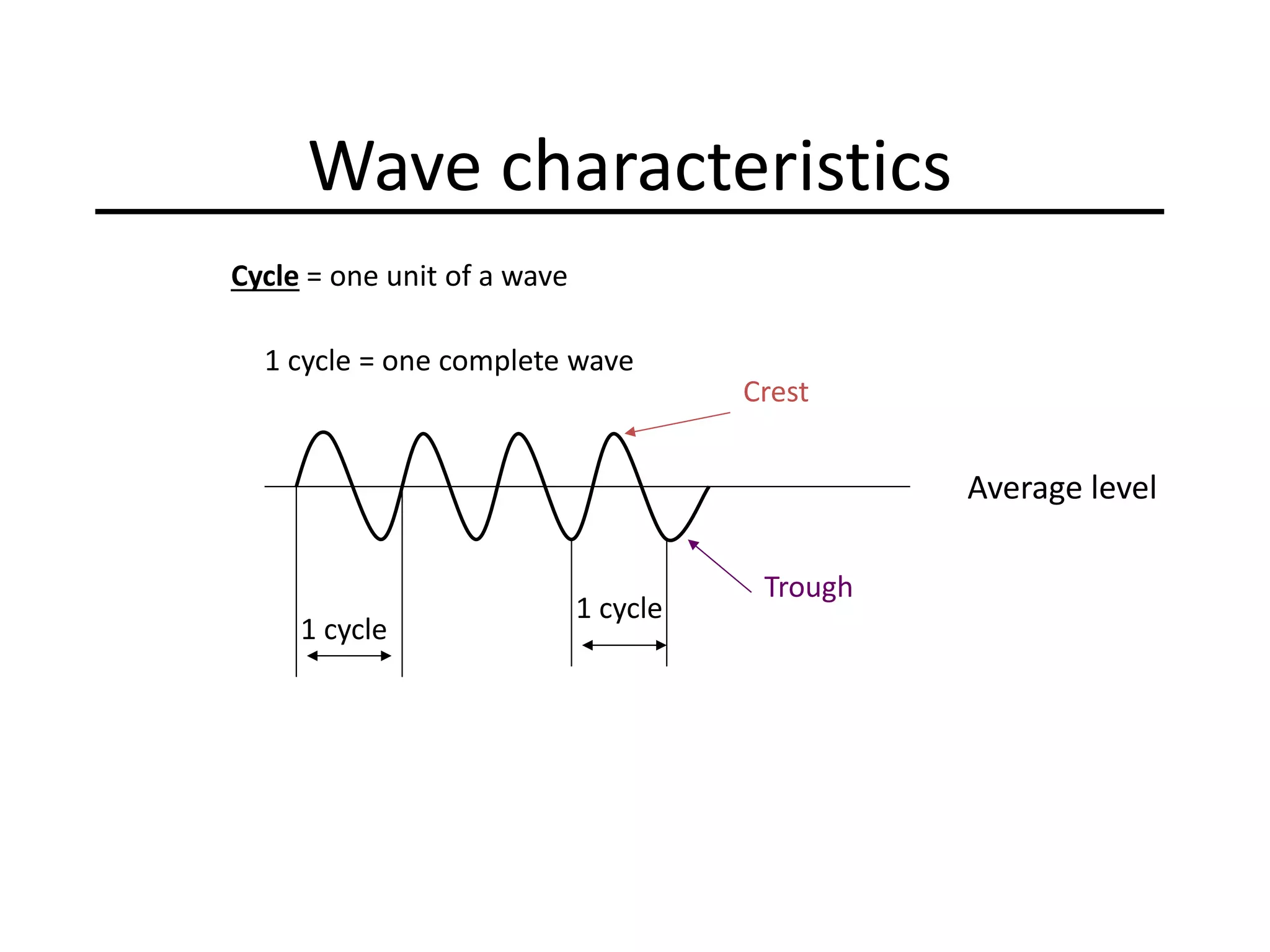
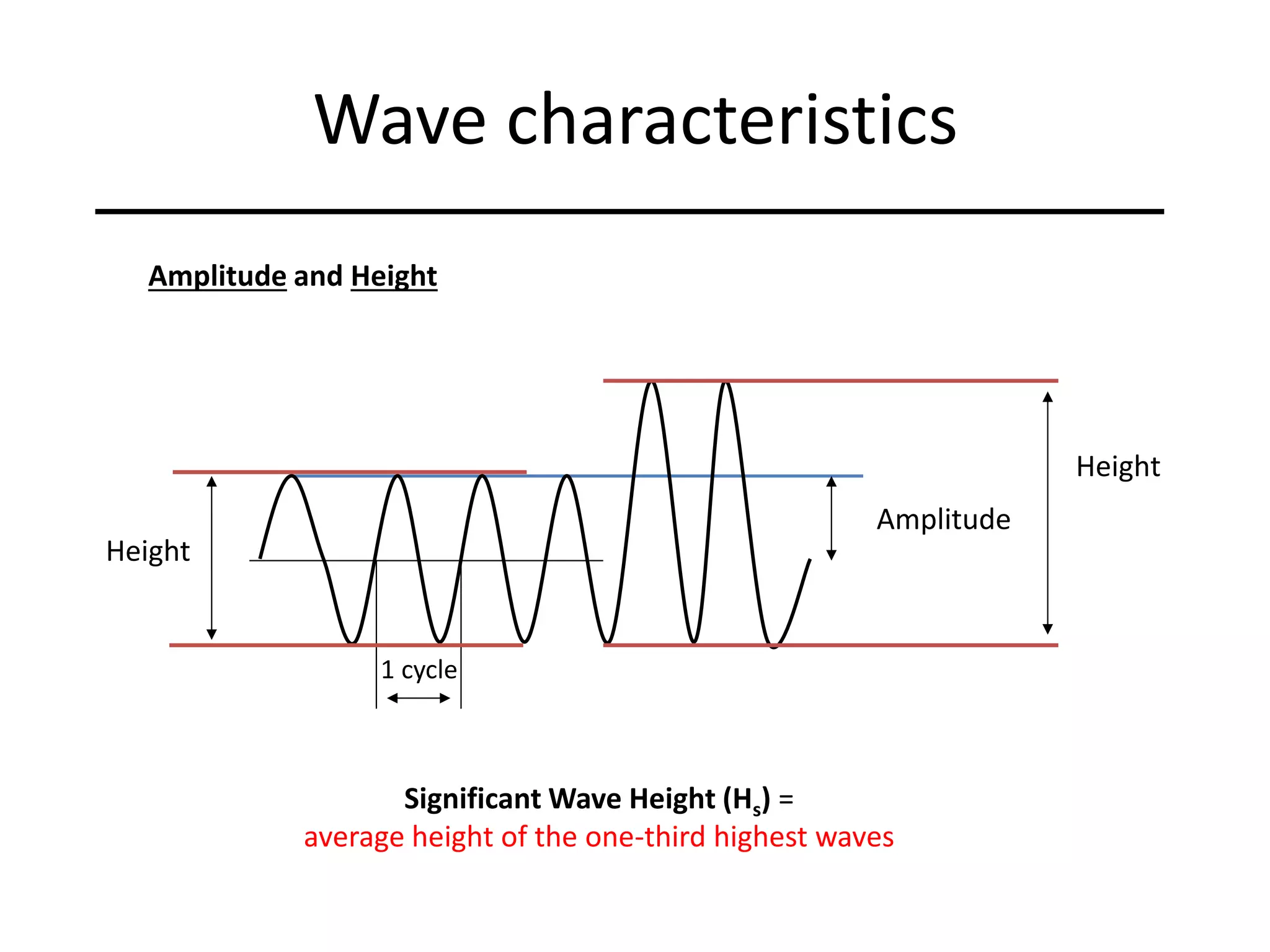
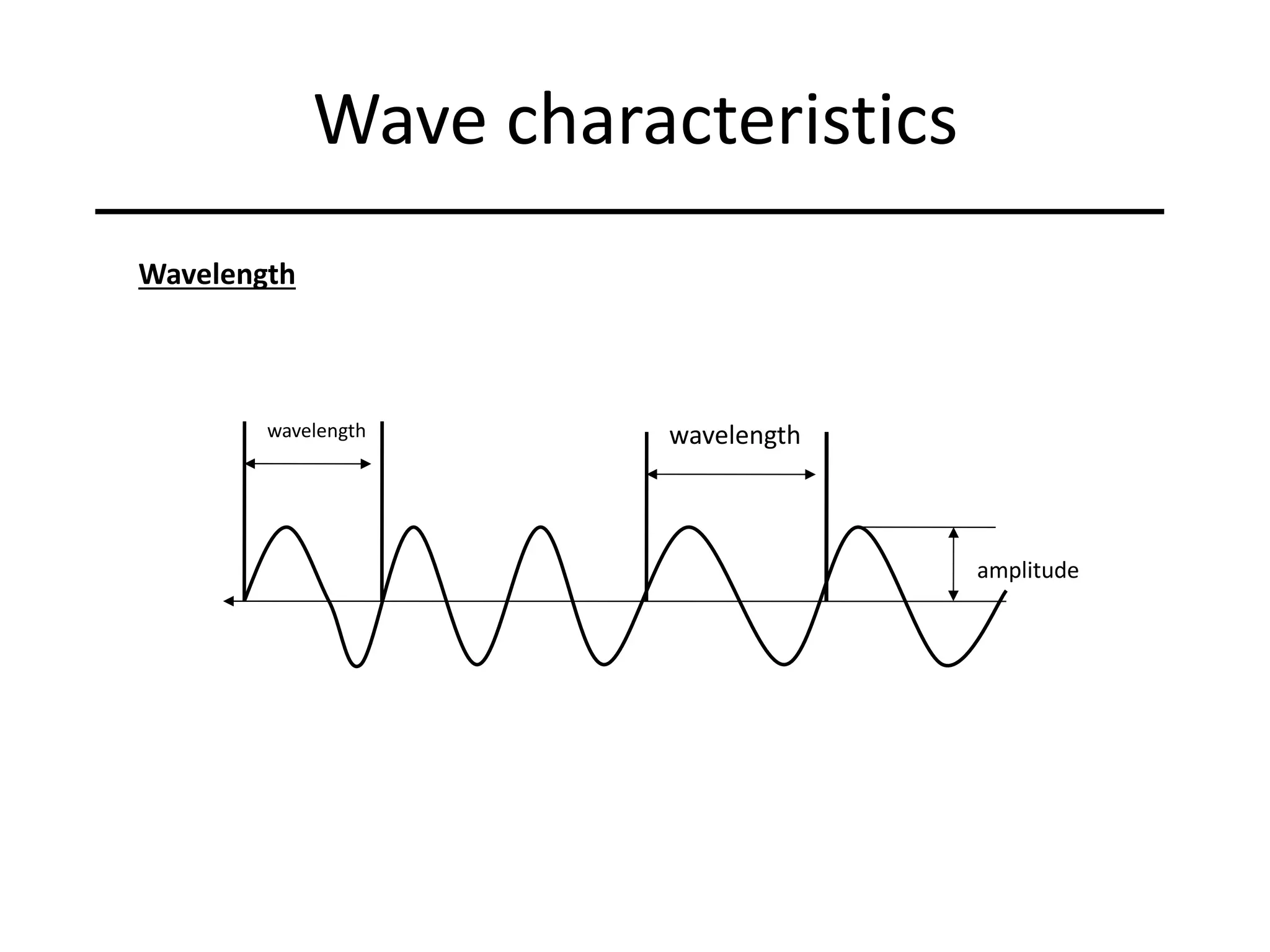
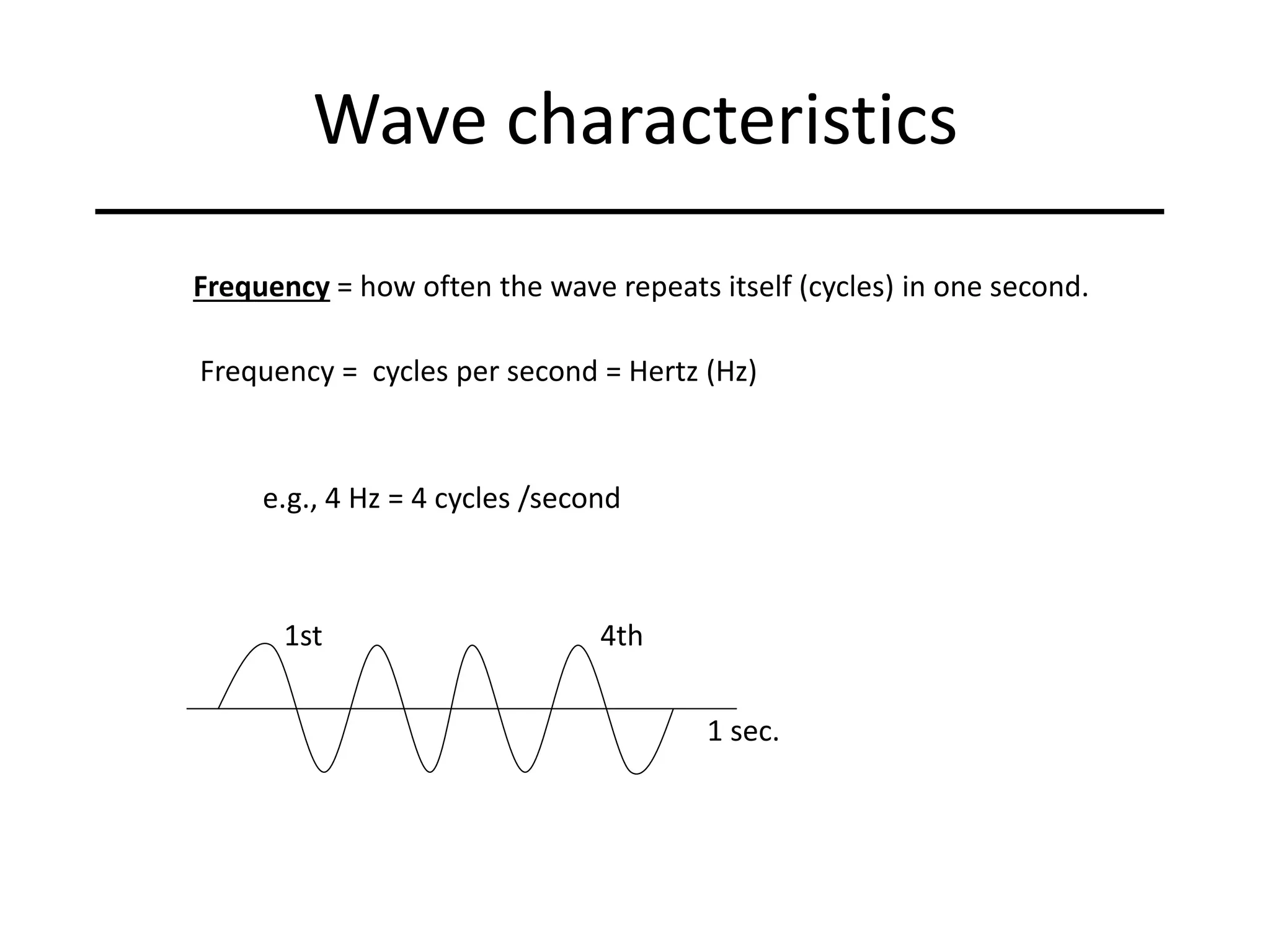
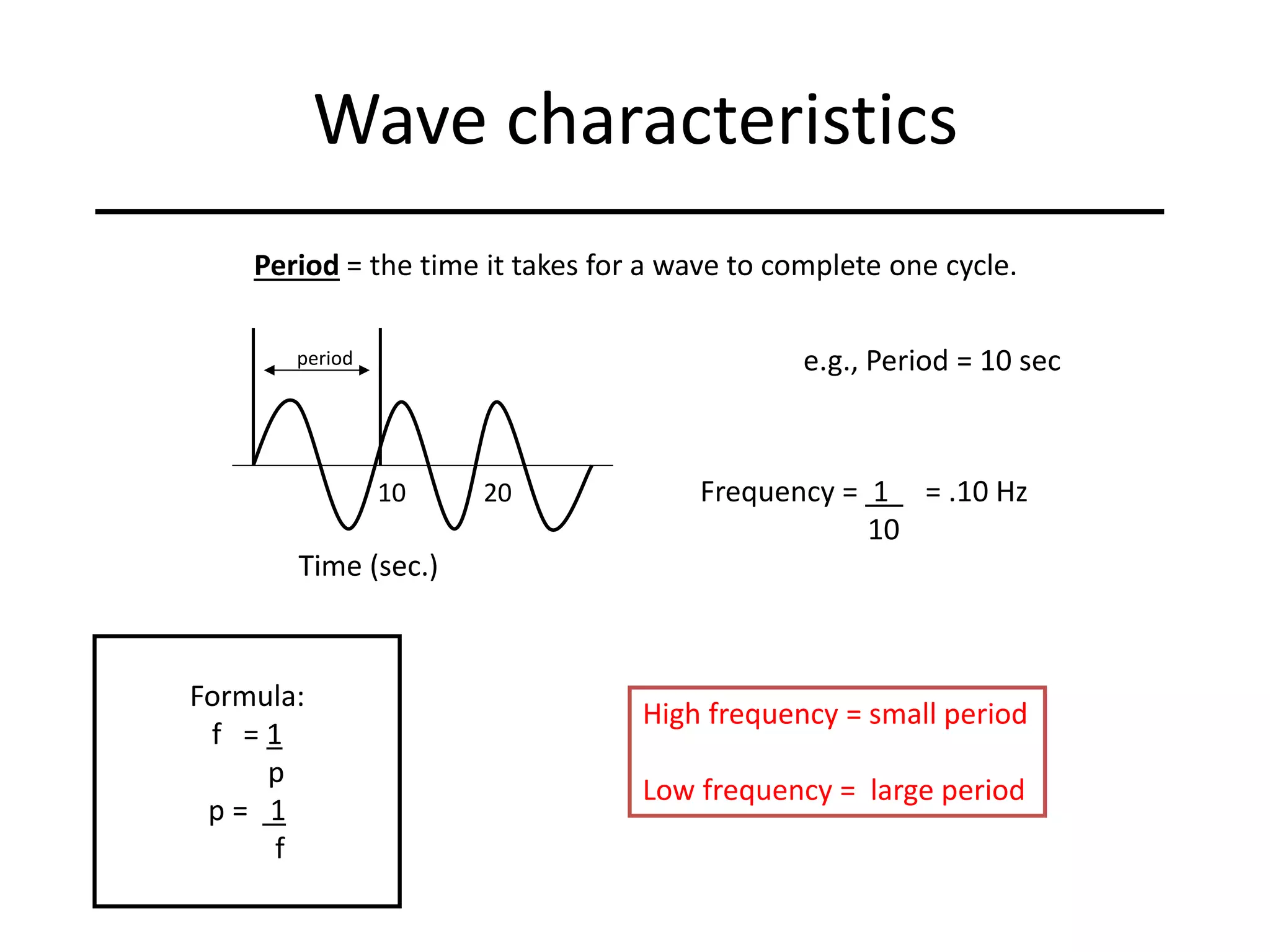
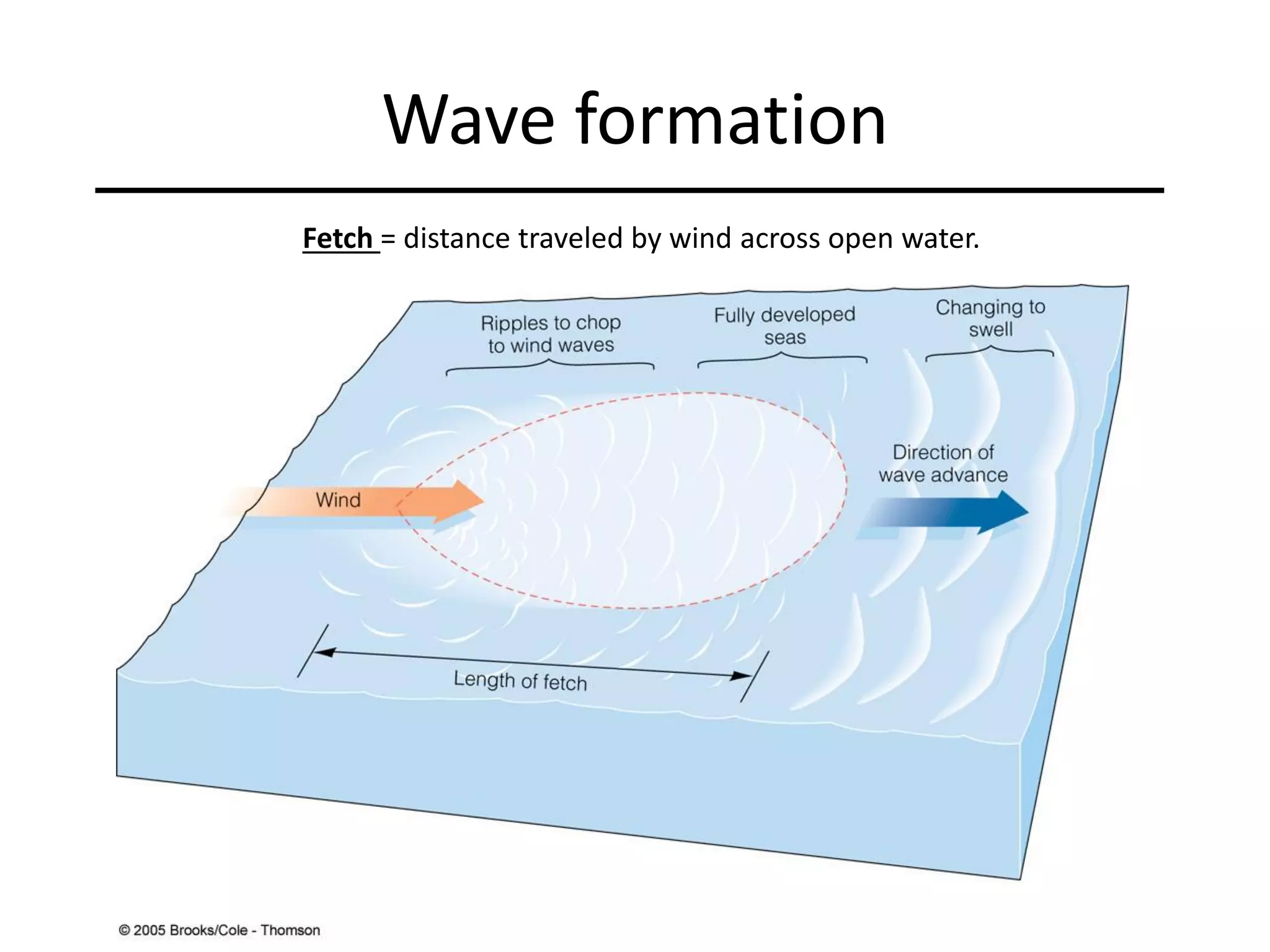
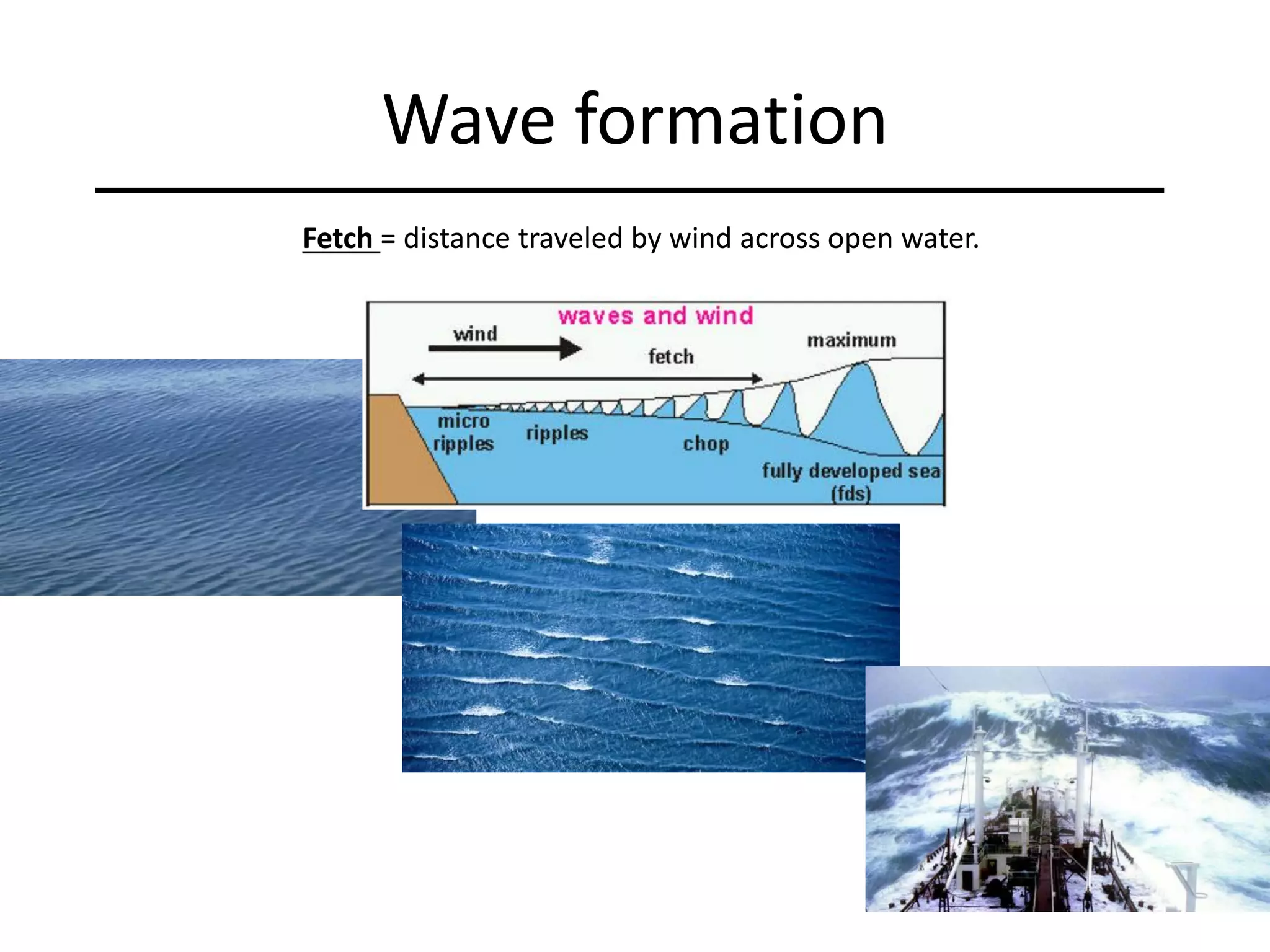
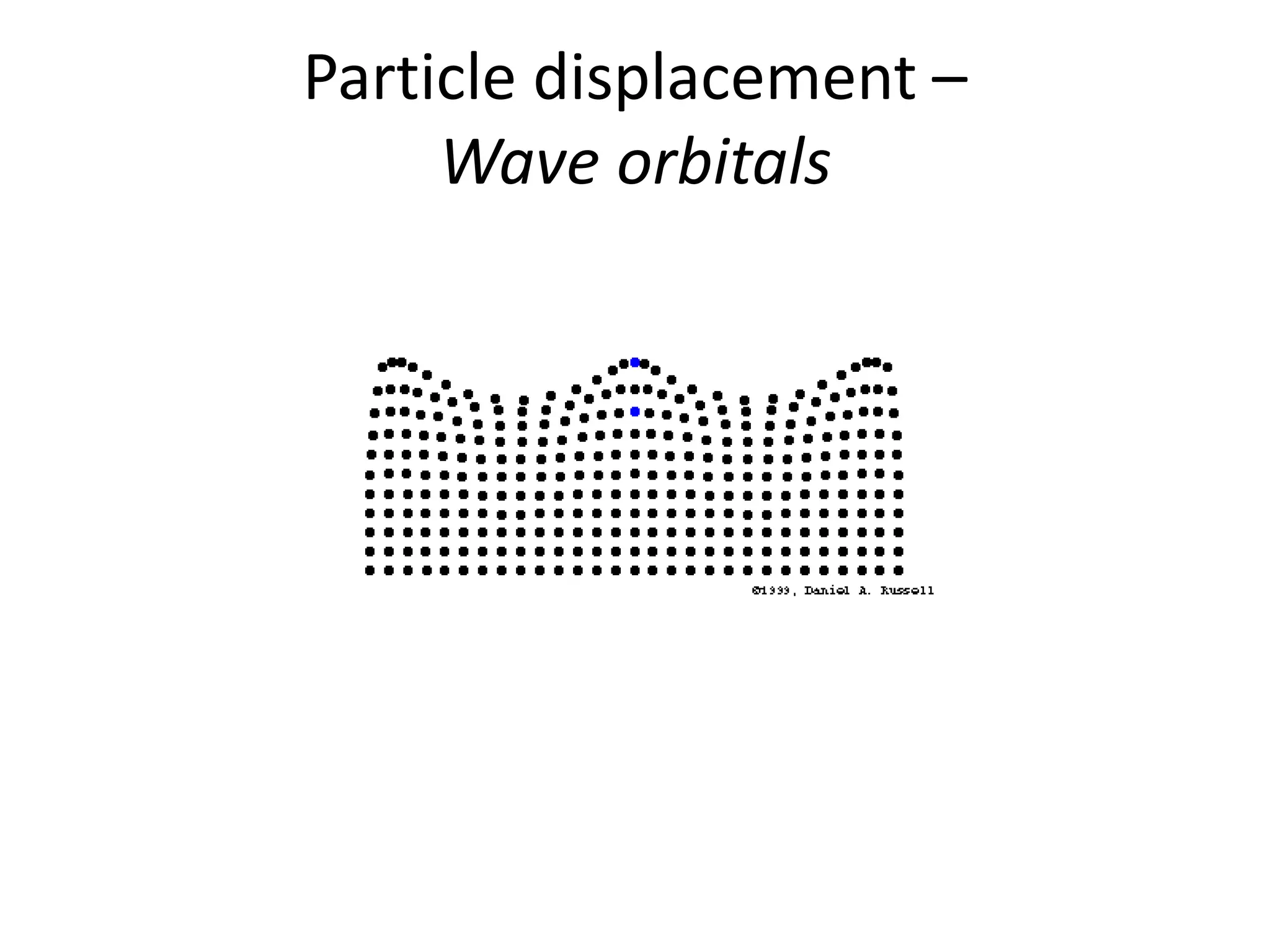
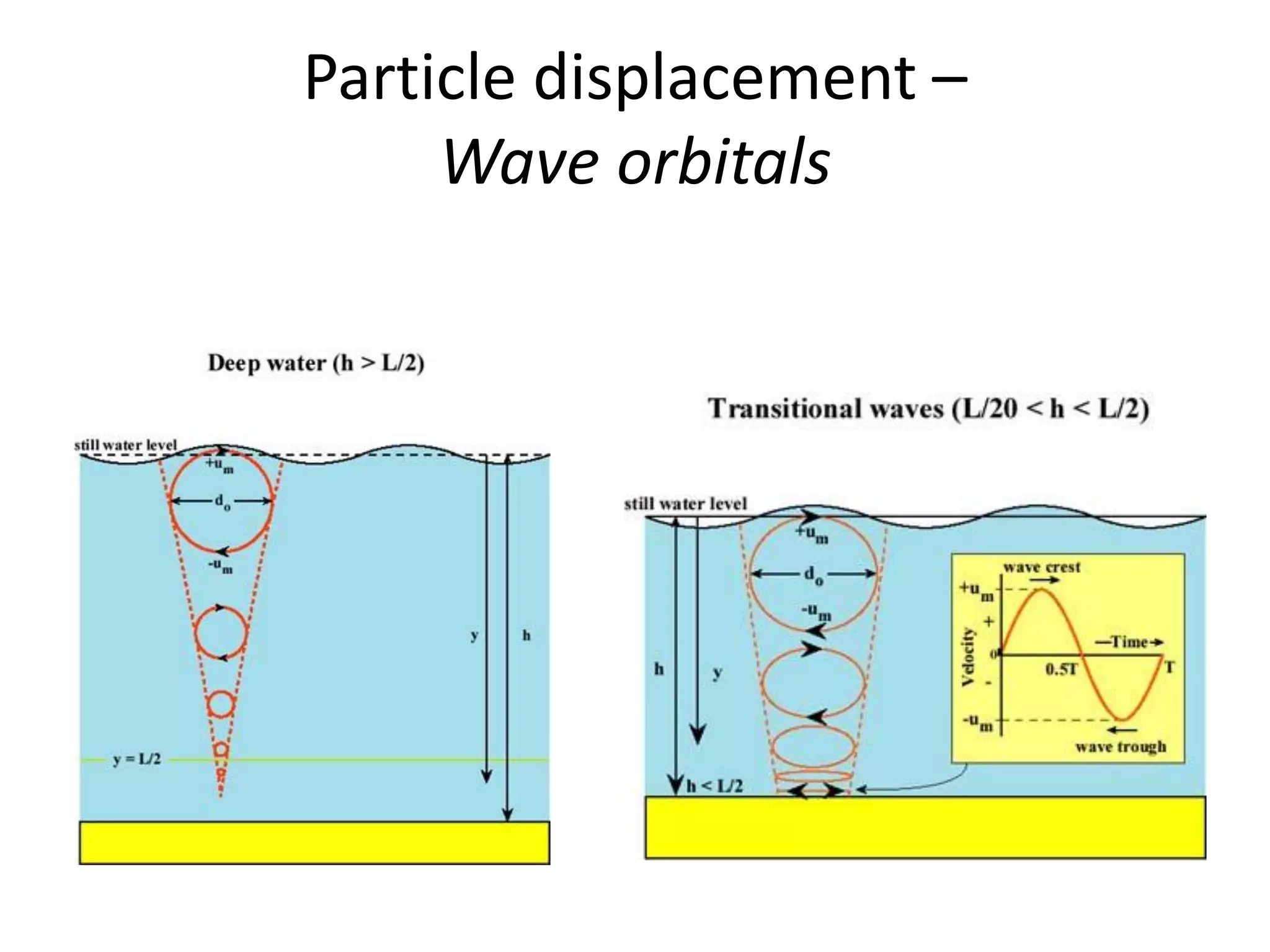
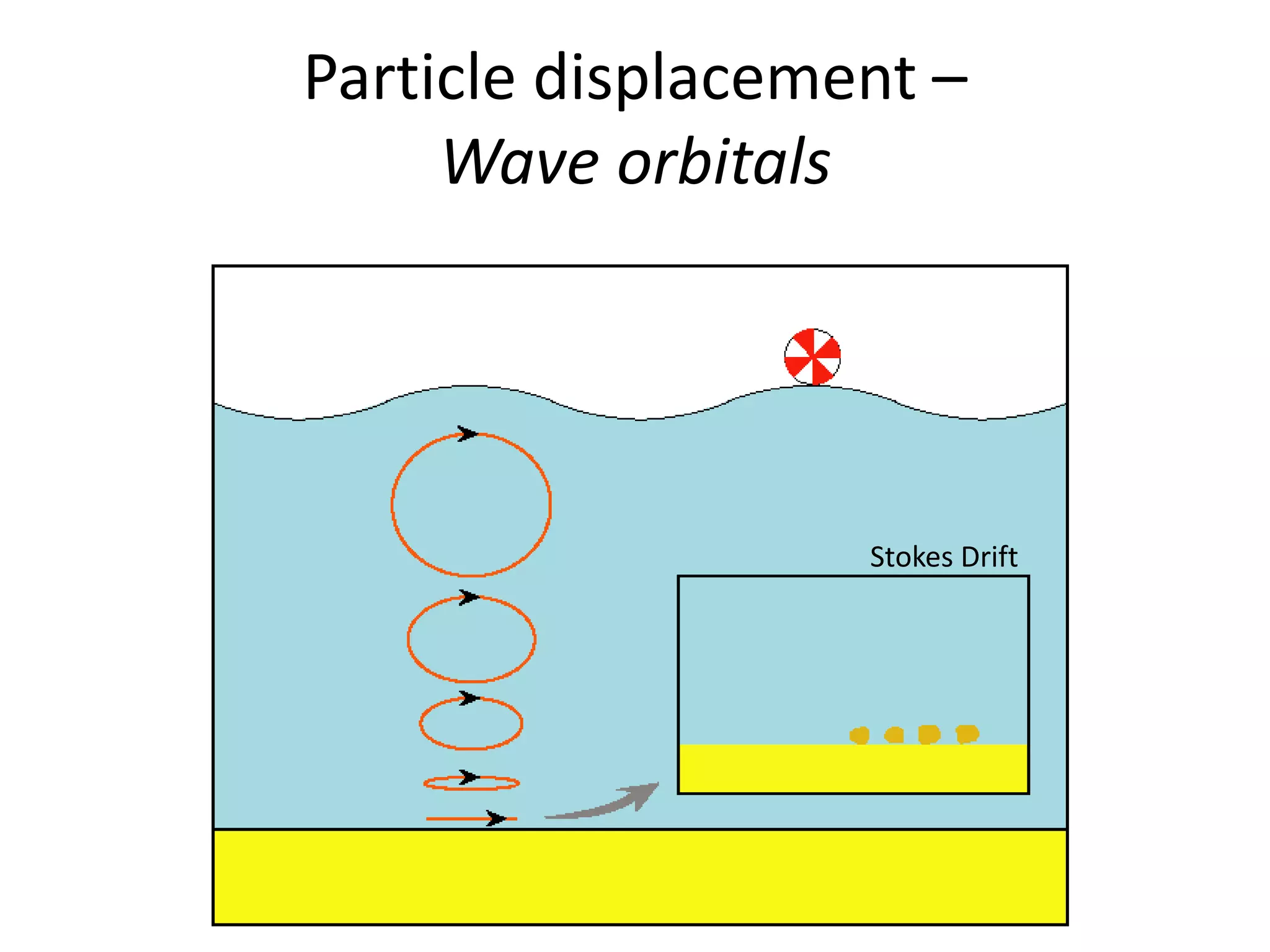
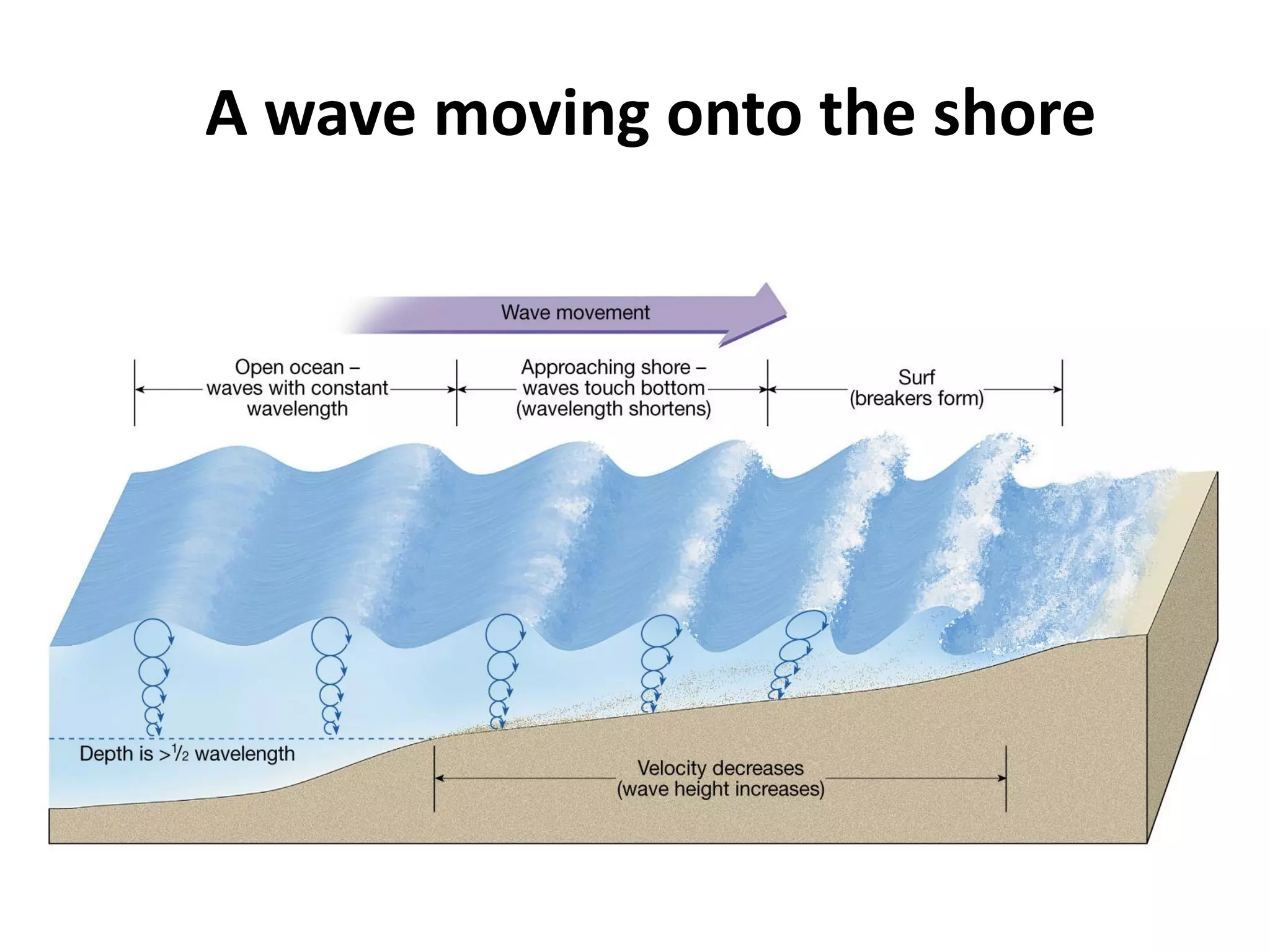
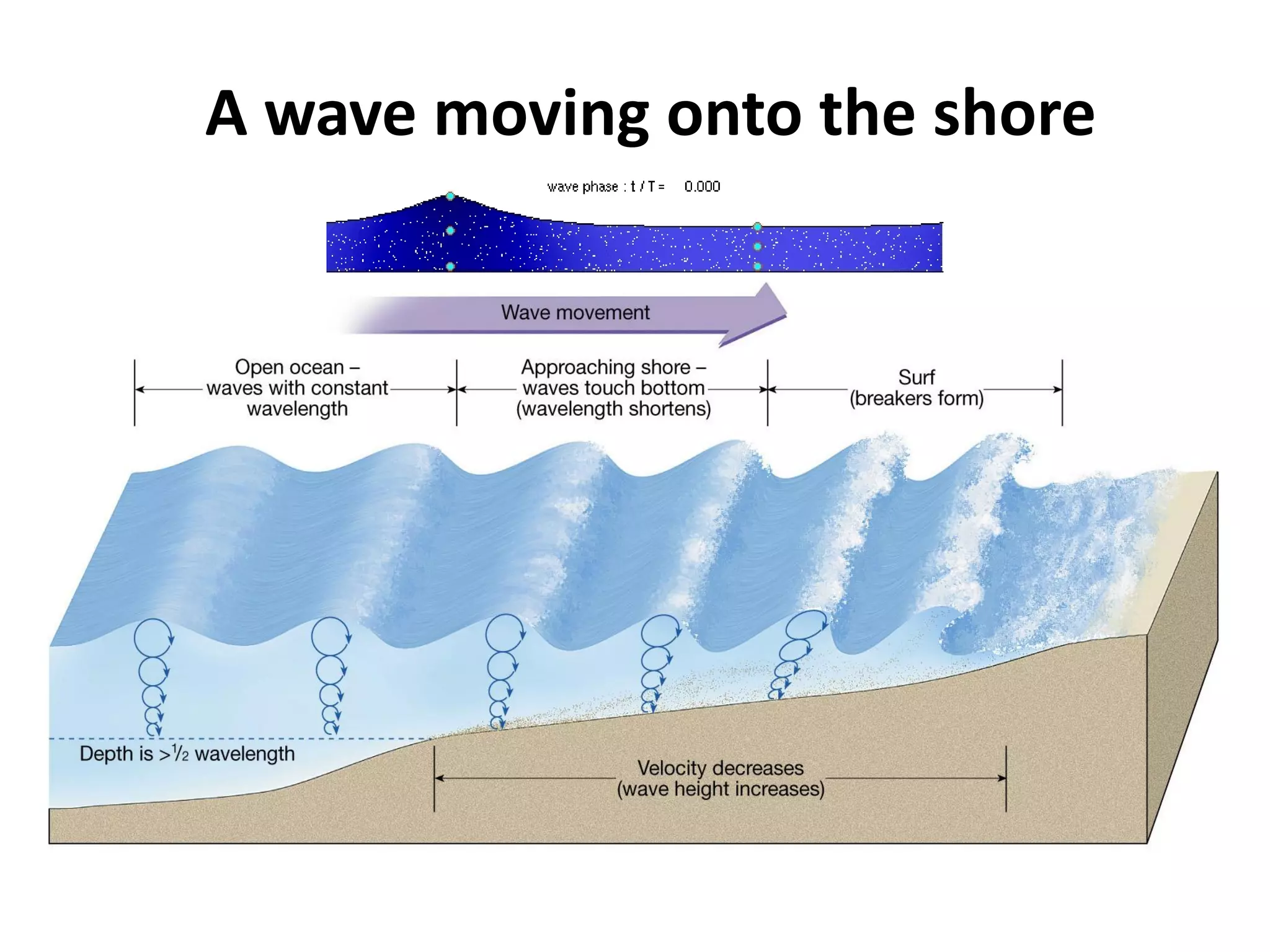
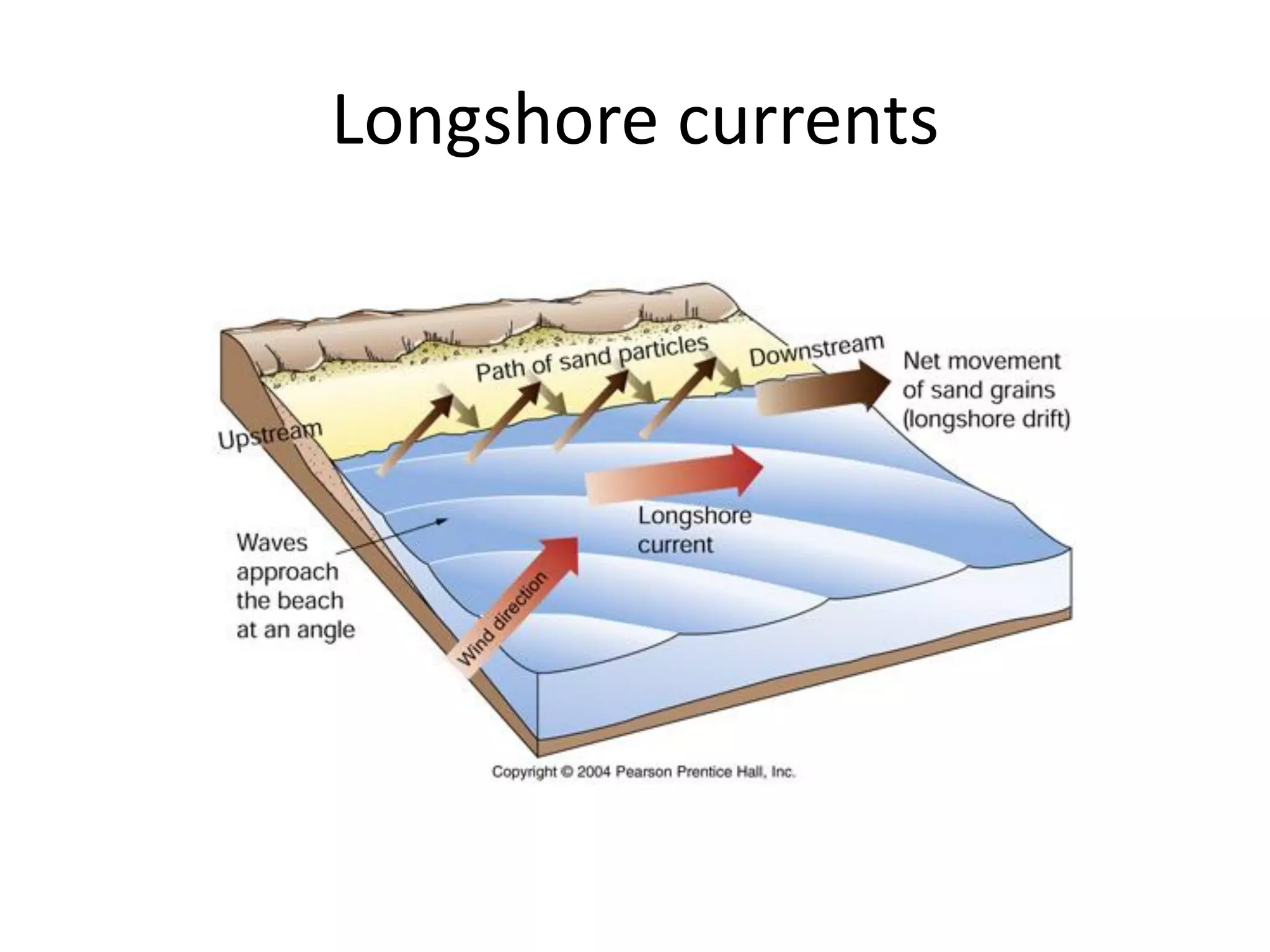
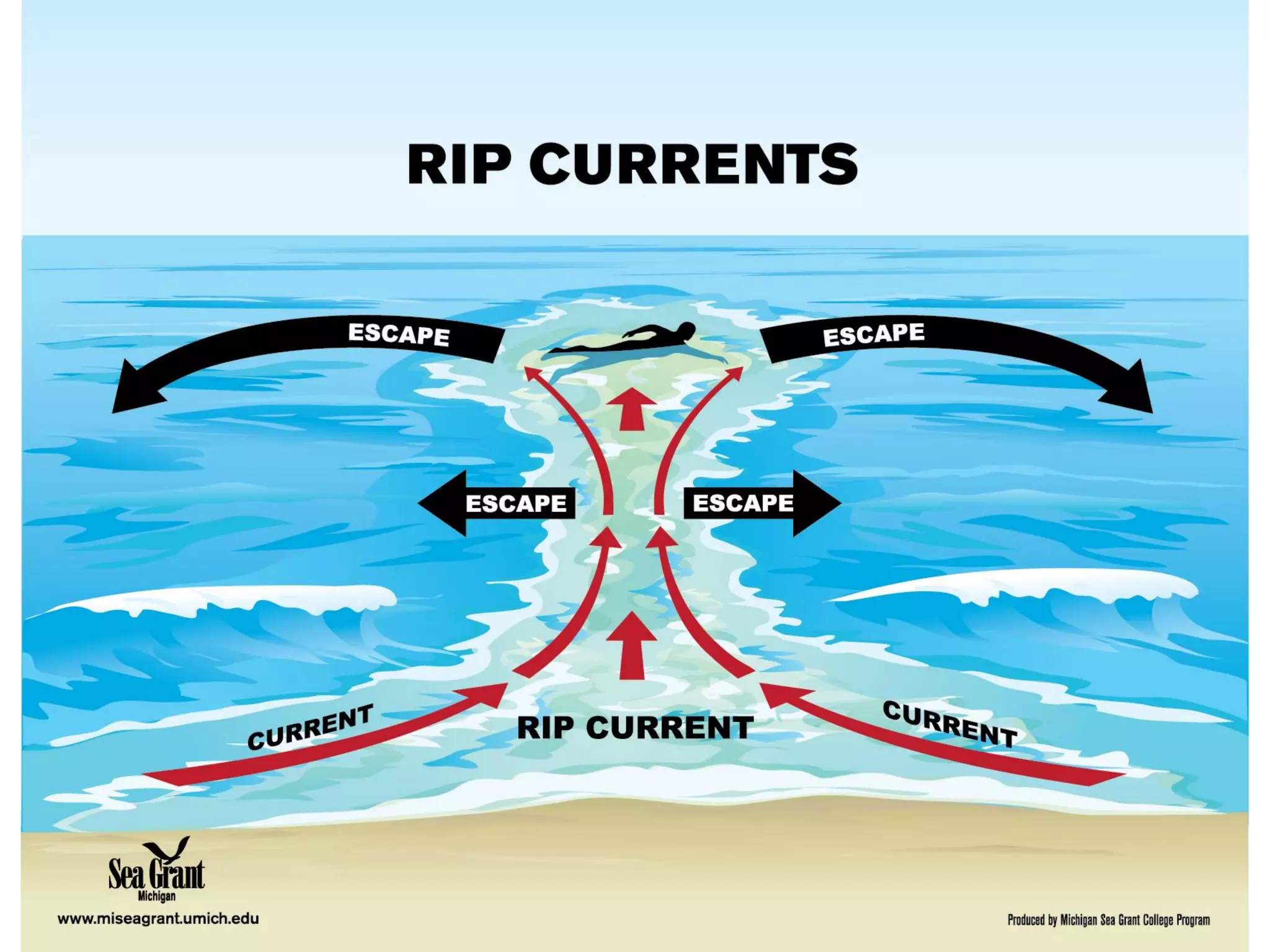
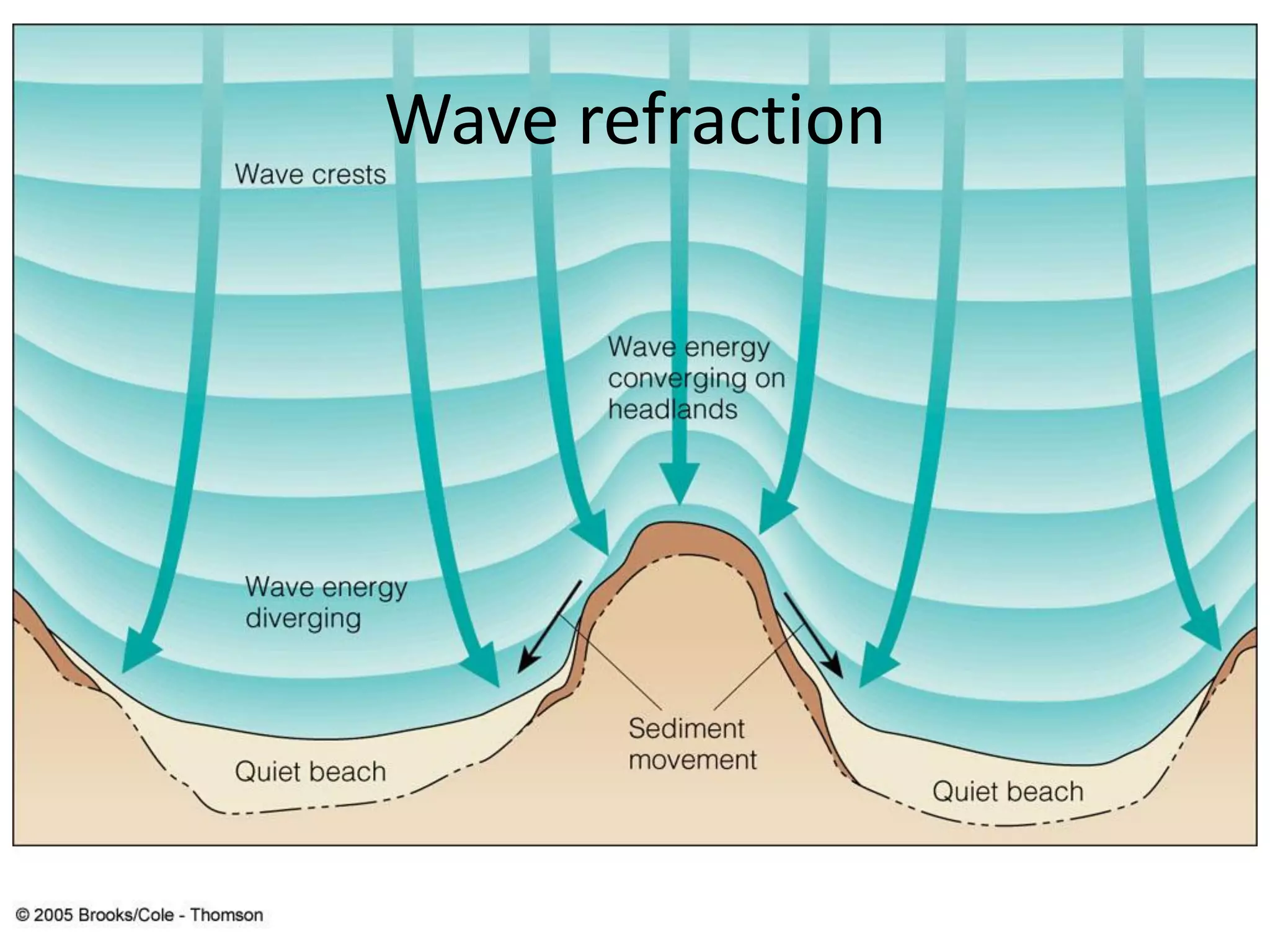
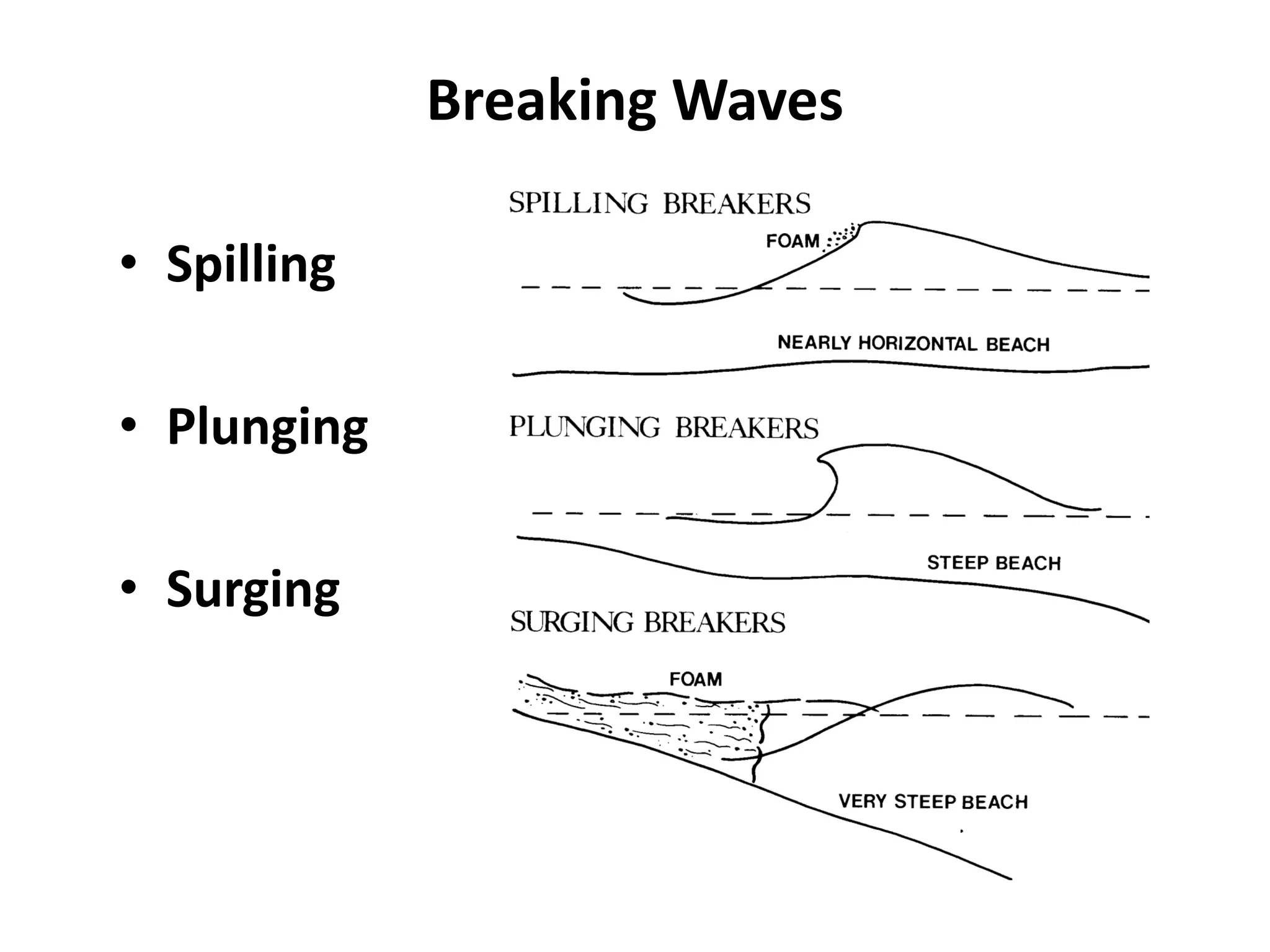
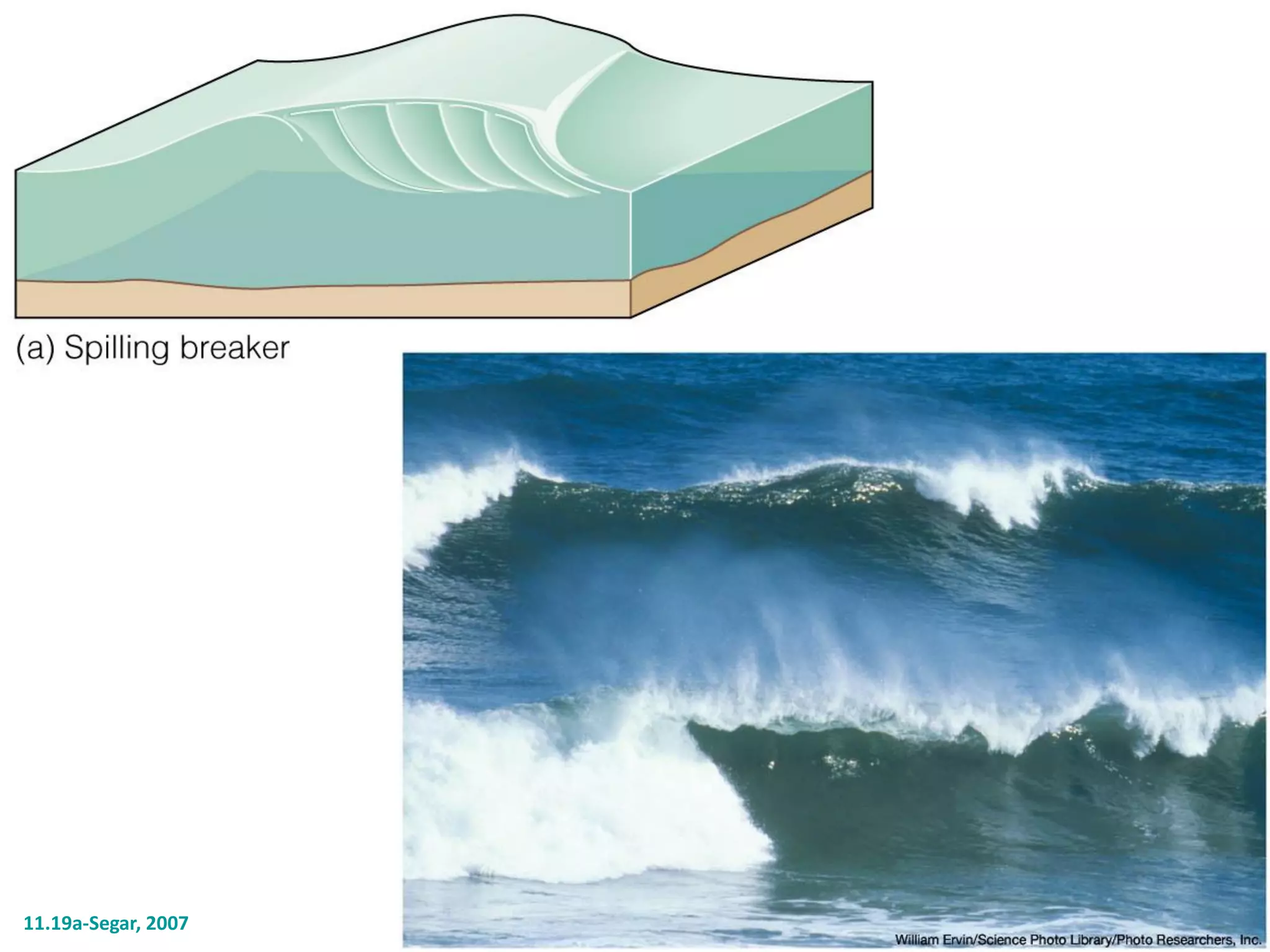
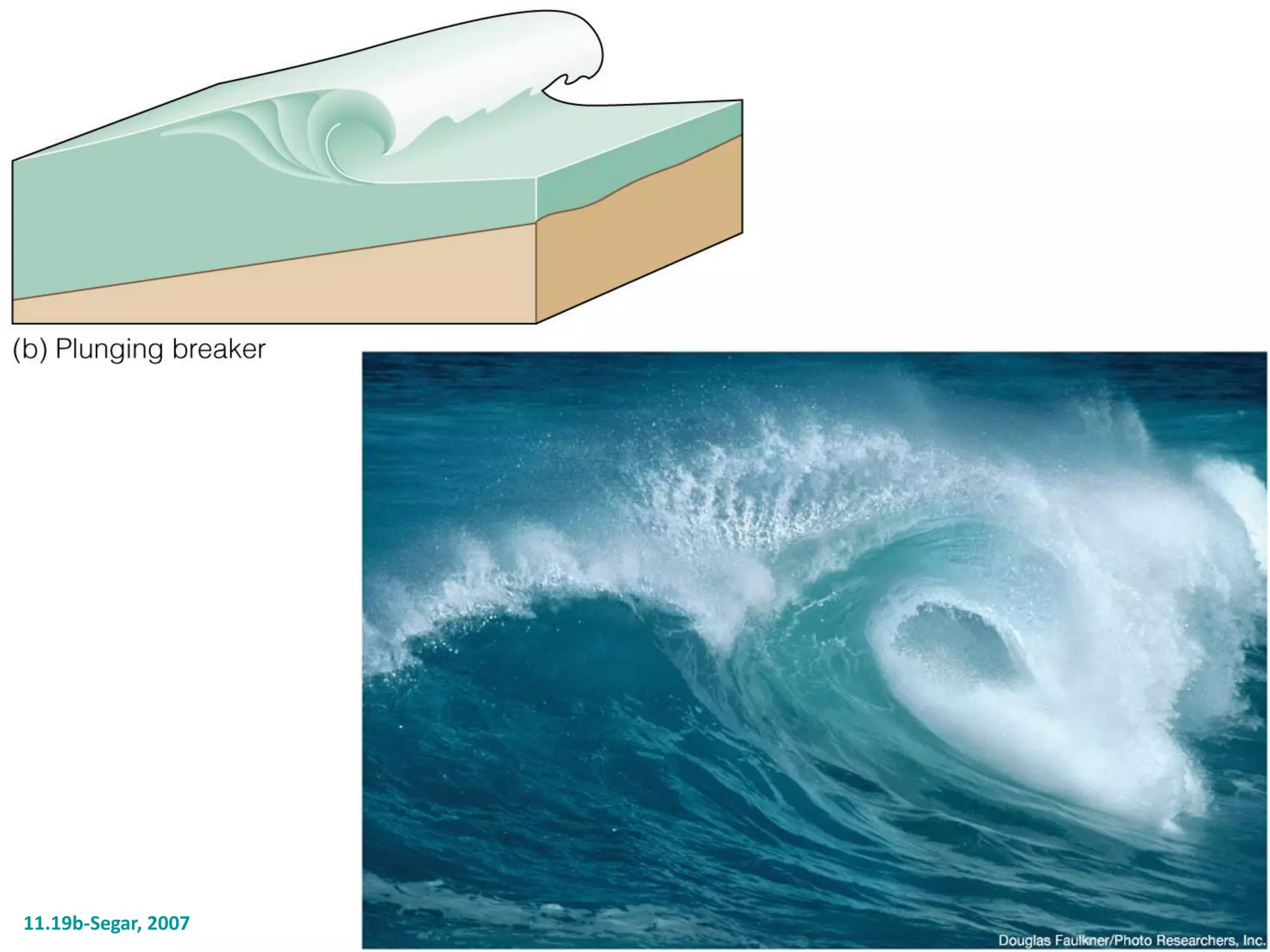
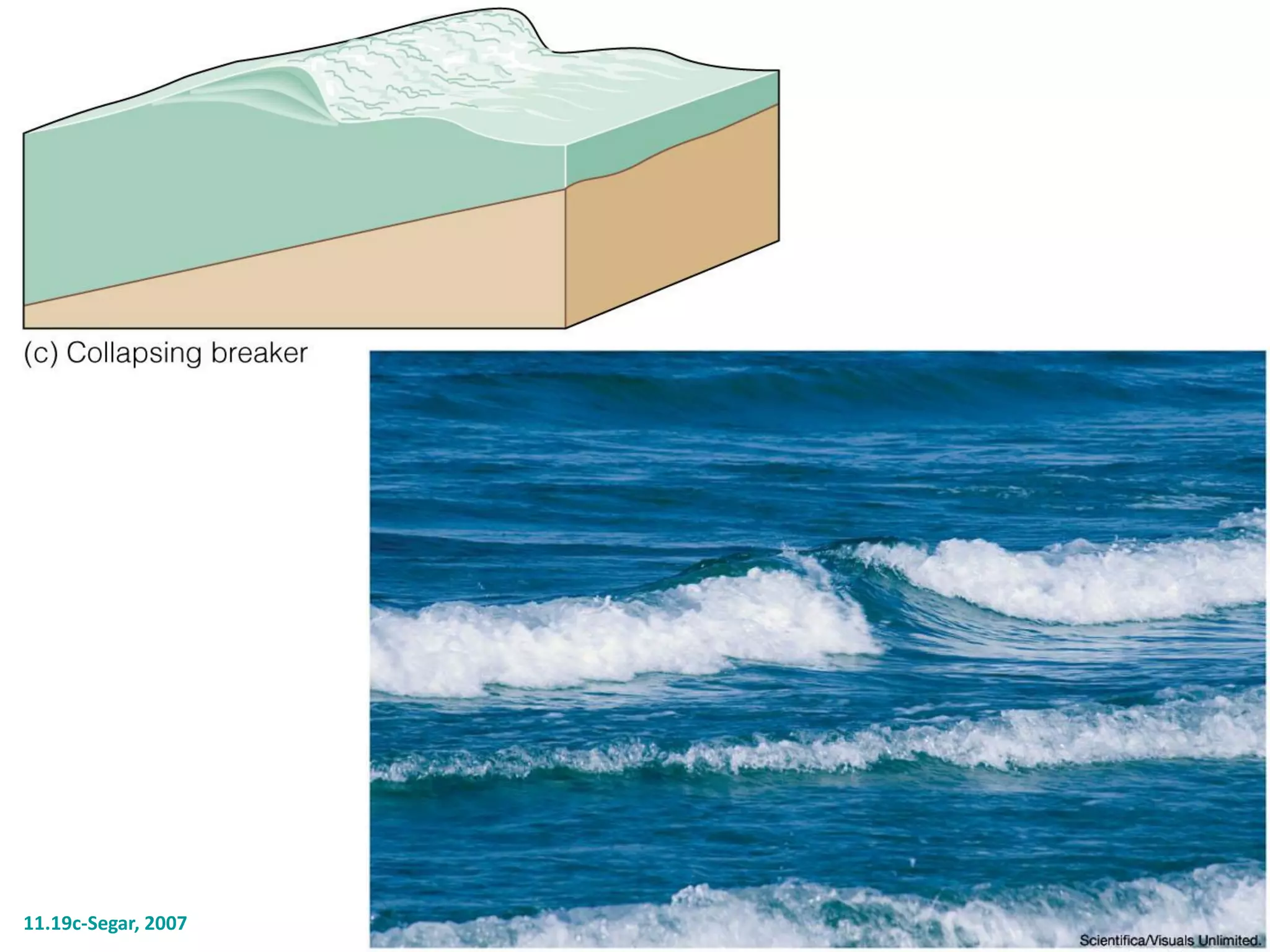
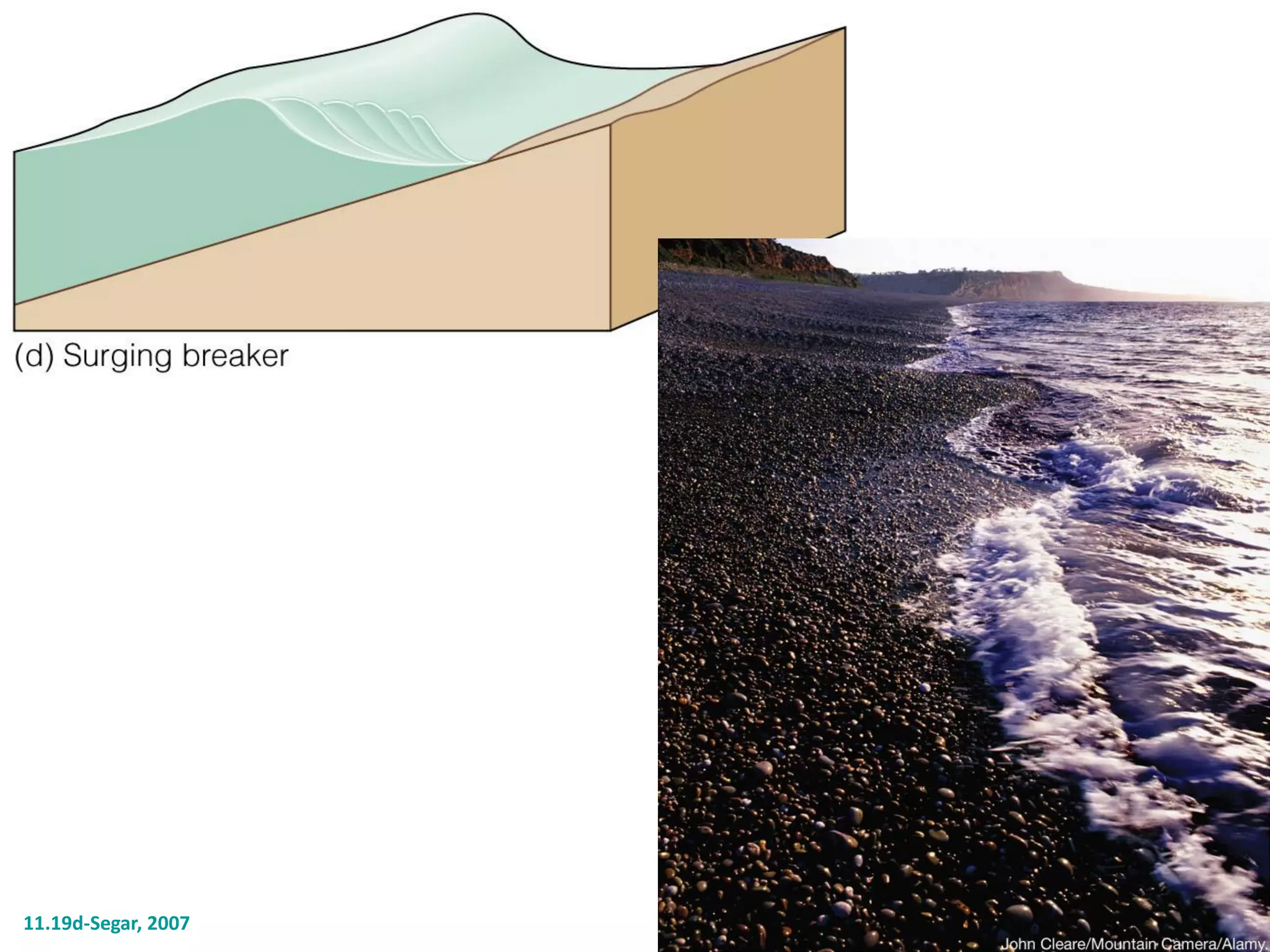
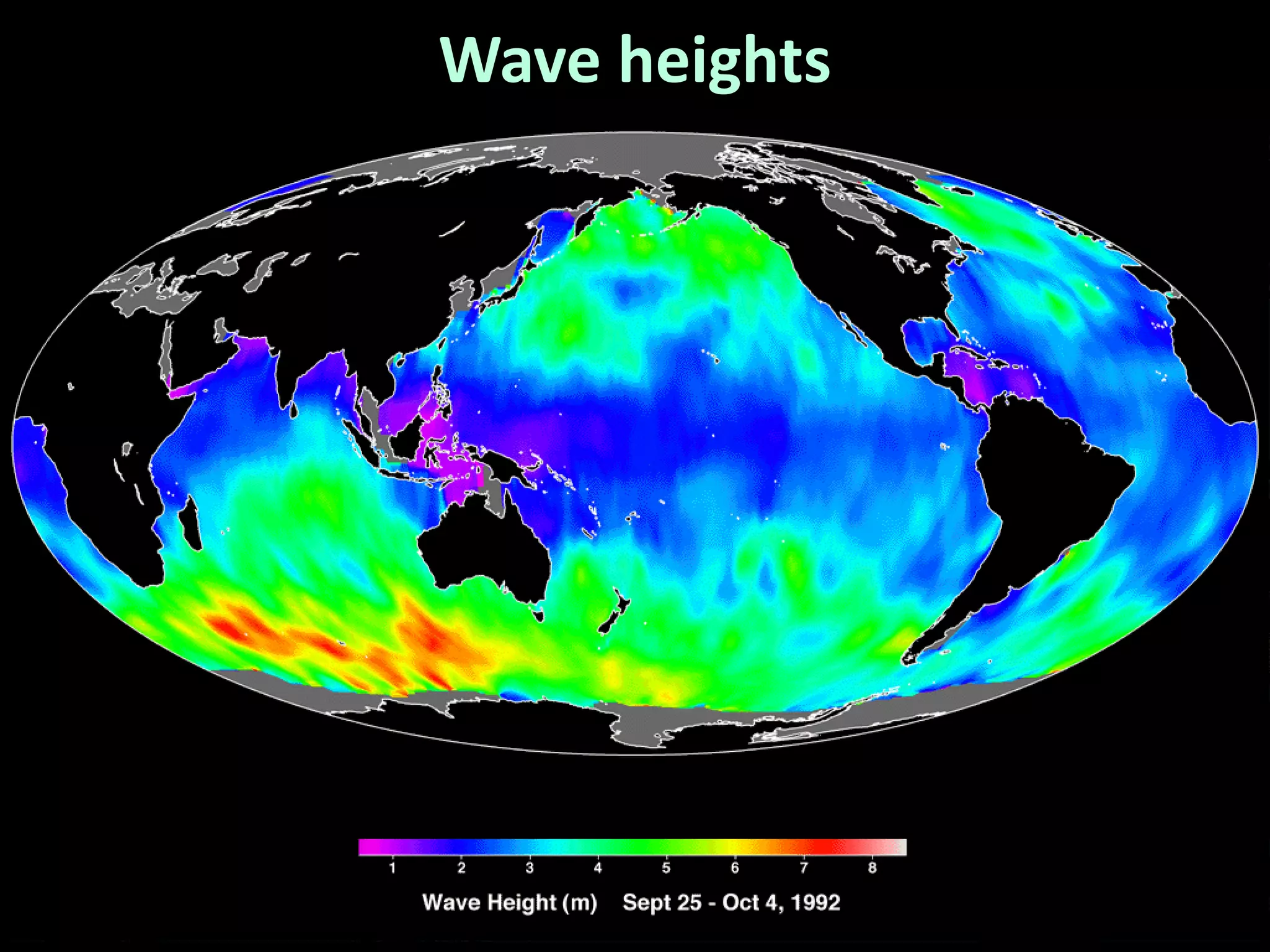
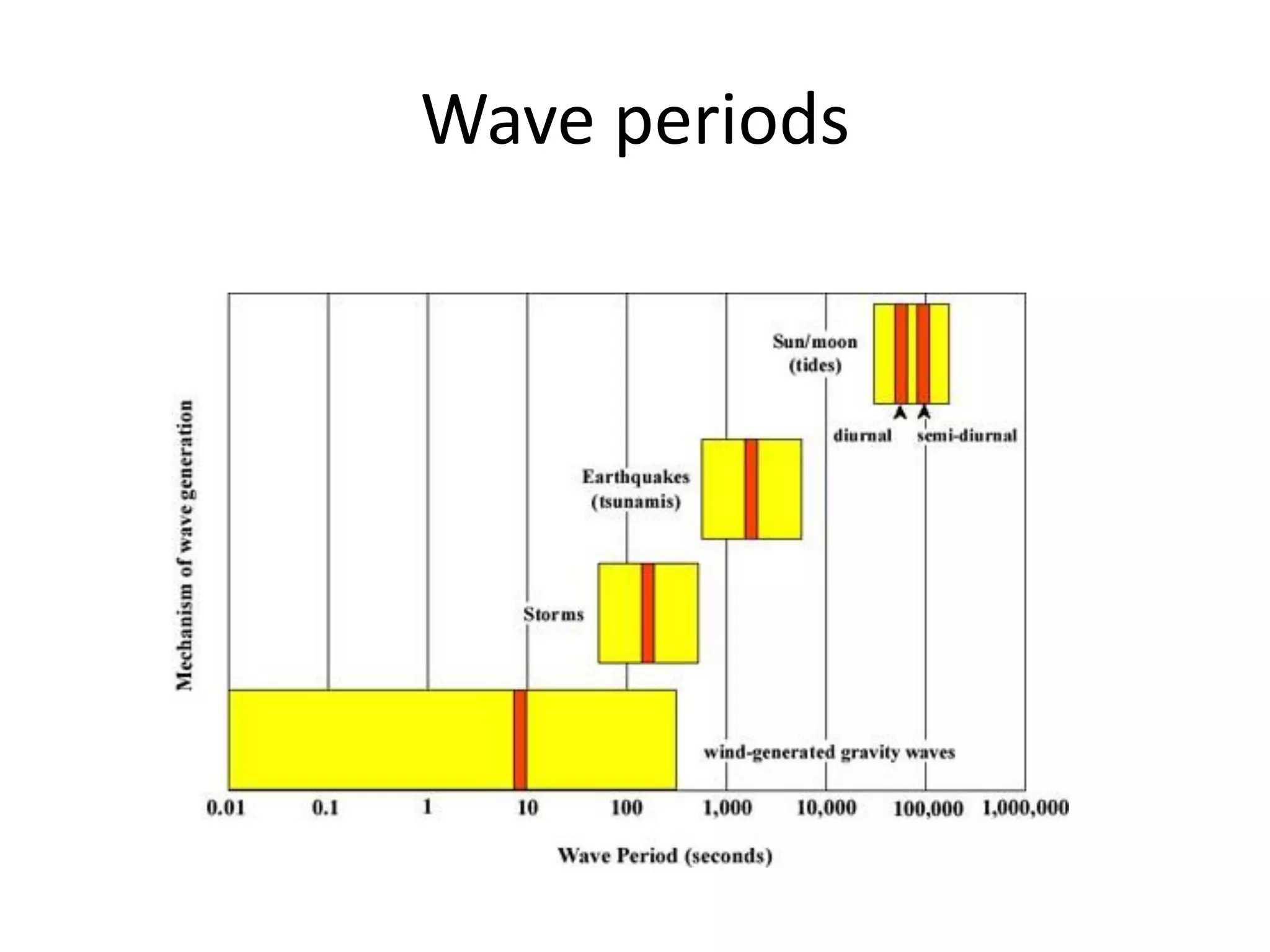
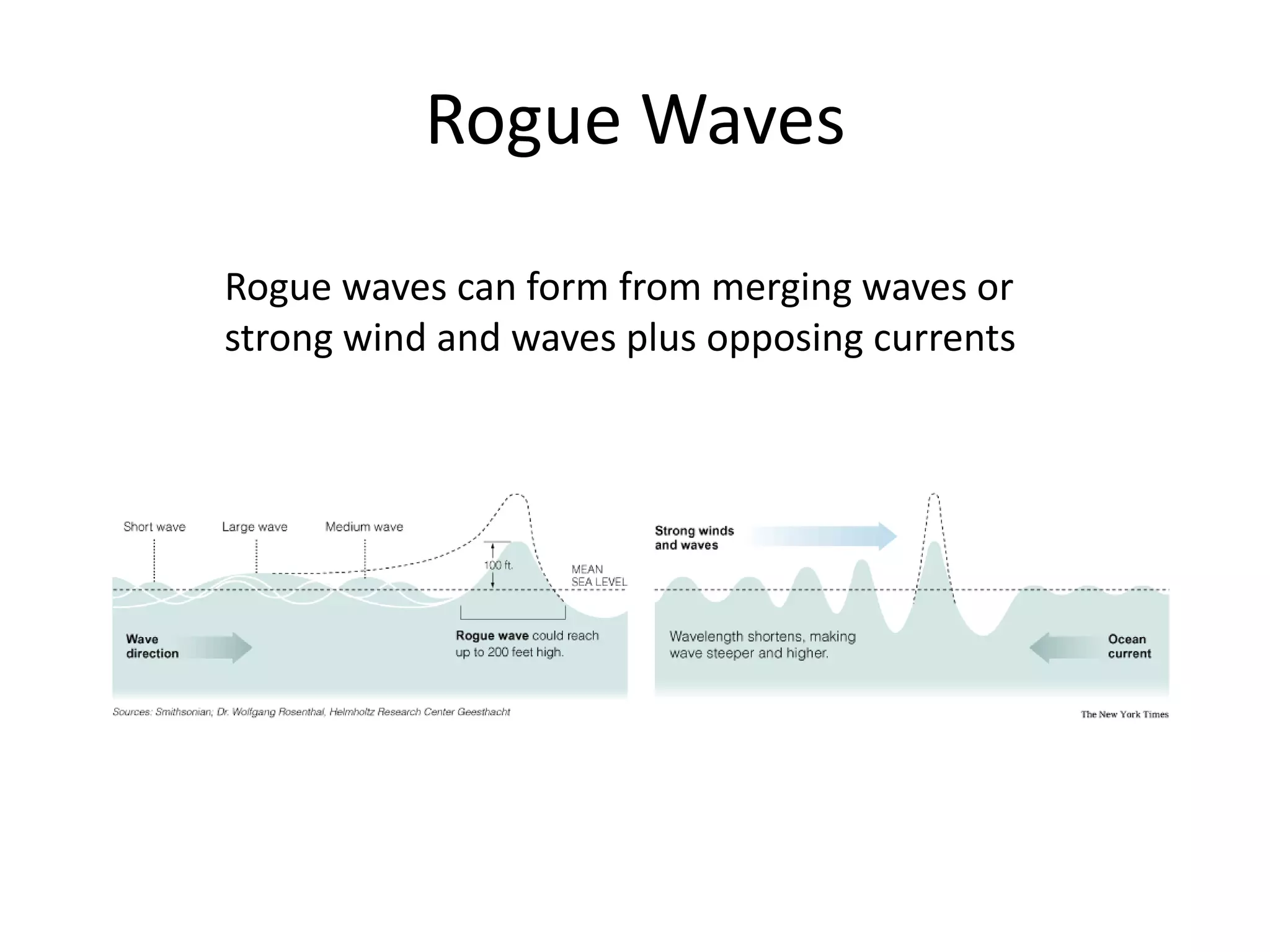
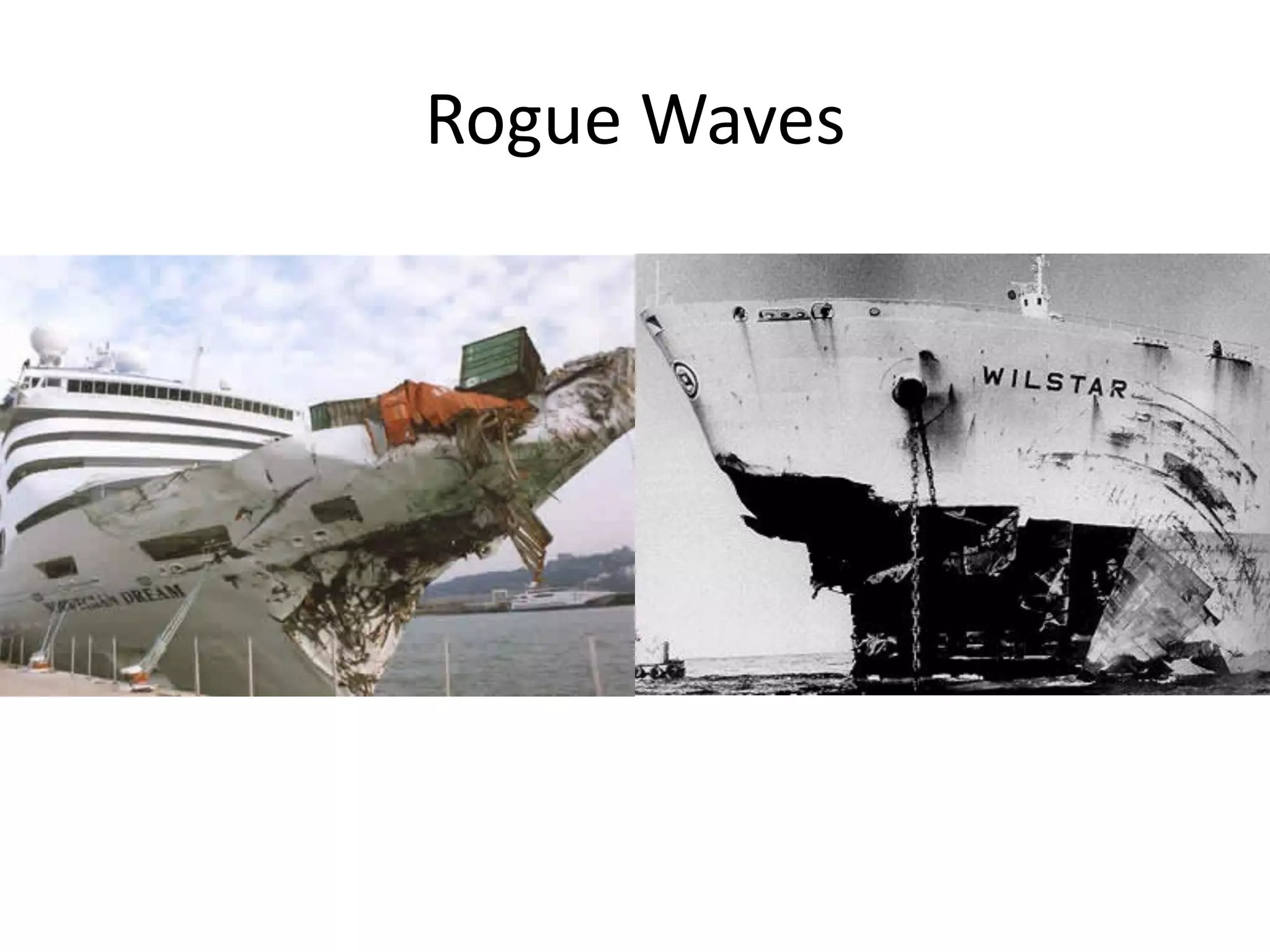
Ocean waves are characterized by their amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and period. Amplitude refers to the height of the wave from still water level to the crest. Wavelength is the distance between two identical points on successive waves. Frequency is the number of waves passing a fixed point per second, while period is the time for one full wave cycle. Wave height depends on factors like fetch (distance over water the wind blows) and breaking occurs when the wave steepness exceeds about 1/7. Breaking waves can be spilling, plunging, or surging.