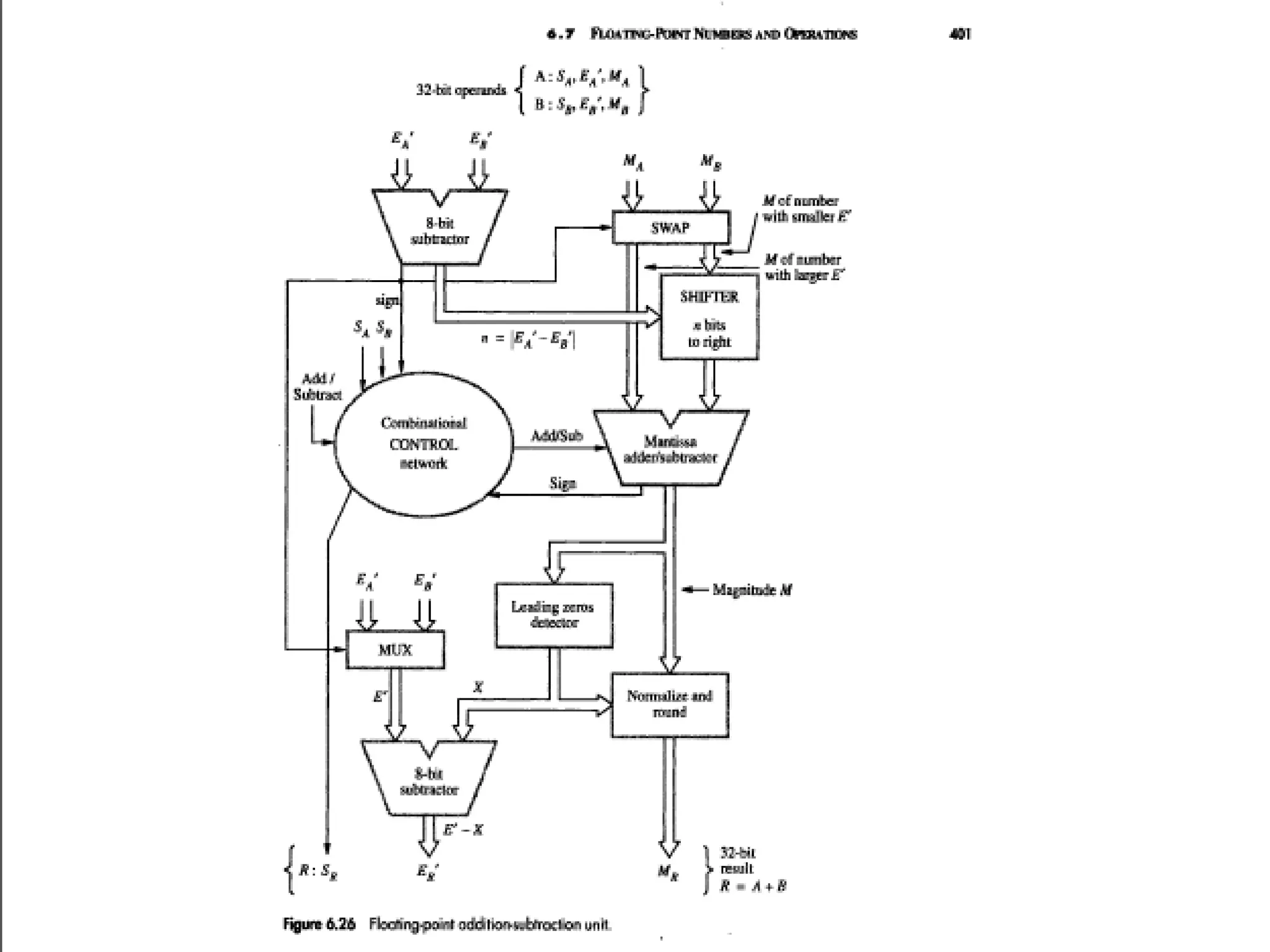
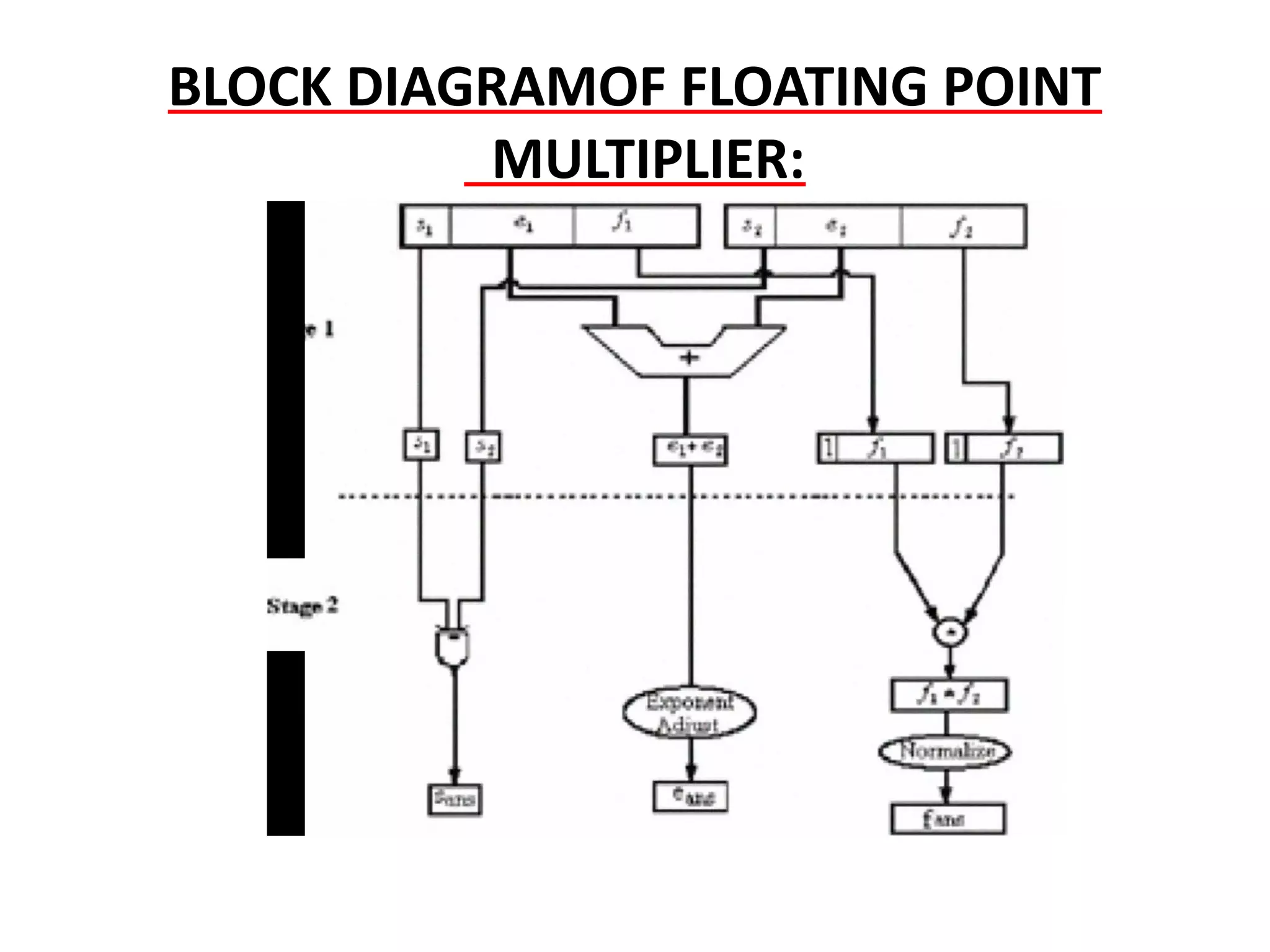
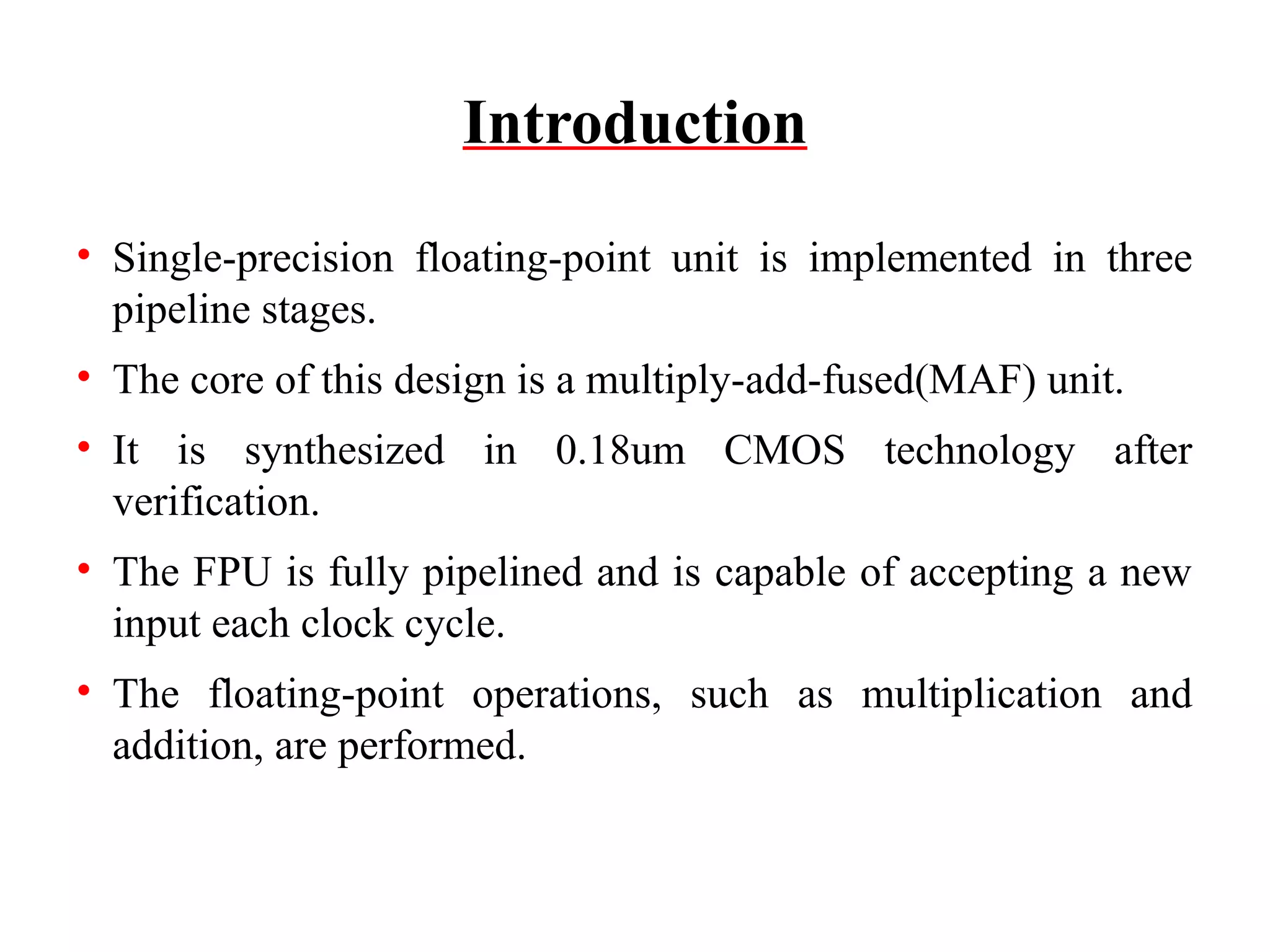
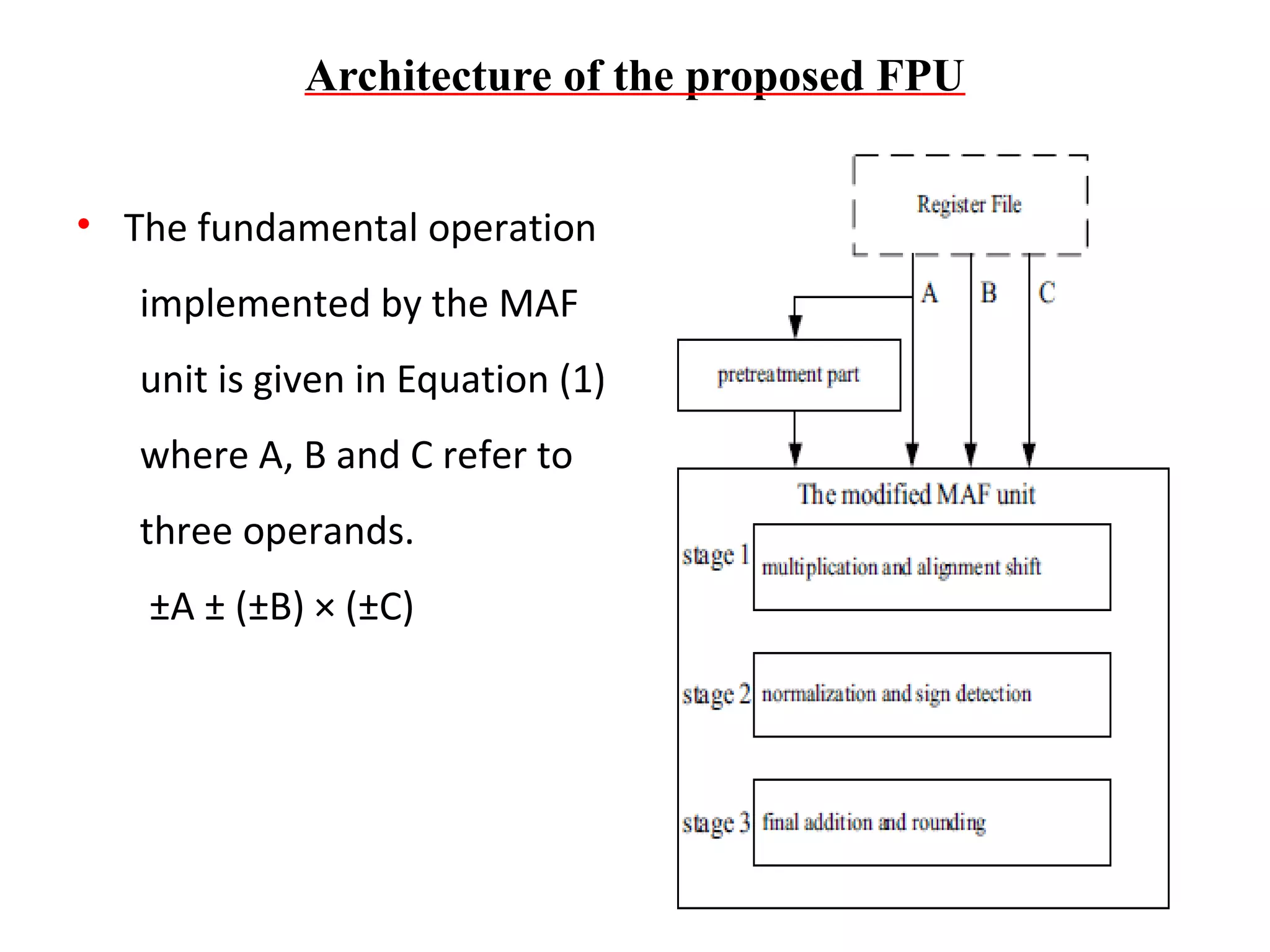
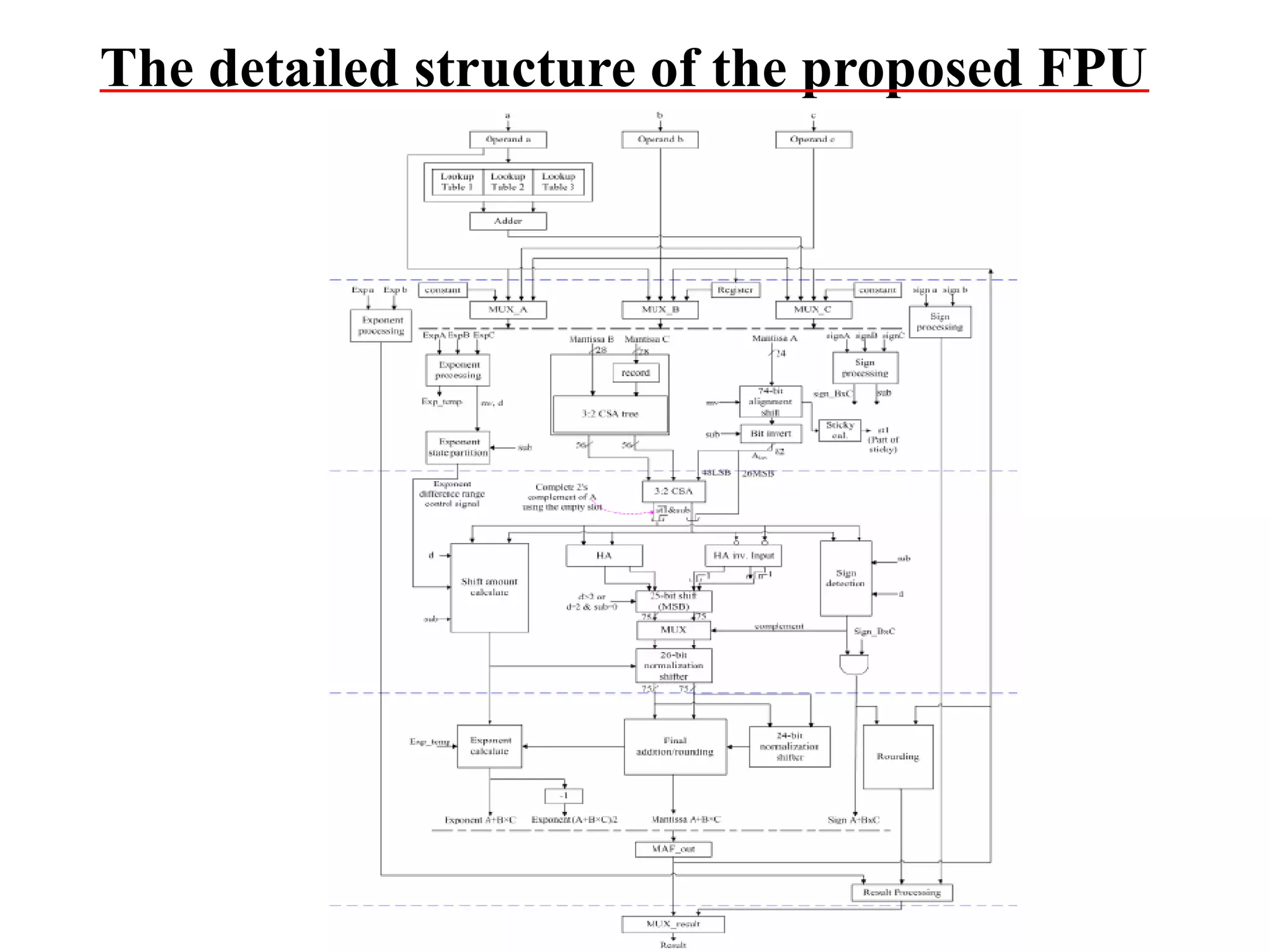
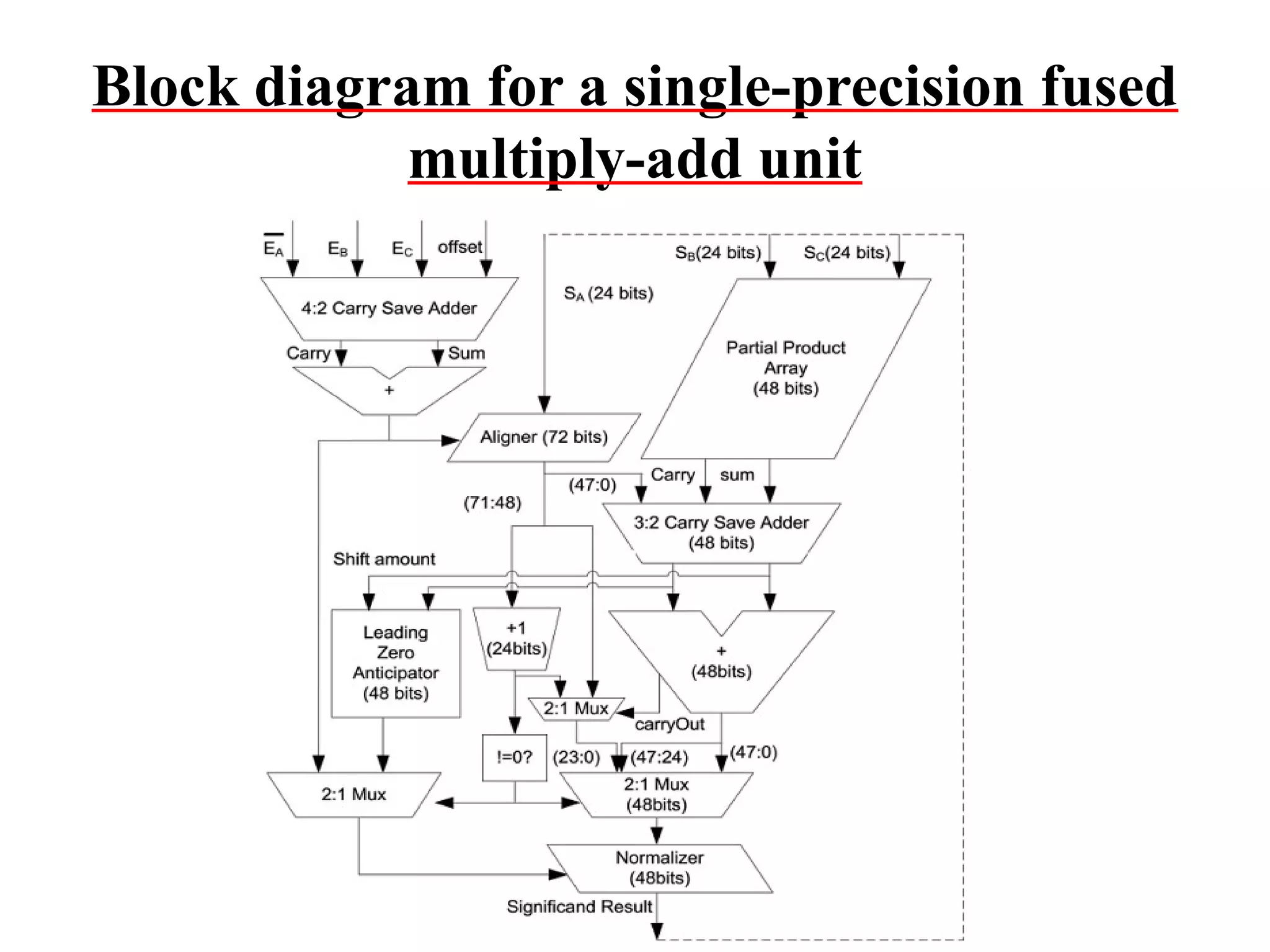
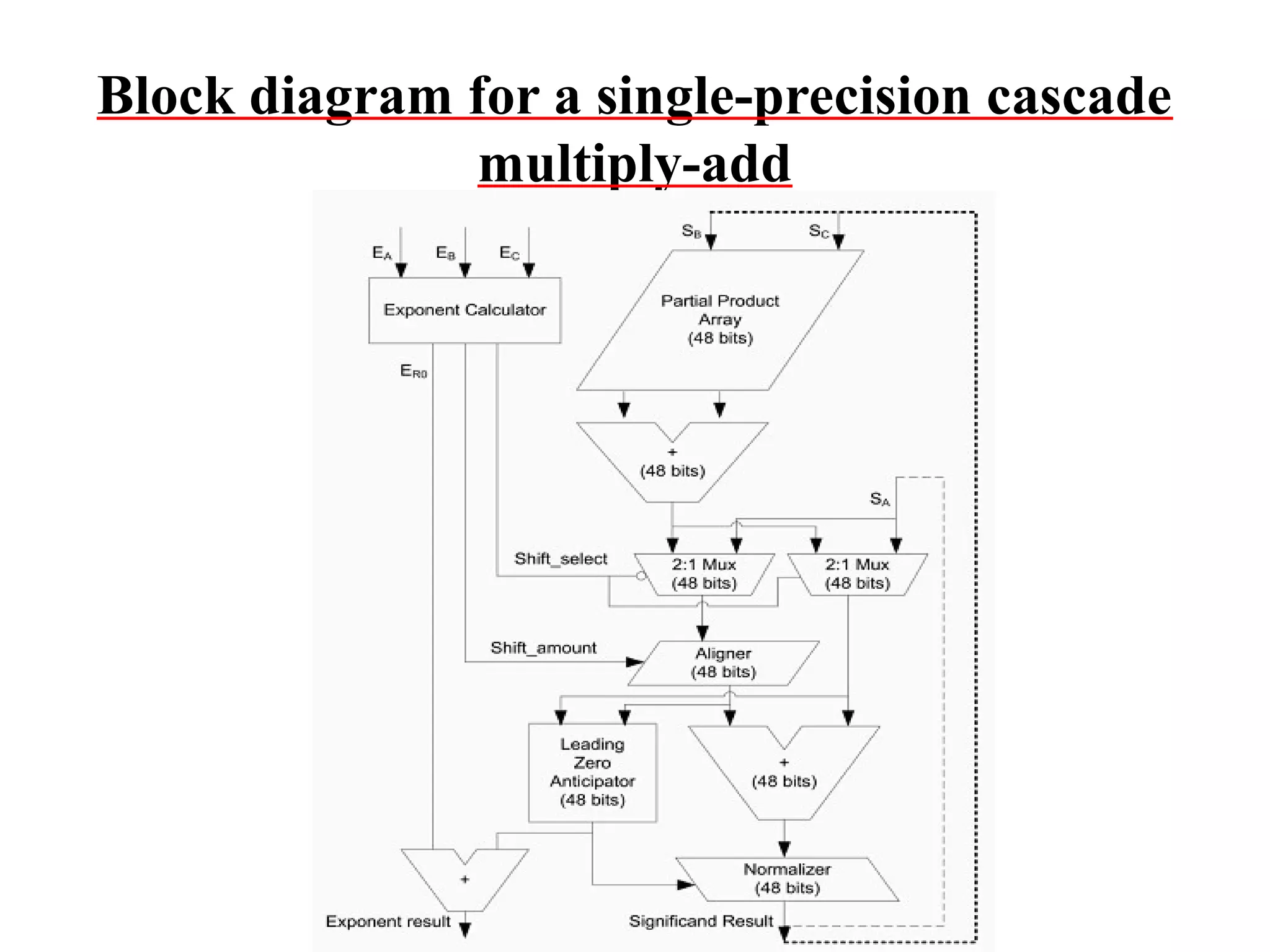
This document summarizes 6 different studies on floating point unit designs. The studies examined fully pipelined single-precision units, energy efficient designs, fused add-subtract units, optimized logarithmic architectures, unified rectangular designs, and an FPGA implementation. The studies described the architectures, advantages like performance and power improvements, and disadvantages like increased complexity. Overall, the document reviews optimizations for floating point units across different technologies.









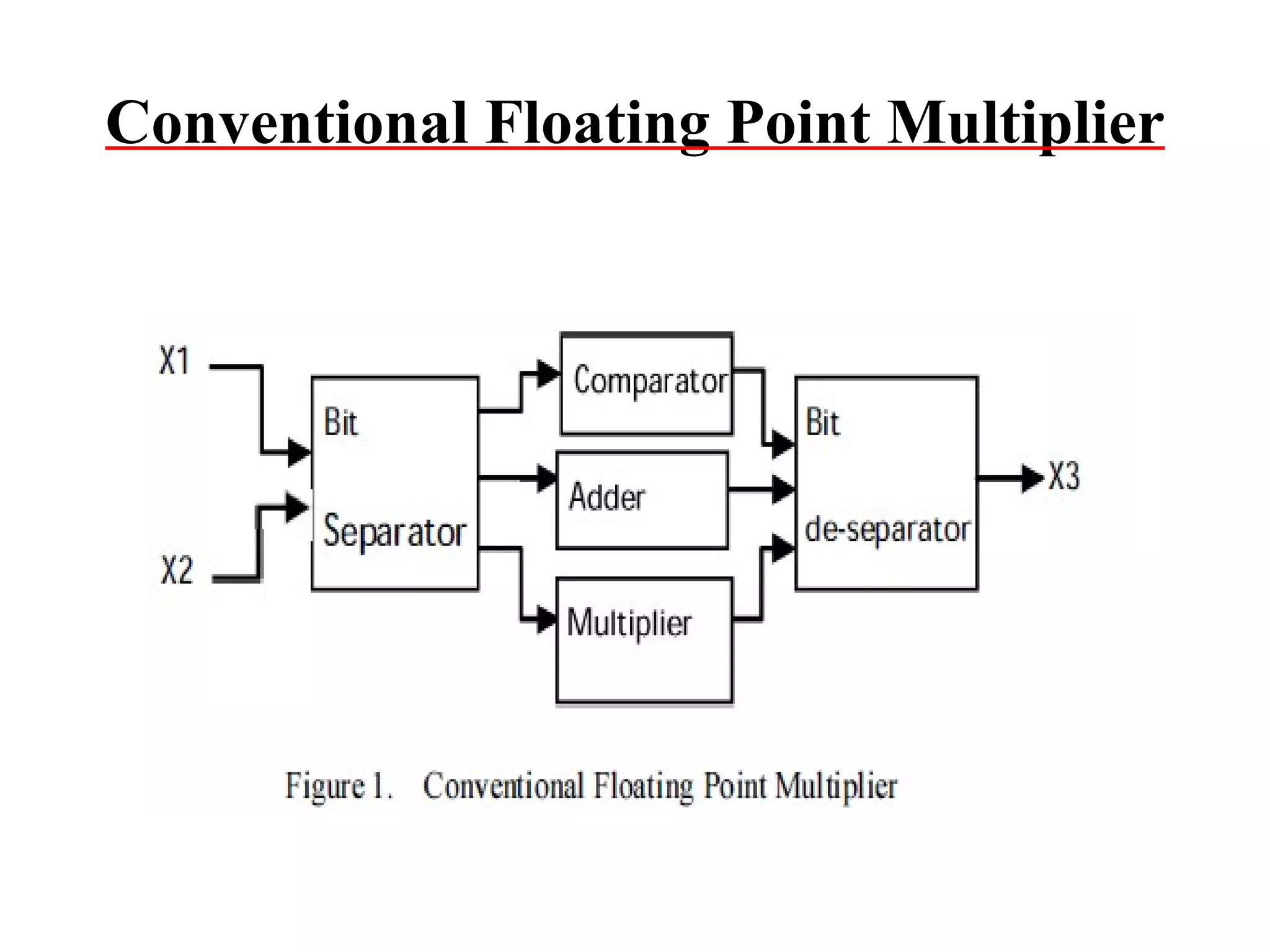
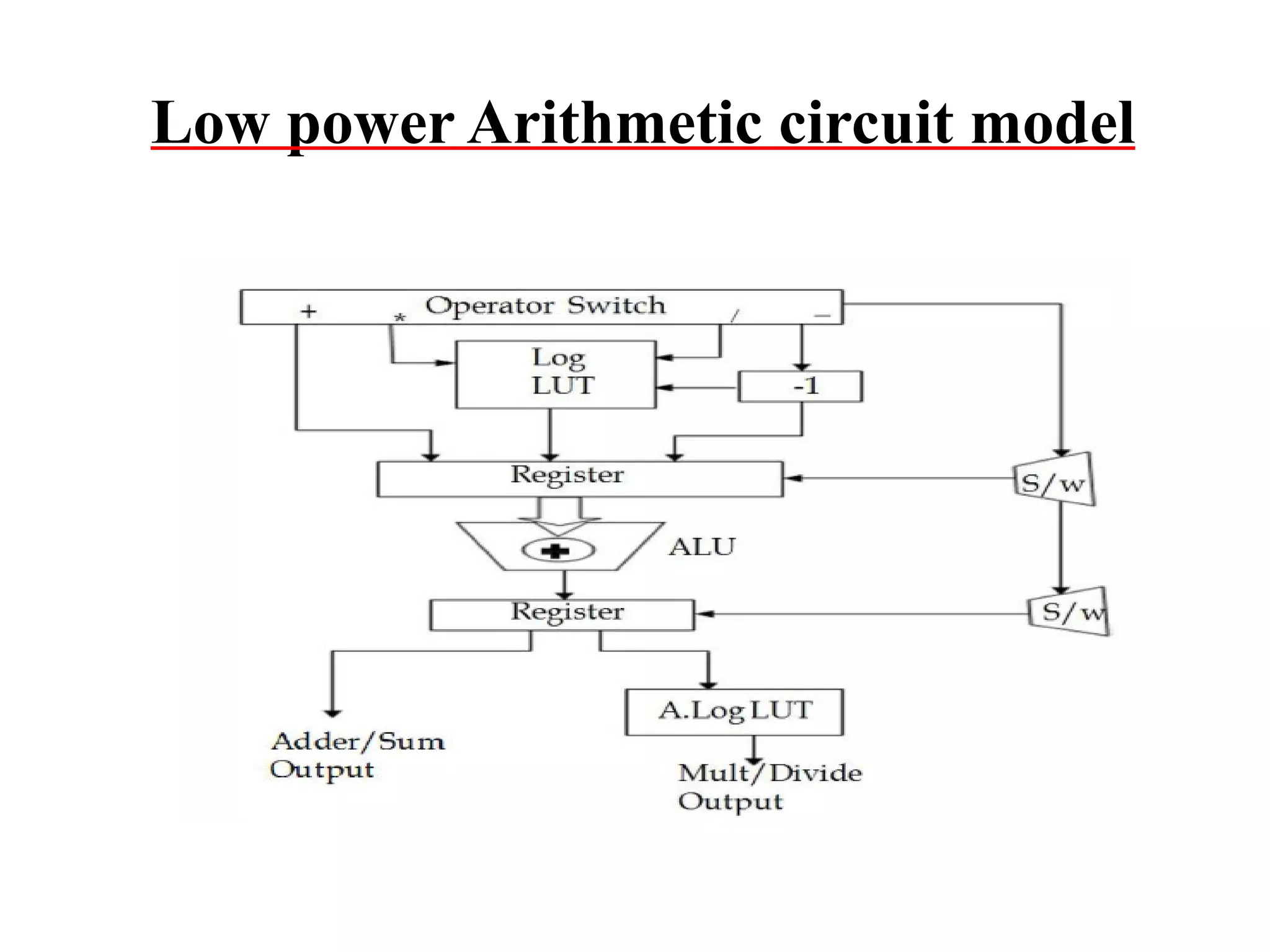



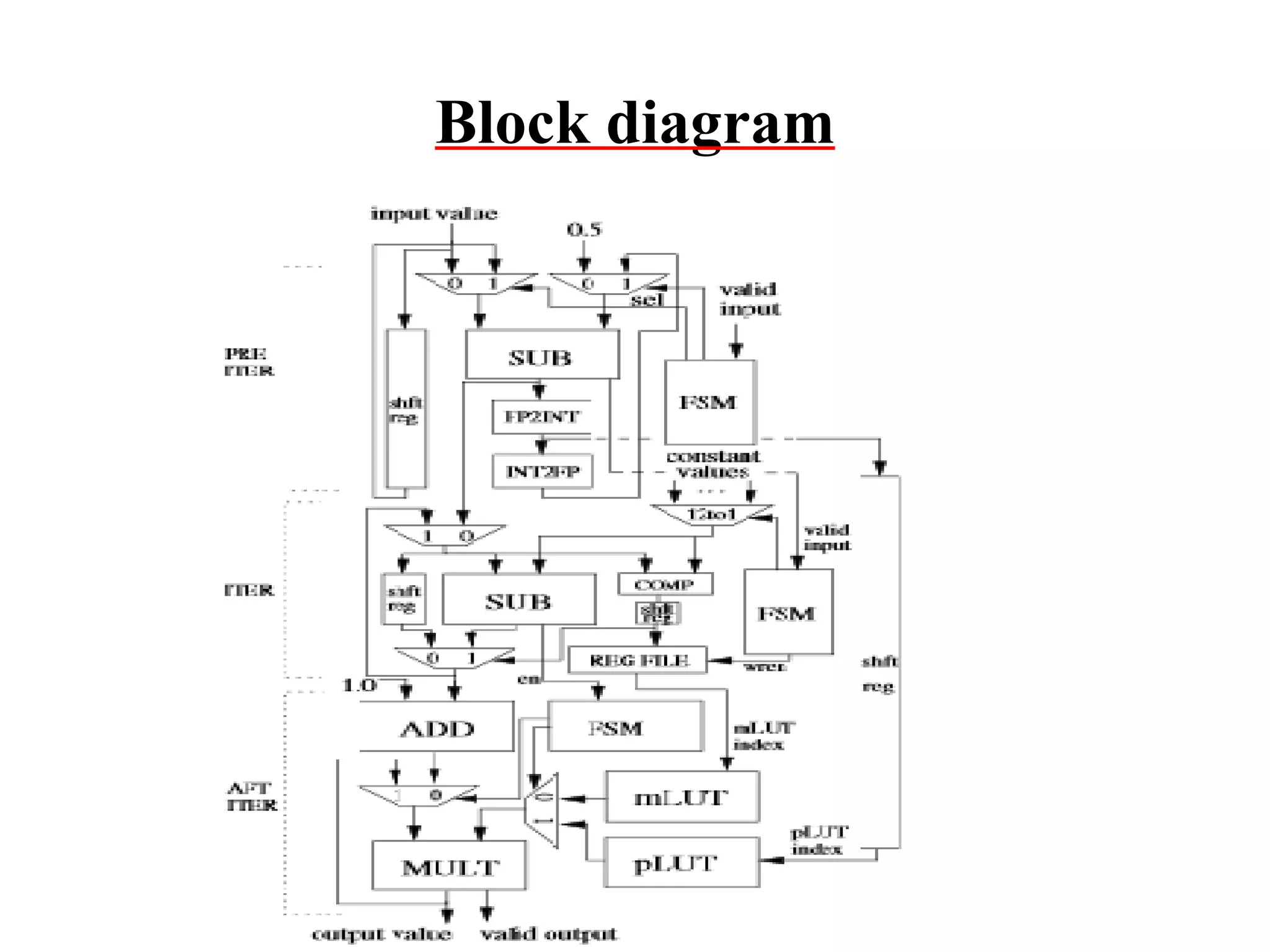
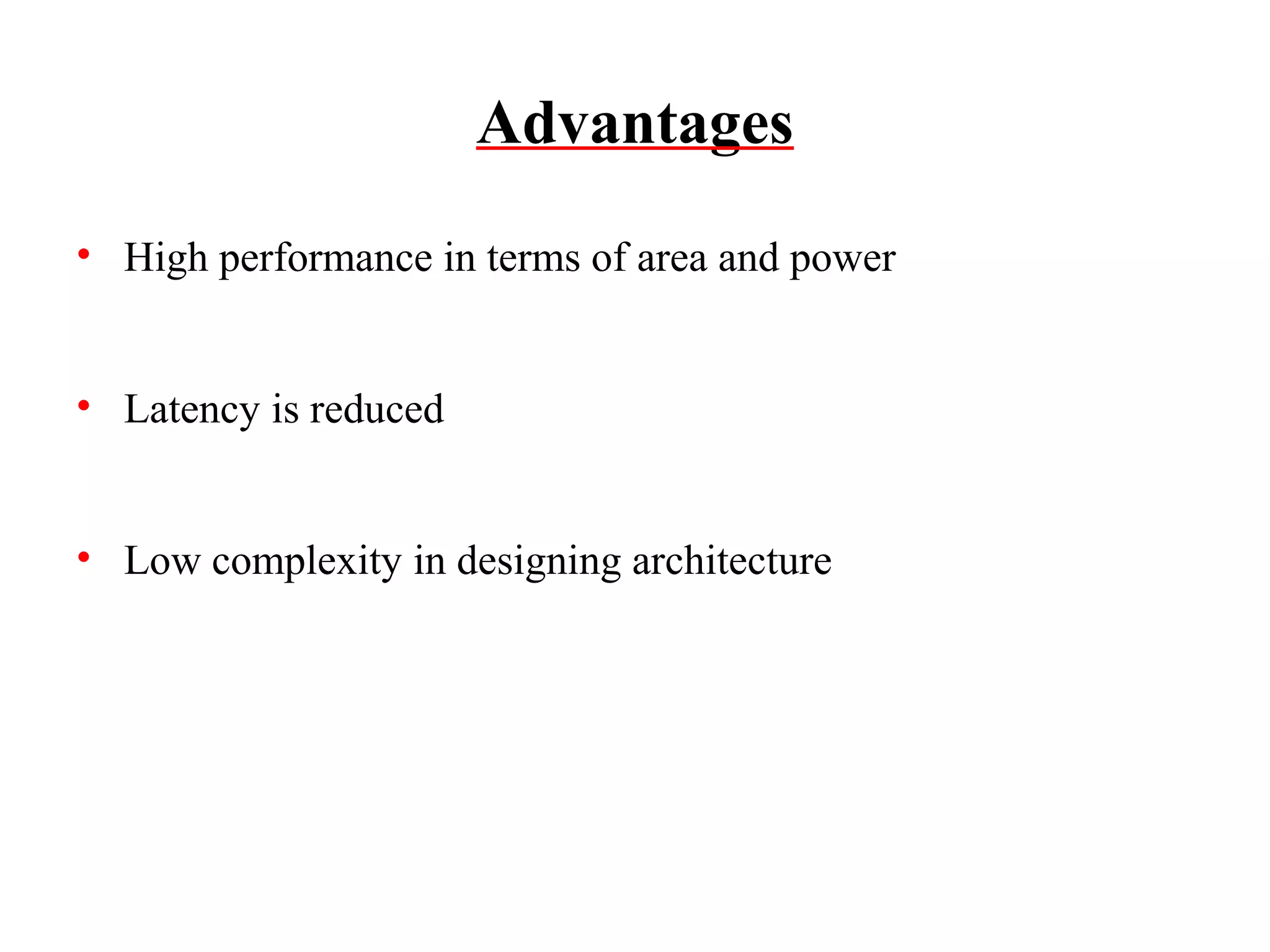

![6.Design & Implementation of Floating point
ALU on a FPGA Processor
• AUTHORS: Prashanth B.u.v P.Anil Kumai, .G Sreenivasulu
• Publication Year: 2012
• Journal Name 2012 International Conference on Computing,
Electronics and Electrical Technologies [ ICCEET].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flu-131027112930-phpapp01/75/Floating-point-units-28-2048.jpg)