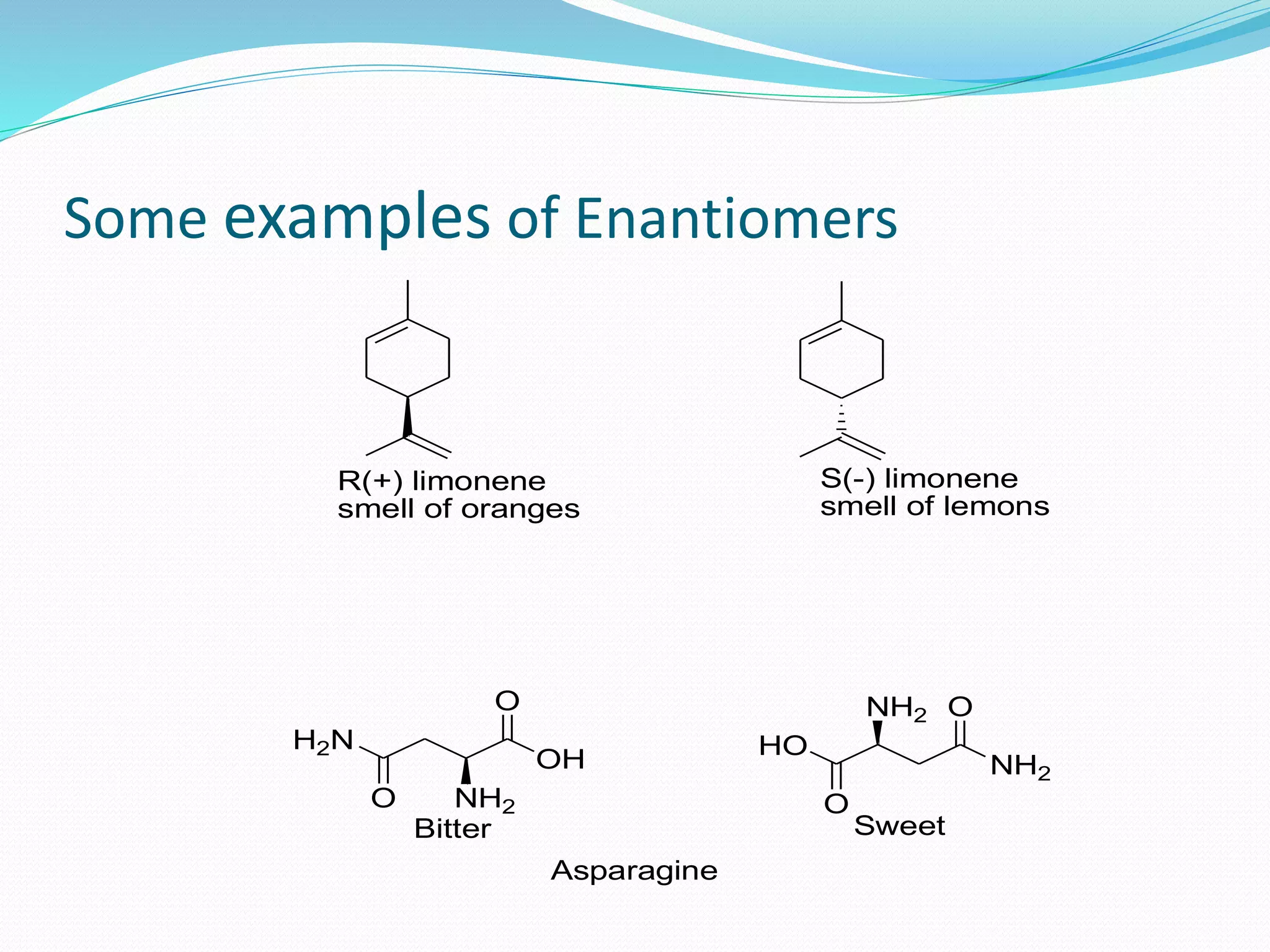
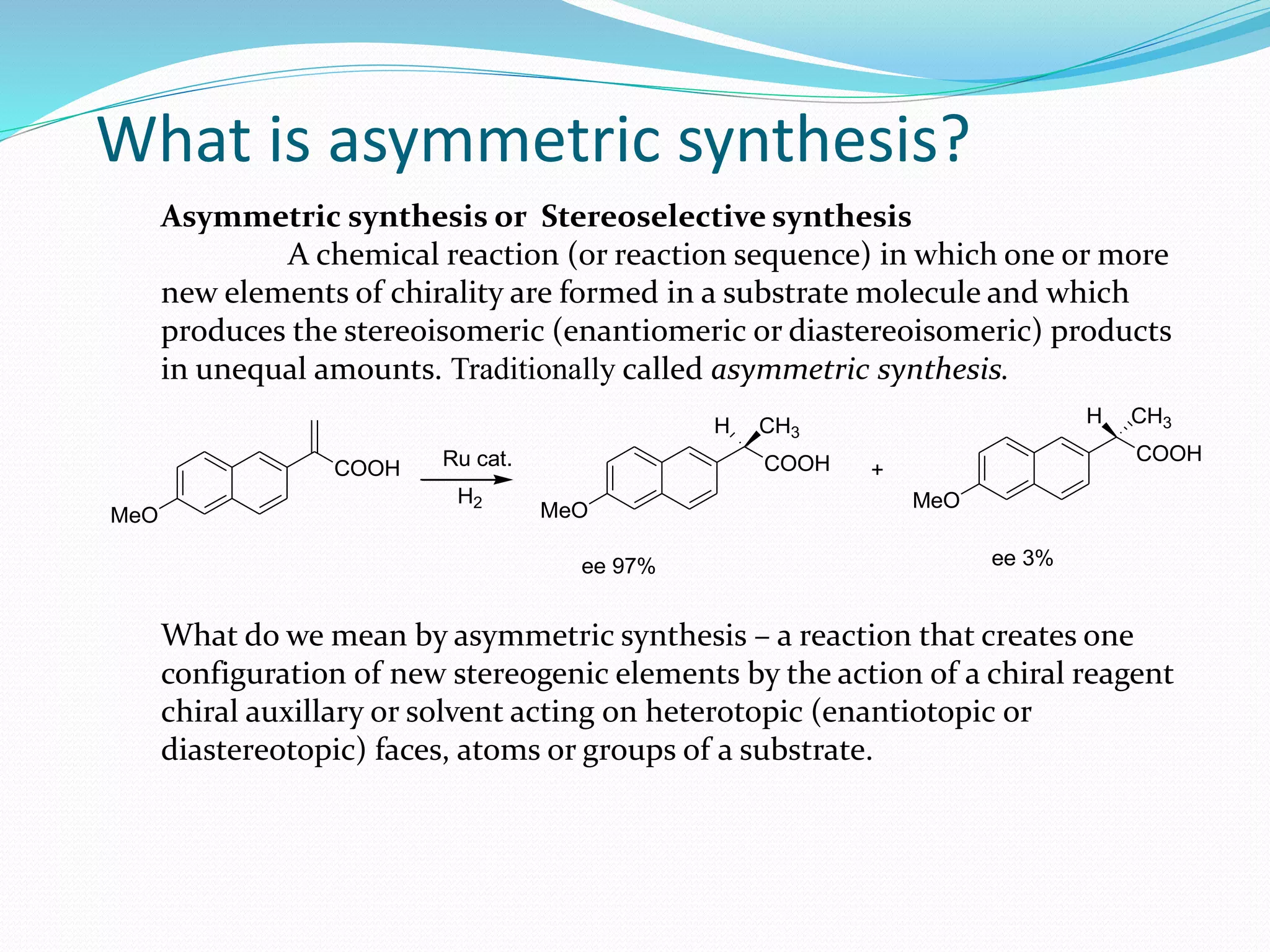
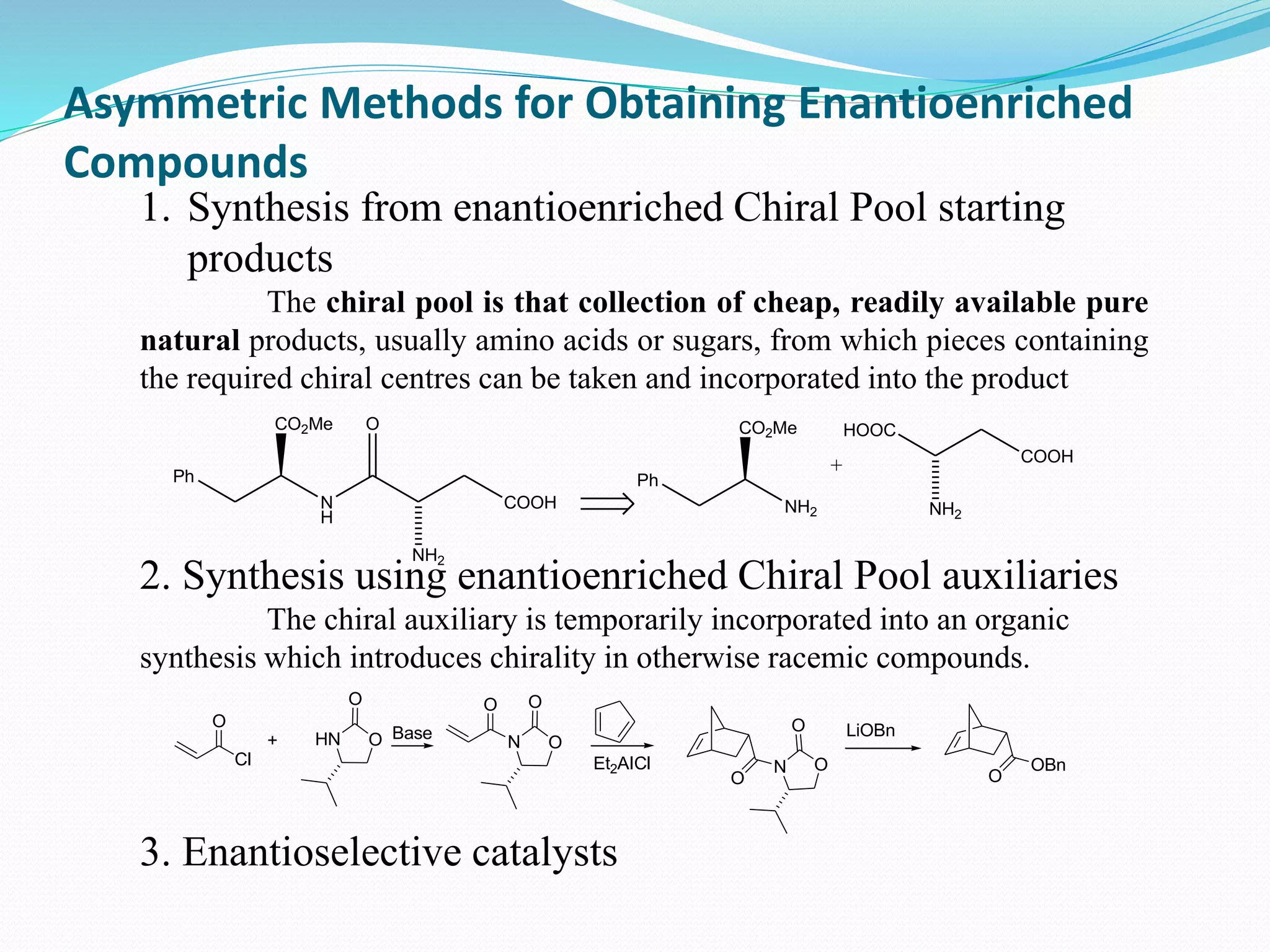
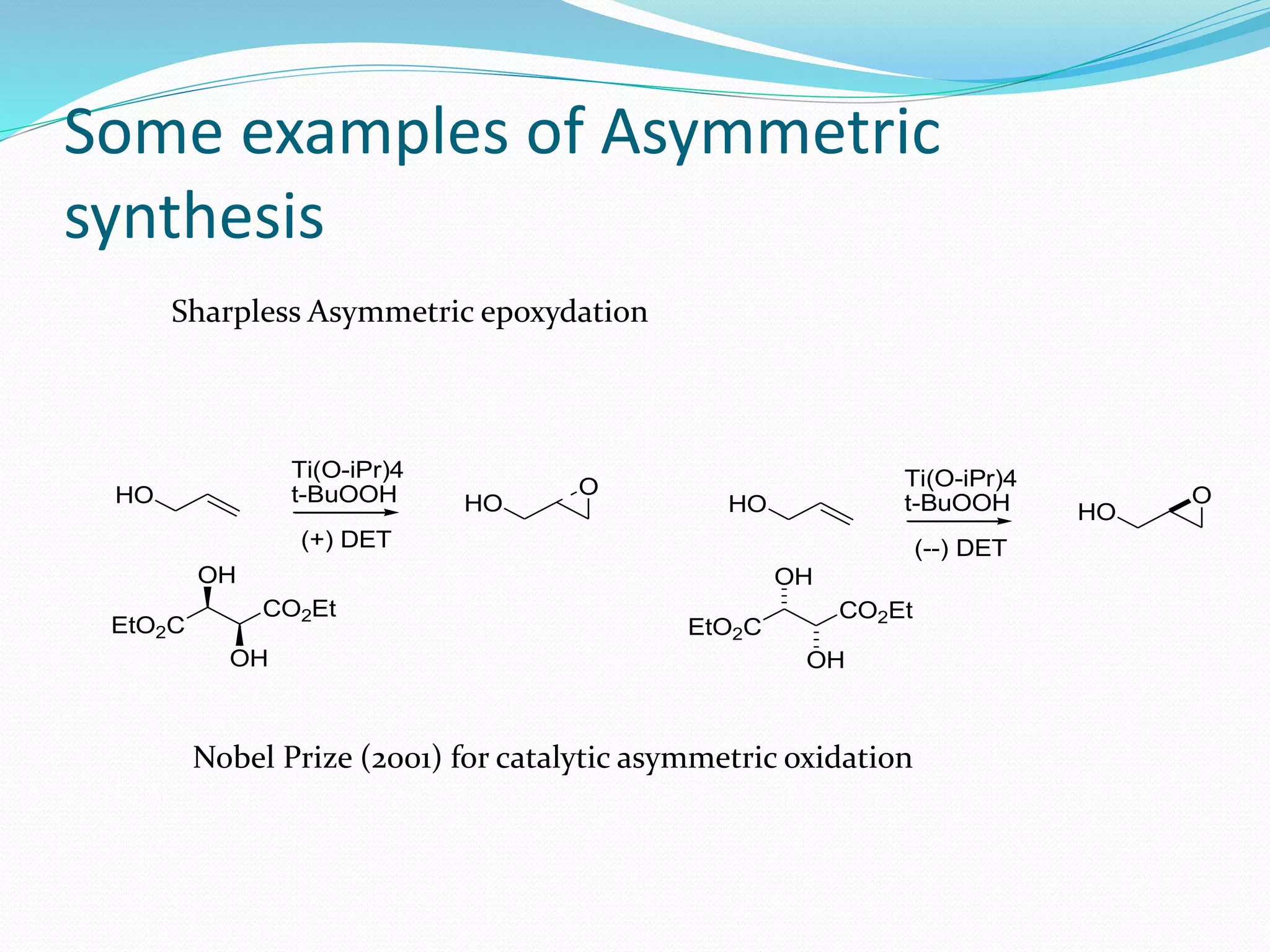
This document discusses asymmetric synthesis, which is a chemical reaction that produces stereoisomeric products in unequal amounts by creating new chiral centers. It provides examples of important biological molecules that are enantiopure, such as amino acids, sugars, and proteins. Common methods for obtaining enantiopure compounds include isolation from natural sources, resolution of racemic mixtures, and asymmetric synthesis. Asymmetric synthesis is described as a reaction where a chiral reagent, auxiliary, or solvent directs the formation of new stereocenters. Examples of important asymmetric reactions mentioned include Sharpless epoxidation and asymmetric reductions.