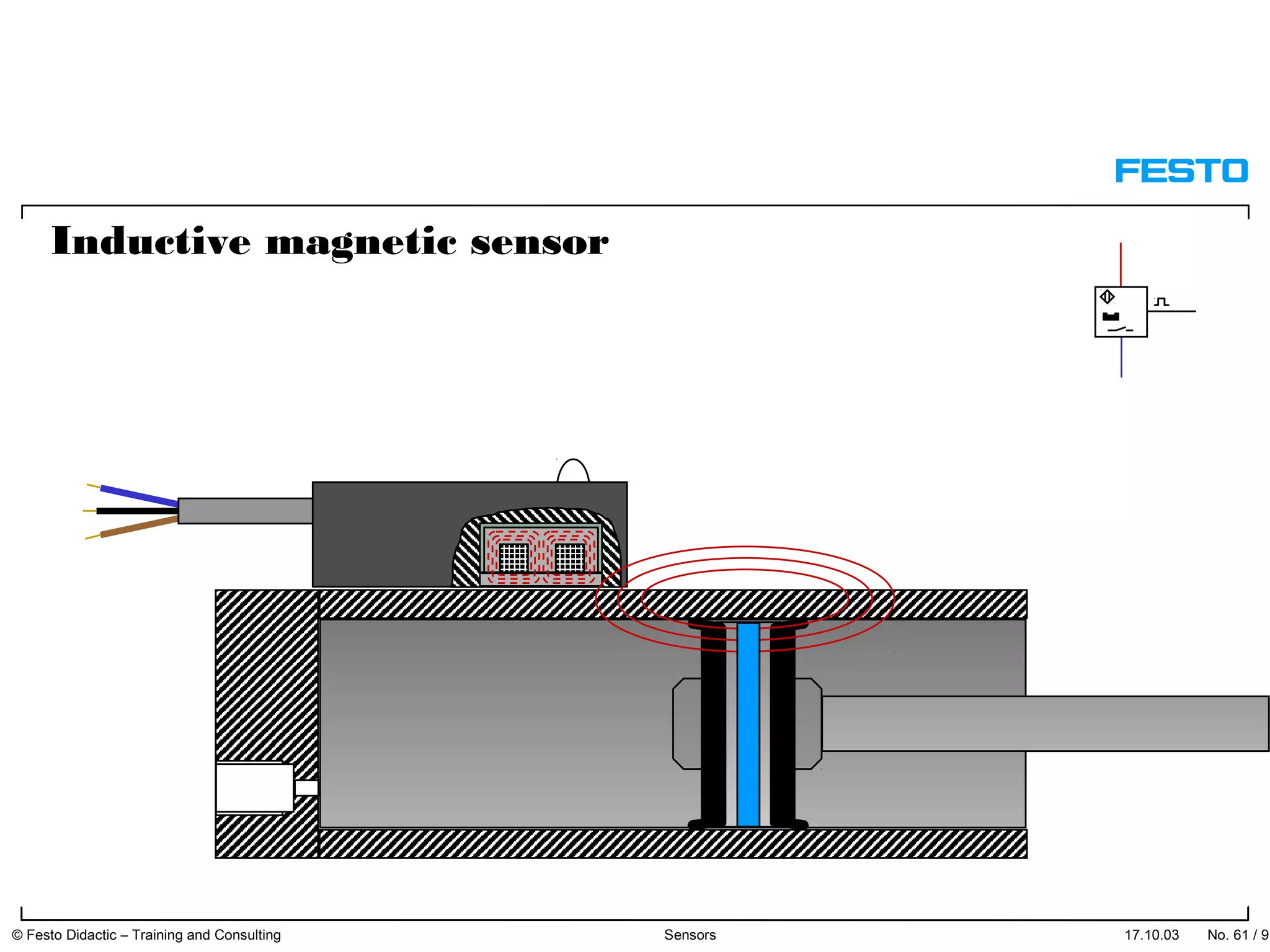
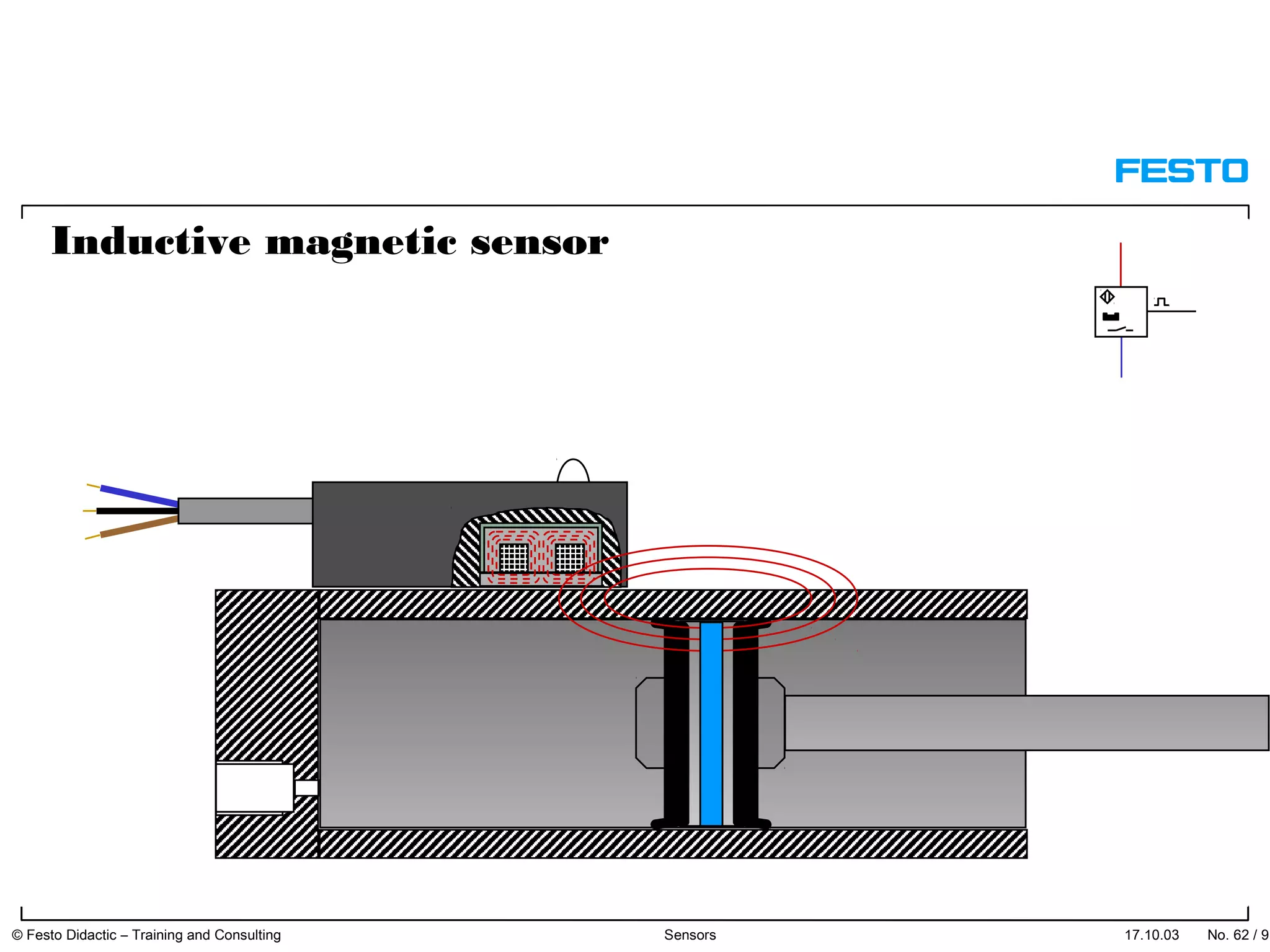
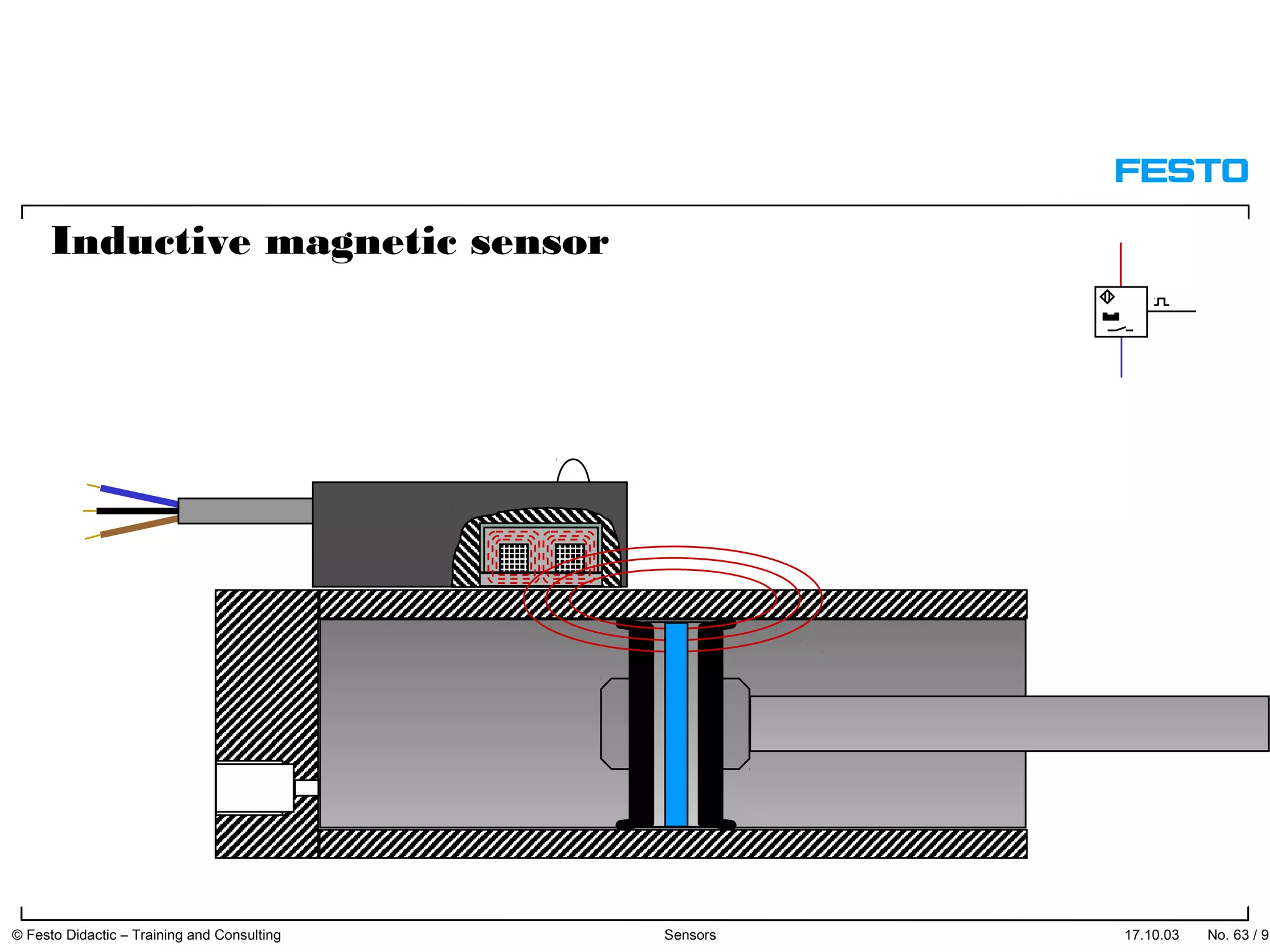
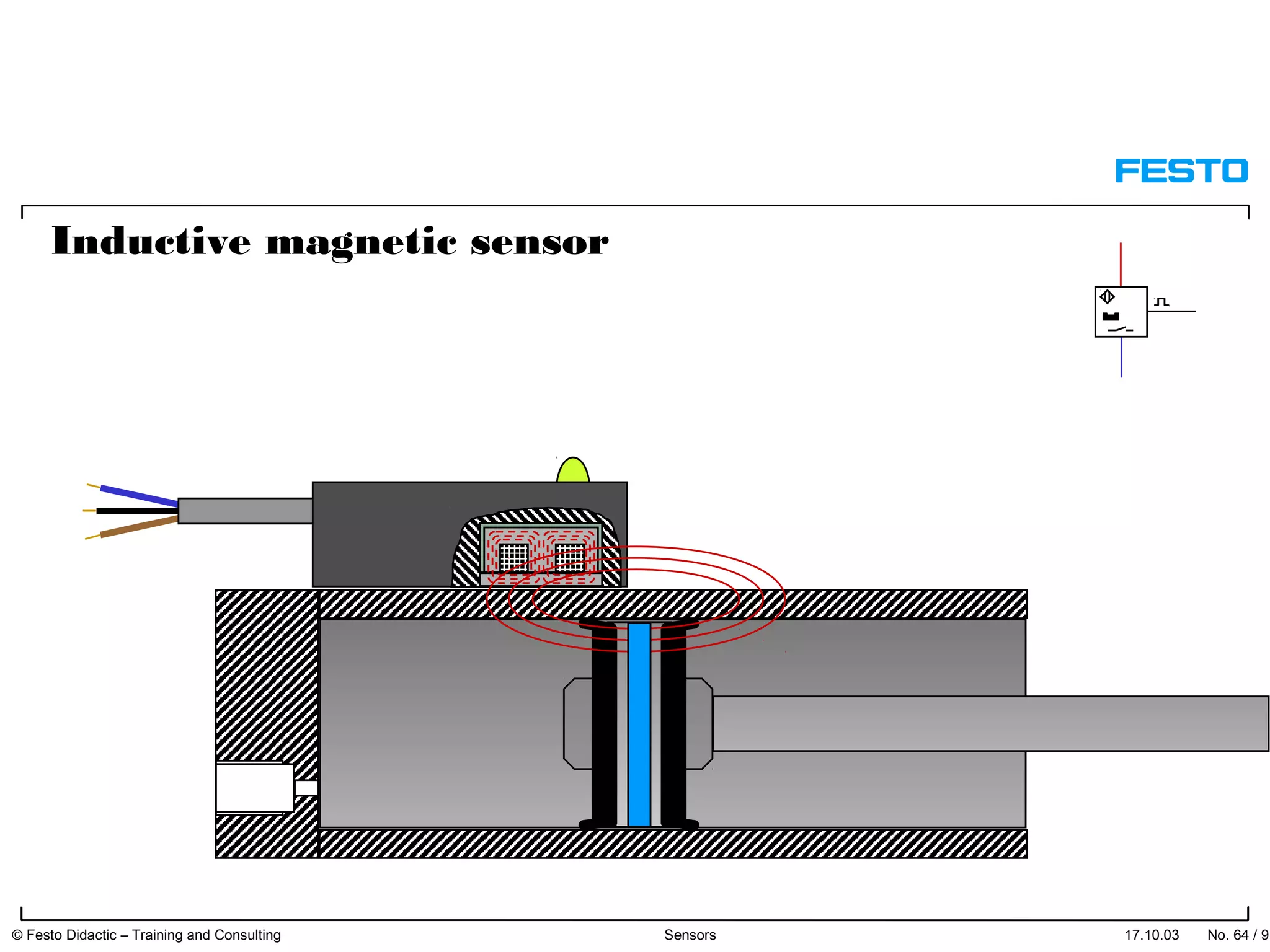
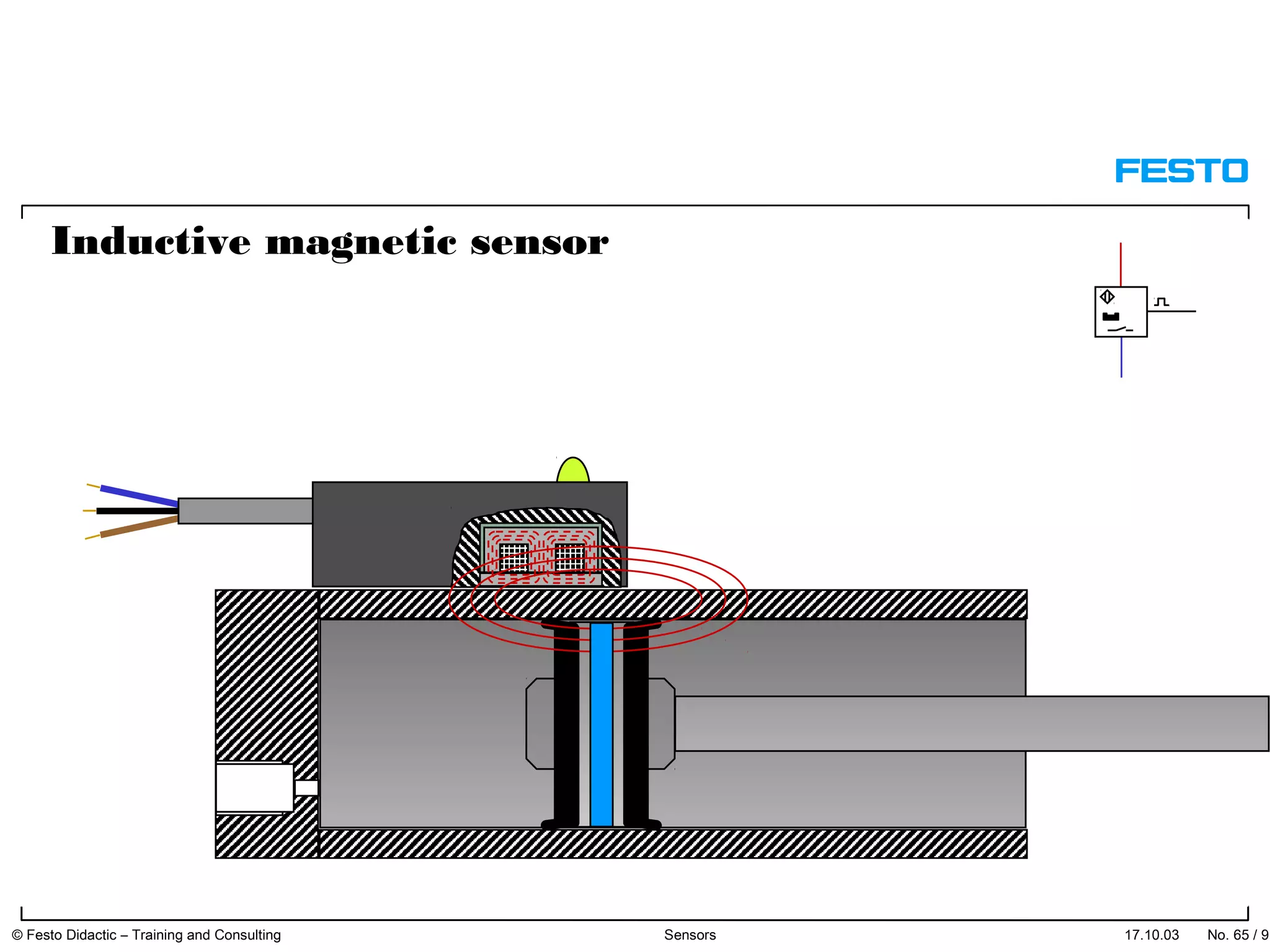
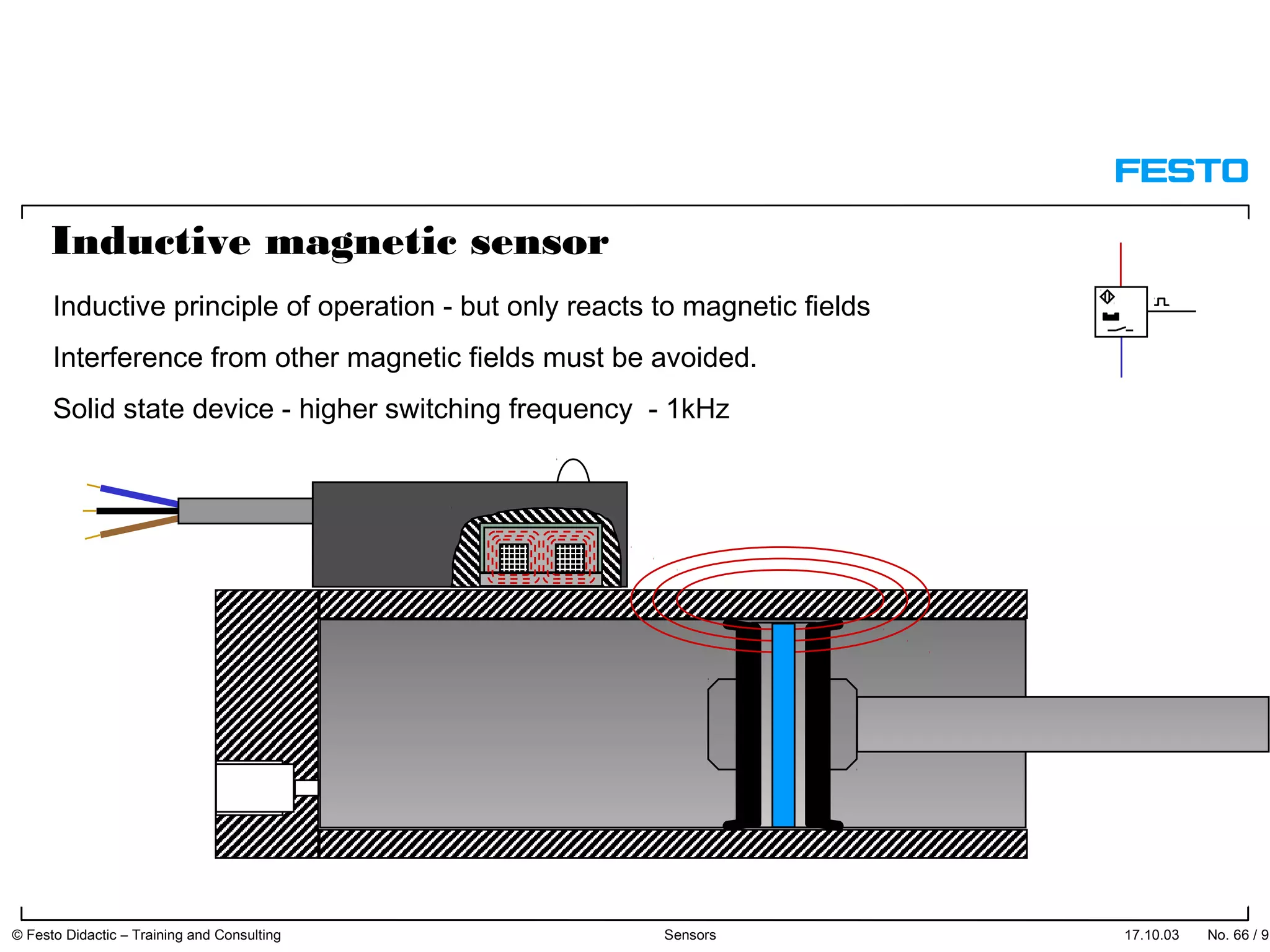
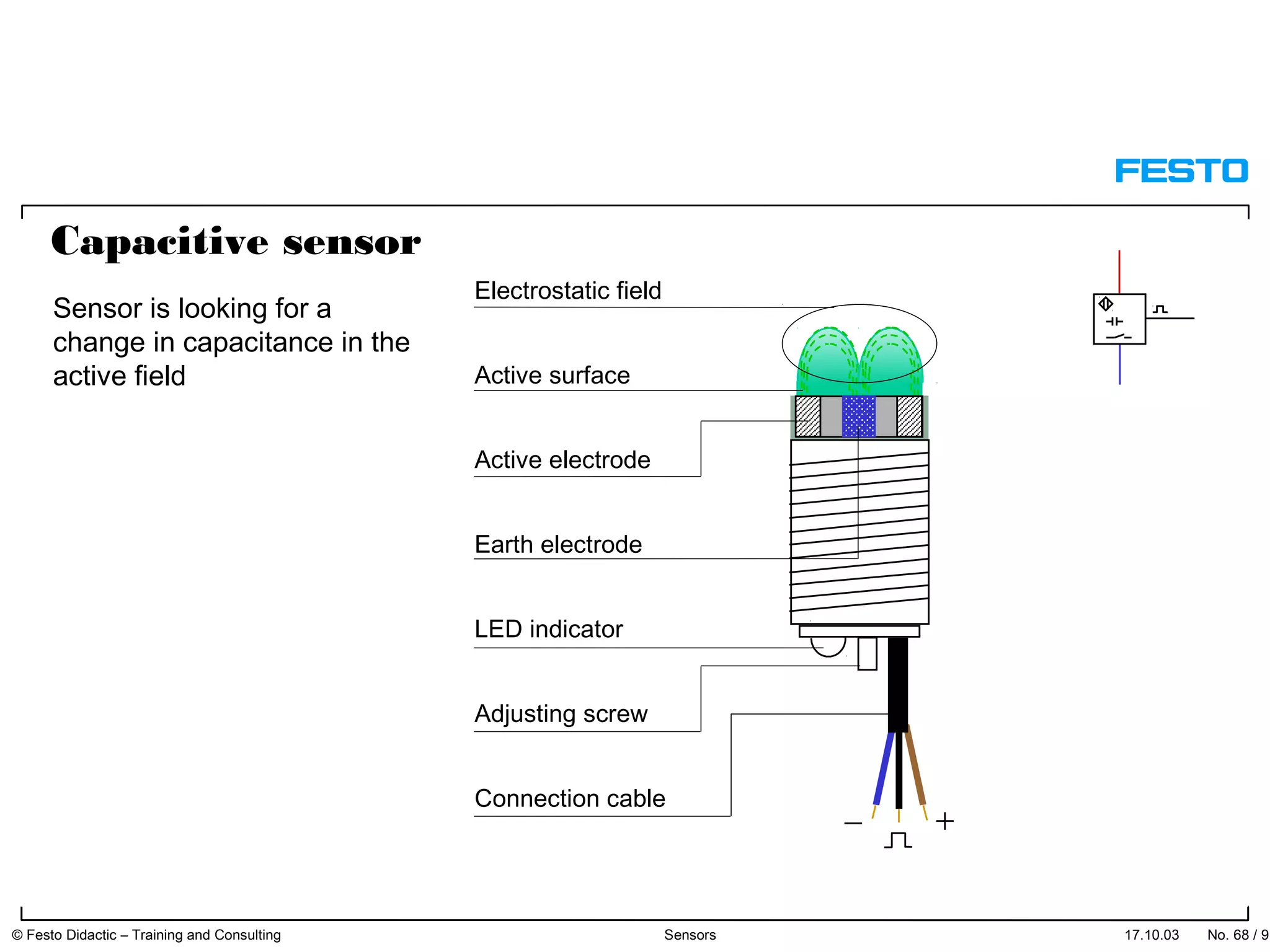
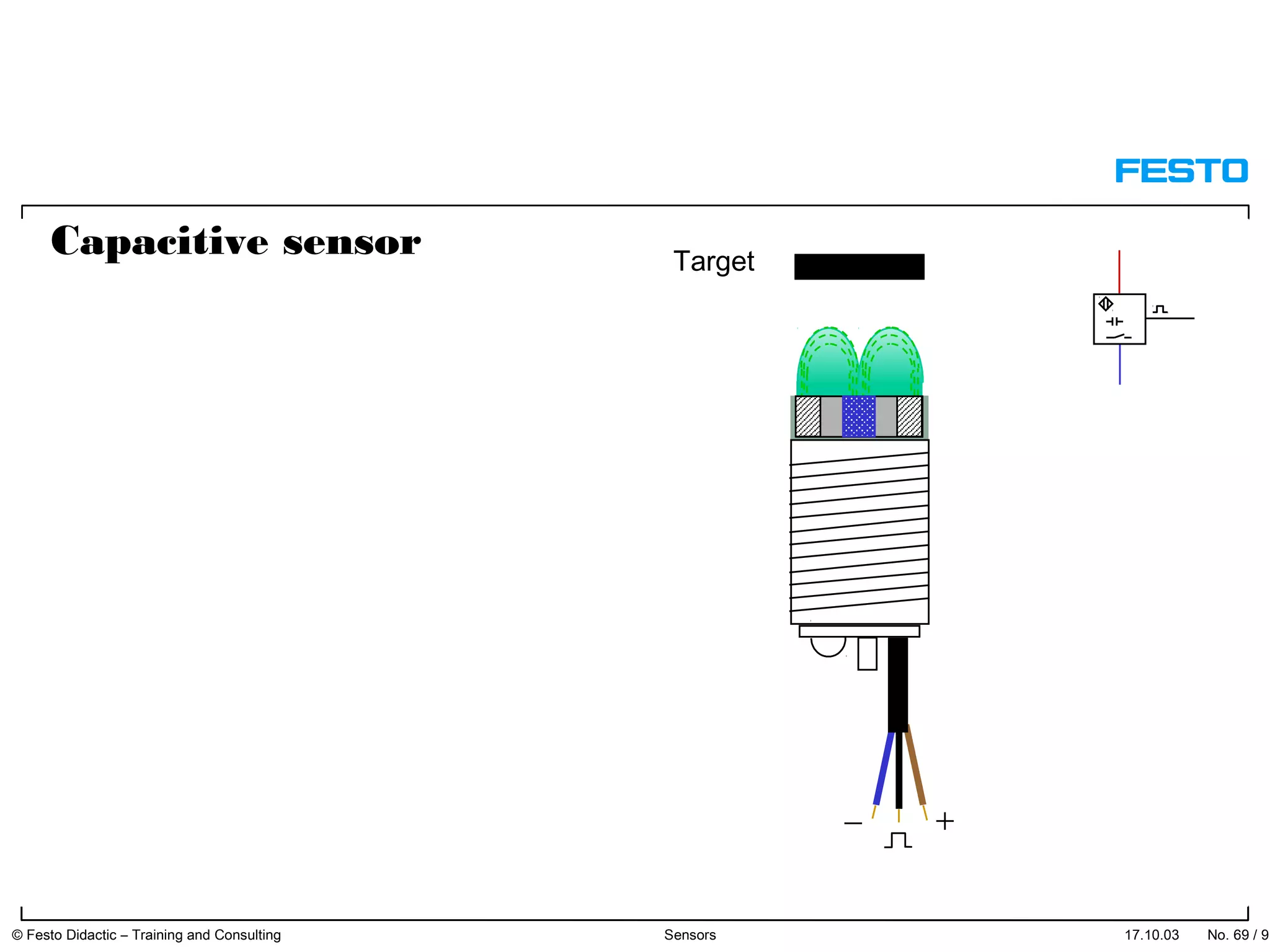
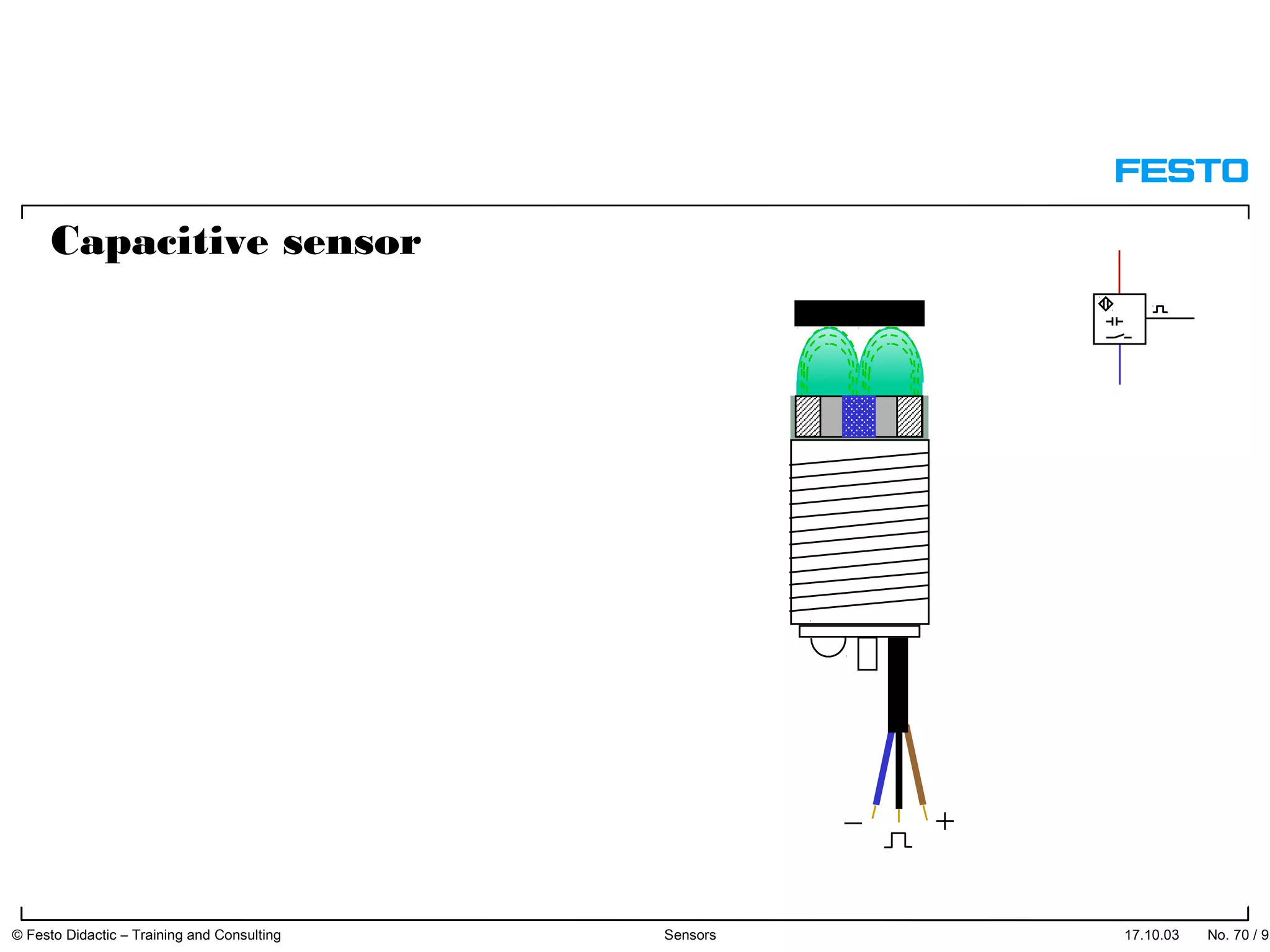
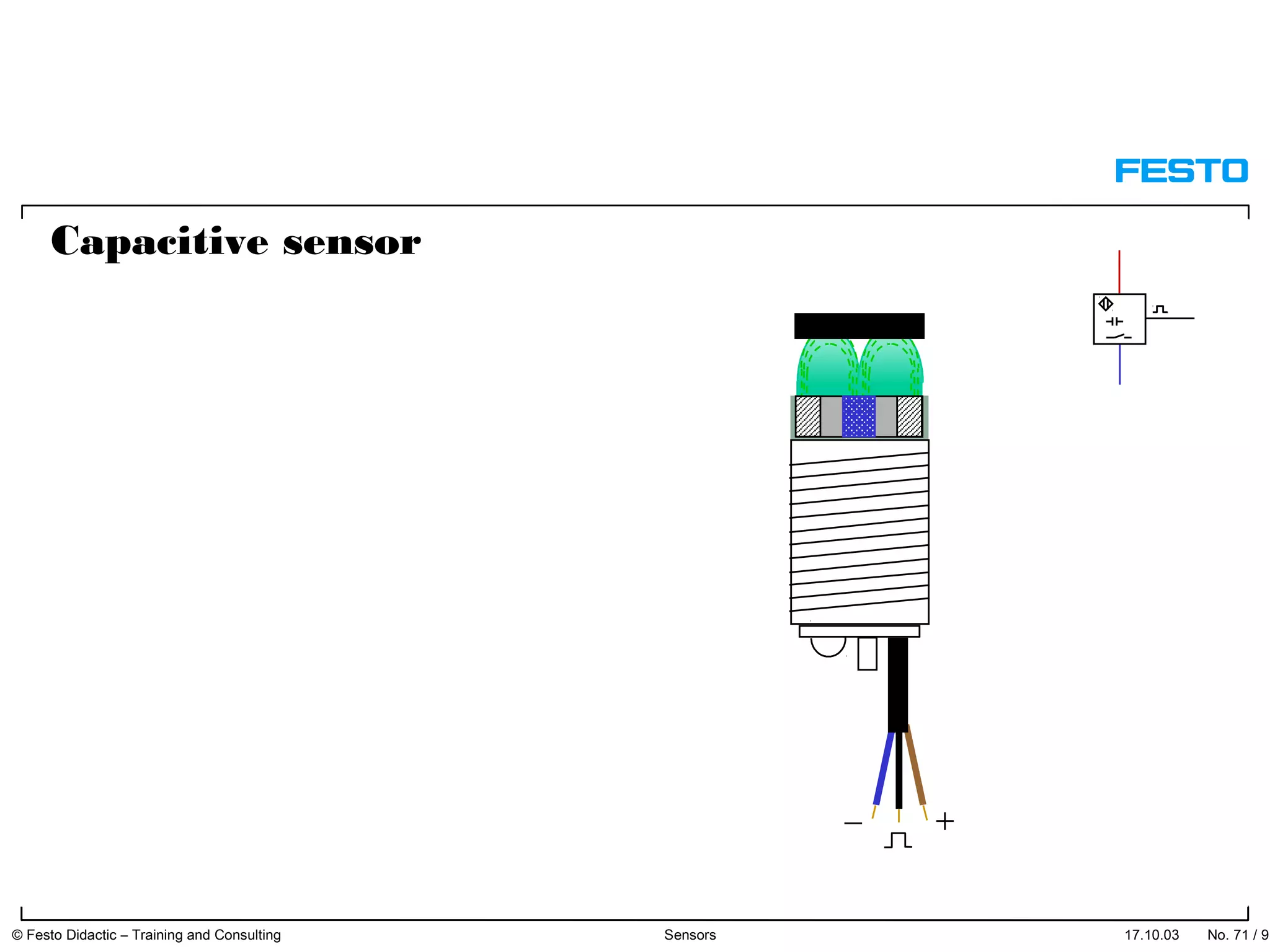
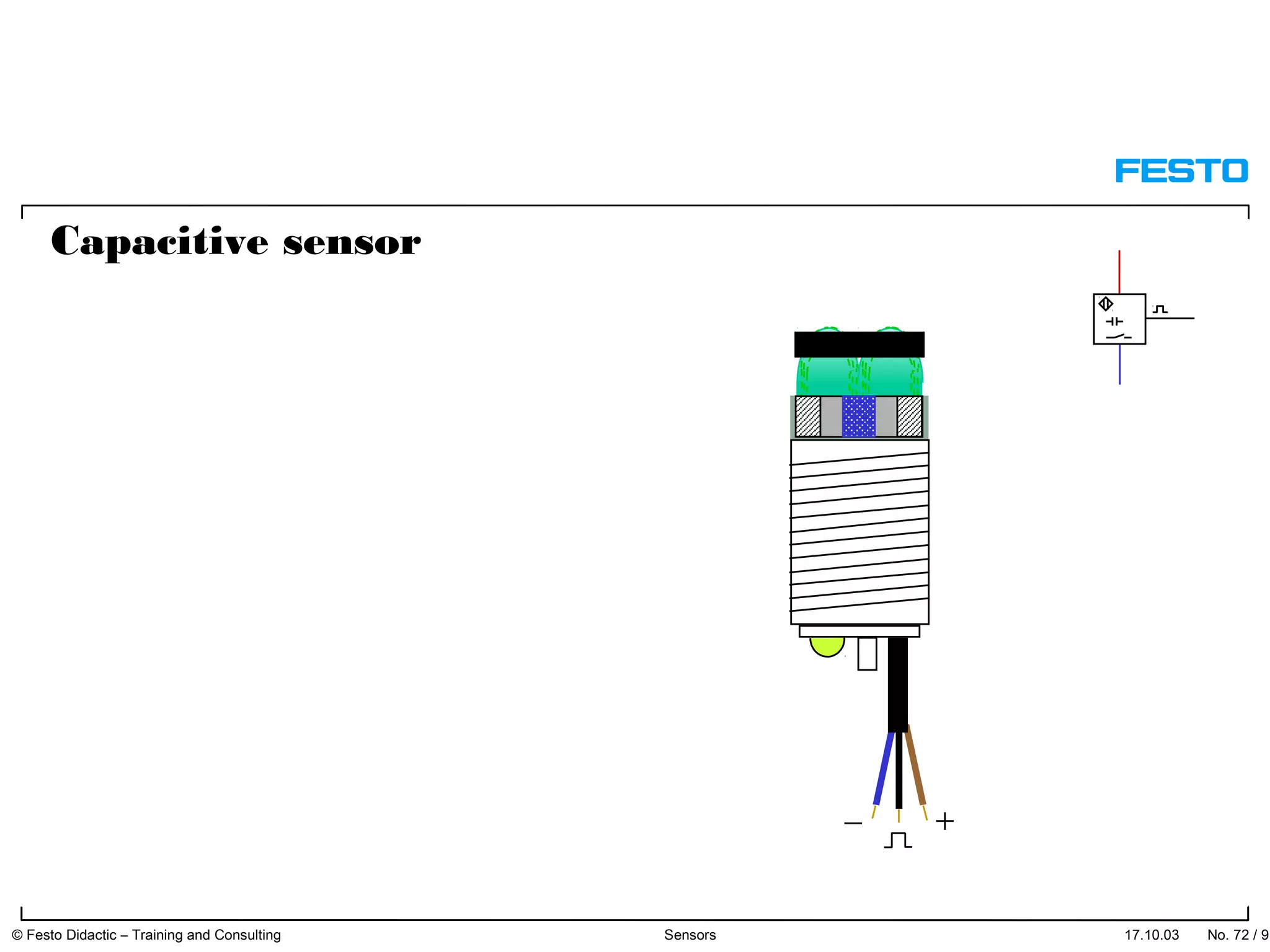
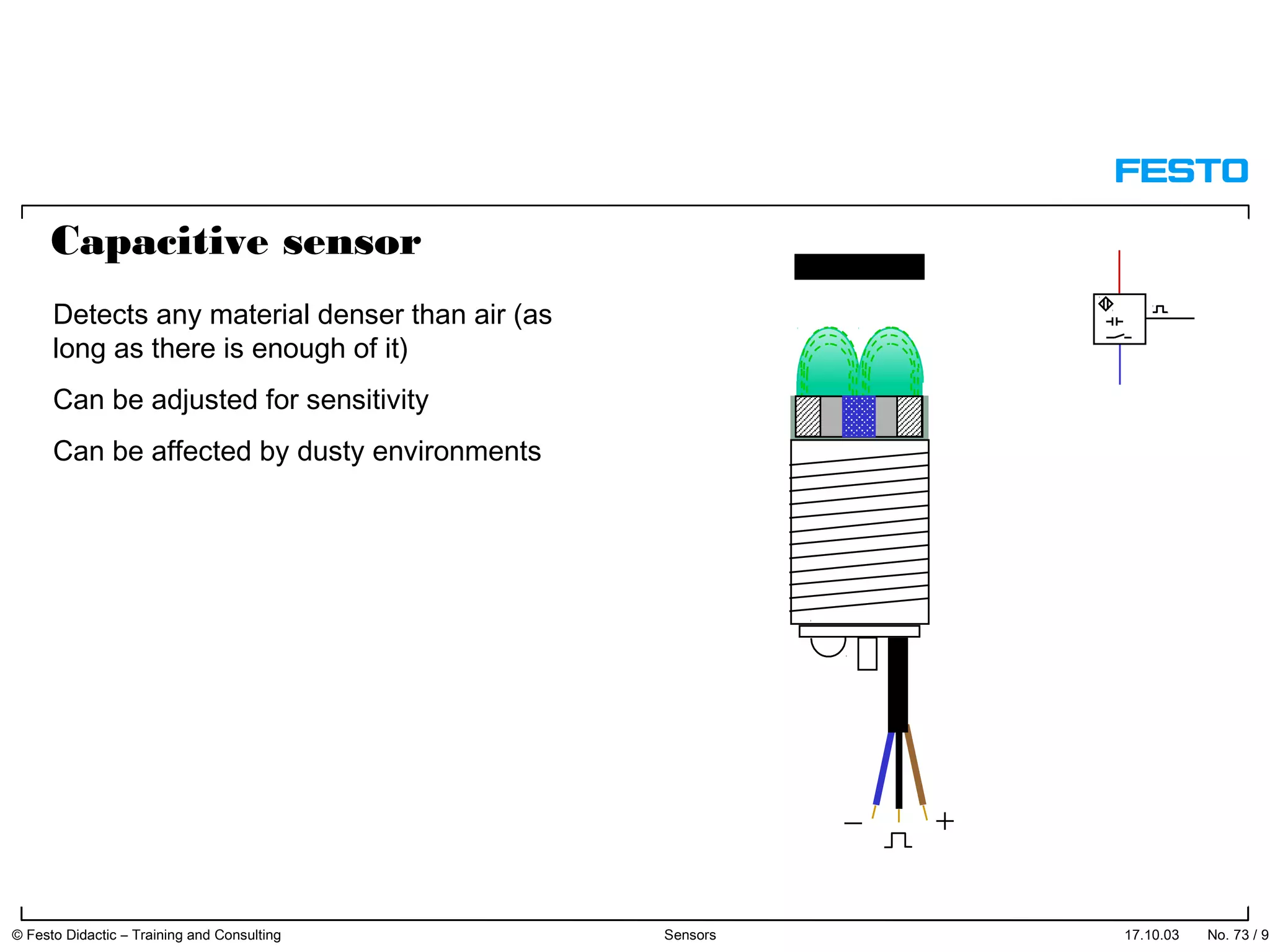
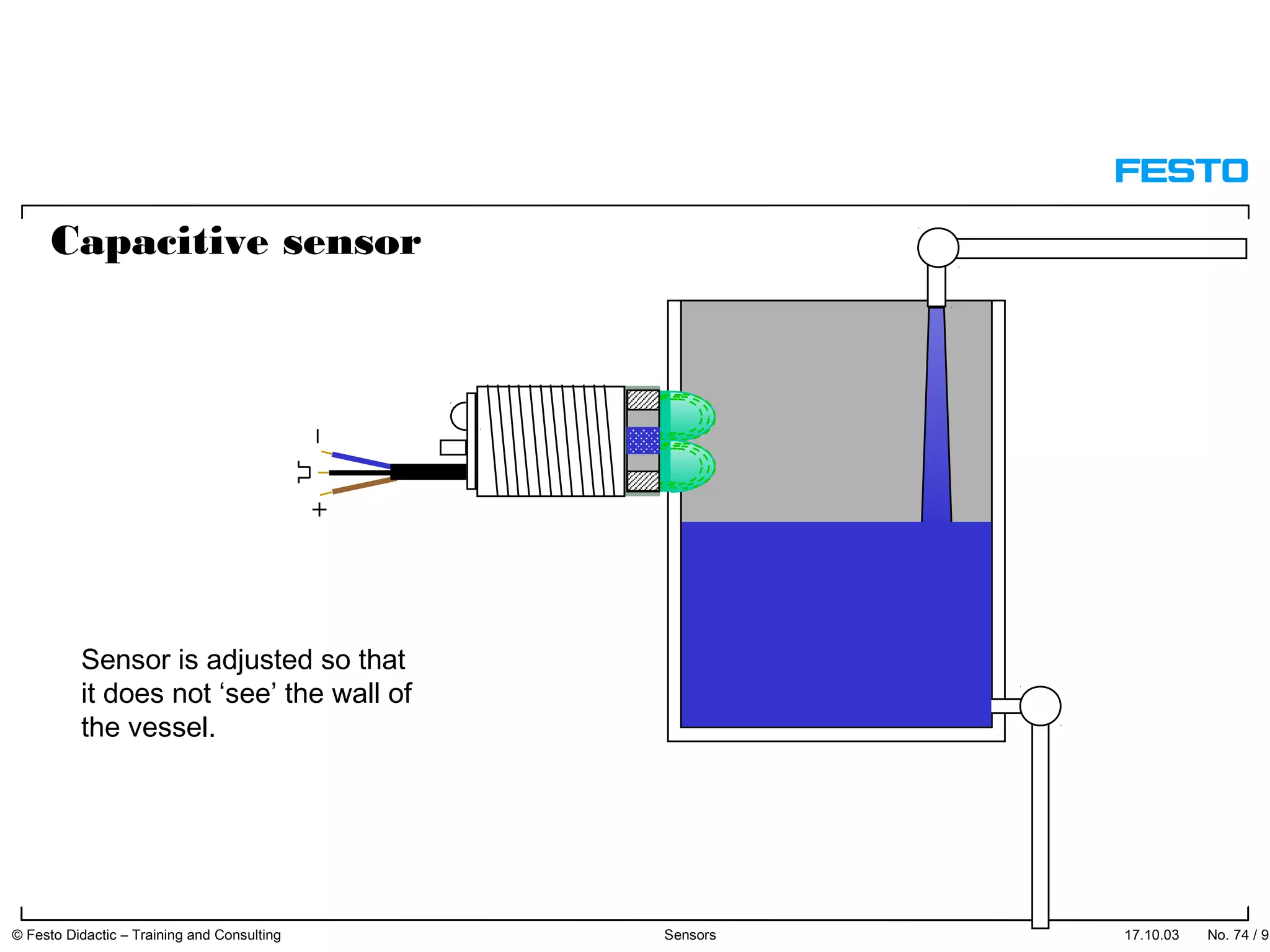
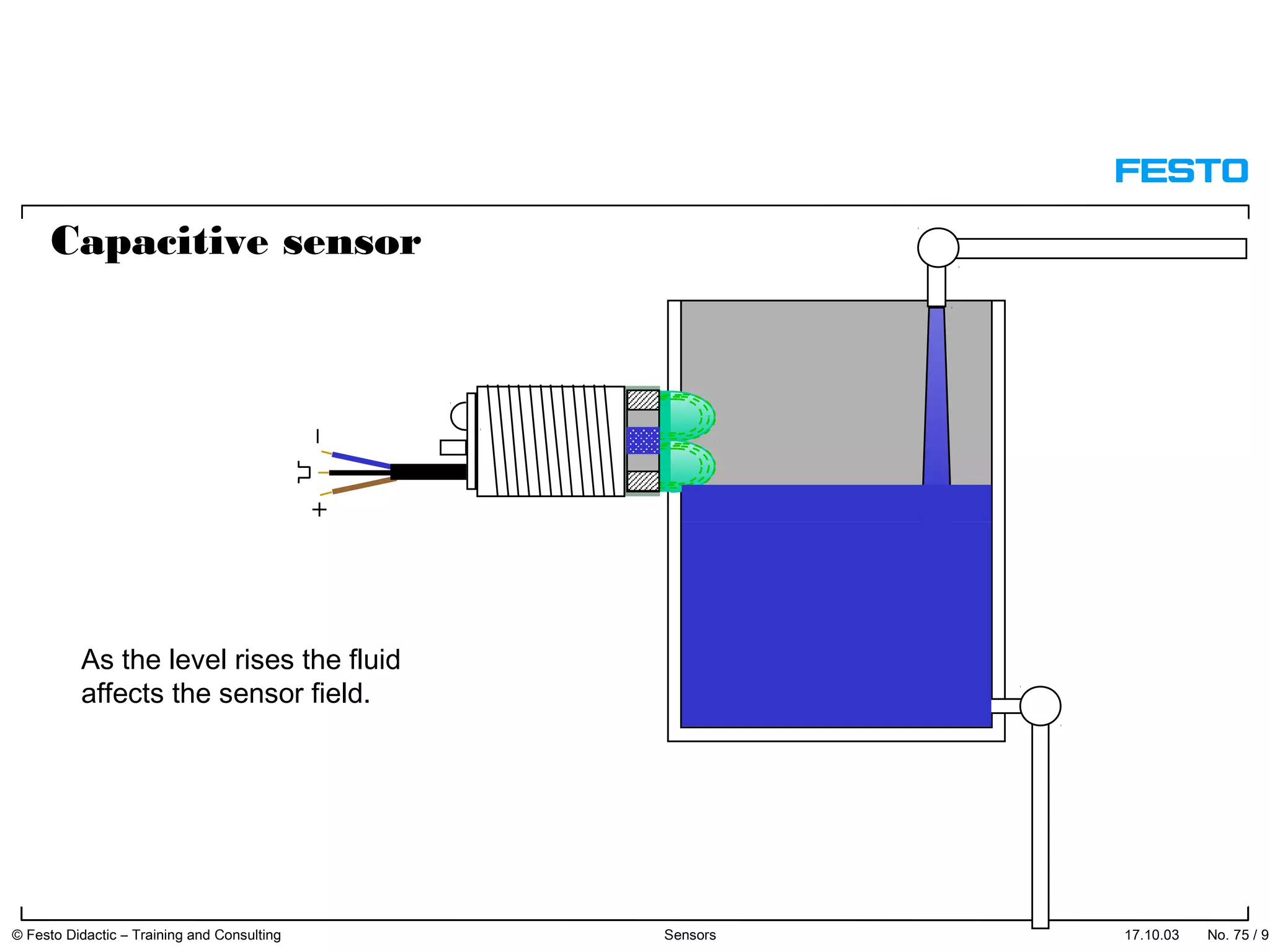
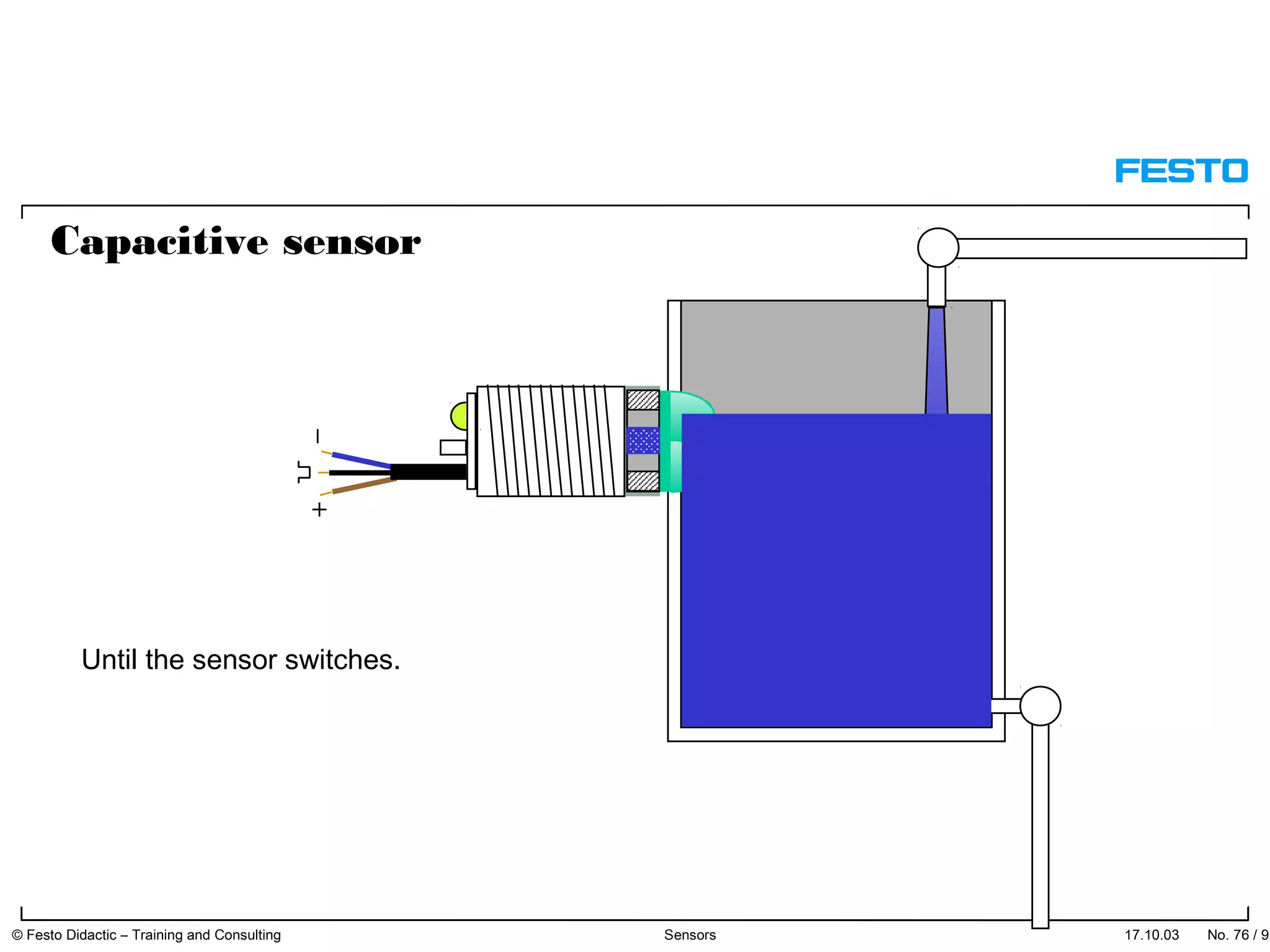
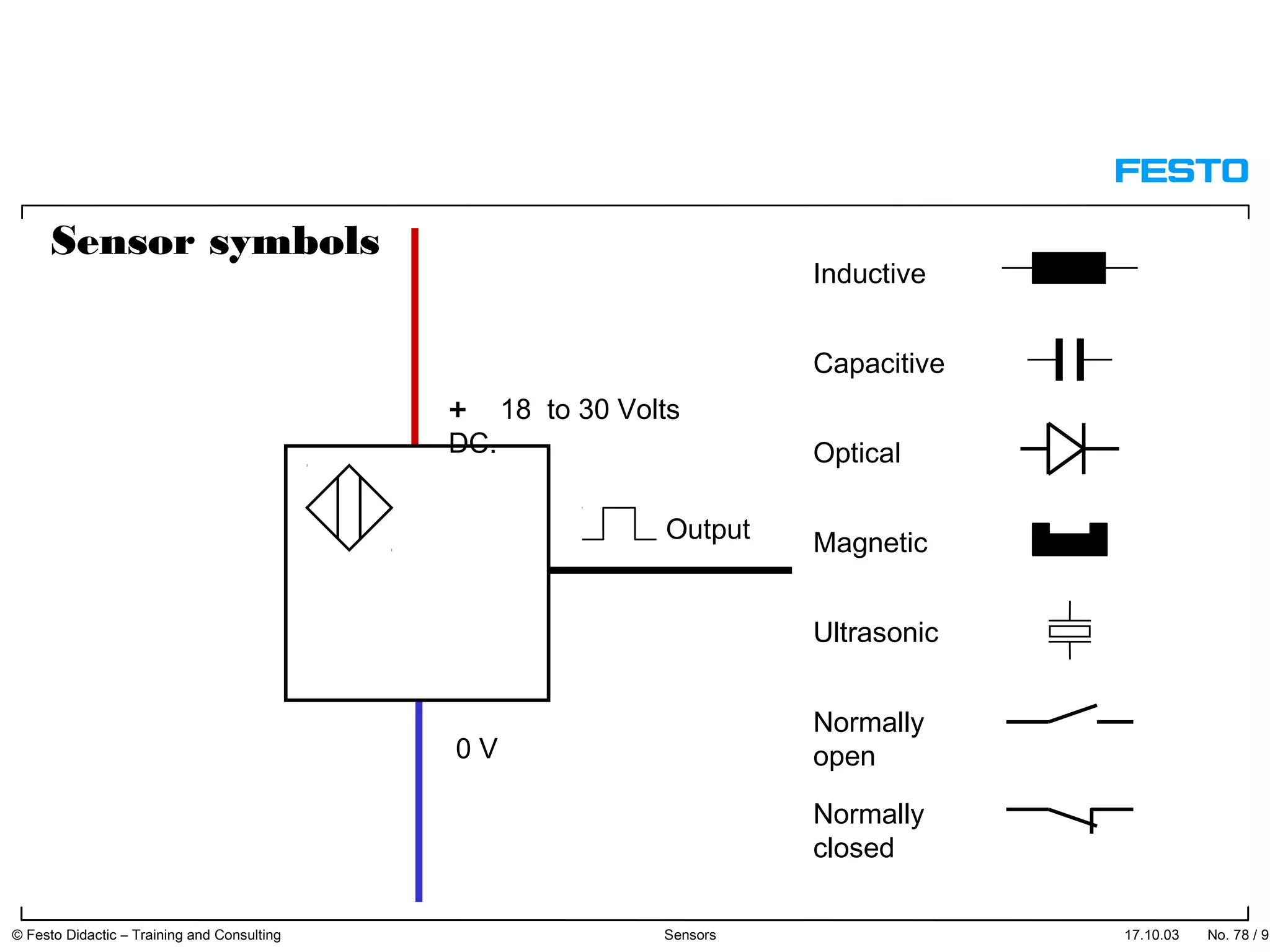
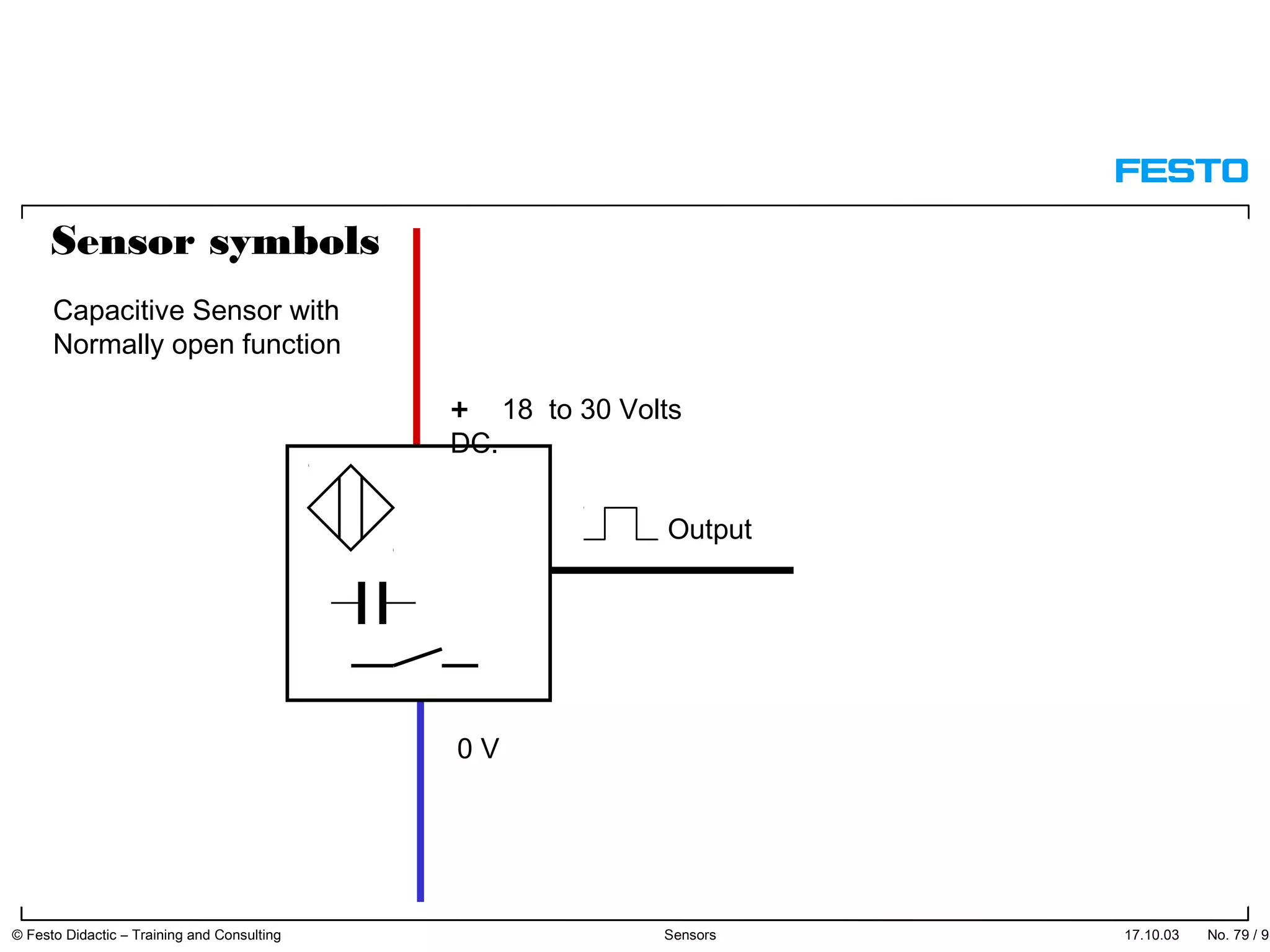
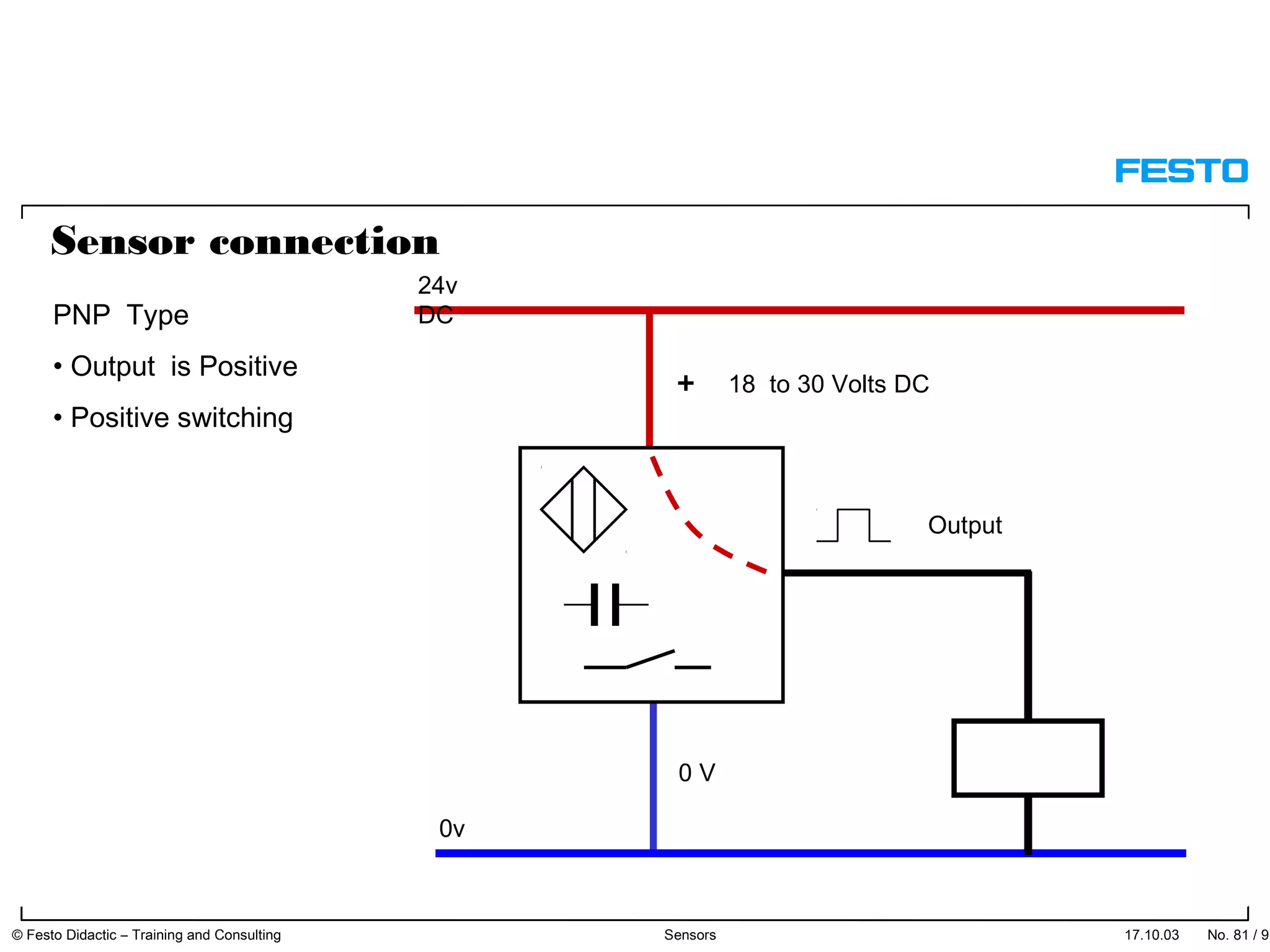
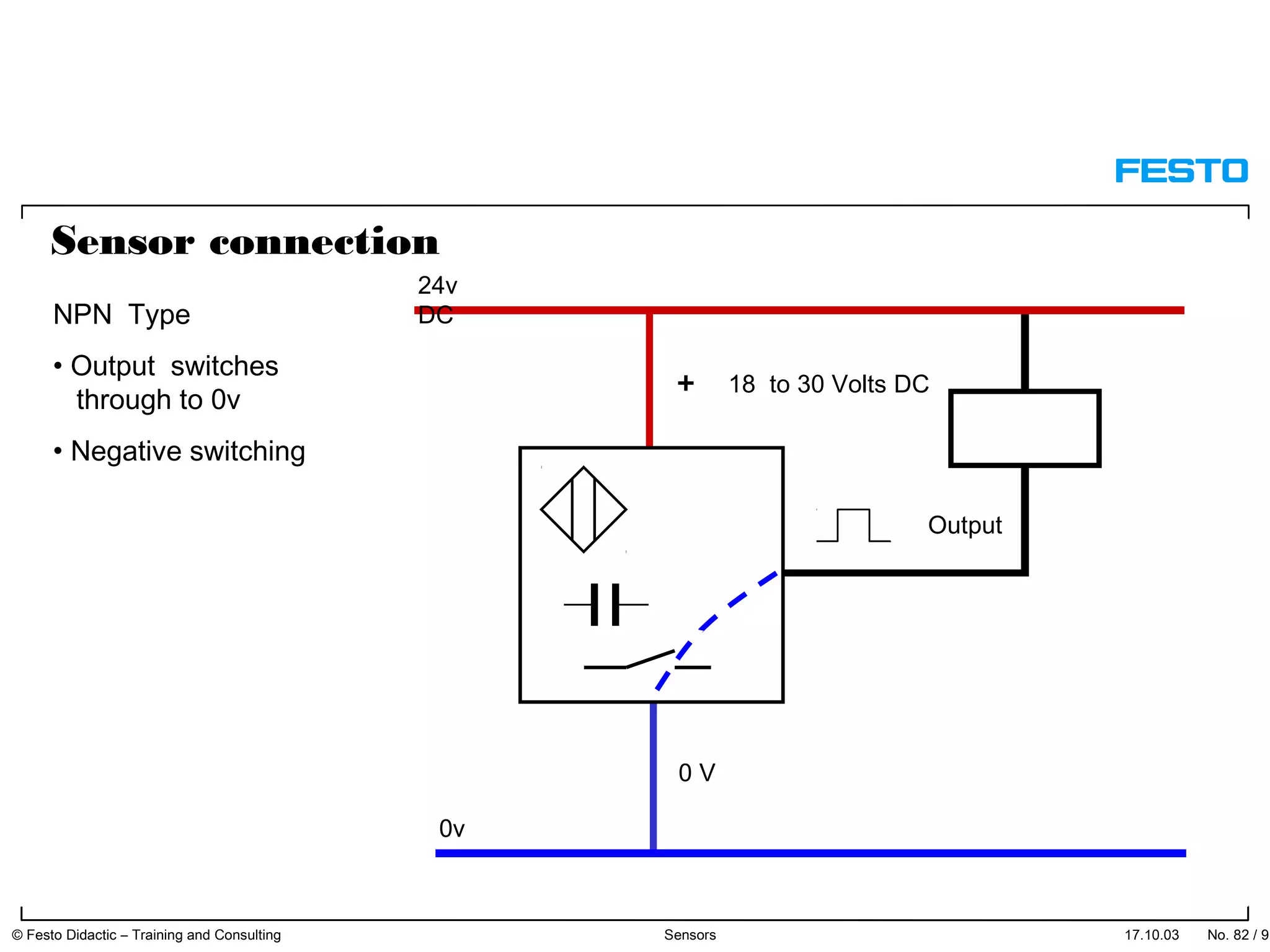
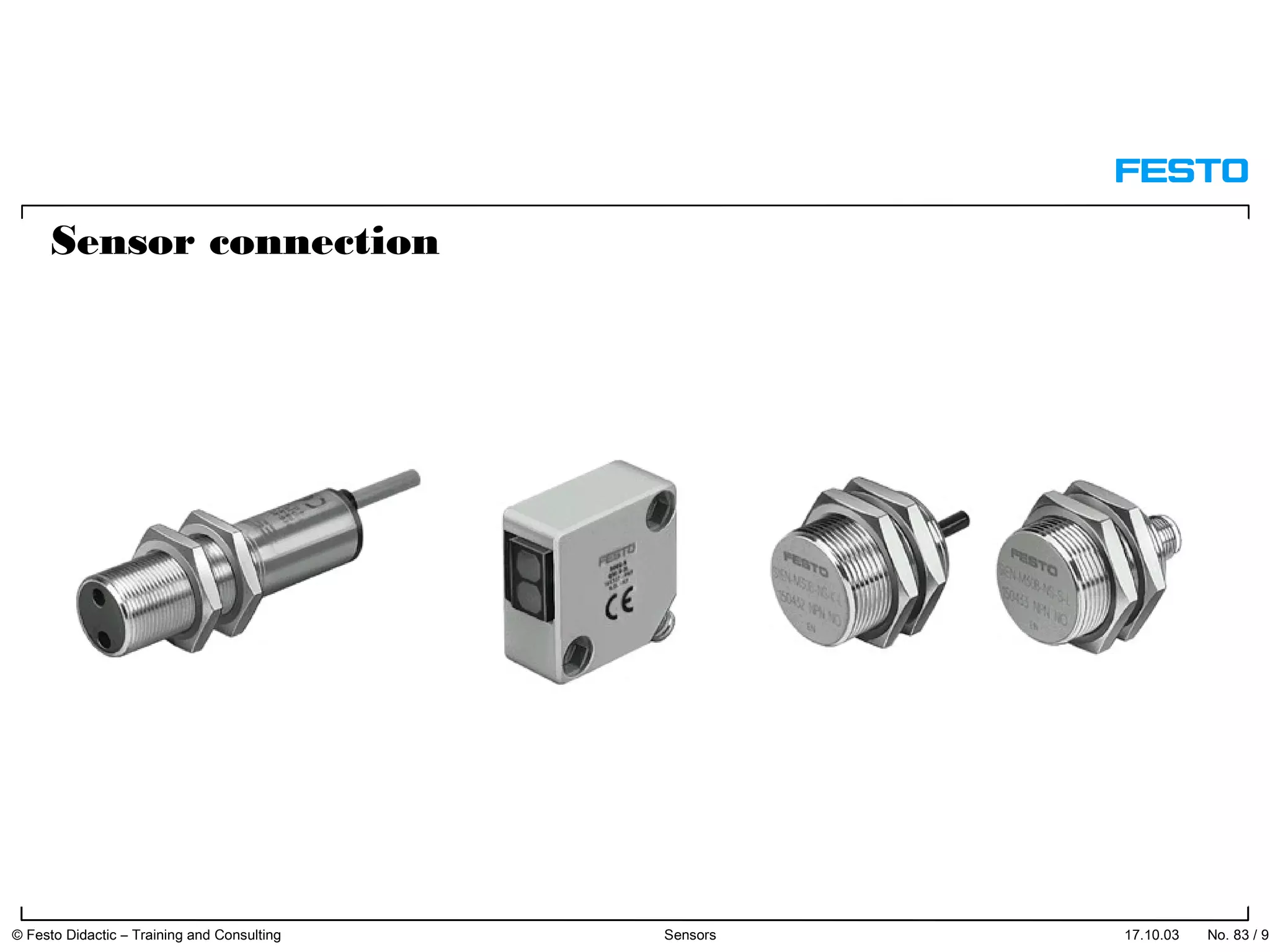
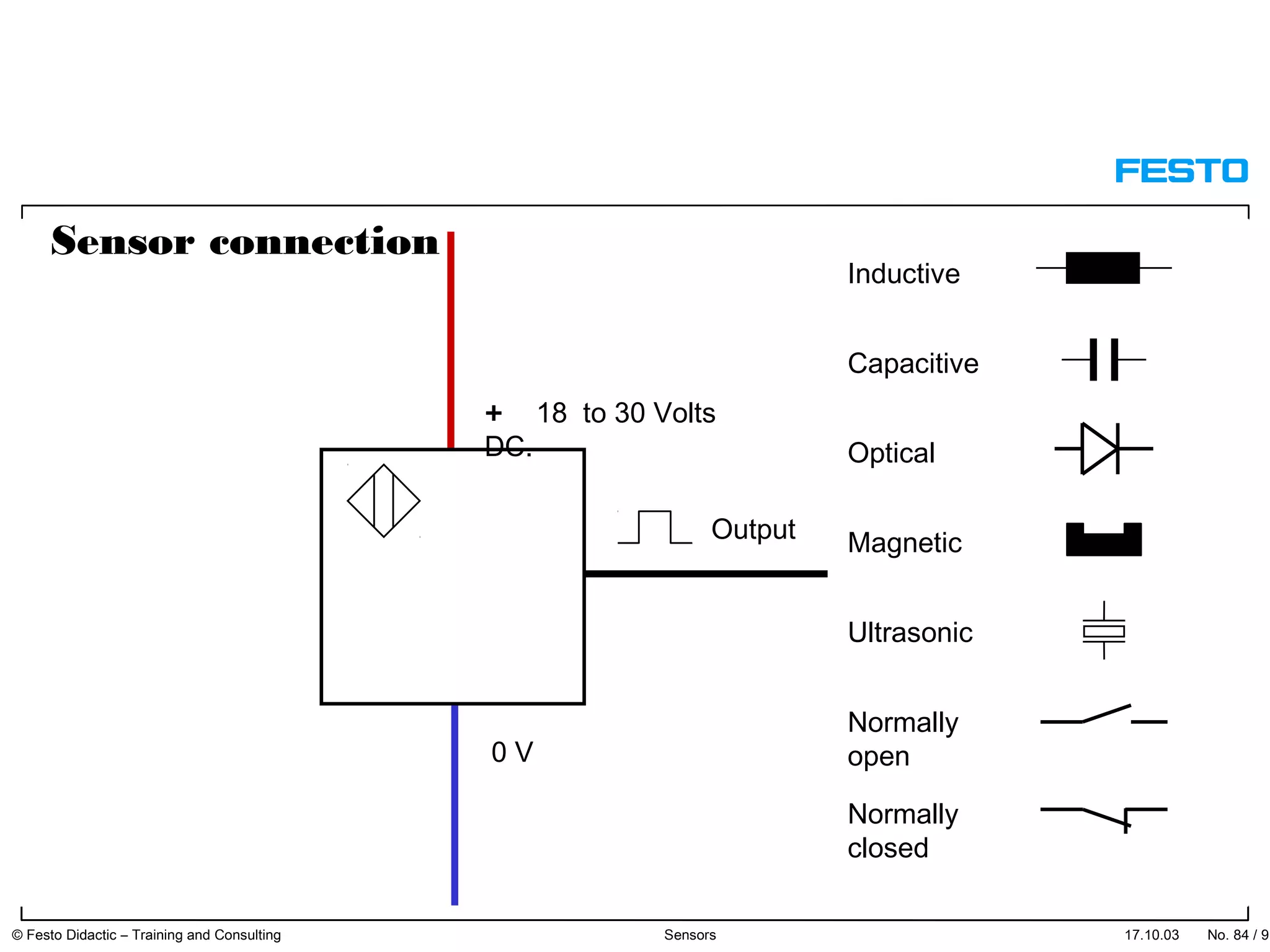
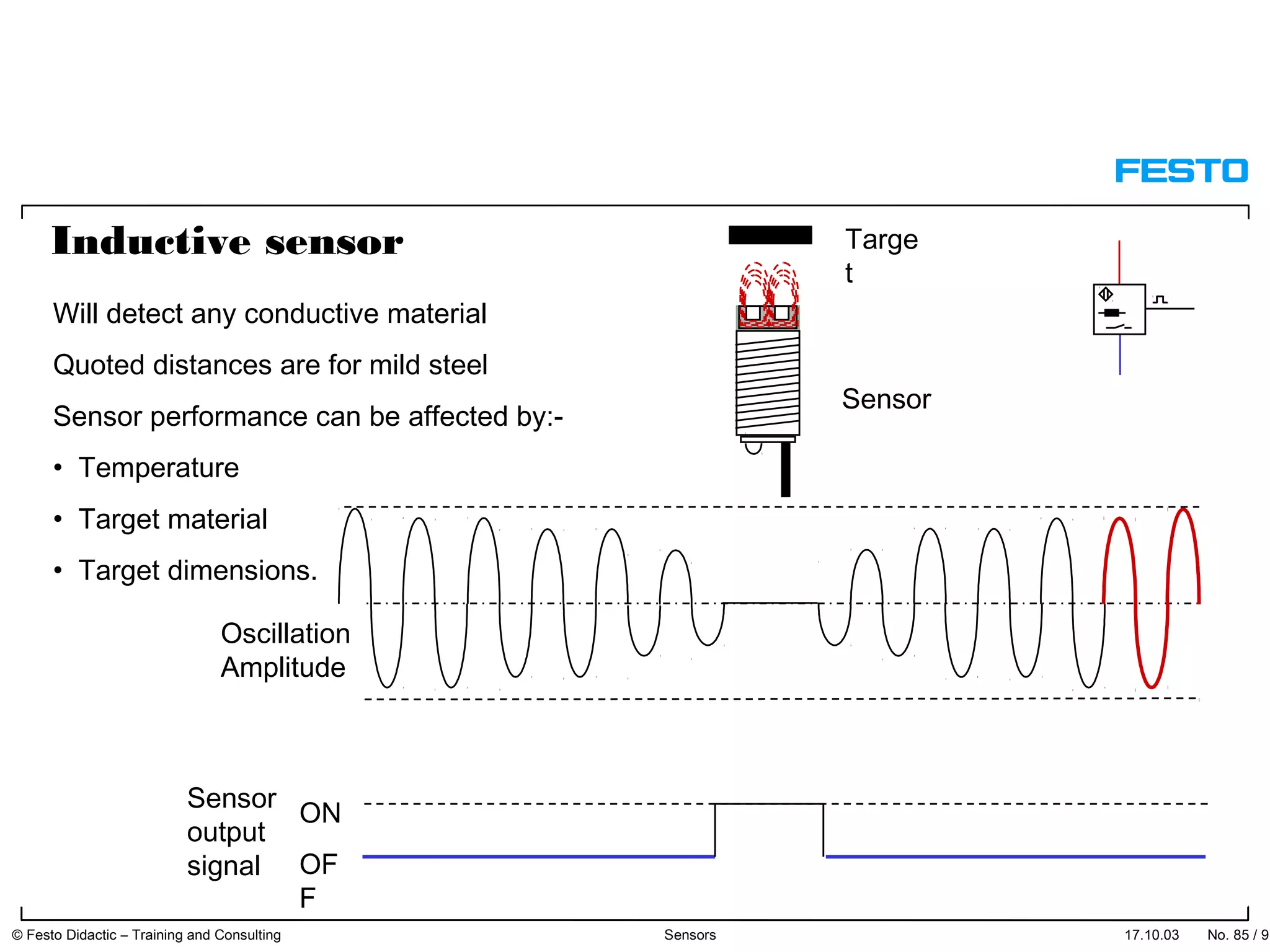
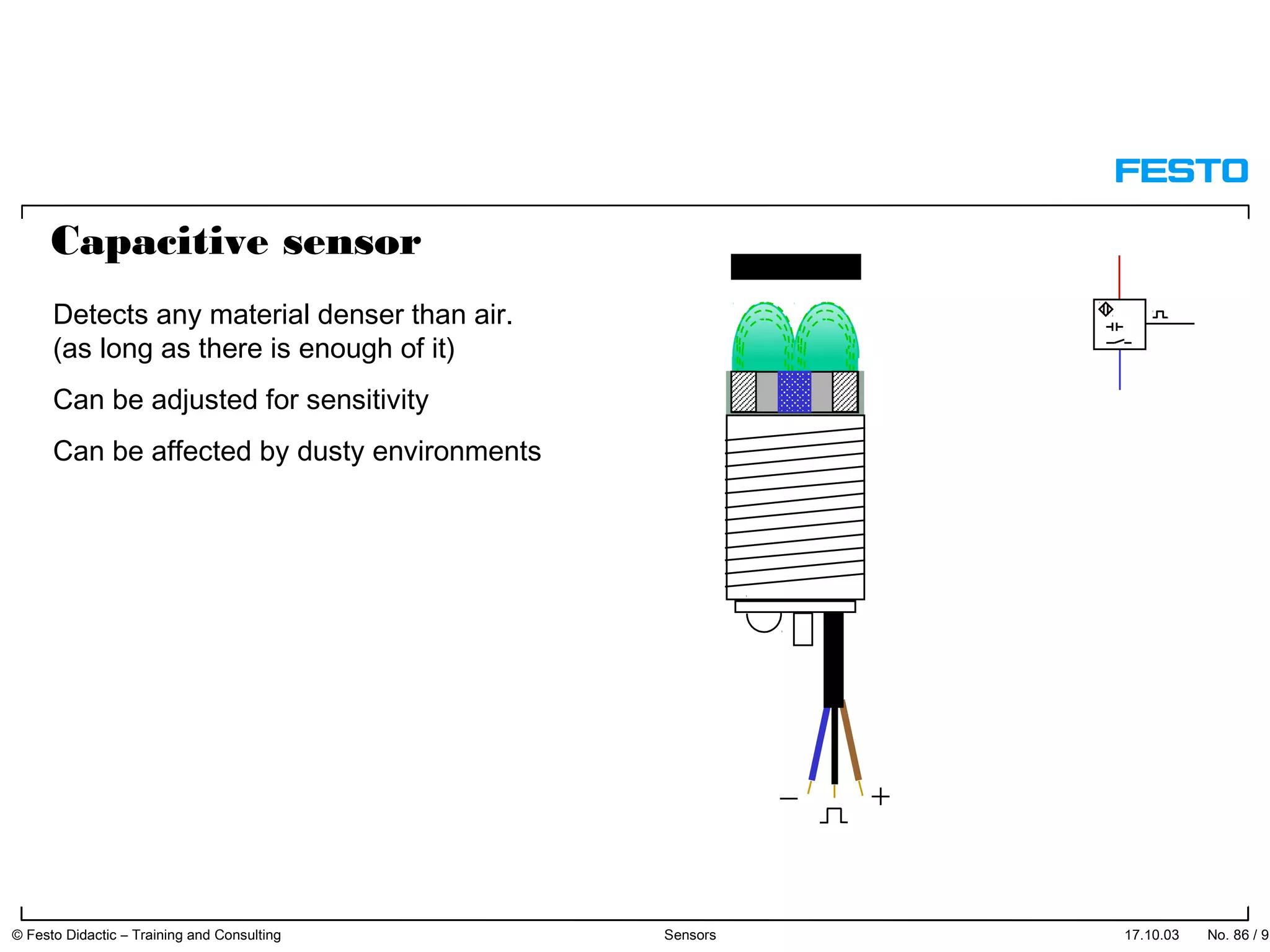
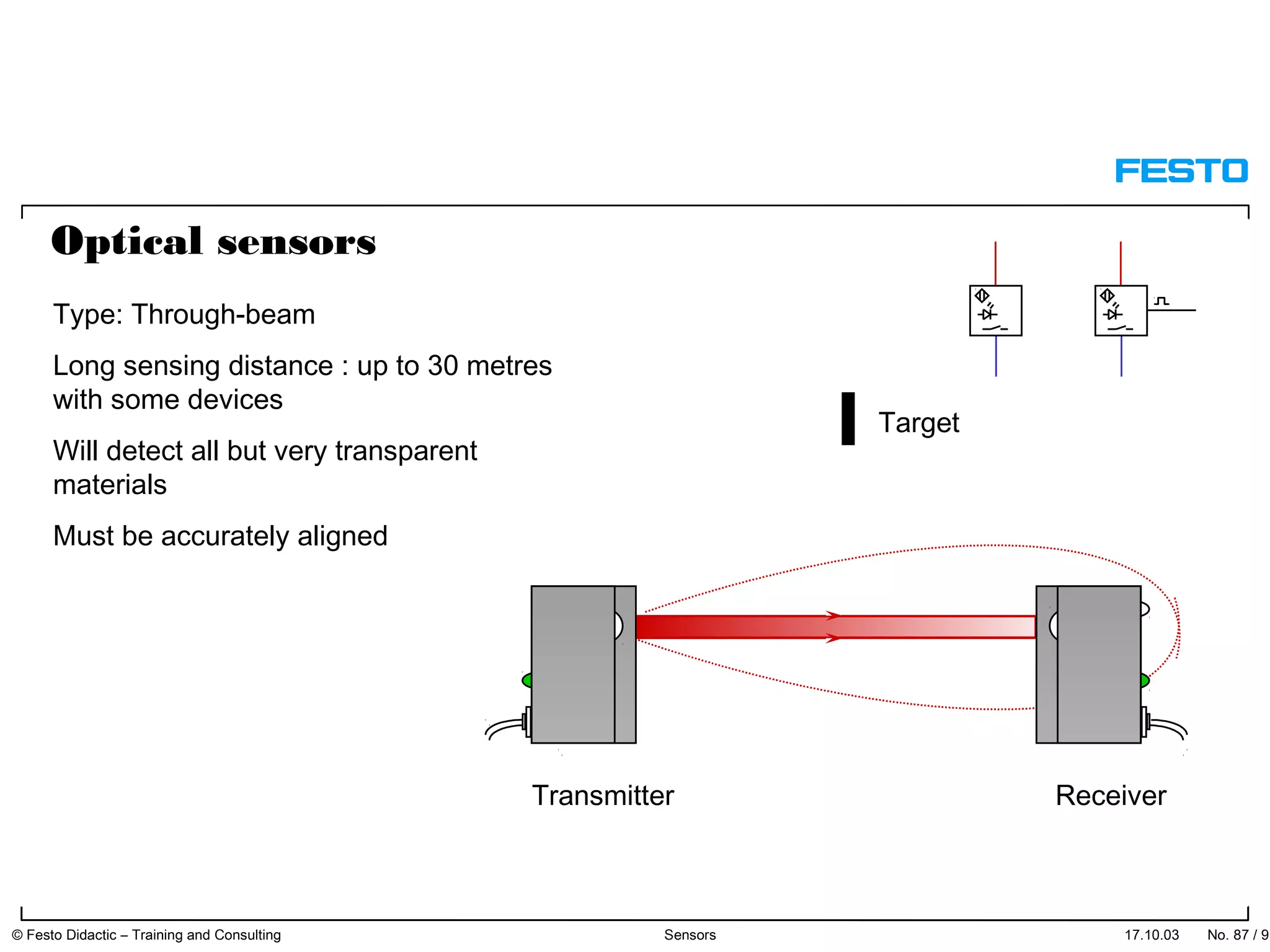
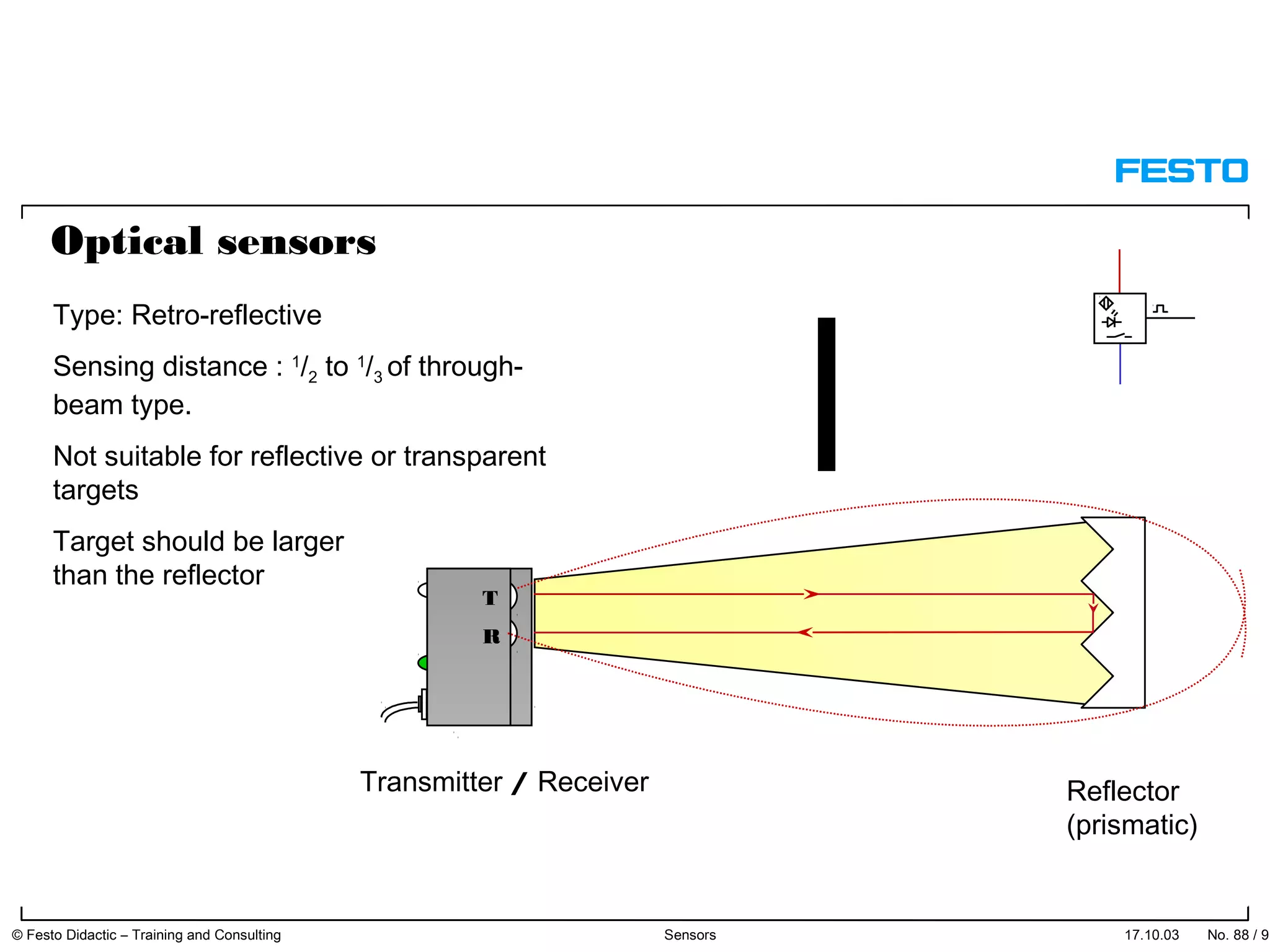
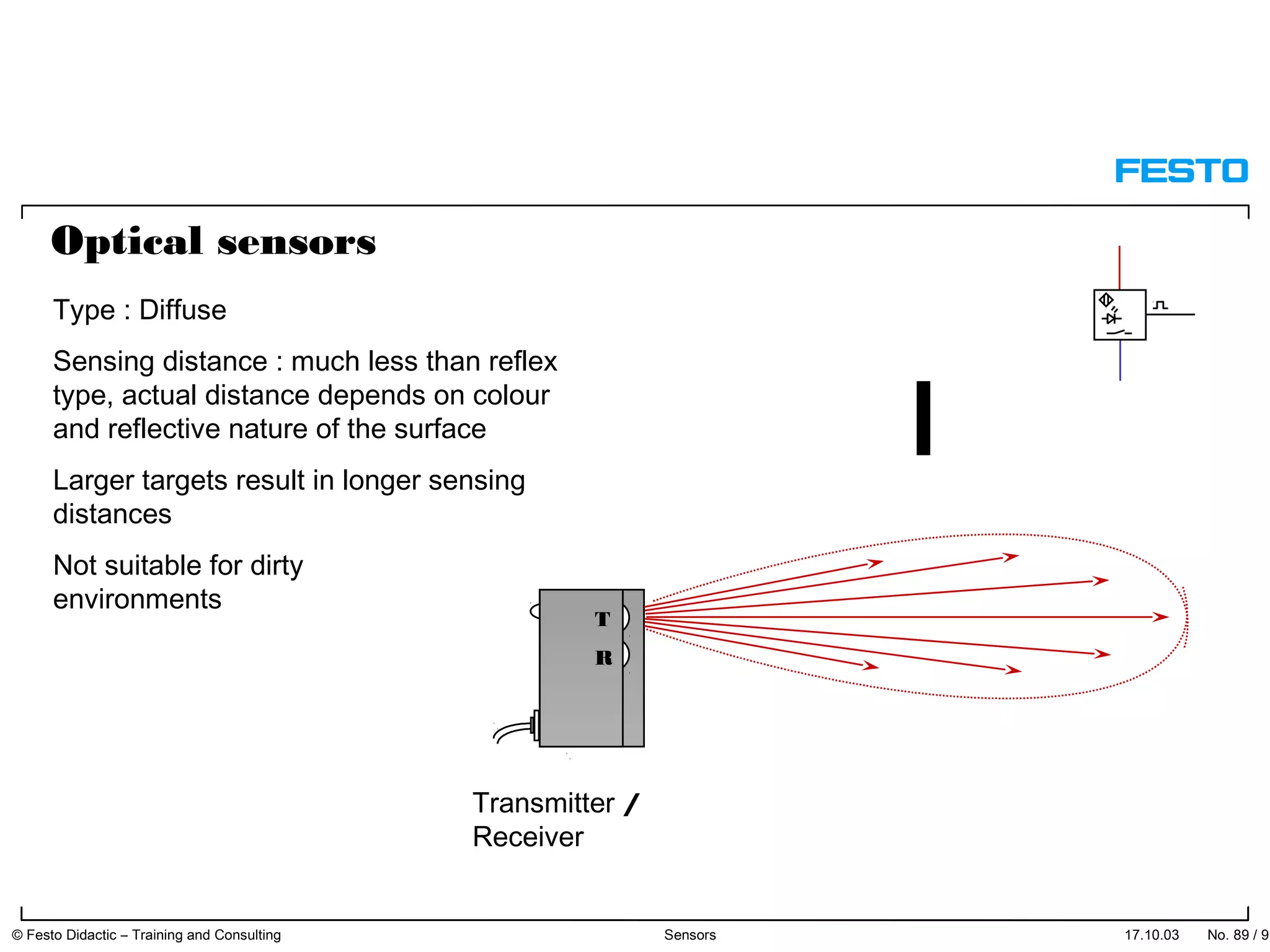
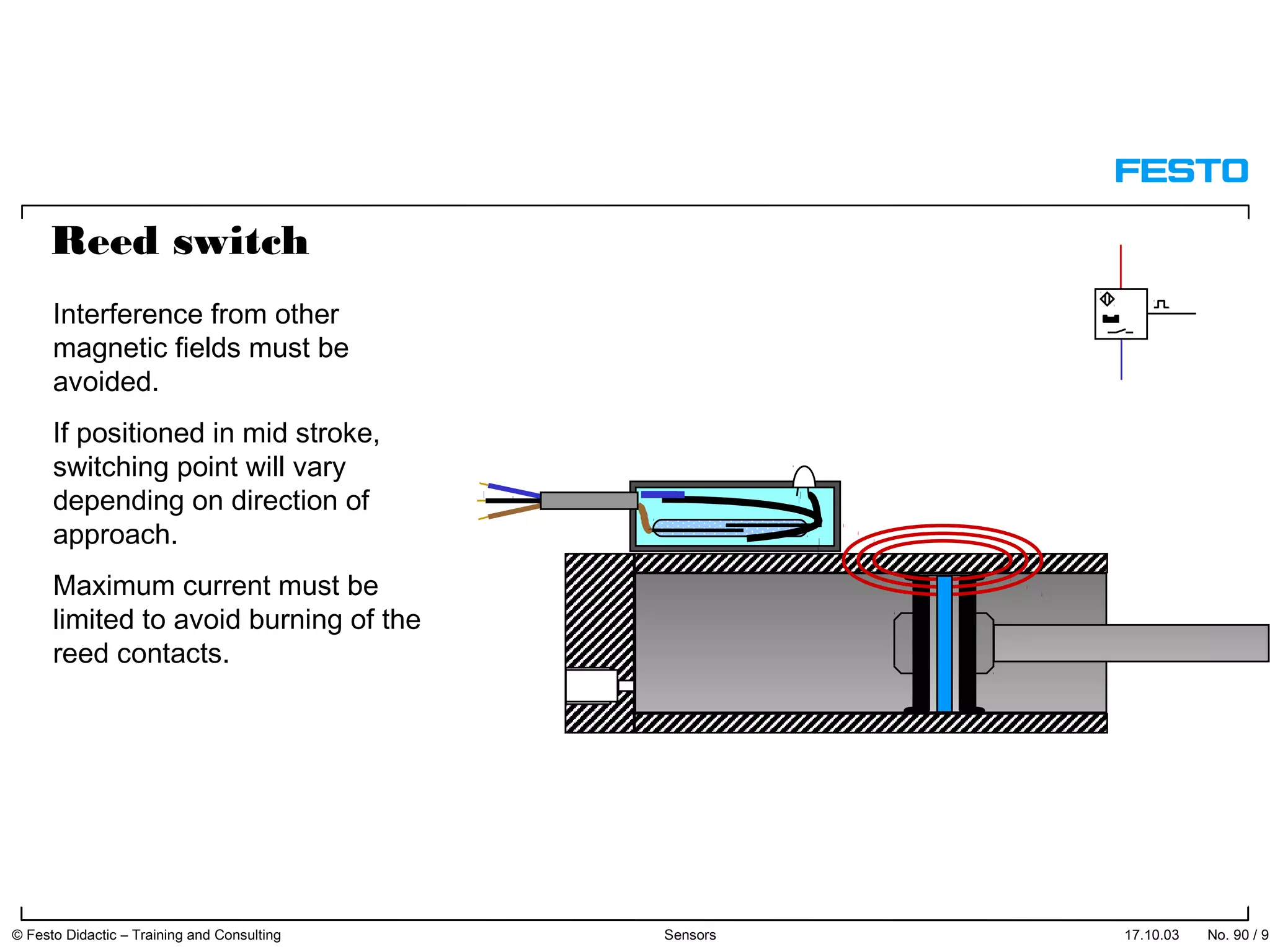
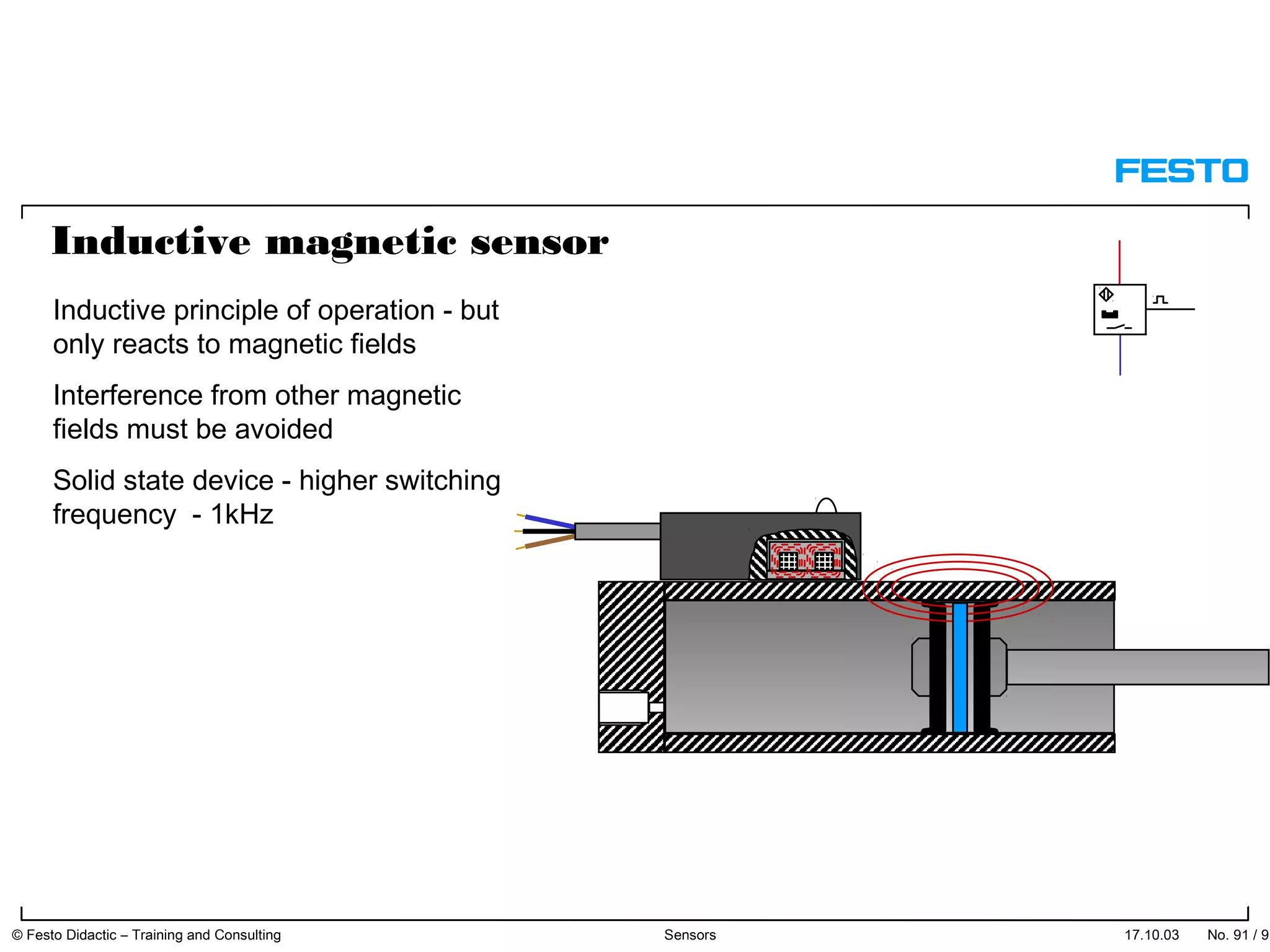
The document discusses different types of proximity sensors including optical, inductive, reed switch, inductive magnetic, and capacitive sensors. It provides diagrams and descriptions of how each sensor type works, including notes on their sensing ranges, target materials detected, and factors that influence performance. The end of the document covers standard symbols used for sensors and connections to control systems.